Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Injections and Withdrawals
Enviado por
DynafromDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Injections and Withdrawals
Enviado por
DynafromDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Injections And Withdrawals
December-01-08
8:29 AM
Injections and Withdrawals
Injections - add to main income spending stream in economy (I,G,X)
Withdrawals - outward flows of funds. Divert funds from the income-spending stream (Savings, Taxes,
M)
Investments and Savings
- Most funds are borrowed by businesses for investments
- Companies keep a portion of their profits to reinvest
- Governments also borrow money - more government borrow, the less ends up with businesses
- Foreign flows
Government purchases and taxes
- Usually government purchase exceeds taxes
- To make up - governments borrow funds in financial markets
- Recent years - T >G, governments - use these excess funds to pay off some of their outstanding debts.
Exports and Imports
- Money spend on imports > exports
- Foreign lenders typically provided funds to Canadian financial markets, with lending by foreigners being
greater than borrowing by foreigners
- This surplus of lending by foreigners has helped make up the shortfall in net exports
Total Injections and Withdrawals
- Total injections. I (I-Planned investments) + g + x
- Total withdrawals: S + T + M
- When total injections exceed total withdrawals, flows into the income-spending stream > flows out. This
implies that real output and spending in the economy expand
- When total withdrawals exceed total injections, flows into the income-spending stream are less than
outflows. The income-spending stream falls and slows down. This implies that real output and spending
in the economy contract.
- Equilibrium : Total injections = total withdrawals
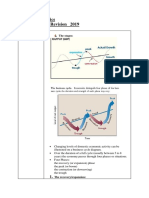
AS
Price Level (GDP Recessionary Gap
DEFLATOR)
AD
Potential Output
Real GDP
Unit 3 - Fiscal Policy Page 1
Equilibrium VS Potential Output
Recessionary Gap - is the amount by which equilibrium output falls short of potential output
- If equilibrium output is below its potential level, unemployment is above the natural unemployment
rate. (The difference between the equilibrium output and potential output is the RECESSIONARY GAP.
Inflationary Gap- is the amount by which equilibrium output exceeds potential output
- If equilibrium output is above its potential output, unemployment is temporarily below the natural
unemployment rate
- When equilibrium output > potential output - inflationary GAP
AD3
AS
AD 1
PRICE LEVEL AD2
Inflation Gap
Recessionary Gap
Equilibrium
REAL GDP
10.3 Practise Questions
1. -
a. Surplus, Inflation gap, economy expands
b. Recessionary gap, deficit
2. -
a. IGX, STM
b. Yes
3. -
a. Below
b. Above
c. Higher
Unit 3 - Fiscal Policy Page 2
Você também pode gostar
- Deflat & Inflat GapsDocumento5 páginasDeflat & Inflat GapsNur Anna Batrisya Binti AzlanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 9 - The MacroeconomyDocumento10 páginasUnit 9 - The MacroeconomyNaomiAinda não há avaliações
- Fiscal Policy, Inflationary & Deflationary GapsDocumento12 páginasFiscal Policy, Inflationary & Deflationary GapsMosAinda não há avaliações
- Slovenia Fiscal Policy 2011Documento83 páginasSlovenia Fiscal Policy 2011dorayAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 29 AnswersDocumento3 páginasIGCSE Economics Self Assessment Chapter 29 AnswersDesre67% (3)
- New Ad & AsDocumento51 páginasNew Ad & Asayushshrimal000_2201Ainda não há avaliações
- Economics Duran and LachicaDocumento1 páginaEconomics Duran and LachicaAaron Daniel DuranAinda não há avaliações
- Monetary LEC1Documento11 páginasMonetary LEC1Nitin SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- MacroDocumento6 páginasMacrocorvids75% (4)
- Macro Cheat SheetDocumento3 páginasMacro Cheat Sheetwerbestuff7054Ainda não há avaliações
- Economic Assignment 2Documento7 páginasEconomic Assignment 2Prateek_Ghai_303Ainda não há avaliações
- Prayoga Dwi Nugraha - Summary CH 10Documento9 páginasPrayoga Dwi Nugraha - Summary CH 10Prayoga Dwi NugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomic Growth and DevelopmentDocumento36 páginasMacroeconomic Growth and DevelopmentRanib SainjuAinda não há avaliações
- The circular flow of income and macroeconomic indicatorsDocumento9 páginasThe circular flow of income and macroeconomic indicatorsjjkjljAinda não há avaliações
- ECO401 FinalTerm NotesDocumento4 páginasECO401 FinalTerm NotesMuhammad FarooqAinda não há avaliações
- Big Push Theory To Reduce Fiscal DeficitDocumento8 páginasBig Push Theory To Reduce Fiscal DeficitInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Macro NotesDocumento28 páginasMacro NotesAlexis RheinAinda não há avaliações
- ECOIndividual Assighnment2Documento11 páginasECOIndividual Assighnment2Mekuriya BeregaAinda não há avaliações
- Fiscal PolicyDocumento78 páginasFiscal PolicyLakshmi NairAinda não há avaliações
- 2.2.1 The Characteristics of ADDocumento25 páginas2.2.1 The Characteristics of AD18kchohanAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4. National IncomeDocumento9 páginas2.4. National Incomevikshit45Ainda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics Concepts ExplainedDocumento22 páginasMacroeconomics Concepts ExplainedUsman Shaukat - 70642/TCHR/BGJTAinda não há avaliações
- MTP Session 5 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From The Blanchard 6 Ed.: Chapter 3 - Entire ChapterDocumento32 páginasMTP Session 5 Reading 1. This Set of Slides 2. From The Blanchard 6 Ed.: Chapter 3 - Entire ChapterDevbratRathAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 3pdf - 211118 - 130431Documento21 páginasCHAPTER 3pdf - 211118 - 130431Amalin IlyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To MacroeconomicsDocumento15 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To MacroeconomicsyizzyAinda não há avaliações
- #Business Economics Session 3 - Macro NDocumento52 páginas#Business Economics Session 3 - Macro NvishnuvvvvvvAinda não há avaliações
- CFA Level I NotesDocumento42 páginasCFA Level I NotesMSA-ACCA100% (6)
- Aggregate Demand in The Closed Economy: 2.1. Introduction: Income-Expenditure Approach Some Important IdentitiesDocumento26 páginasAggregate Demand in The Closed Economy: 2.1. Introduction: Income-Expenditure Approach Some Important IdentitiesProveedor Iptv EspañaAinda não há avaliações
- How the Multiplier Model Explains Changes in OutputDocumento35 páginasHow the Multiplier Model Explains Changes in OutputannsaralondeAinda não há avaliações
- Acroeconomic IMS: U NY SDocumento11 páginasAcroeconomic IMS: U NY SHitisha agrawalAinda não há avaliações
- NYJC Inflation H2 Econs NotesDocumento6 páginasNYJC Inflation H2 Econs NotesDaniel PngAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 (Notes) GDP DefinitionsDocumento20 páginasChapter 2 (Notes) GDP DefinitionsAhmed OusamaAinda não há avaliações
- IS-LM AnalysisDocumento59 páginasIS-LM AnalysisHarshul Bansal100% (1)
- Assignm NT 2 EconDocumento4 páginasAssignm NT 2 EconMeherun MehbuAinda não há avaliações
- Infaltion (Main Slide)Documento27 páginasInfaltion (Main Slide)arthonadAinda não há avaliações
- Year 12 Economics Mid Semester 1 Revision 2019: 1. The Business CycleDocumento27 páginasYear 12 Economics Mid Semester 1 Revision 2019: 1. The Business CycleLucy PhanAinda não há avaliações
- Keynes's Criticism of Say's Law in A MoneyDocumento10 páginasKeynes's Criticism of Say's Law in A MoneyMd. Shakil Ahmed 1620890630Ainda não há avaliações
- Fiscal Policy: Revenues Expenditures DeficitsDocumento21 páginasFiscal Policy: Revenues Expenditures DeficitsPrakash KrishnamoorthyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaDocumento16 páginasChapter Six: National Income Accounting: Basic Concepts: GNP, GDP, Nominal and Real GNP/GDP, and GNP Per CapitaYonas AddamAinda não há avaliações
- Econ ch31 NotesDocumento2 páginasEcon ch31 NotesPaige BurgosAinda não há avaliações
- Fiscal Policy: Adapted From: Belinda P. Ato Prepared By: Daphne MagtibayDocumento29 páginasFiscal Policy: Adapted From: Belinda P. Ato Prepared By: Daphne MagtibayTee MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Factor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Documento25 páginasFactor Payments Y Consumption of Domestically Produced Goods and Services (C)Johanne TangeAinda não há avaliações
- Answers To Online Review Questions: The Classical Long-Run ModelDocumento6 páginasAnswers To Online Review Questions: The Classical Long-Run ModelannfaiAinda não há avaliações
- Business Cycle PresentationDocumento11 páginasBusiness Cycle PresentationfantasybookwyrmAinda não há avaliações
- The Good Market MacroeconomicsDocumento7 páginasThe Good Market MacroeconomicsMavis CAinda não há avaliações
- National Income EquilibriumDocumento14 páginasNational Income EquilibriumAli zizoAinda não há avaliações
- Test 3 ReviewDocumento7 páginasTest 3 ReviewJAL4Ainda não há avaliações
- Econ Review ProjectDocumento5 páginasEcon Review ProjectNing GuangAinda não há avaliações
- Global Markets Exam PrepDocumento14 páginasGlobal Markets Exam Prepbaler73561Ainda não há avaliações
- 10 Aggregate Expenditures ModelDocumento3 páginas10 Aggregate Expenditures Modelcatherine tucayAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 14 - Unemployment and Fiscal Policy - 1.0Documento41 páginasUnit 14 - Unemployment and Fiscal Policy - 1.0Georgius Yeremia CandraAinda não há avaliações
- Session 17 - Fiscal PolicyDocumento54 páginasSession 17 - Fiscal PolicyLakshmi Harshitha mAinda não há avaliações
- 6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocumento62 páginas6 - Aggregate Demand and SupplyMạnh Nguyễn VănAinda não há avaliações
- GDP and Price Level in Short RunDocumento23 páginasGDP and Price Level in Short RunHasnainAinda não há avaliações
- Business EconomicsDocumento5 páginasBusiness Economicsjitendra.jgec8525Ainda não há avaliações
- FTD 992009Documento5 páginasFTD 992009api-25896854Ainda não há avaliações
- Topic 6: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (PART 1) : Case & Fair (Ch. 26)Documento48 páginasTopic 6: Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply (PART 1) : Case & Fair (Ch. 26)chan xianAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures 8-14Documento47 páginasLectures 8-14SHIVAM SHARMAAinda não há avaliações
- CP104 Lecture NotesDocumento19 páginasCP104 Lecture NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures 1-10 BU111Documento27 páginasLectures 1-10 BU111DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Business 121 Lecture NotesDocumento157 páginasBusiness 121 Lecture NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Marginal RevenueDocumento2 páginasMarginal RevenueDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- CP104 Lecture NotesDocumento19 páginasCP104 Lecture NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Lectures 1-10 BU111Documento27 páginasLectures 1-10 BU111DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- BU 111 Course Models (First Midterm)Documento9 páginasBU 111 Course Models (First Midterm)DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- BU 111 Course Models (First Midterm)Documento9 páginasBU 111 Course Models (First Midterm)DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Travel AdvisoriesDocumento1 páginaTravel AdvisoriesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus ReviewDocumento13 páginasCalculus ReviewDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Economics NotesDocumento9 páginasEconomics NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Economics NotesDocumento9 páginasEconomics NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Economics HomeworkDocumento17 páginasEconomics HomeworkDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Unit 7 NotesDocumento20 páginasEconomics Unit 7 NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Export Development CanadaDocumento1 páginaExport Development CanadaDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Unit 3 ReviewDocumento7 páginasCalculus Unit 3 ReviewDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Money SupplyDocumento2 páginasMoney SupplyDynafrom100% (1)
- Roles of The Bank of CanadaDocumento3 páginasRoles of The Bank of CanadaDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Unit 2 TestDocumento4 páginasCalculus Unit 2 TestDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Unit 1 TestDocumento5 páginasCalculus Unit 1 TestDynafrom100% (7)
- The Canadian Economy With An Increase in Personal Income Tax RatesDocumento1 páginaThe Canadian Economy With An Increase in Personal Income Tax RatesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Trade To CanadiansDocumento2 páginasImportance of Trade To CanadiansDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus p145Documento5 páginasCalculus p145DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Southwest AirlinesDocumento2 páginasSouthwest AirlinesDynafrom67% (3)
- Trade RestrictionsDocumento3 páginasTrade RestrictionsDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Economics NotesDocumento56 páginasEconomics NotesDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- The Spending MultiplierDocumento3 páginasThe Spending MultiplierDynafrom100% (1)
- Impact of Fiscal Policy - Budget Surpluses and DeficitsDocumento1 páginaImpact of Fiscal Policy - Budget Surpluses and DeficitsDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- February-02-09 1:26 PM: Unit 1 Page 1Documento7 páginasFebruary-02-09 1:26 PM: Unit 1 Page 1DynafromAinda não há avaliações
- Roles of The Bank of CanadaDocumento3 páginasRoles of The Bank of CanadaDynafromAinda não há avaliações
- ES2011Documento309 páginasES2011adityaverma7Ainda não há avaliações
- Monetary PolicyDocumento34 páginasMonetary PolicyYogesh Kende89% (9)
- Black Wednesday September 16th 1992 Bank of EnglandDocumento34 páginasBlack Wednesday September 16th 1992 Bank of EnglandDivya100% (1)
- DemonetisationDocumento40 páginasDemonetisationAbhinav JainAinda não há avaliações
- What Causes The Business Cycle?Documento3 páginasWhat Causes The Business Cycle?Olga BochkarovaAinda não há avaliações
- 德银 全球投资策略之全球固定收益2021年展望:还需要迎头赶上 2020.12.22 110页Documento112 páginas德银 全球投资策略之全球固定收益2021年展望:还需要迎头赶上 2020.12.22 110页HungAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 - An Introduction To MacroeconomicsDocumento40 páginasChapter 5 - An Introduction To MacroeconomicsDan GregoriousAinda não há avaliações
- More Central Bank Monetary Heroin Will Spark Currency Race To The Bottom, Global ImplosionDocumento2 páginasMore Central Bank Monetary Heroin Will Spark Currency Race To The Bottom, Global ImplosionAbanoubAinda não há avaliações
- Rohlf Keynes and ClassicalDocumento17 páginasRohlf Keynes and Classicalfabs4scribdAinda não há avaliações
- The and It's 21 Century: Philippine Economy Socioeconomic ChallengesDocumento28 páginasThe and It's 21 Century: Philippine Economy Socioeconomic ChallengesRocky PacpacoAinda não há avaliações
- India's Inflation HistoryDocumento67 páginasIndia's Inflation HistoryDr. Pabitra Kumar MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Trader Monthly Research Report: April: by Alex HaywoodDocumento11 páginasTrader Monthly Research Report: April: by Alex Haywoodapi-213311303Ainda não há avaliações
- Inflatable Packers For Grouting: Figure 1 - Fixed End Inflatable Packer Figure 2 - Moving End Inflatable PackerDocumento7 páginasInflatable Packers For Grouting: Figure 1 - Fixed End Inflatable Packer Figure 2 - Moving End Inflatable PackerYahya Ah100% (1)
- MBA 504 Group Assignment 1 Draft LayoutDocumento9 páginasMBA 504 Group Assignment 1 Draft LayoutroseAinda não há avaliações
- Econ Chapter 35Documento2 páginasEcon Chapter 35Matt David TelkerAinda não há avaliações
- Lectura en Ingles Economia 4PCDocumento18 páginasLectura en Ingles Economia 4PCMiguel Angel RuizAinda não há avaliações
- The Demonetization EffectDocumento12 páginasThe Demonetization Effectyogesh079440% (5)
- Chapter 1 PowerpointDocumento3 páginasChapter 1 PowerpointSafdar Khan NiaziAinda não há avaliações
- Inflation AccountingDocumento13 páginasInflation AccountingtrinabhagatAinda não há avaliações
- Credentialism EssayDocumento6 páginasCredentialism EssaychrisdrownAinda não há avaliações
- Eco 158Documento20 páginasEco 158DaniyaNaiduAinda não há avaliações
- Demand for Money: A Review of Theoretical and Empirical IssuesDocumento36 páginasDemand for Money: A Review of Theoretical and Empirical IssuesMehmet RaKsAinda não há avaliações
- Problem SetDocumento14 páginasProblem SetVin PheakdeyAinda não há avaliações
- Level 2 Webinar CMT TutorialDocumento103 páginasLevel 2 Webinar CMT Tutorialmr_agarwal100% (5)
- Economic Forecast ColombiaDocumento3 páginasEconomic Forecast Colombiasuper_sumoAinda não há avaliações
- Egory Mankiw Chapter 1Documento12 páginasEgory Mankiw Chapter 1Dyna MadinaAinda não há avaliações
- Macroeconomics Dde PDFDocumento253 páginasMacroeconomics Dde PDFPankaj GahlautAinda não há avaliações
- ECO202-Practice Test - 22 (CH 22)Documento4 páginasECO202-Practice Test - 22 (CH 22)Aly HoudrojAinda não há avaliações
- RBIBULLC2B6CC46Documento120 páginasRBIBULLC2B6CC46arti guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplier Model Web Chapter Colander HgdAMRUlA2Documento30 páginasMultiplier Model Web Chapter Colander HgdAMRUlA2Himanshu SethAinda não há avaliações