Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Trace of Oxygen from Nose to Lungs to Body
Enviado por
aznknight323Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Trace of Oxygen from Nose to Lungs to Body
Enviado por
aznknight323Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
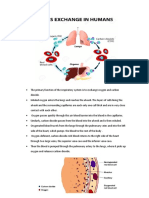
Trace of oxygen from nasal cavity to alveoli Air enters external nares and to nasal vestibule, which open
into nasal cavity superior, inferior, and middle meatuses and conchaes internal nares nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx larynx glottis false vocal cord true vocal cord trachea left and right primary bronchi left and right secondary bronchi left and right tertiary bronchi left and right bronchioles terminal bronchioles respiratory bronchioles alveolar ducts alveolar sac (alveoli) Oxygen from alveoli to pulmonary capillaries Alveolar sac (alveoli), consist of simple squamous epithelium permitting rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide pulmonary capillaries which are across the walls of alveolar ducts and alveoli Oxygen in blood back through heart to capillaries in stomach Deoxygenated blood pick up oxygen and drop off carbon dioxide in pulmonary capillaries pulmonary venules pulmonary veins left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar valve ascending aorta aortic arch thoracic aorta abdominal aorta celiac trunk left gastric artery gastric arterioles gastric capillaries where oxygen is exchanged and nutrient and carbon dioxide is picked up with tissue of the organ Carbon dioxide back to the heart, through heart to alveoli of lungs gastric venules gastric veins hepatic portal vein liver Hepatic vein inferior vena cava right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery pulmonary arterioles pulmonary capillaries where carbon dioxide from tissue is exchange for Oxygen Carbon dioxide from alveoli back out to the nose Carbon dioxide enters alveolar sac (alveoli) --> alveolar ducts respiratory bronchioles terminal bronchioles left and right bronchioles left and right tertiary bronchi left and right secondary bronchi left and right primary bronchi trachea true vocal cord flase vocal cord glottis larynx laryngopharynx oropharynx nasopharynx internal nares superior, middle, inferior meatuses and conchaes nasal cavity nasal vestibule external nares and out to environment where plants will use CO2 to produce oxygen. Passage of air to lungs external nares nostril vestibule nasal cavity consisting of superior, middle, inferior concha and meatus internal nares nasopharynx oropharynx laryngopharynx larynx (epiglottis --> thyroid cartilage --> false vocal cord --> true vocal cord --> cricoid cartilage) trachea left and right primary bronchi secondary bronchi tertiary bronchi bronchiole terminal bronchiole respiratory bronchiole alveolar duct alveoli (where Oxygen diffuse through membrane into the blood and CO2 is exchange) Passage of oxygen exchange in lung and back to heart and to system oxygen pass from alveoli to the capillary beds and into blood while CO2 goes from blood to alveoli and out through passage of respiratory system (above) oxygenated blood travel through capillary beds pulmonary venules pulmonary veins left atrium bicuspid vale left ventricle aortic semilunar valve ascending aorta aortic arch brachiocephalic, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery, thoracic aorta abdominal aorta celiac trunk (branches into left gastric artery, splenic artery, hepatic artery), superior mesenteric artery, left and right renal artery, gonadal artery, inferior mesenteric artery Right and Left common iliac artery Internal iliac artery, external iliac artery from external iliac artery Femoral artery, deep femoral artery from femoral artery Popliteal artery posterior and anterior tibial artery dorsalis pedis artery Blood through intestine to the heart abdominal artery superior mesenteric artery intestinal arteries Intestinal arterioles intestinal capillaries where nutrients and CO2 diffuse to blood, and Oxygen diffuse to the tissue intestinal venules intestinal veins superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver for detoxification of blood hepatic veins inferior vena cava Blood from stomach to inferior vena cava Left and right gastric artery arterioles capillaries venule Left and right gastric vein hepatic portal vein liver for detoxification of blood hepatic veins inferior vena cava
Sugar water to intestine and into blood food and drink enter mouth through lip vestibule tongue oral cavity palatoglossal arch oropharynx epiglottis where it closes the trachea laryngopharynx esophagus lower esophageal sphincter cardiac orifice body of stomach pylorus pyloric sphincter pyloric orifice Duodenum Jejunum where primary nutrient absorption takes place circular fold and villi of mucosa layer where nutrient pass through intestinal tissues and into intestinal capillaries blood with nutrient (glucose and water) intestinal venule intestinal vein Glucose and water in blood to kidneys intestinal veins superior mesenteric vein hepatic portal vein liver for detoxification of blood hepatic veins inferior vena cava Right atrium tricuspid valve right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary trunk pulmonary artery arteriole pulmonary capillaries where deoxygenated blood gets oxygenated and still has nutrients pulmonary venules pulmonary veins left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar ascending aorta aortic arch thoracic aorta abdominal aorta left and right renal artery Trace of blood through kidney to glomerulus left and right renal artery segmental artery interlobar artery arcuate artery interlobular artery afferent arteriole glomerulus Filter blood to filtrate Glomerulus consists of capillary lumen and filtration membrane, where nutrients and fluid small enough to pass through filtration slits. The fluid becomes filtrate and blood exit after through efferent arteriole filtrate enter capsular space of Glomerulus capsule tubular pole proximal convoluted tubule, where reabsorption of ions (Na+ and glucose, and AA) occur and 60-65% water follow by osmosis and enter blood in the peritubular capillaries and return to circulation in vascular system filtrate not reabsorbed in proximal convoluted tubule enter Loop of Henle where more water and solutes are reabsorbed by first going to descending limb of loop of henle, where water is pulled out of due to build-up of gradient on outside of tubule (Water is then reabsorbed in the collecting duct if ADH is present) ascending limb of loop of Henle, where Na+, Cl- are actively pump out creating gradient outside Distal convoluted tubule (reabsorption of water, and Na+ under control of aldosterone) collecting duct to make urine Trace water and gluose reabsorbed in peritubular capillaries back to renal vein blood leave glomerulus through efferent arteriole peritubular capillaries where reabsorbed glucose and water enter interlobular vein arcuate vein interlobar vein segmental vein renal vein Blood in renal vein back to heart Renal vein inferior vena cava Right atrium Water from renal artery to urinary bladder Renal artery segmental artery interlobar artery arcuate artery interlobular artery afferent arteriole glomerulus (where blood plasma passively move out glomerulus and form filtrate) capsular space tubular pole proximal convoluted tubule (where most water and nutrients reabsorption occur), excess water and solutes remain as tubular fluid descending limb of loop of Henle where water is pulled out ascending limb of loop of henle, where Na+ and Cl+ is actively transported out Distal convoluted tuble, where water and Na+ are reabsorbed under control of aldosterone collecting tubules collecting duct (reabsorbed water if ADH is present) papillary duct renal papilla minor calyx major calyces renal pelvis ureter urinary bladder
What did you do this weekend? I went to caf shop with my friends to study for the final exam because I have a lot of exams. On Friday I studied at home because I did not have a car. On Saturday, I went to a coffee shop from 1pm to 6pm to study for chemistry. On Sunday I also went to study at a caf shop. I did not have time this weekend to go out and have fun because I had to study. Qu hiciste este fin de semana? Fui al caf-restaurante con mis amigos a estudiar para el examen final, porque tengo muchos exmenes. El viernes, estudi en casa porque no tena coche. El sbado, fui a un restaurante de caf de una de la tarde a seis de la tarde para estudiar qumica. El domingo, tambin se fue a estudiar en un restaurante cafetera. No tuve tiempo de este fin de semana para salir y divertirse, porque yo tena que estudiar.
What did you learn this semester? This semester was a difficult semester. I spent most of my time studying biology and organic chemistry and little time studying Spanish. That is why I am not getting an A in Spanish that i wanted. In Spanish, I learned to communicate with friends by speaking Spanish. I learned basic Spanish words and used them with my friends. I had little time to practice my Spanish, but I did used a little Spanish with my friends outside Spanish class. I learned many Spanish verbs and how to used them in a sentence. I learned about South America and its cultures, such as food, family, and school. I learned to ask for the time, and how to greet people in Spanish class. If I didnt have to spend most of my time with biology and organic chemistry, I would understand and know more Spanish. Qu aprendiste en este semestre?
Este semestre fue un semestre difcil. Yo la mayor parte de mi tiempo al estudio de la biologa y la qumica orgnica y
poco tiempo estudiando espaol. Es por eso que no estoy recibiendo una A en espaol que yo quera. En espaol, yo aprendido a comunicarse con sus amigos por hablar espaol. Haba poco tiempo para practicar mi espaol, pero s utiliza un poco de espaol con mis amigos fuera de la clase de espaol. Aprend muchos verbos en espaol y la forma de utilizar en una oracin. Aprend sobre Amrica del Sur y culturas, como la comida, la familia y la escuela. Aprend a
preguntar por el tiempo y cmo saludar a la gente en la clase de espaol. Si yo no tenan que pasar la mayor parte de mi tiempo con la biologa y la qumica orgnica, me gustara comprender y conocer ms espaol.
Você também pode gostar
- Accomplishment Report-April 2018Documento2 páginasAccomplishment Report-April 2018Geline Joy D. SamillanoAinda não há avaliações
- Expt No. 2-CarbohydratesDocumento17 páginasExpt No. 2-CarbohydratesNathaniel PulidoAinda não há avaliações
- Measles case study with Koplik's spots and rubeola virusDocumento3 páginasMeasles case study with Koplik's spots and rubeola virusApex Torres0% (1)
- Science G4 Break It DownDocumento51 páginasScience G4 Break It DownYourMakatiPad Properties100% (1)
- Exercise 1Documento14 páginasExercise 1Michelle ViduyaAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento7 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Anatomy and PhysiologyMea DolautaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Physiology Syllabus 2016 UpdatedDocumento5 páginasAnatomy Physiology Syllabus 2016 Updateddats_idjiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Long-Term or Terminal Illness Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Long-Term or Terminal IllnessDocumento31 páginasNursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Long-Term or Terminal Illness Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Long-Term or Terminal IllnessJoanna Mie EstrososAinda não há avaliações
- TFN Reviewer 1 and 2 ReportsDocumento8 páginasTFN Reviewer 1 and 2 ReportsAlisa FujibayashiAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory ModalitiesDocumento87 páginasRespiratory ModalitiesLj Ferolino100% (2)
- 05 - BIOE 211 - Normal Distribution and Hypothesis TestingDocumento29 páginas05 - BIOE 211 - Normal Distribution and Hypothesis TestingJhelloAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm Practice 2011Documento53 páginasMidterm Practice 2011Marina ChengAinda não há avaliações
- Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocumento26 páginasKidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentPatrascu CristiAinda não há avaliações
- Availability of Laboratory Facilities For Effective Teaching-Learning of Social Studies in Atbcoe KangereDocumento25 páginasAvailability of Laboratory Facilities For Effective Teaching-Learning of Social Studies in Atbcoe KangereShuaibu YunusaAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Plan HeadnursingDocumento14 páginasTeaching Plan HeadnursingZed P. EstalillaAinda não há avaliações
- Bloom's of TaxonomyDocumento11 páginasBloom's of TaxonomyVijith.V.kumar0% (1)
- History of Health Education and NursingDocumento3 páginasHistory of Health Education and Nursing3amabelle arevaloAinda não há avaliações
- STS10 - Lecture Notes Chapter 2Documento13 páginasSTS10 - Lecture Notes Chapter 2Andy SwiftAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6. Roles and Functions of A Nurse in The Delivery of Care To A Sick ChildDocumento9 páginasUnit 6. Roles and Functions of A Nurse in The Delivery of Care To A Sick ChildMarlon Glorioso IIAinda não há avaliações
- Antidotes To Different MedicationsDocumento1 páginaAntidotes To Different MedicationsRavneetKalkatAinda não há avaliações
- TFN Transes M1 M7Documento100 páginasTFN Transes M1 M7Kath SolitarioAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System Anatomy PhysiologyDocumento20 páginasDigestive System Anatomy PhysiologyKids JangAinda não há avaliações
- Body Parts Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation A.HairDocumento6 páginasBody Parts Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation A.HairJulia Marie DelfinAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 112 - Rle Skills Lab Performance Checklist Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramDocumento3 páginasNCM 112 - Rle Skills Lab Performance Checklist Obtaining An ElectrocardiogramDominicManlutacAinda não há avaliações
- Filipino Scientists Flash CardsDocumento3 páginasFilipino Scientists Flash CardsannanbAinda não há avaliações
- Colostomy CareDocumento2 páginasColostomy CareMel RodolfoAinda não há avaliações
- TFN Trans 1Documento2 páginasTFN Trans 1Chilled Moo MooAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing SopDocumento3 páginasNursing SopChelsy Sky SacanAinda não há avaliações
- Theoretical FrameworkDocumento2 páginasTheoretical FrameworkLisette CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- Koizer DDocumento2 páginasKoizer DkoizerAinda não há avaliações
- Principles Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisDocumento12 páginasPrinciples Underlying Medical and Surgical AsepsisKiyoteru Hiyama0% (1)
- Gas Exchange Written ReportDocumento11 páginasGas Exchange Written ReportEllanny GloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocumento5 páginasSexually Transmitted InfectionsKANT JAMES D. MAHANAinda não há avaliações
- Registered Nurse Staffing OpportunitiesDocumento6 páginasRegistered Nurse Staffing OpportunitiesleviAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study ThrombocytopeniaDocumento8 páginasCase Study ThrombocytopeniaAmina TariqAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Nursing PHDDocumento2 páginas3 - Nursing PHDIndra GunawanAinda não há avaliações
- Summative ReflectionDocumento5 páginasSummative Reflectionapi-346049731Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary of Nursing Informatics in AsiaDocumento2 páginasSummary of Nursing Informatics in AsiaJake Yvan Dizon0% (1)
- Analytical QuestionsDocumento29 páginasAnalytical Questionsfujoji92Ainda não há avaliações
- Care of the Mother and Child Nursing Case StudyDocumento2 páginasCare of the Mother and Child Nursing Case StudyRoshin TejeroAinda não há avaliações
- Case StudyDocumento2 páginasCase StudyStephanie Onel75% (4)
- My SHN CompilationDocumento57 páginasMy SHN Compilationapi-3718174100% (2)
- 10 Key Characteristics of a Great NurseDocumento6 páginas10 Key Characteristics of a Great NurseAzhin O MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Emergency Room Care Plan for HyperthermiaDocumento7 páginasEmergency Room Care Plan for HyperthermiaNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabAinda não há avaliações
- Resource Unit Lesson 7Documento2 páginasResource Unit Lesson 7api-2797426550% (1)
- Nursing Theory History & ErasDocumento2 páginasNursing Theory History & ErasStarrrAinda não há avaliações
- Case Scenario For Head and Neck ProblemDocumento2 páginasCase Scenario For Head and Neck ProblemJayne VenturanzaAinda não há avaliações
- 3 NomenclatureDocumento45 páginas3 Nomenclaturerusnah chungAinda não há avaliações
- Sample PrognosisDocumento3 páginasSample PrognosisjudssalangsangAinda não há avaliações
- TLG LeukemiaDocumento2 páginasTLG LeukemiaLizzy WayAinda não há avaliações
- Vital SignsDocumento64 páginasVital SignsjodipotpotAinda não há avaliações
- Hair, Face, Nose, Neck, Skin, and NailsDocumento4 páginasHair, Face, Nose, Neck, Skin, and NailsZJ GarcianoAinda não há avaliações
- Prepare for Objective Data CollectionDocumento6 páginasPrepare for Objective Data CollectionChuche Marie TumarongAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Historical Development of PHNDocumento32 páginas02 Historical Development of PHNKailash NagarAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture CH 7 Science, Technology, SocietyDocumento10 páginasLecture CH 7 Science, Technology, SocietyRoberto Pereira da SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Endocrine SystemDocumento11 páginasEndocrine Systemiwan subyadinataAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Informatics: Connecting Technology and Patient Care (First Edition)Documento21 páginasNursing Informatics: Connecting Technology and Patient Care (First Edition)Praveen LoniAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Student Helps Patient Open UpDocumento5 páginasNursing Student Helps Patient Open UpNica SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalDocumento27 páginasDigestive System: Digestive Glands. Alimentary CanalAnkit NariyaAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer AnaphyDocumento11 páginasReviewer AnaphyMaria FelizeAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SectionDocumento62 páginasCardiovascular Sectionaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- C 23Documento9 páginasC 23Tammie Gore100% (1)
- 2017 Handbook V6Documento127 páginas2017 Handbook V6aznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento7 páginasTypes of Cardiovascular Drugsaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- C 24Documento9 páginasC 24Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento3 páginasChapter 2aznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Bates Chapter 2 Flashcards - QuizletDocumento6 páginasBates Chapter 2 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- BrainDocumento1 páginaBrainaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Bates Chapter 4 Flashcards - QuizletDocumento8 páginasBates Chapter 4 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Cultural Competence and Spirituality in NursingDocumento3 páginasCultural Competence and Spirituality in Nursingaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Bates Chapter 1 Flashcards - QuizletDocumento6 páginasBates Chapter 1 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- C 20Documento6 páginasC 20Tammie Gore100% (2)
- Male Genitalia FlashcardsDocumento10 páginasMale Genitalia Flashcardsaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Bates Chapter 3 Flashcards - QuizletDocumento8 páginasBates Chapter 3 Flashcards - Quizletaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Health Assessment QuestionsDocumento3 páginasComprehensive Health Assessment Questionsaznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento3 páginasChapter 3aznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- C 47Documento7 páginasC 47Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6Documento3 páginasChapter 6aznknight323Ainda não há avaliações
- C 46Documento10 páginasC 46Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 49Documento8 páginasC 49Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 48Documento8 páginasC 48Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 25Documento6 páginasC 25Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 45Documento8 páginasC 45Tammie Gore100% (2)
- C 17Documento12 páginasC 17Tammie Gore100% (1)
- C 16Documento13 páginasC 16Tammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 18Documento10 páginasC 18Tammie Gore100% (1)
- C 20Documento6 páginasC 20Tammie Gore100% (2)
- Chapter 19: Neurobiology of Schizophrenia, Mood Disorders, and Anxiety DisordersDocumento7 páginasChapter 19: Neurobiology of Schizophrenia, Mood Disorders, and Anxiety DisordersTammie GoreAinda não há avaliações
- C 15Documento10 páginasC 15Tammie Gore100% (3)
- C 15Documento10 páginasC 15Tammie Gore100% (3)
- Transport in Living PDFDocumento46 páginasTransport in Living PDFaudrey2207023Ainda não há avaliações
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocumento9 páginas9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 Seriesyeelin96Ainda não há avaliações
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocumento20 páginasCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelY. PurwandariAinda não há avaliações
- CAP Case StudyDocumento127 páginasCAP Case StudyMenggay SanDiego100% (1)
- RespiratorypptDocumento16 páginasRespiratorypptNEW GENERATIONSAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocumento41 páginasRespiratory Distress SyndromedicksonsamboAinda não há avaliações
- First Quarterly Examination in Science 9Documento4 páginasFirst Quarterly Examination in Science 9Chai Barcelon86% (7)
- Padhle 10th - Respiration (Life Processes) NotesDocumento11 páginasPadhle 10th - Respiration (Life Processes) NotesSANDHYA KUMARI100% (2)
- Oral Revalida: EmergenciesDocumento74 páginasOral Revalida: EmergenciesCynn AyoAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory Function in Patients Post-Infection by COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento10 páginasRespiratory Function in Patients Post-Infection by COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisHendri WahyudiAinda não há avaliações
- PMR Sains SBP 2009 Serta JawapanDocumento47 páginasPMR Sains SBP 2009 Serta Jawapanhilmi72Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 06Documento47 páginasChapter 06gayathmipereraAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study of BronchitisDocumento34 páginasCase Study of Bronchitisken83% (29)
- Breathing in AmericaDocumento282 páginasBreathing in AmericaGakTauMauKasiNamaApaAinda não há avaliações
- 7biology VII Biology SECLO 2023-24 LP SecondaryDocumento7 páginas7biology VII Biology SECLO 2023-24 LP SecondaryGideon CavidaAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMDocumento3 páginasConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS-03 Zoology: Based On AIATS-03 TYMSparsh MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- SS1 Biology Revison Questions Summer Term 2022Documento27 páginasSS1 Biology Revison Questions Summer Term 2022Abimbola Brodie-MendsAinda não há avaliações
- Analisis Biologi SPM 2004-2019Documento4 páginasAnalisis Biologi SPM 2004-2019Siti ShamzelaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk3 - GLAKDocumento16 páginasGrade 6 - SSES - Science - Q2 - Wk3 - GLAKMelanie TrinidadAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Worksheet Ans 1-G7Documento3 páginasPractice Worksheet Ans 1-G7Ala' ShehadehAinda não há avaliações
- ARDS LectureDocumento58 páginasARDS LecturedrjaikrishAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial Pneumonia Case StudyDocumento11 páginasBacterial Pneumonia Case StudySheila May LumhodAinda não há avaliações
- Biology N5 Past Paper Questions Multicellular Organisms1Documento42 páginasBiology N5 Past Paper Questions Multicellular Organisms1Craig MitchellAinda não há avaliações
- Adjustment To Extrauterine LifeDocumento4 páginasAdjustment To Extrauterine LifeFrancine LaxaAinda não há avaliações
- Oxford Mastering Science 2A Chapter 7 AnswerDocumento28 páginasOxford Mastering Science 2A Chapter 7 AnswerChun Man TseAinda não há avaliações
- Pathology EssayDocumento19 páginasPathology EssayARUNSKAinda não há avaliações
- Quarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sDocumento17 páginasQuarter: 4 / Semester: 2 / WEEK: 4: Online Resource/sTristan Paul PagalananAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 - Respiratory SystemDocumento20 páginasChapter 8 - Respiratory Systemmnurnazri10Ainda não há avaliações
- G9 Science Q1 - Week 1-2 Respiratory-Circulatory-SystemDocumento34 páginasG9 Science Q1 - Week 1-2 Respiratory-Circulatory-SystemSandra Lee LigsaAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Tuberculosis Lung Disease: Clinical Review of An Under-Recognised Global ChallengeDocumento13 páginasPost-Tuberculosis Lung Disease: Clinical Review of An Under-Recognised Global ChallengeBelajarAinda não há avaliações