Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NEW ESSAY Logarithms - Knowing It All About Calculus
Enviado por
samthegirl9Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NEW ESSAY Logarithms - Knowing It All About Calculus
Enviado por
samthegirl9Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Samantha R.
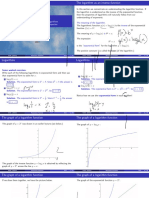
Selman March 22, 2012 Synopsis: Knowing it all About Calculus Summary of Chapter Seven An exponential function is any function that can be written in the form f(x)=bx. In this example b is a positive real number (other than one) and is referred to as the base. When graphing an exponential function, keep in mind that f(x) is the equivalent of the y-coordinate. If you have exponential function y=5x, its inverse would be x=5y. The inverse of an exponential function is called a logarithmic function. The expression y=logax is read y is the logarithm to the base a of x and is equal to the equation x=a . Essentially, we raise y to a to get x. Lets look at a few examples. If 8=2 3 is the exponential function, log28=3 is the logarithmic function. If a=b c is the exponential function, logba=c is the logarithmic function. In this manner, logarithms can be changed into exponential form, or vice-versa, quickly and easily.
y
You will often find yourself needing to simplify logarithmic functions. Say you are given the function log3x=2; to find x you must first change the logarithm into exponential form. This would give you 32=x. Since we know that three squared is nine, x would equal nine. Other times you will need to simplify logarithmic functions containing two or more logarithms. For example, log 3(log6 6). The only thing you need to remember is to start at the innermost point and work outwards. The solution to this problem is shown below: log3(log6 6) = log3(1) 3x= 1 x = 0 Below are three important yet basic properties of logarithms. (1) The logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms. (2) The logarithm of a quotient is the difference of the logarithms. (3) Finally, the logarithm of a number raised to a power is the product of the power and the logarithm of the number. In mathematical form, these are the three basic properties: (1*) logb(xy) = logb x + logb y (2*) logb (x/y) = logb x logb y (3*) logb xr = r logb x Please note that in the above examples x, y, and b are positive real numbers. The variable b is not equal to one and r is a real number. The number e (stay with me) is the base of a special type of logarithm called the natural logarithm. The value of e is approximately 2.718282. Natural logarithms may confuse the beginner at first; instead of using the abbreviation log, natural logarithms use the abbreviation ln. Plus, in addition to the properties shown on above, natural logarithms have the following three properties: (1) ln e = 1 (2) ln ek = k (3) ln 1 = 0
Você também pode gostar
- The Life of Lily Klasner... A Book Report by Samantha Reagan SelmanDocumento5 páginasThe Life of Lily Klasner... A Book Report by Samantha Reagan SelmanSamantha SelmanAinda não há avaliações
- Math Reviewer For QuizbeeDocumento4 páginasMath Reviewer For QuizbeeAdrienne CabanigAinda não há avaliações
- 3.3 Logarithms (Slides 4 To 1)Documento8 páginas3.3 Logarithms (Slides 4 To 1)Your Average Grammar NaziAinda não há avaliações
- Logarithm: Logarithm of Positive Real NumbersDocumento18 páginasLogarithm: Logarithm of Positive Real Numberstj17Ainda não há avaliações
- Math1314 Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento12 páginasMath1314 Logarithmic FunctionsLavinia FlorentinaAinda não há avaliações
- Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento20 páginasLogarithmic FunctionsThomas WashAinda não há avaliações
- LogrithmsDocumento56 páginasLogrithmsPES MASTER GAMEPLAYSAinda não há avaliações
- LogarithmDocumento70 páginasLogarithmElma KitonganAinda não há avaliações
- General Mathematics: Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesDocumento18 páginasGeneral Mathematics: Logarithmic Functions, Equations, and InequalitiesMaster ChooklaAinda não há avaliações
- Math1414 Logarithmetic FunctionsDocumento10 páginasMath1414 Logarithmetic FunctionsNeelesh YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Rasika MaliDocumento18 páginasRasika MaliRachiket Mali 8th AAinda não há avaliações
- 0.4 Exponential and Trigonometric FunctionsDocumento18 páginas0.4 Exponential and Trigonometric FunctionsJazile Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Logarithmic and Exponential FunctionDocumento8 páginasLogarithmic and Exponential FunctionRyoshino AntipadoAinda não há avaliações
- WEEK 8.1 Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento19 páginasWEEK 8.1 Representations of Logarithmic FunctionsOreo ProductionsAinda não há avaliações
- Week 002 Calculus I - Logarithm FunctionsDocumento5 páginasWeek 002 Calculus I - Logarithm Functionsvit.chinnajiginisaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 3.3 LogarithmsDocumento6 páginasLecture Notes 3.3 LogarithmsCjen QuiambaoAinda não há avaliações
- GenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalDocumento24 páginasGenMath11 - Q1 - Mod8 - Logarithmic Equations and Inequalities - Version 4 FinalJERLYN MACADOAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential and Logarithmic EquationsDocumento15 páginasExponential and Logarithmic Equationsmarksman77661Ainda não há avaliações
- Math12-1 - Lesson 10 - Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento20 páginasMath12-1 - Lesson 10 - Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsGabriel R GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Exponentials and LogarithmsDocumento3 páginasExponentials and LogarithmsShahzaib KhurramAinda não há avaliações
- Definitions & Examples: Polynomial FunctionsDocumento17 páginasDefinitions & Examples: Polynomial Functionsshiela valdemoroAinda não há avaliações
- Gen Math Mod 4Documento20 páginasGen Math Mod 4Alessandra Marie PlatonAinda não há avaliações
- LogarithmDocumento24 páginasLogarithmthomas nationalAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2 Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento19 páginas3.2 Logarithmic FunctionsYukiC123Ainda não há avaliações
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 1.4 Algebra 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.HobsonDocumento11 páginas"Just The Maths" Unit Number 1.4 Algebra 4 (Logarithms) by A.J.HobsonNguyen Linh TrangAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra Group 6Documento51 páginasAlgebra Group 6Christel Joy CornitoAinda não há avaliações
- NOTE A Function Has An Inverse If and Only If It Is A One-To-One Function, I.E. One InputDocumento4 páginasNOTE A Function Has An Inverse If and Only If It Is A One-To-One Function, I.E. One InputLuke TrainorAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics GR 12Documento1 páginaMathematics GR 12reacharunkAinda não há avaliações
- Notes 4Documento4 páginasNotes 4defence servicesAinda não há avaliações
- Uide Uestions: 1. What Is Logarithmic Function?Documento7 páginasUide Uestions: 1. What Is Logarithmic Function?Michael John CarascalAinda não há avaliações
- List of Logarithmic IdentitiesDocumento7 páginasList of Logarithmic IdentitiesMuhammedNayeemAinda não há avaliações
- Changing From Exponential To Logarithmic Form: Different Forms?Documento4 páginasChanging From Exponential To Logarithmic Form: Different Forms?Princess Shyne PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Changing From Exponential To Logarithmic Form: Different Forms?Documento4 páginasChanging From Exponential To Logarithmic Form: Different Forms?Joseph CosciaAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento20 páginasExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsKen AguilaAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento20 páginasExponential and Logarithmic FunctionsKen AguilaAinda não há avaliações
- Lawl OgDocumento2 páginasLawl OggblehscribdAinda não há avaliações
- Guc 2029 61 37611 2023-10-29T18 28 36Documento22 páginasGuc 2029 61 37611 2023-10-29T18 28 36Marley EssamAinda não há avaliações
- Project IN General Mathematics: DefinitionDocumento7 páginasProject IN General Mathematics: DefinitionTrishaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Functions of Real Variables 2020 2021Documento48 páginasChapter 2 Functions of Real Variables 2020 2021Thabet HomriAinda não há avaliações
- AsymptotesDocumento4 páginasAsymptotesJamal MesidorAinda não há avaliações
- Finals 1. Nat Log FN, DifferentiationDocumento30 páginasFinals 1. Nat Log FN, DifferentiationAndoy Morales IIIAinda não há avaliações
- Polynomial NotesDocumento25 páginasPolynomial NotesAbdella KarimeAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation of Logarithmic FunctionDocumento11 páginasDifferentiation of Logarithmic FunctionMaria AndresAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Math 1201 Learning JournalDocumento5 páginasUnit 5 Math 1201 Learning JournalKhomani MwewaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 8 Other Transcendental FunctionsDocumento8 páginasLecture Notes 8 Other Transcendental FunctionsJustin Paul TumaliuanAinda não há avaliações
- Math - Logarithmic Functions and Their GraphsExercise 2-2Documento18 páginasMath - Logarithmic Functions and Their GraphsExercise 2-217 JPOR Nichakorn TraipoonsinAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Logaritma, ExpDocumento23 páginas2 Logaritma, ExpfadilrahmatullahmAinda não há avaliações
- Precalc Exp LogDocumento10 páginasPrecalc Exp LogVictor NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Logarithms: Concepts & Theory: Example 1: Find The Value of Log3 2187Documento3 páginasLogarithms: Concepts & Theory: Example 1: Find The Value of Log3 2187DebrajAinda não há avaliações
- Functions RelationsDocumento12 páginasFunctions RelationsArabella MutendeAinda não há avaliações
- Logarithmic FunctionsDocumento2 páginasLogarithmic FunctionsjuliatsyganAinda não há avaliações
- 6 4 Logarithmic FunctionDocumento11 páginas6 4 Logarithmic Functiontarek moahmoud khalifaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 LogDocumento5 páginas4 LogCSP EDUAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2: Introduction To Polynomial FunctionsDocumento8 páginasModule 2: Introduction To Polynomial FunctionsJoan Layos MoncaweAinda não há avaliações
- Motivational Problems On Polynomial FunctionsDocumento4 páginasMotivational Problems On Polynomial FunctionsAnnika SolotkoAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Expression Constants Variables Algebraic Operations Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Exponentiation Rational NumberDocumento8 páginasMathematics Expression Constants Variables Algebraic Operations Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Exponentiation Rational NumberLovely Rose CedronAinda não há avaliações
- Math For Machine Learning: 1.1 Differential CalculusDocumento21 páginasMath For Machine Learning: 1.1 Differential CalculusjoekowalskyAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 8 Other Transcendental FunctionsDocumento8 páginasLecture Notes 8 Other Transcendental FunctionsFaye CabauatanAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsNo EverandAlgebra Secret RevealedComplete Guide to Mastering Solutions to Algebraic EquationsAinda não há avaliações
- Ferdinand Magellan and The Circumnavigation of The Earth An Essay by Samantha SelmanDocumento3 páginasFerdinand Magellan and The Circumnavigation of The Earth An Essay by Samantha Selmansamthegirl9100% (1)
- CSS SynopsisDocumento2 páginasCSS Synopsissamthegirl9Ainda não há avaliações
- The Sinners of Pago Pago Based On W. Somerset Maugham's RainDocumento4 páginasThe Sinners of Pago Pago Based On W. Somerset Maugham's RainSonny SelmanAinda não há avaliações
- Tesla The EnigmaDocumento5 páginasTesla The Enigmasamthegirl9Ainda não há avaliações
- The History of The Pythagorean TheoremDocumento15 páginasThe History of The Pythagorean TheoremSamantha SelmanAinda não há avaliações
- B.Ed 1.5 Year 1 & 2 Assignment Spring 2019Documento11 páginasB.Ed 1.5 Year 1 & 2 Assignment Spring 2019HamaYoun BabAr100% (1)
- 3.17. Creep EquationsDocumento10 páginas3.17. Creep Equationsruchit solankiAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra 2 06 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 2Documento59 páginasAlgebra 2 06 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 2Ziad Al-JoharyAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan K-2006Documento4 páginasLesson Plan K-2006Ricky Antonius LAinda não há avaliações
- Math 121 SyllabusDocumento5 páginasMath 121 SyllabusMax VeladoAinda não há avaliações
- Paul Dawkins - Complex Numbers PrimerDocumento26 páginasPaul Dawkins - Complex Numbers PrimerKobina JamiesonAinda não há avaliações
- Spring - Simple Harmonic Motion Lab - NirantarDocumento14 páginasSpring - Simple Harmonic Motion Lab - NirantarNirantar YakthumbaAinda não há avaliações
- FALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201004476 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 MAT1011 Module 2.1-Laplace Transform Tables 3Documento5 páginasFALLSEM2019-20 MAT1011 ETH VL2019201004476 Reference Material I 02-Aug-2019 MAT1011 Module 2.1-Laplace Transform Tables 3vijayAinda não há avaliações
- Euler's Formula and Trigonometry: 1 The Sine and Cosine As Coordinates of The Unit CircleDocumento11 páginasEuler's Formula and Trigonometry: 1 The Sine and Cosine As Coordinates of The Unit CircleMeral MeralAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide Key Exponential and Linear FunctionsDocumento10 páginasStudy Guide Key Exponential and Linear Functionsapi-276774049Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculus 7th Edition - Ch07Documento81 páginasCalculus 7th Edition - Ch07يقين عبدالرحمنAinda não há avaliações
- Numb3rs Activities Curriculum AlignmentDocumento6 páginasNumb3rs Activities Curriculum AlignmentSm KimAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential FunctionsDocumento29 páginas1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential FunctionsHarmi HarlinaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic MT F3 Notes PDFDocumento297 páginasBasic MT F3 Notes PDFClemence TafitiAinda não há avaliações
- Section 4.1 Exponential Functions An Exponential Function F (X) Is Defined byDocumento15 páginasSection 4.1 Exponential Functions An Exponential Function F (X) Is Defined byAAAinda não há avaliações
- General Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 16: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Exponential FunctionsDocumento27 páginasGeneral Mathematics: Quarter 1 - Module 16: Representing Real-Life Situations Using Exponential FunctionsLeizel Jane LjAinda não há avaliações
- Signal and Linear System Analysis: 2.1 Problem SolutionsDocumento78 páginasSignal and Linear System Analysis: 2.1 Problem SolutionshayAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential Table PDFDocumento2 páginasExponential Table PDFPaul0% (1)
- Thin Layer Drying Kinetics of of RoselleDocumento5 páginasThin Layer Drying Kinetics of of RosellewilsonAinda não há avaliações
- (Textbooks in Mathematical Sciences) Nancy Baxter Hastings, Barbara E. Reynolds, C. Fratto, P. Laws, K. Callahan, M. Bottorff-Workshop Calculus With Graphing Calculators - Guided Exploration With RDocumento420 páginas(Textbooks in Mathematical Sciences) Nancy Baxter Hastings, Barbara E. Reynolds, C. Fratto, P. Laws, K. Callahan, M. Bottorff-Workshop Calculus With Graphing Calculators - Guided Exploration With RAnonymous vcdqCTtS9100% (1)
- Logarithmic Functions Week 7Documento20 páginasLogarithmic Functions Week 7gadraAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Types of FunctionsDocumento2 páginasBasic Types of FunctionsMark Navato100% (1)
- Catania and Reynolds 1968 - Interval ScehdulesDocumento57 páginasCatania and Reynolds 1968 - Interval ScehdulesjsaccuzzoAinda não há avaliações
- Differential EquationDocumento28 páginasDifferential Equationronhuman14Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculus and Vectors - Chapter 1Documento6 páginasCalculus and Vectors - Chapter 1myobAinda não há avaliações
- Exponential Function PDFDocumento2 páginasExponential Function PDFMasonAinda não há avaliações
- Kadi Sarva Vishwavidyalaya: Faculty of Engineering & TechnologyDocumento3 páginasKadi Sarva Vishwavidyalaya: Faculty of Engineering & TechnologychiragAinda não há avaliações
- Jordan's LemmaDocumento3 páginasJordan's LemmaSergey LiflandskyAinda não há avaliações
- ..Documento15 páginas..Fidel Cabiles100% (1)
- PPRV 30 I 3 FinalDocumento89 páginasPPRV 30 I 3 FinalFebriano SobbaAinda não há avaliações