Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Activity Intolerance (NCP)
Enviado por
Sonia Letran SingsonDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Activity Intolerance (NCP)
Enviado por
Sonia Letran SingsonDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
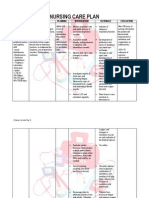
NURSING CARE PLAN
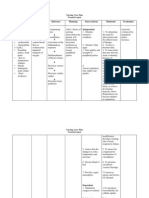
Defining Characteristics Nursing diagnosis: Activity intolerance : level II related to imbalance between oxygen supply and demand secondary to valvular damage S: dali lage ko kapuyon?? as verbalized O:>received sitting on bed,awake, coherent >hair unkempt >diaphoresis noted >dark undereyes noted >pulsating and distended jugular veins >reports f fatigue after activity >hesitancy to do activities >generalized weakness
T=37.8 P=100 bpm R=28cpm, Bp=90/40
Expected Outcome (Ideal)
Intervention and Rationale
Behavioral Outcome (Actual)
Short term: After 8 hours of nursing interventions client will identify activity intolerance and eliminate or reduce the effects when possible Be able to use identifies techniques to enhance activity tolerance
Long term : After 5 days of nursing interventions client will participate willingly in necessary or desired activities
I: Determine patient's perception of causes of fatigue or activity intolerance R: These may be temporary or permanent, physical or psychological. Assessment guides treatment. S:Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.78 I:evaluate current limitations , degree of deficit in light of usual status R: provides comparative baseline S: Doenges et.al. Nurses Pocket Guide p.66-67 I: assess nutritional status R: adequate energy reserves are required for activity S: Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.7
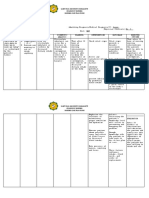
Defining Characteristics Laboratory Results:
Expected outcome (Ideal)
Intervention and Rationale I: Establish guidelines and goals of activity with the caregiver and patient R: motivation is enhanced if the patient participates in goal setting S: Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.78 I: elevate head of bed as tolerated R: enhances lung expansion to maximize oxygenation for cellular uptake S: Doenges et.al. Nursing Care Plans p. 503 I:encourage adequate rest periods R: rest between activities provides time for energy conservation and recovery S: Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.78 I: assist patient and SO to plan for activities for times when she or he has more energy R: not all self care activities need to be completed in the morning S: Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.78 I:encourage verbalization of feelings regarding limitations R: acknowledgement that living with activity intolerance is both physically and emotionally difficult S: Black and Hawaks, Medicalsurgical nursing p.503 I: provide assistance as necessary R: although help is enhanced when client does some things for itself S: Doenges at.al. Nursing Care Plans p.503-504 Collaborative: Sources:
Behavioral Outcome (Actual)
Theoretical Basis: A few patients with rheumatic fever become critically ill with intractable heart failure, serious dysrhythmias, and pneumonia. These patients are treated in an intensive care unit. Most patients recover quickly. However, although the patient is free of symptoms, certain permanent residual effects remain that often lead to progressive valvular deformities. The extent of cardiac damage, or even its existence, might not have been apparent in clinical examinations during the acute phase of the disease. Eventually, however, the heart murmurs that are characteristic of valvular stenosis, regurgitation, or both become audible on auscultation and, in some patients, even detectable as thrills on palpation. Usually, the myocardium can compensate for these valvular defects very well for a time. As long as the myocardium can compensate, the patient remains in apparently good health. With
Doenges et.al. NursingCAre Plans: Individualizing Client Care Across the Life Span, F.A. Davis Company, 7th edition, 2006 Gulanick et.al. Nursing Care Plans: Nursing diagnosis and Interventions, Elsvier Saunders, 6th ed. 2006 Doenges et.al. Nurses Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions and rationales, F.A. Davis Company, 10th ed. 006 Black and Hawaks, MedicalSurgical Nursing: Clinical Management for Positive Outcomes, Elsvier Saunders, 7th ed. 2004 Brunner and Suddarth, Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10th edition, 2008
I: monitor laboratory studies R:identifies deficiencies S: Doenges et.al. Nursing Care Plans p.503-504
continued valvular alterations, the myocardium is unable to compensate , as evidenced by signs and symptoms of heart failure, The decrease in the ejected ventricular volume causes the sympathetic nervous system to increase the heart rate (tachycardia), often causing the patient to complain of palpitations. The pulses become weak and thready. Without adequate CO, the body cannot respond to increased energy demands, and the patient is easily fatigued and has decreased activity tolerance. Fatigue also results from the increased energy expended in breathing and the insomnia that results from respiratory distress, coughing, and nocturia. - Brunner and Suddarth, MedicalSurgical Nursing p.881
I:provide supplemental oxygen as indicated R: maximizes oxygen transport to tissues and improve ability to function S: Doenges et.al. Nursing Care Plans
Você também pode gostar
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento4 páginasNCP Activity IntoleranceKryza Dale Bunado Batican0% (1)
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocumento3 páginasNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyGidget de Leon100% (7)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitDocumento5 páginasNCP Ineffective Tissue Perfusion and Self Care DeficitFrances Anne Pasiliao100% (3)
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Documento2 páginasAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDocumento3 páginasActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for Acute Renal FailureKian Herrera100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 páginaActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- SchistosomiasisDocumento92 páginasSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- ND PrioritizationDocumento1 páginaND PrioritizationBea Dela Cena50% (2)
- Nutrition Imbalance Care PlanDocumento7 páginasNutrition Imbalance Care PlanMariquita BuenafeAinda não há avaliações
- Improving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisDocumento2 páginasImproving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- NCP: DysrhythmiasDocumento12 páginasNCP: DysrhythmiasJavie100% (3)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocumento2 páginasIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocumento1 páginaActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- ACLS Drugs (2010)Documento16 páginasACLS Drugs (2010)RN333100% (2)
- Basic Counselor's Attending Skills & ResponsesDocumento20 páginasBasic Counselor's Attending Skills & ResponsesDARRO6 FOIAinda não há avaliações
- Daily NCPDocumento5 páginasDaily NCPKuennie SabalAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 páginasNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocumento6 páginasActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 páginasNCP Activity IntoleranceKatkat VictorinoAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionClaidelyn De Leyola100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento5 páginasNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimAinda não há avaliações
- SAMPLE NCP For Pernicious AnemiaDocumento3 páginasSAMPLE NCP For Pernicious Anemiainks19100% (7)
- NCP - Acute PainDocumento5 páginasNCP - Acute Painryan50% (2)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento4 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionClariz Basco100% (1)
- NCPDocumento7 páginasNCPMarius Clifford BilledoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceDocumento8 páginasNursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceManuel Jacob YradAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue Perfusionsyderman999Ainda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPTracy Camille EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Chronic Pain and FatigueDocumento6 páginasNCP Chronic Pain and FatigueMary Rose Bell Arias100% (1)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMADocumento5 páginasNCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMAMa. Elaine Carla Tating50% (2)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 páginasNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 páginasNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 páginasNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Self Care DeficitDocumento2 páginasSelf Care DeficitRen Aezzle Garcia Aceveda100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDocumento4 páginasNursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionDiane ReyAinda não há avaliações
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- NCP-Deficient Fluid VolumeDocumento1 páginaNCP-Deficient Fluid Volumejanmichael8Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Intervention Plan for Fracture PatientDocumento2 páginasNursing Intervention Plan for Fracture PatientAce Dioso TubascoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - ConstipationDocumento3 páginasNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Activity IntoleranceDocumento1 páginaNCP For Activity IntoleranceKristine LonyenAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Diarrhea - FeunrmfDocumento7 páginasNCP - Diarrhea - FeunrmfJk SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocumento2 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Near DrowningDocumento1 páginaNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoAinda não há avaliações
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasActivity Intolerancelouie roderosAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Fatigue Liver Cancer Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis Fatigue Liver Cancer Care PlanPC NAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento3 páginasRisk For Decreased Cardiac OutputSid Artemis FriasAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocumento4 páginasNCP Tissue PerfusionLisa Tandog100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyDocumento3 páginasNCP Activity Intolerance Related To Decreased in Oxygen SupplyKyle Stephen TancioAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Bleeding NCP ProperDocumento2 páginasRisk For Bleeding NCP ProperJohn Michael Solis0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NCP FinalDocumento18 páginasNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- NCP (Fatigue)Documento1 páginaNCP (Fatigue)student_019100% (1)
- NCP Gouty ArthritisDocumento21 páginasNCP Gouty ArthritisArianne Kamille Andes67% (3)
- NCPDocumento10 páginasNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaAinda não há avaliações
- Managing Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and RestDocumento2 páginasManaging Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and ResthaniehaehaeAinda não há avaliações
- ECG StripsDocumento3 páginasECG StripsSonia Letran SingsonAinda não há avaliações
- Or Instruments SampleDocumento9 páginasOr Instruments SampleSonia Letran SingsonAinda não há avaliações
- Open Reduction Internal FixationDocumento4 páginasOpen Reduction Internal FixationSonia Letran Singson100% (1)
- SINGSON, Sonia Rufa Joy-Unit2assignmentDocumento9 páginasSINGSON, Sonia Rufa Joy-Unit2assignmentSonia Letran SingsonAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento1 páginaAcute Renal FailureSonia Letran Singson100% (1)
- Dialysis Report - NURS 302Documento3 páginasDialysis Report - NURS 302AmalAinda não há avaliações
- Spilling The Tea Culture Report by - KommuneDocumento88 páginasSpilling The Tea Culture Report by - KommuneSmriti TewariAinda não há avaliações
- GFRAS - NELK - Module 4 Professional EthicsDocumento39 páginasGFRAS - NELK - Module 4 Professional EthicsAssisi-marillac GranteesAinda não há avaliações
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento2 páginasAnnotated Bibliographyapi-708978172Ainda não há avaliações
- CITB Mock Test 50 QuestionsDocumento17 páginasCITB Mock Test 50 QuestionstommyAinda não há avaliações
- Medium Puppy Chicken FormulaDocumento1 páginaMedium Puppy Chicken FormulaPeteRAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatitis: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDocumento87 páginasHepatitis: DR Putra Hendra SPPD Unibayoga yogafenkanoAinda não há avaliações
- Consensus Statements Febrile SeizuresDocumento7 páginasConsensus Statements Febrile SeizuresMattAinda não há avaliações
- MEO - Application FormDocumento7 páginasMEO - Application FormAbdul RahimAinda não há avaliações
- COBADocumento222 páginasCOBArendiAinda não há avaliações
- The School Canteen Follows Guidelines On Operational Management Set by The Department of Education Through DepEd Order NoDocumento3 páginasThe School Canteen Follows Guidelines On Operational Management Set by The Department of Education Through DepEd Order NoChristian Lloyd Latayan64% (14)
- Education and HealthDocumento4 páginasEducation and Healthsagar111033Ainda não há avaliações
- Detection of Brain HemorrhageDocumento8 páginasDetection of Brain HemorrhageIJRASETPublicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Emotion and Support Perceptions in Everyday Social Interaction: Testing The Less Is More'' Hypothesis in Two CulturesDocumento20 páginasEmotion and Support Perceptions in Everyday Social Interaction: Testing The Less Is More'' Hypothesis in Two CulturesAdina MicuAinda não há avaliações
- HR Practices ReportDocumento105 páginasHR Practices Reportamritashelar27100% (4)
- Chap 7 Info SystemDocumento26 páginasChap 7 Info Systemainamikhail954Ainda não há avaliações
- Jean Keeling, Anthony Busuttil Paediatric Forensic Medicine and PathologyDocumento521 páginasJean Keeling, Anthony Busuttil Paediatric Forensic Medicine and PathologyMadul15Ainda não há avaliações
- Administration of Blood and Blood ProductsDocumento4 páginasAdministration of Blood and Blood Productspmnh nqpsAinda não há avaliações
- Biology ProjectDocumento18 páginasBiology ProjectParamdeep Singh100% (1)
- Path-Fit 1-Module-1-3Documento19 páginasPath-Fit 1-Module-1-3Rubina Sadernas MalicdemAinda não há avaliações
- Sports Injuries - StrainDocumento10 páginasSports Injuries - StrainChris SinugbojanAinda não há avaliações
- Gcse Pep Coursework ExampleDocumento8 páginasGcse Pep Coursework Exampleafjwdbaekycbaa100% (2)
- Task 2 Case Notes: James Hutton: Time AllowedDocumento3 páginasTask 2 Case Notes: James Hutton: Time AllowedKelvin Kanengoni0% (1)
- Stress Eating: A Phenomenological StudyDocumento24 páginasStress Eating: A Phenomenological StudyGauis Laurence CaraoaAinda não há avaliações
- SSP032-M01 - SDG 1-3 Group No.2Documento40 páginasSSP032-M01 - SDG 1-3 Group No.2Karl CabaneroAinda não há avaliações
- COPSOQ III Questionnaire 060718Documento6 páginasCOPSOQ III Questionnaire 060718Beatriz Barboza VeraAinda não há avaliações
- Ovarian Cyst and TumorsDocumento81 páginasOvarian Cyst and Tumorselard jimenezAinda não há avaliações
- ConstructivismDocumento16 páginasConstructivismKhoiruddin Bashori50% (2)
- Expanding Possibilities in Distance Learning Revised 2021Documento3 páginasExpanding Possibilities in Distance Learning Revised 2021Rachel Santiago LayaAinda não há avaliações