Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Regis Mani AAOMPT Poster 2008
Enviado por
smokey73Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Regis Mani AAOMPT Poster 2008
Enviado por
smokey73Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
USE OF THRUST AND NON-THRUST MANIPULATION FOR COSTOCHONDRITIS:
A CASE SERIES.
Kaarthick Mani, PT, DPT, MS
Manual Therapy Fellowship
Fellow - Regis University Manual Physical Therapy Fellowship Program
Orthopaedic Physical Therapist, Orthopaedic Therapy Specialists LLC, Warrenville, IL
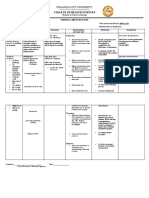
Baseline & Discharge (D/C) Findings NPRSInitial vs. D/C
Purpose:
To describe the examination and manual physical
therapy interventions for patients with sub- 10
Scale 0-
Pain
NPRS(D/C)
10
acute/chronic episodes of recurrent upper thoracic/chest 0
NPRS(Initial)
Case 1 Case 2 Case 3
pain. The purpose is to outline the use of thrust, non- NPRS(Initial) 8 9 8
thrust mobilization/manipulation techniques, rib muscle NPRS(D/C) 2 0 4
energy techniques (MET’s) combined with exercises
for individuals with a diagnosis of costochondritis. Chest ExpansionDifference incm
Approximately 50% of patients attending accident and 10
(U,M, &Lower)
AverageChest
Expansion
emergency departments and out patient cardiac clinics 5
because of chest pain have a non-cardiac basis for their 0
Chest Expansion (Initial)
Case 1 Case 2 Case 3
symptoms. They are often given a non-specific Chest Expansion (Initial) 2.3 2 2.5
diagnosis.
Chest Expansion (D/C) 6.3 4.16 4.1
(1)
It has been suggested that the costovertebral and Conclusion: These patients experienced
costotransverse joints are commonly overlooked a rapid improvement in pain and
sources of atypical chest pain. (2) functions after non-thrust and thrust
mobilization/manipulation and rib MET’s
to thoracic spine region. Clinical
Relevance: A combination of thrust and
non-thrust mobilization/manipulation,
Rib MET’s and scapular strengthening
exercises may be helpful for patients with
a diagnosis of costochondritis.
References: (1) Capwell S, McMurray J. “Chest pain –
please admit”: Is there an alternative? British Medical
Journal 2000;320:951-2
(2) Rabey MI. Costochondritis: Are the symptoms and
sign due to neurogenic inflammation. Two cases
responded to manual therapy directed towards posterior
spinal structures. Manual Therapy 13(2008):82-86
Você também pode gostar
- Master Drug ChartDocumento22 páginasMaster Drug ChartMahadhir AkmalAinda não há avaliações
- Image FilesDocumento264 páginasImage FilesSoksatya Korsal100% (1)
- Surgery NotesDocumento11 páginasSurgery NotesChaoja100% (1)
- Sciatica Relief GuideDocumento15 páginasSciatica Relief GuideElliott Nunez100% (2)
- Comprehensive Examination 1Documento53 páginasComprehensive Examination 1Love Gonzales90% (21)
- Diagram of Pathophysiology CancerDocumento5 páginasDiagram of Pathophysiology CancerKristaMaeC.Lazo0% (3)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocumento2 páginasCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- Dilation and CurettageDocumento15 páginasDilation and Curettagenautilus81Ainda não há avaliações
- Dual Energy Cookbook 1800000007125154Documento24 páginasDual Energy Cookbook 1800000007125154Toufik ToufikAinda não há avaliações
- Patient Positioning (Sims, Orthopneic, Dorsal Recumbent) Guide (2020)Documento28 páginasPatient Positioning (Sims, Orthopneic, Dorsal Recumbent) Guide (2020)JOSHUA DICHOSO100% (1)
- Risk For Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionDocumento4 páginasRisk For Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionMia Grace Garcia100% (1)
- Recommendation LettersDocumento6 páginasRecommendation Lettersapi-436901032Ainda não há avaliações
- Concepts and Recommendations: For IMRT Planning: ICRU 83Documento22 páginasConcepts and Recommendations: For IMRT Planning: ICRU 83Bijay Kumar BarikAinda não há avaliações
- Persiapan Osce Nasional: Dept. Obstetri Dan Ginekologi FK UnairDocumento5 páginasPersiapan Osce Nasional: Dept. Obstetri Dan Ginekologi FK UnairYanis Widhiya NingrumAinda não há avaliações
- X6 CH08 Probes E PDFDocumento44 páginasX6 CH08 Probes E PDFValentin DavalosAinda não há avaliações
- Te 1667 WebDocumento3 páginasTe 1667 WebeguleamrAinda não há avaliações
- Differences in Pain Perception in Children Reporting Joint andDocumento8 páginasDifferences in Pain Perception in Children Reporting Joint andHarshoi KrishannaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 - General PrinciplesDocumento22 páginas1 - General PrinciplesFlorin PanduruAinda não há avaliações
- A New Method To Quantify Manual Paediatric Chest Physiotherapy TechniquesDocumento2 páginasA New Method To Quantify Manual Paediatric Chest Physiotherapy Techniquesbuku fisioAinda não há avaliações
- أسئلة مقابلات 2Documento4 páginasأسئلة مقابلات 2FahadAinda não há avaliações
- The Unofficial Guide To RadiologyDocumento59 páginasThe Unofficial Guide To RadiologywanwaqiuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Final Rectal Cancer GEC ESTRO Handbook of BrachytherapyDocumento14 páginasFinal Rectal Cancer GEC ESTRO Handbook of BrachytherapyRakesh JadhavAinda não há avaliações
- Do We Still Need A Stethoscope - Stats For Top 10 Cardiac Tests - Roland SabbaghDocumento45 páginasDo We Still Need A Stethoscope - Stats For Top 10 Cardiac Tests - Roland SabbaghJason WongAinda não há avaliações
- Segura 2016Documento8 páginasSegura 2016alonsoAinda não há avaliações
- Newsletter Volume 4Documento8 páginasNewsletter Volume 4Deepak Agrawal100% (1)
- S5.M5.WS-MindMapNCP (Didik Prapto Sasongko 6A-3A (A) )Documento2 páginasS5.M5.WS-MindMapNCP (Didik Prapto Sasongko 6A-3A (A) )Didik Prapto SasongkoAinda não há avaliações
- Moore 2006Documento5 páginasMoore 2006Aldo MartínezAinda não há avaliações
- NCCN Head-And-neck 2020 HipofaringeDocumento11 páginasNCCN Head-And-neck 2020 Hipofaringed.ayala1006Ainda não há avaliações
- Pengantar (Fix)Documento21 páginasPengantar (Fix)ubayyumrAinda não há avaliações
- Jospt 2012 4243Documento19 páginasJospt 2012 4243soylahijadeunvampiroAinda não há avaliações
- Penatalakasanaan Awal Kegawatdaruratan Bedah 1Documento69 páginasPenatalakasanaan Awal Kegawatdaruratan Bedah 1Project ByAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento4 páginasNursing Care PlanNecy Tessa C. AcostaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 1097@MD 0000000000019337Documento11 páginas10 1097@MD 0000000000019337Claudia Lorena MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Primario Desconocido NCCN Head-And-neck 2020Documento8 páginasPrimario Desconocido NCCN Head-And-neck 2020d.ayala1006Ainda não há avaliações
- MARGENS - Respostas Mischa Hoogeman Sobre MargensDocumento1 páginaMARGENS - Respostas Mischa Hoogeman Sobre MargensgriloucuraAinda não há avaliações
- 100205HM-SB CRA Poster Final 3Documento1 página100205HM-SB CRA Poster Final 3Osama MariaAinda não há avaliações
- 10em Trauma Case 1Documento7 páginas10em Trauma Case 1bashayer hamadAinda não há avaliações
- Palpation of The Lateral Pterygoid Area in The Myofascial Pain DiagnosisDocumento6 páginasPalpation of The Lateral Pterygoid Area in The Myofascial Pain Diagnosisdavidcosmin186832Ainda não há avaliações
- Drexel University College of Medicine Department of AnesthesiologyDocumento1 páginaDrexel University College of Medicine Department of AnesthesiologydrexelanesthesiaAinda não há avaliações
- Lung Nodule Detection by Microdose CT Versus Chest RadiographyDocumento9 páginasLung Nodule Detection by Microdose CT Versus Chest RadiographyTatiana RecinosAinda não há avaliações
- Aneurysm Bone Cyst of Proximal PhalynxDocumento6 páginasAneurysm Bone Cyst of Proximal Phalynxhemanarasimha gandikotaAinda não há avaliações
- Translating PICO Into Search StrategyDocumento29 páginasTranslating PICO Into Search StrategyAhmad SyaukatAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Oncology Assgn RT Mono BreastDocumento9 páginasClinical Oncology Assgn RT Mono Breastapi-511386954Ainda não há avaliações
- Problem List Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocumento1 páginaProblem List Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning ImplementationJai Go100% (1)
- JCDR 9 RC01Documento4 páginasJCDR 9 RC01Karen MachadoAinda não há avaliações
- Different Intensity Extension Methods and Their Impact On Entrance Dose in Breast Radiotherapy: A StudyDocumento6 páginasDifferent Intensity Extension Methods and Their Impact On Entrance Dose in Breast Radiotherapy: A Studymaryam yaftianAinda não há avaliações
- Exclusion Inclusion: Critical Pathways Are Not A Substitute For Sound Professional JudgementDocumento2 páginasExclusion Inclusion: Critical Pathways Are Not A Substitute For Sound Professional Judgementjoshua elnissiAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocumento5 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDhianne TagamaAinda não há avaliações
- RM Abdomen Basico Guglielmo2016Documento22 páginasRM Abdomen Basico Guglielmo2016Michelle SalinasAinda não há avaliações
- ESC - Diagnosis of HFDocumento29 páginasESC - Diagnosis of HFDumora FatmaAinda não há avaliações
- Palliative WorksheetDocumento4 páginasPalliative WorksheetrayAinda não há avaliações
- All India Institute of Medical Science Mangalagiri APDocumento1 páginaAll India Institute of Medical Science Mangalagiri APsantoshnavin2020Ainda não há avaliações
- D I C T: OSE N Omputed Omography B C SDocumento24 páginasD I C T: OSE N Omputed Omography B C SYUSRI1997Ainda não há avaliações
- Csi Written Assignment 1Documento10 páginasCsi Written Assignment 1api-633102425Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment 8 - Agostina MininiDocumento2 páginasAssignment 8 - Agostina MininiAgostina MiniAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To Sim CircuitDocumento9 páginasIntro To Sim CircuitodealowAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map PDFDocumento36 páginasConcept Map PDFHaleigh SokolowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Sanaani NURSING CARE PLANDocumento2 páginasSanaani NURSING CARE PLANNur SanaaniAinda não há avaliações
- Articulo 1recto SuperiorDocumento7 páginasArticulo 1recto SuperiorCarolinaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 1097@MD 0000000000019337Documento10 páginas10 1097@MD 0000000000019337Claudia LorenaAinda não há avaliações
- Ce Midw PDFDocumento52 páginasCe Midw PDFMadhusudan SamantaAinda não há avaliações
- Research Open Access: Guang-Hua Jin, Li-Xin Chen, Xiao-Wu Deng, Xiao-Wei Liu, Ying Huang and Xiao-Bo HuangDocumento8 páginasResearch Open Access: Guang-Hua Jin, Li-Xin Chen, Xiao-Wu Deng, Xiao-Wei Liu, Ying Huang and Xiao-Bo HuangGiang VũAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomics CT Scan Protocol (Spanish)Documento1 páginaAnatomics CT Scan Protocol (Spanish)Eduar LeonAinda não há avaliações
- English-Patient-Rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation-User-Manual June-2010 0Documento24 páginasEnglish-Patient-Rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation-User-Manual June-2010 0chandni saxenaAinda não há avaliações
- Mincarellidelores 3719186 106548909 7047 001 Proposal GroupMINCARELLI Presentation 1Documento11 páginasMincarellidelores 3719186 106548909 7047 001 Proposal GroupMINCARELLI Presentation 1Manda ReemaAinda não há avaliações
- Borang Pemeriksaan-Mammografi 1Documento2 páginasBorang Pemeriksaan-Mammografi 1hsentosaoshAinda não há avaliações
- Par Format For Physiotherapy of NHM OdishaDocumento7 páginasPar Format For Physiotherapy of NHM Odishakrishna bptAinda não há avaliações
- Regis WilsonCGH AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis WilsonCGH AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Thomas AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Thomas AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis WilsonAT AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis WilsonAT AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Overy AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Overy AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73100% (2)
- Regis McCracking AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis McCracking AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Leal AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Leal AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Koppenhaver AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Koppenhaver AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Dennison AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Dennison AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Garvey AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Garvey AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Kirkland AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Kirkland AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis MacDonald AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis MacDonald AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Chovvath AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Chovvath AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- Regis Carpenter AAOMPT Poster 2008Documento1 páginaRegis Carpenter AAOMPT Poster 2008smokey73Ainda não há avaliações
- 10th Monthly Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalDocumento92 páginas10th Monthly Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalmilesmoffeitAinda não há avaliações
- Centers For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesDocumento6 páginasCenters For Disease Control and Prevention's Sexually Transmitted Diseases Infection GuidelinesabhinavrautAinda não há avaliações
- Chakra-Chart Deborah KingDocumento2 páginasChakra-Chart Deborah KingLaura Dafina Drãguț100% (2)
- Drug Study RopivacaineDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Ropivacainerica sebabillonesAinda não há avaliações
- Esophageal Perforation: Diagnostic Work-Up and Clinical Decision-Making in The First 24 HoursDocumento7 páginasEsophageal Perforation: Diagnostic Work-Up and Clinical Decision-Making in The First 24 HourssyaifularisAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts of DiseaseDocumento55 páginasConcepts of DiseaseKailash NagarAinda não há avaliações
- 1n2 OrganicSD-drshakyaDocumento26 páginas1n2 OrganicSD-drshakyaUMESH KANDELAinda não há avaliações
- 2UDocumento47 páginas2Uucnursingcesdev2008100% (3)
- 2015 Revised American Thyroid Association Guidelines For The Management of Medullary Thyroid CarcinomaDocumento44 páginas2015 Revised American Thyroid Association Guidelines For The Management of Medullary Thyroid CarcinomaBeni BolngAinda não há avaliações
- Oral RevalidaDocumento3 páginasOral RevalidaJaye DangoAinda não há avaliações
- Ferraris M La HermeneuticaDocumento310 páginasFerraris M La HermeneuticaantoniomarkusAinda não há avaliações
- CSF Catalogue enDocumento76 páginasCSF Catalogue enHarshitShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- Polymyalgia Rheumatic Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento2 páginasPolymyalgia Rheumatic Symptoms Diagnosis and TreatmentHas SimAinda não há avaliações
- Craniectomia 3Documento8 páginasCraniectomia 3Vlady78Ainda não há avaliações
- Urology Quiz 9 MCQ AnswerDocumento2 páginasUrology Quiz 9 MCQ Answeruroquiz100% (2)
- 65 Interview Questions For Nurses.13Documento3 páginas65 Interview Questions For Nurses.13natalieshirleyAinda não há avaliações
- 53 JMSCRDocumento7 páginas53 JMSCRAddinul FitryAinda não há avaliações
- NCRP Report 155 AapmDocumento266 páginasNCRP Report 155 AapmFISICO CADAVIDAinda não há avaliações
- AgonistsDocumento25 páginasAgonistsOfficially RandomAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainDocumento11 páginas1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainGhofran Ibrahim HassanAinda não há avaliações
- ACOG Practice Bulletin On Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocumento5 páginasACOG Practice Bulletin On Thyroid Disease in Pregnancygenerics54321Ainda não há avaliações
- LDN Information PackDocumento17 páginasLDN Information PackkindheartedAinda não há avaliações