Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
General Economics, Taxation, Land Reform & Entrepreneurship
Enviado por
Rochelle Esteban0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações7 páginasThis document provides a course syllabus for "General Economics with Taxation and Land Reform and Entrepreneurship". The 3-credit course will cover basic economic concepts including supply and demand, prices, economic systems, and taxation. It will also cover the land reform program in the Philippines and entrepreneurship. The syllabus outlines 9 weeks of topics, assessment methods, and learning objectives aligned with the program outcomes of the institution.
Descrição original:
Título original
Ss 121 Economics
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document provides a course syllabus for "General Economics with Taxation and Land Reform and Entrepreneurship". The 3-credit course will cover basic economic concepts including supply and demand, prices, economic systems, and taxation. It will also cover the land reform program in the Philippines and entrepreneurship. The syllabus outlines 9 weeks of topics, assessment methods, and learning objectives aligned with the program outcomes of the institution.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações7 páginasGeneral Economics, Taxation, Land Reform & Entrepreneurship
Enviado por
Rochelle EstebanThis document provides a course syllabus for "General Economics with Taxation and Land Reform and Entrepreneurship". The 3-credit course will cover basic economic concepts including supply and demand, prices, economic systems, and taxation. It will also cover the land reform program in the Philippines and entrepreneurship. The syllabus outlines 9 weeks of topics, assessment methods, and learning objectives aligned with the program outcomes of the institution.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 1 of 7
MAPA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
School of Languages, Humanities and Social Sciences
COURSE SYLLABUS
1. Course Code : SS121
2. Course Title : General Economics with Taxation and Land Reform and
Entrepreneurship
3. Pre-requisite : none
4. Co-requisite : none
5. Credit / Class Schedule : 3 units
6. Course Description : The course is the study of Economics as an essential aspect of life covering basic
economic problems, prevailing economic systems, prices of goods and services
and economic growth. Integrated in this course, is the study of the basics of
taxation, the various types of national internal revenue taxes and the Land
Reform Program of the Philippines and Entrepreneurship.
VISION
Napua shall be an international center of excellence in technology education by:
Providing instructions that are current in content and state-of-the art in delivery;
Engaging in cutting-edge research; and
Responding to the big local and global technological challenges of the times
MISSION
a) The mission of Napua !nstitute of Technology is to disseminate, generate, preserve and apply scientific,
engineering, architectural and !T knowledge.
b) The !nstitute shall, using the most effective means, provide its students with professional and advanced
scientific and engineering, architectural and information technology education through rigorous and up-
to-date academic programs with ample opportunities for the exercise of creativity and the experience of
discovery.
c) !t shall implement curricula that, while being steeped in technologies, shall also be rich in the humanities,
languages and social sciences that will inculcate ethics.
d) The !nstitute shall advance and preserve knowledge by undertaking research and reporting on the results
of such inquiries.
e) The !nstitute, singly or in collaboration with others, shall bring to bear the world's vast store of
knowledge in science, engineering and other realms on the problems of the industry and the community
in order to make the Philippines and the world a better place.
MISSION
PROGRAM EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES
a b c d e
1. To Provide students with solid foundation in mathematics, basic
sciences, physics and general chemistry and their application to
engineering, architecture and other related disciplines.
2. To compliment the technical training of the students with proficiency
in oral and written communications.
3. To instill in the students human values and cultural refinement
through the humanities and social sciences.
+. To inculcate high ethical standards in the students through its
integration in the learning activities.
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 2 of 7
7. Program Outcomes and Relationship to Program Educational Objectives
Program
Educational
Objectives
Program Outcomes
1 2 3 4
(a)
An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and
engineering
(b)
An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to
analyze and interpret data
(c)
An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet
desired needs
(d) An ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams
(e)
An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering
problems
(f) An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility
(g) An ability to communicate effectively
(h)
The broad education necessary to understand the impact of
engineering solutions in a global and societal context
(i)
A recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-
long learning
(j) A knowledge of contemporary issues
(k)
An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering
tools necessary for engineering practice.
8. Course Objectives and Relationship to Program Outcomes:
Program Outcomes Course Objectives
The students should be able to:
a b c d e f g h i j k
1. Gain a clear understanding of Economics and its
significance to our lives.
2. Appreciate the goal of Economics which is social
justice.
3. Analyze how prices are affected by the interaction
between supply and demand of goods and services.
4. Learn the value of a sound business idea.
5. Realize the importance of Taxation in the existence of
sovereign state.
6. Comprehend and compute the different types of
national internal revenue taxes.
7. Understand the Agrarian Reform problems in the
Philippines and appreciate the Comprehensive
Agrarian Reform Program (CARP) under R.A. No.
6657.
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 3 of 7
9. Course Coverage :
Week Topic Methodology Assessment
1 Orientation
Economics Defined Lecture and Discussion Recitation
Nature of Economic Choice
Types of Economic Systems Analysis of newspaper Recitation
The Economic Resources
Economic Goals
Divisions of Economics
readings
2 Stock & Flow Concepts Lecture QUIZ
The Circular Flow of Goods,
Services and Income
The Production Process Lecture with graphical Assignment
The Flow of Goods Among
Producing Firms
illustrations of flow of the
production process Recitation
Good & Income Flow Among
Household & various types
of Producers
Analysis of prevailing economic
situations and Graphical
illustrations of the Circular flow of
Goods & income of household
firms
Recitation
Income Flow
The Concept of Equilibrium
The Effect of Savings &
Investments
Flow in a Market with Govt. &
Foreign Countries
3 Market Defined Lecture Seatwork
How a Market Functions
Market Demand Lecture and Discussion QUIZ
Non-Price Determinants of
Demand
With graphical illustration of the
Law of Supply and Demand
Effect of Changes in Non-Price
Determinants of Demand
Market Supply Assignment
Non-Price Determinants of
Supply
Effect of Changes in Non-Price
Determinants of Supply
Market Equilibrium
4 Elasticity Defined Lecture Recitation
Elasticity of Demand
Price Elasticity of Demand
Lecture with Graphical illustration
of the elasticity of supply and
demand
Implications of Price Elasticity
of Demand
Cross Elasticity of Demand
Determinants of Demand Elasticity
Newspaper and magazine readings Homework
Elasticity of Supply
Classification of Supply
Elasticity
Determinants of Supply
Elasticity
Lecture and Discussion
QUIZ
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page + of 7
5 The Concept of Production Use of chart to show the Seatwork
Transforming Input into
Outputs Cost of production
Production Functions
Analysis of the Production Process
Production with one variable
Input Homework
Cost of Products
Production with two variable
Inputs
Kinds of Market Structure
Output of Price under Pure
Competition
Price and Output Determination
under Monopoly
Price and Output
Determination under
Oligopoly
Price Determination under
Monopolistic Competition
M I D T E R M E X A M I N A T I O N
6 Definition of Taxation Lecture and Discussion Recitation
Importance and Purposes of
Taxation
Definition of Tax
Essential Characteristics of Tax
Theory and Basis of Taxation Discussion Recitation
Nature of the Power of Taxation
Basic Principles of a Sound Tax
System
Classification of Taxes Analysis of tax Recitation
Taxes Distinguished from
other Terms
Limitations on the Power of
Taxation
Tax Evasion and Tax Avoidance:
Definition and Distinction
7 Kinds of Taxes Under Existing Discussion QUIZ
Laws
Kinds of National Revenue Taxes
Definition of: Income, Income
Tax, Gross Income, and
Taxable Income
Personal and Additional Exercises on the
Exemptions Computation of Individual computations of
Computation of Individual Income Tax Income Tax
Income Tax
Filing of Returns and Payment
of Tax
Definition and Nature of Estate Lecture and Discussion Recitation
And Inheritance Taxes
Definition and Kinds of Donation
or Gift Tax
Tax Imposed on Net Gift
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 5 of 7
8
Value-added Tax: Definition
and Nature Discussion Recitation
Rates and Bases of the VAT
Overseas Communication Tax
Amusement Tax
Definition and Nature of Excise Discussion QUIZ
Tax
Documentary Stamp Tax
Travel Tax
Energy Tax
Meaning of Land Reform Lecture and Discussion Seatwork
Meaning of Agrarian Reform
Components of Agrarian Reform:
Land Tenure Structure,
Production Structure,
Structure of Supporting
Services
9 Aspects of Agrarian Reform:
Reading of newspapers and
magazines Oral Report
Economic, Socio-cultural
Biblical, Moral, Legal, and
Political
Implementation of Agrarian
Reform
The Philippine Agrarian Problem: Discussion Recitation
A Historico-political Survey
of Agrarian Problems and
Agrarian Legislations
Necessity of Agrarian Reform
in the Philippines Lecture and Discussion QUIZ
Objections to Agrarian Reform
10 Role of the Farmer in Agrarian Discussion Assignment
Reform
Role of the Landlord in Agrarian
Reform
Selected Constitutional Provisions Discussion Recitation
Relevant to Agrarian Reform
The CARP (Comprehensive Lecture and Discussion Recitation
Agrarian Reform Program)
Republic Act No. 6657
Need for CARP
Objectives of the CARP
The CARL (Comprehensive
Agrarian Reform Law)
11 F I N A L E X A M I N A T I O N
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 6 of 7
10. Course Outcomes and Relationship to Course Objectives/ Program Outcomes
Course Outcomes
A student completing this course should at
the minimum be able to:
Course Objectives Program Outcomes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 a b c d e f g h i j k
Meaning of demand and supply
Different forms of business
organizations and the social
responsibilities of Management
Definition, importance, and purpose of
taxation
Different filing systems of the various
kinds of national internal revenue taxes
Different aspects of agrarian reform
Necessity of agrarian reform in the
Philippines
Constitutional Provisions relevant to
agrarian reform
Appraise the value of the course.
Analyze and evaluate the prevailing
economic system
Analyze the price system and the
regulatory function of the government.
Understand the explanation of economic
development and growth.
Analyze the limitations on the power of
taxation.
Develop the ability to compute the
individual income tax.
Discriminate insights into the Philippine
agrarian problem.
Develop an appreciation for the
provisions of the Comprehensive
Agrarian Reform Program (CARP)
R.A. No. 6657.
11. Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component:
Engineering topics 10%
General education component -90 %
12. Textbook: Medina, Roberto G., Principles of Economics, Quezon City, Rex Bookstore, 2003
13. Course Evaluation :
The minimum requirement for a passing grade is 60% final grade average from the following:
Quizzes 30 %
Recitation 20 %
Oral Proficiency 10 %
Seatwork/Homework 10 %
Co-curricular Activities 5 %
Midterm Examination 10%
Pre-Final Examination 15%
TOTAL 100 %
Course Title:
General Economics with
Taxation and Land Reform
and Entrepreneurship
Date Effective:
1
st
Qtr
SY2005-2006
Date Revised:
June 30, 2005
Prepared by:
Dr. Nestor N. Asuncion
Approved by:
Prof. Amalia S. Baltazar Page 7 of 7
Aside from academic deficiency, other grounds for a failing grade are:
Cheating during examinations
More than 20 % of the total number of meetings in a quartermester
Failure to take the final examination with no valid excuse.
14. Other References:
a. De Leon, Hector S., Textbook on Agrarian Reform and Taxation (with Cooperatives), 3
rd
Edition,
Quezon City, Rex Bookstore, Inc., 2000.
b. Fajardo, Feliciano R., Economics, Third Edition, Rex Bookstore, Inc., reprinted March 2004.
c. Pagoso, Introductory Economics, Revised Edition, Rex Bookstore, Inc.
d. Nollado, Jose, Principles of Agrarian Reforms, Cooperatives and Taxation, 16
th
and Revised
National Bookstore Inc., 1991.
15. Course Materials Made Available:
Course goals and instructional objectives
Course schedule for lectures and exams
End of course self-assessment report
16. Committee Members:
Prof. Remedios V. Trajano Social Science Cluster leader
Dr. Nestor M. Asuncion Group Leader, General Economics with TLR and Entrepreneurship
Prof. Benigno Agapito Member
Você também pode gostar
- Sell Your SongsDocumento82 páginasSell Your Songsapi-3697728100% (2)
- Principles of Economics With TLRDocumento5 páginasPrinciples of Economics With TLRmhel20010100% (1)
- The Final Guide To The 1099-MISC Form Online For The FreelancerDocumento4 páginasThe Final Guide To The 1099-MISC Form Online For The FreelancerJohn olsonAinda não há avaliações
- Memorandum of Agreement Land SaleDocumento4 páginasMemorandum of Agreement Land SaleJM CamalonAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRDocumento11 páginasBasic Economics With Taxation and Agrarian Reform: Dr. Vicente S. Betarmos, JRPlatero RolandAinda não há avaliações
- ABM - Business Finance CGDocumento7 páginasABM - Business Finance CGDonald Bose MandacAinda não há avaliações
- Senior High School Orientation For Students and ParentsDocumento42 páginasSenior High School Orientation For Students and ParentsArjhayee Jaron92% (13)
- Four Important Criteria or Tips For Giving A Winning Teaching DemonstrationDocumento3 páginasFour Important Criteria or Tips For Giving A Winning Teaching DemonstrationRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Part IV DP - FinalDocumento54 páginasPart IV DP - FinalRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Macroeconomics Theory and Practice - SyllabusDocumento4 páginasIntro To Macroeconomics Theory and Practice - SyllabusHoney Hon67% (3)
- EconomicsDocumento329 páginasEconomicsKabutu Chuunga100% (2)
- Principles of EconomicsDocumento10 páginasPrinciples of EconomicsClaire E JoeAinda não há avaliações
- Foundations of Education PDFDocumento65 páginasFoundations of Education PDFMkesvillon Dhark60% (5)
- Syllabus in Basic Economics, Taxation, and Land ReformDocumento4 páginasSyllabus in Basic Economics, Taxation, and Land Reformmigs_mansueto91% (22)
- NSSCO Economics SyllabusDocumento24 páginasNSSCO Economics Syllabusmukwame0% (1)
- Social ScienceDocumento39 páginasSocial ScienceCarlo Sablaon CallosAinda não há avaliações
- ECONOMICS SYLLABUS LAND REFORM TAXATIONDocumento7 páginasECONOMICS SYLLABUS LAND REFORM TAXATIONNolram Leuqar100% (2)
- Economics of Education 1st Edition Lovenheim Solutions ManualDocumento11 páginasEconomics of Education 1st Edition Lovenheim Solutions Manuallovellednayr984100% (19)
- CIR Vs Filinvest Development CorporationDocumento2 páginasCIR Vs Filinvest Development CorporationKent UgaldeAinda não há avaliações
- CIR V FMFDocumento21 páginasCIR V FMFPatatas SayoteAinda não há avaliações
- Mapúa Institute of Technology:: General Economics With Taxation and EntrepreneurshipDocumento5 páginasMapúa Institute of Technology:: General Economics With Taxation and EntrepreneurshipJomarie CabuelloAinda não há avaliações
- SS12 SyllabusDocumento7 páginasSS12 SyllabusDiana Jane Terez LazaroAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Economics S2d Sem SY 2014 2015Documento6 páginasBasic Economics S2d Sem SY 2014 2015Wynn Francis Jr NuñalAinda não há avaliações
- Un nivers sity of Cent f tral Pu unjab b Fac culty of Ma anagemen Studies nt s Academ Year 20 mic 012Documento5 páginasUn nivers sity of Cent f tral Pu unjab b Fac culty of Ma anagemen Studies nt s Academ Year 20 mic 012Ali IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Economics OLEVELSDocumento5 páginasEconomics OLEVELSYu Yu Maw100% (1)
- Institute of Business and Public AffairsDocumento7 páginasInstitute of Business and Public AffairsFatima BagayAinda não há avaliações
- SOC. SCI. 2 SyllabusDocumento10 páginasSOC. SCI. 2 SyllabusMark Angelo S. Enriquez67% (3)
- GTUC Basic Economics Course OutlineDocumento4 páginasGTUC Basic Economics Course OutlineJayne Aruna-NoahAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Syllabus PDFDocumento10 páginasEconomics Syllabus PDFNolram LeuqarAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of EconomicsDocumento5 páginasPrinciples of EconomicsBersabe, Rey-ann Aizelle C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Economic Geography Syllabus 2020 RealDocumento8 páginasEconomic Geography Syllabus 2020 Realalinacherkunova204Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Economic GeographyDocumento2 páginasIntroduction to Economic Geographymoebius70Ainda não há avaliações
- Understanding Economics, Agrarian Reform and TaxationDocumento6 páginasUnderstanding Economics, Agrarian Reform and TaxationAlvin Kris Alic100% (1)
- Aeco 201Documento2 páginasAeco 201Prateek TekchandaniAinda não há avaliações
- Business Economics 1Documento57 páginasBusiness Economics 1John ChiwaiAinda não há avaliações
- Betar BSN3Documento6 páginasBetar BSN3Shannie PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- GEEC 203 - Introduction To EconomicsDocumento18 páginasGEEC 203 - Introduction To Economicscerenkomurcu61Ainda não há avaliações
- Thesis Economic GrowthDocumento6 páginasThesis Economic Growthfjn3d3mc100% (2)
- Microeconomics EN SB 2023Documento9 páginasMicroeconomics EN SB 2023chumnhomauxanhAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 4 StudentsDocumento15 páginasTopic 4 StudentsTy VoAinda não há avaliações
- SOSC107 (Economics With LRT)Documento9 páginasSOSC107 (Economics With LRT)Jenica RiaAinda não há avaliações
- BAE101 Introduction To Economics With LRTDocumento5 páginasBAE101 Introduction To Economics With LRTPatty NicolasAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Microeconomics Chapter 1Documento71 páginasIntroduction to Microeconomics Chapter 1Faye Erica HerberoAinda não há avaliações
- 2006 - ECON 201 - Basic Micro-Economics With Taxation and Land ReformDocumento7 páginas2006 - ECON 201 - Basic Micro-Economics With Taxation and Land ReformSoriano D'cruz RosanneAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Hindi XI 2011Documento146 páginasEconomics Hindi XI 2011Ashish DiwakarAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Grade 9 TextbookDocumento130 páginasEconomics Grade 9 TextbookYonas100% (3)
- Class XI Economics 2011Documento159 páginasClass XI Economics 2011Ramita Udayashankar0% (1)
- Economic AnalysisDocumento8 páginasEconomic AnalysisJoan GardoceAinda não há avaliações
- Note Buad829 Mod1 e7iy8uc55twyqkpDocumento128 páginasNote Buad829 Mod1 e7iy8uc55twyqkpashamohartessAinda não há avaliações
- Global Economic Environment: Gerardo JacobsDocumento8 páginasGlobal Economic Environment: Gerardo JacobsGuzmán Noya NardoAinda não há avaliações
- General Certificate of Education Syllabus Ordinary Level Economics 2281 For Examination in June and November 2009Documento9 páginasGeneral Certificate of Education Syllabus Ordinary Level Economics 2281 For Examination in June and November 2009mstudy123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Obe Ecmf 013Documento5 páginasObe Ecmf 013AmalMdIsaAinda não há avaliações
- First Year:: Course Name Course DescriptionDocumento5 páginasFirst Year:: Course Name Course Descriptionmuntean_bogdan3120Ainda não há avaliações
- Collective Innovation Processes: Principles and PracticesNo EverandCollective Innovation Processes: Principles and PracticesAinda não há avaliações
- Emerging Trends in TV EtDocumento41 páginasEmerging Trends in TV EtGilbert MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsDocumento7 páginasEcon 2106 Principles of MicroeconomicsWalid Asif JanjuaAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Economics Economic ProblemsDocumento2 páginasApplied Economics Economic ProblemsLsrc Lala RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For ECON 1160 Principles of Economics 1Documento4 páginasSyllabus For ECON 1160 Principles of Economics 1Ben MoneyAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Eco Course ModuleDocumento18 páginasPrinciples of Eco Course ModuleVansh AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Basic MicroeconomicsDocumento128 páginasBasic MicroeconomicsTrixie Jane MolodAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 101 - Session 1Documento17 páginasEcon 101 - Session 1SaharaJhoycee100% (1)
- Syllabus Applied MicroeconomicsDocumento11 páginasSyllabus Applied Microeconomicstramnguyen.31221026352Ainda não há avaliações
- Economic Geography Dissertation TopicsDocumento4 páginasEconomic Geography Dissertation TopicsPayToWritePapersSingapore100% (1)
- Public Finance: Daeyong@phbs - Pku.edu - CNDocumento6 páginasPublic Finance: Daeyong@phbs - Pku.edu - CNSprasadAinda não há avaliações
- BSc IT Basic EconomicsDocumento3 páginasBSc IT Basic EconomicsAmoama EvansAinda não há avaliações
- Macro EconomicsDocumento152 páginasMacro EconomicsOmotosho StephenAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Economics CCDocumento3 páginasIntroduction To Economics CCtheirontemple03Ainda não há avaliações
- Eco 100Documento2 páginasEco 100alikaltayAinda não há avaliações
- Course Syllabus ECON 2302-Principles of MicroeconomicsDocumento5 páginasCourse Syllabus ECON 2302-Principles of MicroeconomicsFRANCIS D. SACROAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Qualitative Research?Documento9 páginasWhat Is Qualitative Research?Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Lawson Logic Model Community SchoolsDocumento1 páginaLawson Logic Model Community SchoolsRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Lawson Logic Model Community SchoolsDocumento1 páginaLawson Logic Model Community SchoolsRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Collaborative Activity: Classroom Management TheoriesDocumento28 páginasCollaborative Activity: Classroom Management TheoriesRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Editable RPMS PORTFOLIO For Teachers (SY 2020-2021)Documento29 páginasEditable RPMS PORTFOLIO For Teachers (SY 2020-2021)Notaly Mae Paja BadtingAinda não há avaliações
- Editable RPMS PORTFOLIO For Teachers (SY 2020-2021)Documento29 páginasEditable RPMS PORTFOLIO For Teachers (SY 2020-2021)Notaly Mae Paja BadtingAinda não há avaliações
- Fiscaladministrationhistoryoverviewdefinitionlgubudgetprocessbydaisyt Besing Mpa 120916195508 Phpapp02 PDFDocumento34 páginasFiscaladministrationhistoryoverviewdefinitionlgubudgetprocessbydaisyt Besing Mpa 120916195508 Phpapp02 PDFRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Pol Gov Dec. 4 7Documento1 páginaPol Gov Dec. 4 7Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
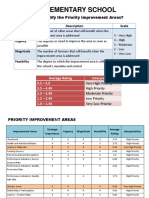
- Maligaya Elementary School: How To Identify The Priority Improvement Areas? Criteria Description ScaleDocumento8 páginasMaligaya Elementary School: How To Identify The Priority Improvement Areas? Criteria Description ScaleRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of The Philippines Pangasinan State University School of Advance Studies Urdaneta CityDocumento1 páginaRepublic of The Philippines Pangasinan State University School of Advance Studies Urdaneta CityRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics Answer SheetDocumento1 páginaUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics Answer SheetRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Pol Gov Dec. 11 14Documento1 páginaPol Gov Dec. 11 14Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Synthesis World ReligionDocumento5 páginasSynthesis World ReligionRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Ucsp: Chapter 1: Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsDocumento48 páginasIntroduction To Ucsp: Chapter 1: Understanding Culture, Society, and PoliticsRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Financing Educational SystemsDocumento2 páginasFinancing Educational SystemsRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- DO - s2016 - 036 Policy Guidelines On Awards and Recognition For The Kto12 Basic Ed.Documento19 páginasDO - s2016 - 036 Policy Guidelines On Awards and Recognition For The Kto12 Basic Ed.Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Sheet For Practical Research 1Documento3 páginasActivity Sheet For Practical Research 1Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Development Plan for Functional and Behavioral CompetenciesDocumento1 páginaDevelopment Plan for Functional and Behavioral CompetenciesJohn Michael Benson100% (1)
- Honors Awards DRECMNHS 2018Documento12 páginasHonors Awards DRECMNHS 2018Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Development Plan for Functional and Behavioral CompetenciesDocumento1 páginaDevelopment Plan for Functional and Behavioral CompetenciesJohn Michael Benson100% (1)
- Comparative Analysis Paper RubricDocumento1 páginaComparative Analysis Paper RubricRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Analysis Paper RubricDocumento1 páginaComparative Analysis Paper RubricRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Confucianism 150708022734 Lva1 App6892Documento11 páginasConfucianism 150708022734 Lva1 App6892Rochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- DO s2016 036Documento17 páginasDO s2016 036Mart Dumali SambaludAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation1 150503111226 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocumento18 páginasPresentation1 150503111226 Conversion Gate01 PDFRochelle EstebanAinda não há avaliações
- Treasury RulesDocumento25 páginasTreasury Rulesjon snow snowAinda não há avaliações
- Modul 10Documento9 páginasModul 10Herdian KusumahAinda não há avaliações
- RMC No. 73-2019 - Annex ADocumento1 páginaRMC No. 73-2019 - Annex ALeo R.Ainda não há avaliações
- TCS AnniversaryDocumento5 páginasTCS AnniversaryVitlesh PanditaAinda não há avaliações
- Analyze Company Balance Sheet Years 2021-2022Documento4 páginasAnalyze Company Balance Sheet Years 2021-2022shanizaAinda não há avaliações
- Employer Employee Relationship ServicetaxDocumento6 páginasEmployer Employee Relationship ServicetaxsridharanAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE UGC NET Dec 2014 Syllabus For CommerceDocumento5 páginasCBSE UGC NET Dec 2014 Syllabus For CommerceCharly JeromeAinda não há avaliações
- Modified Purchase Manual: 1.0 IntroductoryDocumento40 páginasModified Purchase Manual: 1.0 IntroductoryAbdul Rashid QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Place of Effective Management (PoEM) GuidelinesDocumento14 páginasPlace of Effective Management (PoEM) GuidelinesLEKHA DHILIP KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- NTC Memorandum Circular No 9-8-91 IDocumento4 páginasNTC Memorandum Circular No 9-8-91 Inyan nyan nyanAinda não há avaliações
- PRUlife-partner Eng PDFDocumento12 páginasPRUlife-partner Eng PDFAmirul IzzadAinda não há avaliações
- Chrome It Inc Manufactures Special Chromed Parts Made To TheDocumento3 páginasChrome It Inc Manufactures Special Chromed Parts Made To Thetrilocksp SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Estate QuizDocumento6 páginasEstate QuizJedi DuenasAinda não há avaliações
- InvoiceDocumento1 páginaInvoiceIlayaraja RajaAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Economics Asia Pacific 7th Edition Gans Test BankDocumento26 páginasPrinciples of Economics Asia Pacific 7th Edition Gans Test Bankbeckhamkhanhrkjxsk100% (25)
- International Shipping OffersDocumento1 páginaInternational Shipping Offersone powerAinda não há avaliações
- 26 - Determining The Optimal Tax in MiningDocumento6 páginas26 - Determining The Optimal Tax in MiningMatias FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Services Under GST - Taxguru - inDocumento10 páginasConstruction Services Under GST - Taxguru - inSHYAM RADHYEAinda não há avaliações
- Tax Canonical DoctrinesDocumento20 páginasTax Canonical DoctrinesJay Indestructible HerreroAinda não há avaliações
- Credit Training PackDocumento37 páginasCredit Training PackSohailuddin AlaviAinda não há avaliações
- PBT1 Mock ExamDocumento8 páginasPBT1 Mock ExamLee NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- The Outbreak of The French RevolutionDocumento10 páginasThe Outbreak of The French RevolutionZara KnightAinda não há avaliações
- The Economic Benefits of Reducing Violent CrimeDocumento76 páginasThe Economic Benefits of Reducing Violent CrimeCenter for American Progress100% (1)