Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Market Equilibration Process
Enviado por
Hitesh PanchalDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Market Equilibration Process
Enviado por
Hitesh PanchalDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Running head: MARKET EQUILIBRATION PROCESS
Market Equilibration Process Hitesh Panchal ECO/561 July 4, 2011 Richard M. Mclntire Ph.D.
MARKET EQUILIBRATION PROCESS Market Equilibration Process
Every business faces the law of demand and supply; the businesses that prosper will have something unique to give to the consumer base so the demand will be higher for such service or product. There are times when businesses only strive during certain time of the seasons and these companies must know the different market equilibrium for that specific month. The perfect example with regards to demand and supply is our family business, my parents and I own two motels that has great marketing demand but the problems lies with the over cluster of other properties. When consumers have alternatives to their decision than as a business we are no longer a monopoly but more a pure competitors market and this lowers the demand for our business. When discussing the law of demand and supply the perfect property to discuss is our downtown location, which is in Fresno, CA. This property has a great advantage because it is walking distance to the convention center and when there are events or concerts the demand for our property rises, so in this case there will be shortage since we cannot accommodate every client after all the rooms are taken. When we know the demand is high we are willing to raise the price much more than our average daily rate to make more profit but this will shift the market equilibrium up because every person has a limit to how much they can spend. During the slow seasons for example during Thanksgiving and Christmas there is much lower demand and higher supply so the market equilibrium will shift lower since consumers have more options on prices. When there isnt a demand for our service our fixed cost does stay the same regardless of the market condition so as business owners we have to account for that. When we know there is going to be high demand for a certain event we have to understand what people are willing to pay so there isnt any shortage of rooms left at the end of the night. By examining the average
MARKET EQUILIBRATION PROCESS rate per that day we can account for how much people are willing to pay and by getting a higher rate our profit margin definitely increases. When there is high demand for the rooms during the
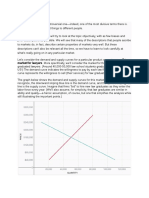
busy time our service is inelastic, so if we raise our price by double there is still a market for our rooms because people are willing to pay to stay comfortably close to the event. When the demand becomes less than our property becomes elastic, so to keep customers coming we might have to reduce our price to fill up the rooms.
So Price Do So Do
Price
Market Equilibrium
Do So
Demand increases and there will be a higher market equilibrium.
Price
Supply increase due to the price being lower, so the market equilibrium will shift to a lower line.
MARKET EQUILIBRATION PROCESS Reference McConnell, C. R., Brue, S. L., & Flynn, S. M. (2009). Economics. Principles, Problems, and Policies (18th ed.). Columbus, OH: McGraw-Hill Company.
Você também pode gostar
- Modern Monetary Theory and Practice An Introductory by William Mitchell, L. Randall Wray, Martin Watts PDFDocumento397 páginasModern Monetary Theory and Practice An Introductory by William Mitchell, L. Randall Wray, Martin Watts PDFAhmed DanafAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Consumer AwarenessDocumento16 páginasReport On Consumer AwarenessShailesh Sharma82% (22)
- The Myth of Manipulation The Economics of Minimum WageDocumento65 páginasThe Myth of Manipulation The Economics of Minimum WageAndrew Joliet100% (1)
- How To Draw Supply and DemandDocumento15 páginasHow To Draw Supply and DemandEgyptian Treasure100% (1)
- Supply and Demand Trading GuideDocumento41 páginasSupply and Demand Trading Guideswaraj100% (1)
- Basic Economics: Author of The Vision of The AnointedDocumento48 páginasBasic Economics: Author of The Vision of The AnointedAvishek PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Market Dynamics Through Demand and SupplyDocumento12 páginasUnderstanding Market Dynamics Through Demand and SupplyJoJi Malik100% (9)
- The Real Estate Primer: The Golden Rules of Buying and SellingNo EverandThe Real Estate Primer: The Golden Rules of Buying and SellingAinda não há avaliações
- The Assumptions Economists Make PDFDocumento376 páginasThe Assumptions Economists Make PDFMazen AlbsharaAinda não há avaliações
- Strikingly Different Selling: 6 Vital Skills to Stand Out and Sell MoreNo EverandStrikingly Different Selling: 6 Vital Skills to Stand Out and Sell MoreAinda não há avaliações
- Price: Maximizing Customer Loyalty through Personalized PricingNo EverandPrice: Maximizing Customer Loyalty through Personalized PricingAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 Fuhrmann B Introduction To Business and EconomicsDocumento64 páginas2019 Fuhrmann B Introduction To Business and EconomicsDaka Radhiyan YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Economics Chapter 2-3Documento6 páginasApplied Economics Chapter 2-3Joan Mae Angot - Villegas100% (1)
- Summary Of "Principles Of Economics" By Alfred Marshall: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo EverandSummary Of "Principles Of Economics" By Alfred Marshall: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESAinda não há avaliações
- Supply and DemandDocumento2 páginasSupply and DemandMIHAELACARMEN OLTIANUAinda não há avaliações
- Supply and Demand Factors Affect IndividualsDocumento5 páginasSupply and Demand Factors Affect IndividualsRISHABH JAINAinda não há avaliações
- Homework Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium QuantityDocumento5 páginasHomework Equilibrium Price and Equilibrium Quantityh4a0nawc100% (1)
- Elasticity: Learning ObjectivesDocumento32 páginasElasticity: Learning ObjectivesIchda Qomariah50% (2)
- The Laws of Supply and DemandDocumento17 páginasThe Laws of Supply and Demanddharshini deivasigamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Supply and Demand Research Paper TopicsDocumento6 páginasSupply and Demand Research Paper Topicshqeoguplg100% (1)
- Economics Chapter 2 14Documento84 páginasEconomics Chapter 2 14Jarren BasilanAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Law of DemandDocumento5 páginasResearch Paper On Law of Demandt1s1gebes1d3100% (1)
- Microeconomics AssignmentDocumento5 páginasMicroeconomics AssignmentPratham BhansaliAinda não há avaliações
- BACC1 Lecture Note #3Documento6 páginasBACC1 Lecture Note #3Lea AndreleiAinda não há avaliações
- Demand and Supply: Start Up: Crazy For CoffeeDocumento32 páginasDemand and Supply: Start Up: Crazy For CoffeeLu CheAinda não há avaliações
- Economics - Demand and Supply NotesDocumento4 páginasEconomics - Demand and Supply NotesgabrielleAinda não há avaliações
- The Law of Supply and Demand Is A Theory That Explains The Interaction Between The Sellers of A Resource and The Buyers For That ResourceDocumento5 páginasThe Law of Supply and Demand Is A Theory That Explains The Interaction Between The Sellers of A Resource and The Buyers For That Resourceaakash pandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Economics PDFDocumento20 páginasBasic Economics PDFRonaldo AssisAinda não há avaliações
- Economics AssignmentDocumento3 páginasEconomics AssignmentBrian aruwaAinda não há avaliações
- Demand and SupplyDocumento13 páginasDemand and Supplymafiawars21Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 2 Transcript (English)Documento72 páginasWeek 2 Transcript (English)Adik TanAinda não há avaliações
- ImpactDocumento6 páginasImpactDinak ConsultingAinda não há avaliações
- Price Determination in MatketsDocumento6 páginasPrice Determination in MatketsIgnite NightAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 - Demand and SupplyDocumento32 páginasUnit 3 - Demand and SupplyLillian NgubaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Application of Demand and SupplyDocumento9 páginasChapter 2: Application of Demand and SupplyAjilAinda não há avaliações
- ApplEcon Module 1Documento10 páginasApplEcon Module 1Alec FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Act Eva 2 MicroeconomiaDocumento11 páginasAct Eva 2 MicroeconomiaJuan Pablo Bernal AgudeloAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Economics in 40 WordsDocumento5 páginasUnderstanding Economics in 40 WordsKrissela SolorzanoAinda não há avaliações
- BSBA BE 1-3 Group Report on Demand and SupplyDocumento22 páginasBSBA BE 1-3 Group Report on Demand and SupplyFeane LamasanAinda não há avaliações
- PricingStrategy IntroductionDocumento6 páginasPricingStrategy IntroductionKaren GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial EconomicsDocumento24 páginasManagerial EconomicsRudydanvinz BernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Basic of Micro EconomicsDocumento19 páginasBasic of Micro EconomicsshossainaisAinda não há avaliações
- Market Forces of Supply & DemandDocumento5 páginasMarket Forces of Supply & DemandLiezel Garcia MacatuladAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of Demand and Supply: Submitted By: Bipul Deka Roll No: 05 B.Pharm 4 YearDocumento7 páginasLaws of Demand and Supply: Submitted By: Bipul Deka Roll No: 05 B.Pharm 4 YearLulu BritanniaAinda não há avaliações
- Course Lesson ThreeDocumento14 páginasCourse Lesson Threeyng guesAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 4 NotesDocumento34 páginasMod 4 NotesMew MewAinda não há avaliações
- The-Implications-of-Market-Pricing-Report-week-4Documento4 páginasThe-Implications-of-Market-Pricing-Report-week-4Ex PertzAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Lecture IIDocumento19 páginasEconomics Lecture IIAditya kumar guptaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply For Goods and Services - Principles of EconomicsDocumento19 páginas3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply For Goods and Services - Principles of EconomicsPuneet SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Supply and DemandDocumento4 páginasSupply and Demandscholta00Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is MicroeconomicsDocumento6 páginasWhat Is MicroeconomicsjuliaAinda não há avaliações
- Upward DemandDocumento6 páginasUpward DemandchelleAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment EconomicsDocumento5 páginasAssignment Economicsprateek25.035460Ainda não há avaliações
- MECO 111-Chapter 4 (Demand and Supply)Documento24 páginasMECO 111-Chapter 4 (Demand and Supply)zainabmossadiqAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Assessments Program - MBA - Operations Subject - Managerial Economics Assessment Type - Internal Assessment (Subjective Assignment)Documento18 páginasInternal Assessments Program - MBA - Operations Subject - Managerial Economics Assessment Type - Internal Assessment (Subjective Assignment)sakalidhasavasanAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Economics Week 5Documento8 páginasApplied Economics Week 5SETH JOHN AGRUDAAinda não há avaliações
- Law of Supply and DemandDocumento6 páginasLaw of Supply and DemandArchill YapparconAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - The Market SettingDocumento18 páginasChapter 3 - The Market SettingJeannie Lyn Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Quarterly Review: Are You A Gambler?Documento4 páginasQuarterly Review: Are You A Gambler?Nicholas FrenchAinda não há avaliações
- Resources 2Documento6 páginasResources 2kerminabosyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1Documento15 páginasChapter 1James SitohangAinda não há avaliações
- CH 3 Supply Demand TheoryDocumento31 páginasCH 3 Supply Demand TheoryLutfun Nesa Aysha 1831892630Ainda não há avaliações
- Reflection Paper in Micro-Economics - MingoyDocumento23 páginasReflection Paper in Micro-Economics - MingoyRochelle BustaliñoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No 2 MiDocumento4 páginasAssignment No 2 MiNasir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Purchasing Power Parity Master ThesisDocumento6 páginasPurchasing Power Parity Master Thesisaprilcharltontulsa100% (2)
- Chapter 1 Microeconomics by David Besanko Ronald Braeutigam Test BankDocumento18 páginasChapter 1 Microeconomics by David Besanko Ronald Braeutigam Test BankNupur KasliwalAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Question Preview-NehaDocumento158 páginasComprehensive Question Preview-NehaPiyushhBhutoriaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3Documento40 páginasTopic 3Minato MeaAinda não há avaliações
- Law of Supply and DemandDocumento2 páginasLaw of Supply and DemandJoyce Anne GarduqueAinda não há avaliações
- Elasticity of Demand and Supply: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 13EDocumento47 páginasElasticity of Demand and Supply: Lipsey & Chrystal Economics 13EJudhaAinda não há avaliações
- 12 STD Business Math 10 Mark FaqsDocumento18 páginas12 STD Business Math 10 Mark FaqsAhamedIqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Harvard Syllabus MGMT S-5033 Summer 2019Documento7 páginasHarvard Syllabus MGMT S-5033 Summer 2019dhaminiAinda não há avaliações
- A Level Economics Papers Nov2010 PDFDocumento97 páginasA Level Economics Papers Nov2010 PDFLincolnt LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Ethereum TheTripleHalving SquishChaosDocumento79 páginasEthereum TheTripleHalving SquishChaosMuy SantosAinda não há avaliações
- The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework For Macroeconomic AnalysisDocumento75 páginasThe IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework For Macroeconomic AnalysisAbdelrahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento43 páginasChapter 2Sintayehu DerejeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 20: Simultaneous Equation Models - IntroductionDocumento32 páginasChapter 20: Simultaneous Equation Models - IntroductionLucy SitinjakAinda não há avaliações
- Theory of Demand and SupplyDocumento45 páginasTheory of Demand and SupplyThabo ChuchuAinda não há avaliações
- Development Studies ReadingDocumento107 páginasDevelopment Studies ReadingAmit TripuraAinda não há avaliações
- Economic Question Bank With Solutions PDFDocumento172 páginasEconomic Question Bank With Solutions PDFlimuAinda não há avaliações
- The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocumento28 páginasThe Market Forces of Supply and DemandJustin MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Exercises For ECO120 (Chapter 1-4)Documento15 páginasExercises For ECO120 (Chapter 1-4)Celyn Anne Jati EkongAinda não há avaliações
- Component 1 - Exemplar MCQS: QuestionsDocumento11 páginasComponent 1 - Exemplar MCQS: QuestionsSalman ShakirAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis General and Partial EquilibriumDocumento8 páginasAnalysis General and Partial EquilibriumavantikaAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDocumento19 páginasEcon 122 Week 1 9 by DwexDestinyAinda não há avaliações
- HyperpptDocumento22 páginasHyperpptnanthigaAinda não há avaliações
- FTU2 - Microeconomics 2 - Trần Thông Tú - 1201017440Documento65 páginasFTU2 - Microeconomics 2 - Trần Thông Tú - 1201017440Trần Thông TúAinda não há avaliações
- Market PerfectDocumento35 páginasMarket PerfectLoretta D'SouzaAinda não há avaliações