Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP and Drug Study For Case in Sle
Enviado por
Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP and Drug Study For Case in Sle
Enviado por
Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
24 XIII.
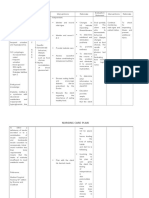
NURSING CARE PLAN Assessment Abnormal cues: >Malar or "butterfly" rash on the face >Discoid skin rash on hands, thighs and scalp >Photosensitivity >oral mucous membrane ulcers >joint pain >Patient is not oriented to time and place, forgetful -sunken eyes -Fatigue and weakness -poor appetite -dependent in her ADL -presence of alopecia Vital signs: RR=24 cpm Temp= 36.5C Laboratory results: -Antinuclear Anti Body result is 7. -HGB, HCT, RBC, platelet are decreased -WBC is increased -serum sodium Rationale Predisposing Nursing diagnosis: Gender: Female Race: Asian Impaired tissue Precipitating integrity related to Infection: UTI , inflammation, altered Pneumonia circulation as evidence by malar rash on the face, Unknown etiology discoid skin rashes on hands, scalp and defective immune thighs, oral mucous regulatory membrane ulcers and mechanism presence of alopecia. Loss of immune Nanda definition: tolerance Damage to mucous membranes, corneal, increase antigenic integumentary or load subcutaneous tissues excess T cell, defective B cell suppression and Source: shifting of T helper 1 to Th2 immune Doenges, et al. responses Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. b cell hyperactivity Davis company. 2010 production of pathogenic Nursing diagnosis Desire outcome After 32 hours of nurse-client interaction the client will be able to: Independent: 1. Verbalize understanding of condition and causative factors. 1. a. identify underlying condition or pathology involved in tissue injury -serves as baseline data and will suggests treatment options, as well as clients desire and ability to protect self, and potential for recurrence of tissue damage - this could have an impact in tissue health 2. Goal met. The patient takes medication to minimize itching. The patient also verbalizes gakatol pa sa dyapon pero indi na grabe. 1. Goal met. The patient was able to understand and identify her present condition. Nursing intervention Justification Evaluation After 32 hours of nurse-client interaction the client will be able to:
b. note poor hygiene and health practices 2. Demonstrate progressive improvement in 2. wound or lesion a. Assess blood healing through supply and sensation behavior and on affected area by lifestyle changes and checking the site for prevent redness, discharges, complications or temperature and recurrence doing sensory tests. b. Note skin color, texture, and turgor
-to evaluate actual/or potential impairment in circulation
-determines the extent or
25 slightly decreased >history of Rheumatoid Arthritis (2004) >history of UTI (March2011) Weakness: >Poor immune system >gender: female >poor hygiene >does not cooperate in treatment >does not exercise Strengths/wellness: >strong support system >strong financial support autoantibodies and assess areas of pigmentation of color changes c. inspect skin on daily basis, describing wound lesions and rashes characteristics observed 3. Maintain optimal nutrition and physical well-being. d. encourage adequate periods of rest and sleep involvement of injury -promotes timely intervention and revision of plan of care
immune complexes complement activation tissue injury and damage Impaired tissue integrity related to inflammation, altered circulation as evidence by malar rash on the face, discoid skin rashes on hands, scalp and thighs, oral mucous membrane ulcers and presence of alopecia. Source: Smeltzers S.C, et,al. Brunner & Suddarths Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 12th ed.
-to limit metabolic demands, maximize energy available for healing and meet comfort needs -to minimize condition and promote healing
3. a. maintain appropriate moisture environment for particular wound
b. reposition client, -to enhance involving client in understanding and reasons for and cooperation decisions about times and positions c. encourage early ambulation or mobilization -promotes circulation and reduces risk associated with immobility and prevent excessive tissue pressure
3. Goal met. The patient cooperates measures to improve nutrition and physical well-being. At the first day, patient was observe to have poor appetite but during the fourth day patient can be seen eating her meals gradually with the help of her folks.
26 4. identify measure in preventing and treatment regimens to enhance healing d. provide optimum nutrition and increased protein intake -to provide a positive nitrogen balance to aid in skin and tissue healing and to maintain a general good health. -to maintain general good health and skin turgor 4. Goal met. The patient was able to know the appropriate regimen and prevention with regards to her disease condition. Through incidental health teaching she was able to understand more about the treatment given to her especially the medications and procedures.
4. a. emphasize importance of adequate nutritional and adequate fluid intake b. assist client in understanding and following medical regimen and developing program of preventive care. c. discuss importance of health as well as measures to maintain proper skin functioning 5. Review laboratory results pertinent to causative factors Collaborative: 1. Monitor and administer medications as
-enhances cooperation and optimizing outcomes
- for changes indicative of healing or presence of infection, complications.
-to determine and assess the contributing factors -to be aware of all the medication client is taking, noting possible interaction
27 Ordered such as, Lasix, Predisone, Cozar, Norvasc, Merrem, Calvit and KCl. 3. Assist with diagnostic procedures or cumulative effects
-May be necessary to determine extent of impairment.
4. Assist in -to maintain gains identifying ongoing and continue of treatment needs and progress rehabilitation for the individual like physical and occupational therapy.
Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. Davis company. 2010
Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. Davis company. 2010
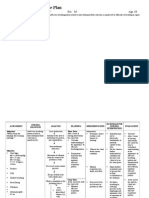
28 ASSESSMENT Actual Abnormal Cues: Appears very tired and weak Lethargic Compromised concentration and mentation changes like disorientation to place, incoherent responses, and focusing on the feelings of weakness of her whole body Inability to perform activites of daily living independently Poor muscle stregth Hgb result of 115 g/L and 104 g/L (normal: 120-160 g/L) last November 15 and November 17 lab results Hct result of 0.32 L/L and 0.30 L/L(normal: 0.40-0.54 L/L) on November 15 and 17 lab results repectively Serum sodium results of 130 (normal: 137143 mEq/dL) and serum potassium result of 2.60 (normal: 3.6NURSING DIAGNOSIS Fatigue related to immune system pathology as evidenced by patients appearance of weakness and tiredness, lethargy, inability to perform activities independently, poor muscle strength, Hgb result of 115 g/L and 104 g/L (normal: 120-160 g/L) last November 15 and November 17 lab result, Serum sodium results of 130 (normal: 137-143 mEq/dL) and serum potassium result of 2.60 (normal: 3.6-5.1 mg/dL) on November 15 lab result RATIONALE DESIRED OUTCOME/ NURSING GOALS After 32 hours of nursing interventions, the client will be able to: 1. Report improved sense of energy a. Note patients belief of what is causing the fatigue and what relieves it b. Evaluate aspect of learned helplessness that may be manifested by giving up -to assess contributing factors NURSING INTERVENTIONS Independent Nursing Interventions: JUSTIFICATION EVALUATION After 32 hours of nursing interventions, the client was able to:
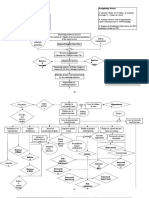
Predisposing Gender: Female Race: Asian Precipitating Infection: UTI , Pneumonia Unknown etiology Female estrogen hormones Manifestations of heightened levels of estrogen during puberty and pregnancy Unknown cause of estrogen influencing the immune response of the HLA system in chromosome 6 Human Leukocyte
-can perpetuate a cycle of fatigue, impaired functioning, and increased anxiety and fatigue
c. Accept reality of patients report of fatigue and do not underestimate effect on the quality of life the client experiences d. Instruct methods to conserve energy (e.g. plan steps of activity before beginning so that all
-to assist patient in coping with fatigue
1. Goal met. When asked if patient still feels extremely tired, she was able to claim, kapoy e, pero lain gid ya sang sadto nga week, comparing the fatigue she has felt last week, which was more severe. Practices to conserve energy were done through the help of her significant others by assisting her to do activities of daily living. She also sleeps most of the time on our duty hours to conserve energy. Then at the last day of duty, she was already able to stand and able to hold conversations longer than the conversations she had upon first admission.
Definition: An overwhelming sustained sense of exhaustion and decreased capacity for physical and
-to reduce energy expenditure
29 5.1 mg/dL) on mental work at usual November 15 lab work level result Vebal reports of Indi ko pagsamuka anay, nakapoy ko. With health history of easy fatigability and body weakness 7 months prior admission and with decreased Hgb, Hct, potassium and sodium results of lab tests after consultation to physician. Risk Factors/Weaknesses: Poor appetite Episodes of joint pain Noncompliance to some medical interventions and laboratory tests Hospital environment (too warm and noisy) Sleep deprivation Poor financial support Knowledge deficit of disease process and treatment Wellness/strengths: Good emotional Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (9th ed.). F.A. Davis Company.2004. p 232. Antigen Class 1 and 2 in chromosome 6 possess multiple genes influenced in acquiring SLE 2. Perform activities of daily living and desired activities at level of ability needed materials are at hand) e. Provide environment conducive to relief of fatigue ( e.g.provide electric fan, etc.) f. Provide means to decrease environmental noise (e.g. earplugs, etc.) g. Provide diversional activities. Avoid overstimulation/und erstimulation (cognitive and sensory) h. Discuss routines to promote restful sleep (e.g. uninterrupted periods of rest, longer sleep periods at night, etc.) a. Determine ability to participate in activities/ level of mobility b. Note daily energy -temperature and level of humidity are known to affect exhaustion
Fewer or defective macrophages in the body Defective clearance of early apoptotic cells Secondary necrosis of the cells Release of nuclear fragments as potential autoantigens Impaired membrane integrity of dendritic cell Induced maturation of dendritic cells
-when sleep deprivation is present, it adds to fatigue -impaired concentration can limit ability to block competing stimuli/distractions
2. Goal partially met. Patient was able to perform her activities of daily living through the help of her significant others. The greatest feat that the patient made during our duty week was that she was able to stand on the last day, although her basic daily activities were still done with assistance.
-to assist patient to establish a sleep pattern
3. Participate in recommended treatment program
-to provide baseline data for the nurses plan of activities -helpful in 3. Goal met. Patient was able to show participation through
30 support for the family Willingness to follow nursing interventions Have strong faith in God Various autoantibody productions Production of antinuclear antibody, anti-phospholipid and other specific autoantibodies Anti-erythrocyte antibody activation Formation of defective immune complex Hemolysis Reduced RBC count Decrease in oxygen available for cellular uptake Fatigue Appearance of tiredness and f. Involve patient and significant others in schedule planning -to increase awareness of the treatment and rehabilitation to patient and significant others -to manage patient within their limits of ability -to assist patient with limited mobility patterns determining pattern/timing of activity -to assess contributing factors listening while the student nurse gives accidental and prepared health teachings about the disease and its treatment. Although they had troubles with their finances, most of the highly needed medical interventions were followed. Significant others also assisted with the patient as evidenced by their willingness to accept information given by the student nurse. They also able to give simple examples of how to conserve the patients energy like not disturbing her in her sleep and keeping their voices down to make her rest. They also did their part in assisting her with her activities of daily living.
c. Interview significant others regarding specific changes observed on patient d. Establish realistic activity goals with the patient e. Plan care to allow adequate rest periods. Schedule activities for periods when patient has the most energy
-enhances commitment to promoting optimal outcomes -to maximize participation
g. Encourage to do whatever is possible (e.g.self-care, sit up, etc.) h. Assist with selfcare needs; keep bed in low position and
31 inability to perform activities of daily living independently Source: Smeltzers S.C, et,al. Brunner & Suddarths Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 12th ed. assist in ambulation as indicated a. Discuss the disease process relevant to patient b. Discuss therapy regimen relating to individual causative factors -understanding the disease can help the client understand the treatment regimen -to help patient and significant others understand the relationship of disease and treatment and to elicit their cooperation on the treatment regimen -to encourage participation of patient and significant others in health management of patient
c. Assist patient and significant others to develop a plan of activity and exercise within the individuals capability d. Instruct patient in ways to monitor responses to activity and significant signs and symptoms e. Promote overall health measures (e.g. nutrition(High CHO, Normal CHOn, low Fat), adequate fluid
-indicates the need to alter the activity level
-presence of anemia/hypoxemia reduces oxygen for available cellular uptake and
32 intake of 1.5-2L/day, contributes to fatigue appropriate intake of vitamins and minerals as prescribed especially iron, etc.)
Collaborative interventions: a. Administer medications related to patients condition (e.g. pain relievers, antimalarials, etc.) b. Assist with medical procedures as indicated c. Administer blood transfusions properly as indicated. Report any allergic reactions. Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide(9th ed.). F.A. Davis Company.2004. pp 232-234. -to promote wellness of patient
-to assist in measures to relieve patients condition -to supplement blood components and increase oxygen for cellular uptake
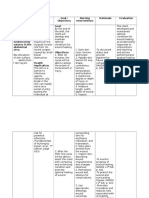
33 RISK NCP Assessment Abnormal cues: >easy fatigability and weakness >Patient is not oriented to time and place, forgetful >Photosensitivity >presence of alopecia >Malar or "butterfly" rash on the face >Discoid skin rash on hands, thighs and scalp >oral mucous membrane ulcers >joint pain >sunken eyes >poor appetite >dependent in her ADL >poor muscle tone Vital signs: RR=24 cpm Temp= 36.5C Nursing diagnosis Nursing diagnosis: Rationale Desire outcome After 32 hours of nurse-client interaction the client will be able to: Independent: 1. Verbalize understanding of individual factors that contribute to possibility of injury 1. a. Perform thorough assessment regarding safety issues when planning for client care and/or preparing for discharge from care. -failure to accurately assess and intervene or refer these issues can place the client at needles risk and creates negligence issues for the healthcare practitioner. -affects clients ability to protect self and/or others, and influences choice of interventions and teaching -to identify risk for falls 1. Goal met. The patient was able to gain information about factor that may contribute to place patient at risk for injury. Nursing intervention Justification Evaluation After 32 hours of nurse-client interaction the client will be able to:
Predisposing Gender: Female Risk for injury Race: Asian related to tissue Precipitating damage, autoimmune Infection: UTI , dysfunction, Pneumonia abnormal blood profile , disorientation and Unknown etiology altered mobility as evidence by malar immune system rash on the face, activation discoid skin rashes on hands, scalp and thighs, oral mucous altered immune membrane ulcers and response presence of alopecia, weakness, disoriented to time soluble mediators and place, (cytokines) photosensitivity. Nanda definition: Endothelial / cellular response Autoimmunity Tiisue or organ involvement
b. note clients age, gender, developmental stage, decision making ability and level of cognition c. assess clients muscle strength, gross and fine motor coordination 2. a. provide healthcare within culture of safety
Laboratory results: -Antinuclear Anti Body result is 7. -HGB, HCT, RBC, platelet are decreased -WBC is increased -serum sodium slightly decreased
At risk of injury as a result of environmental conditions interacting with the individuals adaptive and defensive resources.
2. Modify environment as
-to prevent errors resulting in client injury, promote
2. Goal met. The patient was able to encourage how to protect herself and
34 >history of Rheumatoid Arthritis (2004) >history of UTI (March2011) Weakness: >Poor immune system >gender: female >lack of patients cooperation >poor hygiene >does not cooperate in treatment >does not exercise .poor environmental sanitation Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. Davis company. 2010 Risk for injury related to tissue damage, autoimmune dysfunction, abnormal blood profile , disorientation and altered mobility as evidence by malar rash on the face, discoid skin rashes on hands, scalp and thighs, oral mucous membrane ulcers and presence of alopecia, weakness, disoriented to time and place, photosensitivity. Source: Smeltzers S.C, et,al. Brunner & Suddarths Textbook of Medical Surgical Nursing. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 12th ed. indicated to enhance safety. b. monitor environment for potentially unsafe conditions and modify as needed. ty c. inform client regarding all treatment and medication client safety and model safety behaviors for patient. -to assist patient to reduce or correct individual risk factors. -in order for the patient to be aware of all the treatment that the patient is receiving and to gain patients cooperation -to alleviate stress and anxiety in order to prevent further harm to patient. -exercises promote good circulation to the body. Thus, improving the body to be more health and prevent from further injury -to monitor patients condition. -to prevent patient from at risk for falls. 3. Goal met. The patient demonstrate lifestyle changes such as having exercises even while in bed with assistance. Patient was able to be aware of safety precautions in order to protect herself. enhance her awareness and knowledge about safety things and necessary precaution to be done to prevent her to be at risk for injury.
Strengths/wellness: >strong support system >strong financial support >strong religious belief
d. encourage use of techniques to reduce or manage stress and vent emotions 3. a. encourage and assist in frequent range-of-motion exercises
3. Display behaviors, lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors and protect self from injury.
b. check vital sign every 4 hours c. position patient to a comfortable position and side rails up
35 d. stress importance of monitoring conditions and risk that may contribute to occurrence of injury Collaborative: 1. Assist in treatments and provide information regarding clients disease/condition. -to provide proper information about the disease and treatments that would help the client achieve independence as well being. -in order that patient may be aware in that she may also be able to protect herself.
2. Administer medications such as; Lasix, Predisone, Cozar, Norvasc, Merrem, Calvit and KCl as ordered using the 10 rights to medication Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. Davis company. 2010
-to alleviate itchiness, and to correct fluid and electrolyte balance and also to regulate blood pressure.
Source: Doenges, et al. Nurses Pocket Guide (12 Ed.). F.A. Davis company. 2010
36
XIV. DRUG STUDY C H E C K
Generic Name: Amlodipine besylate Brand Name: Norvasc Classification: Cardiovascular agent; calcium channel blocker; antihypertensive agent Inhibits calcium ion influx across cardiac and smooth muscle cells, thus decreasing myocardial contractility and oxygen demand; also dilates coronary arteries and arterioles.
Treat hypertension
Not affected by meals. It is given once a day.
Tell patient to report significant swelling of face or extremities.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of dose-related peripheral or facial edema that may not be accompanied by weight gain; rarely, severe Report shortness of breath, palpitations, irregular heartbeat, edema may cause discontinuation of drug. nausea, or constipation to physician Monitor BP with postural changes. Report postural hypotension. Monitor heart rate; doserelated palpitations (more common in women) may occur.
37
Generic Name: Furosemide Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop diuretic Inhibits sodium and chloride reabsorption at proximal and distal tubules and ascending loop of Henle. Promotes water and sodium excretion.
Treat hypertension
Not affected by meals. It is given every twelve hours (q12h) IVTT.
Advise patient to stand slowly to prevent dizziness, not to drink alcohol and to minimize strenuous exercise in hot weather. Instruct patient to report ringing in ears, severe abdominal pain or sore throat and fever because they may indicate toxicity.
Assess patients underlying condition before starting therapy. Monitor weight, peripheral edema, breath sounds, blood pressure, fluid intake and output, and electrolyte, glucose, BUN, and carbon dioxide levels. Monitor uric acid level, especially if patient has a history of gout. Be alert to adverse reactions and drug interactions.
38
Generic name: Losartan potassium Brand name: Cozaar Classification: Antihypertensive drug Inhibits vasoconstrictive and aldosterone-secreting acion of angiotensin II receptor on the surface of vascular smooth muscle and other tiaaue cells.
Lowers high blood pressure
Not affected by meals. It is given once a day (OD).
Tell patient to avoid salt substitutes; these products may contain potassium, which can cause high potassium level. Notify healthcare provider if these serious side effects occur: swelling of face, eyes, lips or tongue and difficulty of breathing.
Monitor patients blood pressure to evaluate effectives of drug therapy. When used alone, drug has less of an effect on blood pressure. Assess patients renal function (BUN and creatinine levels) regularly. Monitor for signs of allergic reaction. Closely monitor patient especially during first few weeks of therapy.
39
Generic name: Prednisone Brand name: Prelone Classification: Corticosteroids Decreases inflammation, mainly by stabilizing leukocyte lysosomal membranes; and influences protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
Suppresses immune response; stimulates bone marrow
Given orally with food if possible to reduce GI irritation. It is given once a day every am and once every pm.
Tell patient to take drug with food or milk. Teach patient signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency: fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, fever, anorexia, nausea, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting. Instruct patient not to stop drug abruptly or without prescribers consent.
Determine whether patient is sensitive to other corticosteroids. Weigh patient daily; report sudden weight gain to prescriber. Monitor for Cushingoid effects: moon face, buffalo hump, central obesity, thinning hair, hypertension and increased susceptibility to infection. Watch for depression or psychotic episodes.
40
Generic name: Meropenem Brand name: Merrem IV Classification: Miscellaneous anti-infectives Inhibits cell wall synthesis in bacteria. It readily penetrates cell wall of most gram positive and gram negative bacteria to reach penicillin-binding protein targets.
Prevent complicated skin and skin structure infections
Not affected by meals. It is given every eight hours (Q8h).
Tell patient to report adverse effects if drug or signs and symptoms of superinfection. Advise patient to report loose stools to prescriber.
Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity before giving first dose. Monitor patient for signs of superinfection. Drug may cause overgrowth of non susceptible bacteria or fungi. Periodic assessment of organ system functions including renal, hepatic and hematopoietic function is recommended.
41
Generic name: Tramadol + Paracetamol Brand name: Ultram Classification: Opioid analgesics; central nervous system drugs Centrally acting synthetic analgesic compound not chemically related to opioids. Thought to bind to opiate receptors and inhibit reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin levels.
Relieve moderate to moderately severe pain
Not affected by meals. It is given thrice a day (TID).
Tell patient to avoid driving or other hazardous activities that require mental alertness until drugs CNS effects are known. Advise patient to check with prescriber before taking OTC drugs because drug interactions can occur. Instruct patient not to stop drug abruptly or without prescribers consent.
Reassess patients level of pain at least 30 minutes after administration. Monitor patients cardiovascular and respiratory status. Withhold dose and notify prescriber if respiration is below 12cpm. Monitor bowel and bladder function. Anticipate need for laxative.
42
43
C Generic name: levofloxacin Brand name: Levaquin Classification: Antibiotic, florquinolone Bactericidal: interferes with DNA by inhibiting DNA gyrase replication in susceptible gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, preventing cell reproduction
H treats bacterial infection
E Administer without regards to meals with a glass of water; given twice a day per Orem
C Instruct patient to drink plenty of fluids while taking this drug Instruct to report rash, visual changes, severe GI problems, weakness, tremors
K Arrange for culture and sensitivity tests before beginning therapy Ensure patient is well hydrated Administer oral drug without regard to meals with a glass of water; separate oral drug from other cation administration, including antacids by at least 2 hours Discontinue at any sign of hypersensitivity (rash, photophobia) or at complaint of tendon pain, inflammation or rupture
44
C Generic name: Potassium Chloride Brand name: Potassium Chloride Classification: Electrolyte Principal intracellular cation of most body tissues, participates in a number of physiologic processesmaintaining intracellular tonicity, transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle, maintenance of normal renal function; also plays a role in carbohydrate metabolism and various enzyme reaction
H prevent and correct potassium deficiency
E C Not affected by meals Caution patient not to use salt substitutes
K Agitate prepare IV solution to prevent of potassium, do not add potassium to an IV bottle in Report toughing of the hands or the hanging position feet unusual tiredness or weakness, feeling of heaviness Monitor IV injection sites in legs, severe nausea, regularly for necrosis, tissue vomiting, abdominal pain,black sloughing and phlebitis or tarry stools, pain at IV injection site Monitor cardiac rhythm carefully during IV administration
45
C Generic name: Eperisone Brand name: Eperisone Classification: Antispasmodic Eperisone acts by relaxing both skeletal muscles and vascular smoothmuscles, and demonstrates a variety of effects such as reduction of myotonia, improvement of circulation, and suppression of the pain reflex.The drug inhibits the vicious cycle of myotonia by decreasing pain,ischaemia, and hypertonia in skeletal muscles, thus alleviating stiffnessand spasticity, and facilitating muscle movement.
H Treats muscle spasm
E Should be taken with food; given three times a day per Orem
C Report fever, erythema, blistering, itching, ocular congestion or stomatitis
In the event of symptoms such as redness, itching, urticaria, or edema of the face and other parts of the body,dyspnoea etc, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate measures taken Patients should be carefully observed, treatment Discontinued and approriate measures taken, in the event of symptomssuch as fever, erythema, blistering, itching, ocular congestion or stomatitis, etc
46
C Generic name: Multivitamins with Buclizine Brand name: Multivitamins with Buclizine Classification: Multivitamins supplement Buclizine is a piperazine antihistamine with antimuscarinic and moderate sedative properties. It is used mainly for its antiemetic action and in the treatment of migraine in combination with analgesics.
H Treats nausea, vomiting and dizziness
E Should be taken with food. (Take within hr before meals.) Given once a day
C Avoid over the counter drugs; may contain ingredients that cause serious reactions with drug Avoid alcohol; serious sedation could occur Report difficulty breathing; hallucinations, remors, loss of coordination; visual disturbances, irregular heart beat
K Assess orientation, reflexes, affects; visual examinations; P, BP;RR, adventitious sounds; bowel sounds, normal GI output, normal urinary output
47
C Generic name: Potassium Chloride Brand name: Potassium Chloride Classification: Electrolyte Principal intracellular cation of most body tissues, participates in a number of physiologic processesmaintaining intracellular tonicity, transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle, maintenance of normal renal function; also plays a role in carbohydrate metabolism and various enzyme reaction
H prevent and correct potassium deficiency
E Not affected by meals
C Caution patient not to use salt substitutes
Agitate prepare IV solution to prevent of potassium, do not add potassium to an IV bottle in Report toughing of the hands or the hanging position feet unusual tiredness or weakness, feeling of heaviness Monitor IV injection sites in legs, severe nausea, regularly for necrosis, tissue vomiting, abdominal pain,black sloughing and phlebitis or tarry stools, pain at IV injection site Monitor cardiac rhythm carefully during IV administration
48
X.V HEALTH TEACHING PLAN Medication 1. Generic name: Furosemide Brand name: Lasix C: Loop Diuretic H: Treat hypertension E: Not affected by meals. It is given every twelve hours (q12h) IVTT. C: Advise patient to stand slowly to prevent dizziness, not to drink alcohol and to minimize strenuous exercise in hot weather K: Monitor weight, peripheral edema, breath sounds, blood pressure, fluid intake and output, and electrolyte, glucose, BUN, and carbon dioxide levels. Exercise Exercise plays its part in the treatment of lupus. It is very important to keep muscles & joints active for a variety of reasons. Muscles need to be toned in order to function adequately. The size of the muscle & its blood circulation depend on its function (where the muscle is & what it does). Physical therapy is very beneficial to the patient who is trying to maintain muscle integrity & tone. Joints depend on tendons & the calcification of bones. These in turn depend on continued movement. Significant bone loss through osteoporosis occurs when bones are not used regularly. Encourage significant other to do passive ROM (Range of motion) exercises for the client. Treatment The goal for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus 1.Dietary regulationalcohol restriction. 2. Treatment of associated condition. Monitor intake and output to identify the output and fluid replacement needs. Vital signs taking every hour to assess any changes on health status Encourage fluid intake to replace fluid and blood loss and to maintain blood pressure and renal function Administer medications as ordered to prevent infections Encourage and assist significant other to turn Hygiene For maintaining skin integrity: 1. Keep skin clean while relieving itching and dryness. Sponge bath Mild soap added to water to moisturize the skin. 2. Keep nails short and trimmed to prevent excoriation. 3. Keep hair clean and moisturized. Outpatient Adherence to pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. Stress to patient and family the importance of follow-up examinations and treatment because of changing physical status. Allowing monitoring of symptoms, disease activities, and treatment of side effects. Refer patient for continuous physical therapy for the improvement of the condition.. Diet Suggested diet is DASH diet (high in fruits and vegetables, moderate in low-fat dairy products, and low in mimimal protein, has a substantial amount of plant protein from legumes and nuts Promote intake of vegetable-value protein foods: soy protein, broccoli
2. Generic name:
The client must have a high fiber 4. Provide or encourage vegetable diet, such oral hygiene to as a medium-size minimize dryness of oral piece of fruit (an mucous membranes. Refer patient to a orange, small Preventive dental nutritionist because of the banana, mediumhygiene care in dietary changes required. size apple). Lupus patients is very important. Get enough sleep and Advice client to Chlorhexidine mouthwashes could rest. avoid foods or help contain drinks that contain
49 Prednisone Brand name: Prelone C: Corticosteroids H: Suppresses immune response; stimulates bone marrow E: Given orally with food if possible to reduce GI irritation. It is given once a day every am and once every pm. 1. Musculoskeletal activity (designed to enhance flexibility & mobility) Types of Activities: Passive ROM Exercises Duration: 10-15 minutes Frequency: Everyday, 2-4 hours and move the patient to prevent bed sores and immobility Avoid sun exposure. Sunscreens and clothing covering the extremities can be helpful to prevent flares. periodontal disease. Mucous membrane ulcers can be treated with hydrogen peroxide gargle, buttermilk gargle, or steroid impregnated gel. 5. Proper food preparation Avoid too much sun exposure and wear protective clothing to prevent direct sunlight. Use sunsceen and suunblocks to protect the skin. Use sunglasses for cases of photosensitivity. alcohol, alcohol restriction is a must because of clients condition. The client should consume amounts of necessary calories to maintain moderate body weight. Fat intake should be limited to 30% of the total calories Instruct patient to limit fluid intake to 500-600 ml/day. Include foods rich in zinc. These foods include oysters, meats, seafood, poultry and eggs. Include rich sources of iron in your diet. To increase absorption, consume with an acidcontaining food or one with vitamin C. Sources of iron
Prescribed medications: NSAIDs: For people with joint or chest pain or fever, drugs that 2. Stretching Exercises C: Teach patient signs and (to specifically target decrease inflammation, symptoms of adrenal joint weakness) called nonsteroidal insufficiency: fatigue, anti-inflammatory muscle weakness, joint Types of Activities: pain, fever, anorexia, drugs (NSAIDs), are Chin-to-chest. Raise the nausea, shortness of often used. Although back of the person's head breath, dizziness, fainting. some NSAIDs, such as up from the bed. Gently ibuprofen and tip his chin toward his K: Monitor for chest. Try to rest the naproxen, are available Cushingoid effects: moon person's chin on his over the counter, a face, buffalo hump, chest if possible. doctors prescription is central obesity, thinning necessary for others. Head turns. Put one hand hair, hypertension and NSAIDs may be used increased susceptibility to on each side of the alone or in person's face. Turn the infection. person's head toward the combination with other right as if he were types of drugs to looking over his right 3. Generic name: losartan control pain, swelling, shoulder. Then slowly Brandname: Cozaar and fever. Even though turn the person's head so some NSAIDs may be he is looking over his
50 C: antihypertensives, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, Management of hypertension left shoulder. Turn the head only far enough so that the person's nose is lined up above their shoulder. purchased without a prescription, it is important that they be taken under a doctors direction. Antimalarials: Antimalarials are another type of drug commonly used to treat lupus. These drugs were originally used to treat malaria, but doctors have found that they also are useful for lupus. A common antimalarial used to treat lupus is hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil1). It may be used alone or in combination with other drugs and generally is used to treat fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and inflammation of the lungs. Corticosteroids: The mainstay of lupus treatment involves the use of corticosteroid include cream of wheat, liver, beef, lamb, pork, chicken, turkey, eggs, fish, beans baked with molasses, prunes, prune juice, apricots, green peas, enriched breads, and cereals Take medications with food to decrease the irritating effect on the stomach and small intestine. Foods and drugs taken together also increase the time available for the absorption of the drug. Include foods rich in Vitamin D. These include foods primarily of animal origin: eggs, butter, milk, fish oils, cereals, margarines and breads. This
H: the blood pressure of Head tilts. Put one of the patient will be your hands on each side lowered. of the person's face. Tilt the head to the side, E: Medication usually bringing the right ear given once a day, the toward the right same time per day. shoulder. Then slowly tilt the person's head to C: Tell patient to avoid bring the left ear toward salt substitutes; these the left shoulder. products may contain potassium, which can Intensity: cause high potassium Start with minimal level. stretching, gradually increasing K: Monitor patients blood pressure to evaluate effectives of drug therapy. Duration: When used alone, drug 15-20 minutes has less of an effect on blood pressure. Frequency: 2-4 times a week 3.Ankle & Foot Exercises Types of Activities: How to start: Hold the right ankle with one hand. Put your other
4. Generic name: Amlodipine besylate Brandname: Norvasc
51 C: Cardiovascular agent; calcium channel blocker; antihypertensive agent H: Treat hypertension E: Not affected by meals. It is given once a day. C: Report shortness of breath, palpitations, irregular heartbeat, nausea, or constipation to physician K: Special Precautions for patients w/ impaired hepatic & renal function, CHF. Elderly. Pregnancy & lactation. 5. Generic name: Meropenem Brand name: Merrem IV C: Miscellaneous antiinfectives H: Prevent complicated skin and skin structure infections E: Not affected by meals. It is given every eight hours (Q8h). hand on the bottom of the foot. Ankle bends. Push the person's foot so his toes point up toward the ceiling. Then put your hand on top of the foot and push the foot down again. Ankle rotation. Hold the ankle with one hand. Hold the person's upper foot with your other hand. Gently turn the foot and ankle in circles. Toe bends. With your palm on top of the person's foot, curl the toes down toward the sole (bottom) of the foot. Then straighten and stretch the toes. Toe spreads. Use your fingers to spread the toes apart one at a time. Then bring them together again. Intensity: Gradually increasing from soft to moderate pressure. Duration: 2-3 Sessions, 15-20 hormones, such as prednisone (Deltasone), hydrocortisone, methylprednisolone (Medrol), and dexamethasone (Decadron, Hexadrol). Corticosteroids are related to cortisol, which is a natural antiinflammatory hormone. They work by rapidly suppressing inflammation. Immunosuppressives: For some patients whose kidneys or central nervous systems are affected by lupus, a type of drug called an immunosuppressive may be used. Immunosuppressives, such as cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) and mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept), restrain the overactive immune along with calcium decreases the risk of osteoporosis. Include foods rich in Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine). These foods include whole grain cereals, breads, liver, avocados, spinach, green beans, bananas, fish, poultry, meats, nuts, potatoes, green leafy vegetables. Increase your intake of foods high in Vitamin C. These foods include broccoli, oranges, strawberries, cauliflower, cantaloupe, cabbage and green peppers.
52 C: Tell patient to report adverse effects if drug or signs and symptoms of superinfection. K: Obtain specimen for culture and sensitivity before giving first dose. 6. Generic name: Tramadol + Paracetamol Brand name: Ultram C: Analgesic H: Relieve moderate to moderately severe pain E: Not affected by meals. It is given thrice a day (TID). minutes a day Frequency: 2-4 times a week. Consultation must be done first before engaging to any exercise programs. This is to ensure the safety and limitations of exercises intended for end stage renal disease patients. Encourage significant other (wife) to do ROM (range of motion) exercises on the time required to prevent immobility of the patient. system by blocking the production of immune cells. These drugs may be given by mouth or by IV infusion. BLyS-specific inhibitors: Belimumab (Benlysta), a Blymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) protein inhibitor, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2011 for patients with lupus who are receiving other standard therapies, including those listed above. Given by IV infusion, it may reduce the number of abnormal B cells thought to be a problem in lupus. Alternative and complementary therapies: Because of the nature and cost of the medications used to treat lupus and the potential for serious side
Instruct significant other to perform proper stretching and warm up C: ell patient to avoid driving or other hazardous activities before engaging patient to a activities that require higher intensity ROM mental alertness until exercises. drugs CNS effects are K: Reassess patients level of pain at least 30 minutes after administration. 7. Generic name: Calcium Aerobic conditioning exercise is the best exercise for lupus patients.
53 +Vit D Brandname: Calvit C: Dietary supplements H: improve and strengthen bones and joints E: Should be taken with food, swallow whole and do not chew. C: Monitor blood pressure, ECG, renal function, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, serum, and urine calcium concentrations. K: Avoid using two (2) hours prior to or until four (4) hours after taking other medications 8. Generic name: Levofloxacin Brand name: C: Antibiotic, florquinolone H: treat fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, and inflammation of the lungs. E: With or without meals effects, many patients seek other ways of treating the disease. Some alternative approaches people have tried including special diets, nutritional supplements, fish oils, ointments and creams, chiropractic treatment, and homeopathy. Diagnostic tools for lupus: Medical history Complete physical examination Laboratory tests: Complete blood count (CBC) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) Urinalysis Blood Chemistries Complement levels Antinuclear antibody tests (ANA) Other autoantibody tests (anti-DNA, antiSm, anti-RNP, anti-Ro [SSA], anti-La [SSB]) Anticardiolipin antibody test
54 with a glass of water C: Report rash, visual changes, severe GI problems, weakness, tremors K: Discontinue at any sign of hypersensitivity (rash, photophobia) or at complaint of tendon pain, inflammation or rupture 9. Generic name: KCL Brand name: C: Electrolyte H: Replaces potassium and maintains potassium level E: Taken with or after meals with full glass of water or fruit juice C: Report toughing of the hands or feet unusual tiredness or weakness, feeling of heaviness in legs, severe nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain,black or tarry stools, pain at IV injection site K: Monitor IV injection sites regularly for Skin Biopsy Kidney Biopsy
55 necrosis, tissue sloughing and phlebitis 10. Generic name: Eperisone Brand name: C: antispasmodic H: Relaxation of hypertonic skeletal muscles, Improves intramuscular blood flow, Reduction of muscle spindle sensitivity via motor neurons, Vasodilatation and augmentation of blood flow. E: After meals C: Report symptoms such as fever, erythema, blistering, itching, ocular congestion or stomatitis, etc K: Monitor symptoms such as redness, itching, urticaria, or edema of the face and other parts of the body,dyspnoea etc, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate measures
56 taken 11. Generic name: Multivitamins with Buclizine Brand name: Multivitamins with Buclizine C: Antihistamines & Antiallergics H: Relieved Motion sickness, migraine, nausea, pruritic skin disorders E: Should be taken with food. (Take within hr before meals.) C: Report signs of hypersensitivity. K: Make sure it is taken after meals to prevent GI disturbances.
57
Você também pode gostar
- Nursing Care Plan for SLE Patient with Joint PainDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for SLE Patient with Joint PainAlex MarieAinda não há avaliações
- Fatigue Related To Autoimmune Disease As Evidenced by Patient Inability To Maintain Usual Level of Physical ActivityDocumento5 páginasFatigue Related To Autoimmune Disease As Evidenced by Patient Inability To Maintain Usual Level of Physical ActivityJordz PlaciAinda não há avaliações
- Managing SLE with Fatigue, Pain, Skin Issues and Knowledge DeficitsDocumento4 páginasManaging SLE with Fatigue, Pain, Skin Issues and Knowledge DeficitsICa Marlina0% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and InjuryDocumento4 páginasAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and Injuryprickybiik50% (2)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasNCP Activity Intolerancekeiii_21Ainda não há avaliações
- Self Care Deficit BahtingDocumento1 páginaSelf Care Deficit BahtingNaj SoliveresAinda não há avaliações
- NCP HyperthermiaDocumento6 páginasNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Surgical CasesDocumento10 páginasNCP For Surgical Caseslouie roderosAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing SLE Patient with Rash, Alopecia and Joint PainDocumento13 páginasAssessing SLE Patient with Rash, Alopecia and Joint PainMary Mae Bercacio Buella100% (3)
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocumento5 páginasNCP Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirementsrusnani100% (1)
- HoplessnessDocumento16 páginasHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocumento19 páginasNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPLornz E. Cantos100% (1)
- GENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANDocumento4 páginasGENERAL SANTOS DOCTORS’ MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION NURSING CARE PLANFran LanAinda não há avaliações
- Assist withambulation- Assist withactivities ofdaily living- To promotehealing- To promoteindependenceDocumento2 páginasAssist withambulation- Assist withactivities ofdaily living- To promotehealing- To promoteindependenceDanielJosephLimAinda não há avaliações
- NCP and DrugsDocumento13 páginasNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPTracy Camille EscobarAinda não há avaliações
- Altered Nutrition Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 páginasAltered Nutrition Nursing DiagnosisAndrea BroccoliAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Documento2 páginasNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For OxygenationDocumento6 páginasNCP For OxygenationChriz LechAinda não há avaliações
- SchistosomiasisDocumento92 páginasSchistosomiasisIvan Juan75% (4)
- Tachycardia NCPDocumento2 páginasTachycardia NCPRemita Hutagalung50% (4)
- DM NCPDocumento8 páginasDM NCPCaress Mae Gubaton CabudoyAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocumento2 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumo Hemoperitoneum Stab Wound Case StudyDocumento7 páginasPneumo Hemoperitoneum Stab Wound Case StudyMari Jasmeen Estrada Noveda100% (1)
- Systemic Lupous Erythematosus (SLE)Documento46 páginasSystemic Lupous Erythematosus (SLE)Power La Victoria Floro100% (1)
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDocumento3 páginasASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzAinda não há avaliações
- Pain NCP BillrothDocumento2 páginasPain NCP BillrotharjayAinda não há avaliações
- Altered Renal Perfusion CRFDocumento5 páginasAltered Renal Perfusion CRFGen Ramos- SolisAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 páginaAcute Pain NCPJed AvesAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDocumento4 páginasNursing Care for Impaired MobilityTITLEPreventing Peripheral Neurovascular Issues TITLERelieving Acute Pain from InflammationDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocumento1 páginaImpaired Gas Exchange NCPCj AlconabaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE)deric88% (25)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPDocumento2 páginasIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleDocumento5 páginasCues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleJamie IcabandiAinda não há avaliações
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care Plan PDFDocumento3 páginasRheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care Plan PDFIzhra MargateAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento4 páginasNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocumento3 páginasWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Sensory PerceptionDocumento2 páginasNCP Sensory PerceptionGina TangneneiAinda não há avaliações
- Leukemia PainDocumento1 páginaLeukemia PainmawelAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocumento2 páginasDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- NCP For FractureDocumento4 páginasNCP For FracturejpAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orDocumento6 páginasPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orLoren EstefanAinda não há avaliações
- NCP IcuDocumento2 páginasNCP Icujennelyn losantaAinda não há avaliações
- Nanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Documento3 páginasNanda 11 Edi. P. 620-621Besael Baccol0% (1)
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocumento6 páginasAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For InjuryDocumento4 páginasRisk For InjuryJanina Patricia BuddleAinda não há avaliações
- Assess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesDocumento2 páginasAssess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesNolan Cabral100% (1)
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Documento2 páginasR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoAinda não há avaliações
- COURSE TASK 2 Mrs. Clot's and Alexa's Case - POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ADocumento10 páginasCOURSE TASK 2 Mrs. Clot's and Alexa's Case - POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ASHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOSAinda não há avaliações
- NCP ImmobilityDocumento2 páginasNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- NCP For Imbalanced NutritionDocumento6 páginasNCP For Imbalanced NutritionMelvin MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Icu NCPDocumento4 páginasIcu NCPdrsabuegAinda não há avaliações
- Daily NCPDocumento5 páginasDaily NCPKuennie SabalAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Ugib NCPDocumento5 páginasUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- Manage Angina with MedicationsDocumento10 páginasManage Angina with MedicationsPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Acute Pain NCSDocumento3 páginasNCP Acute Pain NCSPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- SERVICE OF PROCESS AND NEGLIGENCEDocumento5 páginasSERVICE OF PROCESS AND NEGLIGENCEPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- X. Pathophysiology Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocumento3 páginasX. Pathophysiology Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- My Lesson DesignDocumento5 páginasMy Lesson DesignPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Calcium channel blocker and antacid drug studiesDocumento28 páginasCalcium channel blocker and antacid drug studiessfkjalkhsafgAinda não há avaliações
- HemophiliaDocumento4 páginasHemophiliaPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP RiskDocumento2 páginasNCP RiskPaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Actual 1Documento2 páginasNCP Actual 1Paolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- OAU004301 UMG8900 Data Configuration and Routine Maintenance R003 ISSUE2!0!20050622Documento56 páginasOAU004301 UMG8900 Data Configuration and Routine Maintenance R003 ISSUE2!0!20050622firas1976Ainda não há avaliações
- Stylistics: The Routledge Handbook of Stylistics Edited by Michael BurkeDocumento56 páginasStylistics: The Routledge Handbook of Stylistics Edited by Michael BurkeAmmara FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Hazard and Operability Study (Hazop) : Dr. M. Azam SaeedDocumento39 páginasHazard and Operability Study (Hazop) : Dr. M. Azam SaeedMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- Jim Kwik - 10 Morning Habits Geniuses Use To Jump Start The Brain - YouTube Video Transcript (Life-Changing-Insights Book 15) - Stefan Kreienbuehl PDFDocumento5 páginasJim Kwik - 10 Morning Habits Geniuses Use To Jump Start The Brain - YouTube Video Transcript (Life-Changing-Insights Book 15) - Stefan Kreienbuehl PDFCarlos Silva100% (11)
- THE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODDocumento17 páginasTHE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODFranchesca Revello100% (1)
- Gliding Birdflight Basis AviationDocumento172 páginasGliding Birdflight Basis AviationErnest DevensonAinda não há avaliações
- Manguangan and Mamanwa TribeDocumento5 páginasManguangan and Mamanwa TribeFiel Zechariah Aenna100% (1)
- Existing culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaDocumento9 páginasExisting culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaGilbert Gabrillo JoyosaAinda não há avaliações
- Diss Q1 Week 7-8Documento5 páginasDiss Q1 Week 7-8Jocelyn Palicpic BagsicAinda não há avaliações
- Circuit Theory NOV-DeC 2014Documento12 páginasCircuit Theory NOV-DeC 2014sunil1237Ainda não há avaliações
- 50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesDocumento5 páginas50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesRae Angela GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionDocumento6 páginasAssignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionFitria Rakhmawati RakhmawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17. Bothriocephalus Acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934: December 2012Documento16 páginasChapter 17. Bothriocephalus Acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934: December 2012Igor YuskivAinda não há avaliações
- Entrepreneurial Mindset and Opportunity RecognitionDocumento4 páginasEntrepreneurial Mindset and Opportunity RecognitionDevin RegalaAinda não há avaliações
- Aug. 16, 2019 - Friday Aug. 16, 2019 - FridayDocumento3 páginasAug. 16, 2019 - Friday Aug. 16, 2019 - FridayYssh GozumAinda não há avaliações
- Bai Tap LonDocumento10 páginasBai Tap LonMyNguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Integrative Teaching Strategy - Module #6Documento10 páginasIntegrative Teaching Strategy - Module #6Joann BalmedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Women's Health: HysterectomyDocumento7 páginasWomen's Health: HysterectomySuci RahmayeniAinda não há avaliações
- 05 The Milesian NaturalistsDocumento18 páginas05 The Milesian NaturalistsDr René Mario Micallef, SJ, STDAinda não há avaliações
- Unified Field Theory - WikipediaDocumento24 páginasUnified Field Theory - WikipediaSaw MyatAinda não há avaliações
- NafsDocumento3 páginasNafsMabub_sddqAinda não há avaliações
- Notification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalDocumento2 páginasNotification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalRomuald Leo PiongAinda não há avaliações
- Conceptual analysis of developing Europe strategy and external border securityDocumento2 páginasConceptual analysis of developing Europe strategy and external border securityДанаAinda não há avaliações
- HTTPDocumento40 páginasHTTPDherick RaleighAinda não há avaliações
- BVRT PDFDocumento8 páginasBVRT PDFAleena Zaidi100% (1)
- W3 05 Ahu KocakDocumento24 páginasW3 05 Ahu KocakClaudiaAinda não há avaliações
- Ajzen - Constructing A Theory of Planned Behavior QuestionnaireDocumento7 páginasAjzen - Constructing A Theory of Planned Behavior QuestionnaireEstudanteSax100% (1)
- Adverbs Further ReadingDocumento17 páginasAdverbs Further ReadingᅳAinda não há avaliações
- PROACTIVITYDocumento8 páginasPROACTIVITYShikhaDabralAinda não há avaliações
- Analogy and LogicDocumento2 páginasAnalogy and LogicCOMELEC CARAinda não há avaliações