Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cellular Aberration
Enviado por
Frances GaviolaDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cellular Aberration
Enviado por
Frances GaviolaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Malignant squamos cell carcinomaadenocacinoma multiple myeloma lioblastoma fibrosarcoma Osteosarcoma
Benign glioma lipoma fibroma neuroma Meningioma
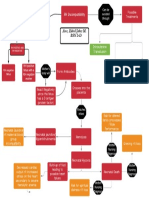
TERMINOLOGIES Tumor lumps, mass, swelling Neoplasm- abnormal growth of mass tissue that has no purpose; benign or malignant Benign neoplasm does not invade other tissues Malignant neoplasm metastasizes to other tissues and organs Neoplasia Any new or continued cell growth not needed for normal development or replacement of dea and damaged tissue Cancer malignant neoplasm Extravasation leakage of medication from the vein into the subcutaneous tissue Dysplasia bizarre cell growth resulting in cells that differ in size, shape or arrangement form other cells of the same type of tissue. Alteration in size, shape and organization of cells Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular tissues Anaplasia cells that lack normal cell characteristic and differ in shape and organization with respect to their cells of origin Carcinoma composed of epithelial cells Carcinogenesis process of transforming normal cells into malignant cells Carcinoma in situ confined to the local areas; 1st stage of cancer Sarcoma cancer that arises from the connective tissues Differentiation the process of maturation of a cell line of cancer cell Tumor markers chemicals found in the blood that are produced by certain cancer Apoptosis program cell death Staging process of determining the size and spread or metastasis of a tumor Tumor-specific antigen(TSA) - protein on the membrane of cancer cells that distinguishes the malignant cell from a benign cell of the same tissue type WARNING SIGNS OF CANCER >>CAUTION US! o C- change in bladder and bowel habits o A - sore that does not heal o U- unusual bleeding or discharges o T- thickening or lump in the breast o I-ndigestion and difficulty in swallowing o O- overt changes in wart or mole o N- nagging cough and hoarseness of voice o U -nexplained anemia o S - udden unexplained weight loss CELLULAR ABERRATION A group of disorders characterized by abnormal cell growth and the ability to metastasize with potential in killing the host.
What Is Cancer? CANCER is a complex of diseases which occurs when normal cells mutate into abnormal cells that take over normal tissue, eventually harming and destroying the host A large group of diseases characterized by: o Uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells Apoptosis, or cell suicide, is the mechanism by which old or damaged cells normally self-destruct. o Proliferation (rapid reproduction by cell division) Oncogenes are genes whose PRESENCE in certain forms and/or over activity can stimulate the development of cancer. When oncogenes arise in normal cells, they can contribute to the development of cancer by instructing cells to make proteins that stimulate excessive cell growth and division. o Invasion and metastasis. (spread or transfer of cancer cells from one organ or part to another not directly connected) Invasion refers to the direct migration and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Metastasis refers to the ability of cancer cells to penetrate into lymphatic and blood vessels, circulate through the bloodstream, and then invade normal tissues elsewhere in the body. Derived from the Latin crab which means cancer o The crab first came to describe the disease of malignant tumours when Hippocrates, the Greek father of medicine, saw the cut surface of a breast cancer, and described it as "carcinos" - it looked like a crab with legs stretching outwards. He later coined the word "carcinoma" - "crab swelling". Later, the Roman physician Celsus translated this into Latin directly into cancer, and this name became the name we unfortunately know well WHAT ARE THE WARNING SIGNS OF CANCER CAUTION US! o C- change in bladder and bowel habits o A - sore that does not heal o U- unusual bleeding or discharges o T- thickening or lump in the breast o I-ndigestion and difficulty in swallowing o O- overt changes in wart or mole o N- nagging cough and hoarseness of voice o U -nexplained anemia o S - udden unexplained weight loss
ETIOLOGY/CAUSATIVE FACTORS Viruses / bacteria Chemical carcinogens (e.g. cigarette smoke) Radiation Physical stressors Hormonal factors Genetic factors
Você também pode gostar
- Pscy PrelimDocumento20 páginasPscy PrelimAinah Batua-anAinda não há avaliações
- Post Test - Psych-Prof. Alviz - SCDocumento4 páginasPost Test - Psych-Prof. Alviz - SCKristen FajilanAinda não há avaliações
- LCPDDocumento7 páginasLCPDakoismeAinda não há avaliações
- Ca 2 Cardiovascular-Oxygenation Assignment Part 1Documento8 páginasCa 2 Cardiovascular-Oxygenation Assignment Part 1Joseph AbangAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeDocumento1 páginaBlood Pressure Measurement Is An Important Part of The Patient's Data Base. It Is Considered To BeMir MirAinda não há avaliações
- Special Enhancer Drills PDFDocumento8 páginasSpecial Enhancer Drills PDFMcbry TiongAinda não há avaliações
- FNCPDocumento17 páginasFNCPRaquel M. MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Community NursingDocumento3 páginasCommunity NursingEthan Marcos GoAinda não há avaliações
- Personal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesDocumento15 páginasPersonal-Soc Interpretation: Tower of 4 CubesteuuuuAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Ab ActivitiesDocumento7 páginasCell Ab ActivitiesJanelle Cabida Supnad100% (1)
- Intensive Nursing Practicum: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocumento9 páginasIntensive Nursing Practicum: Bachelor of Science in NursingMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular AberrationDocumento71 páginasCellular AberrationKris TejereroAinda não há avaliações
- CBQ Legal Ethical MNGTDocumento23 páginasCBQ Legal Ethical MNGTyzak jouleAinda não há avaliações
- CHNDocumento7 páginasCHNAbdurrahim MlntdAinda não há avaliações
- Post Partum AssessmentDocumento3 páginasPost Partum Assessmentdanica grace gubaAinda não há avaliações
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDocumento2 páginasHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Situation 1Documento18 páginasSituation 1Maler De VeraAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Test Rle70.medical Ward NMMC Cagayan de Oro CityDocumento6 páginasPre Test Rle70.medical Ward NMMC Cagayan de Oro CityLouresa Mae TAinda não há avaliações
- CoparDocumento4 páginasCopar.fayefen100% (4)
- Larynx Cancer Case Study AndrewDocumento13 páginasLarynx Cancer Case Study Andrewapi-273146320Ainda não há avaliações
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDocumento52 páginasHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- Funda ReviewerDocumento8 páginasFunda ReviewerChamelli RobinAinda não há avaliações
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocumento24 páginasCommunity Health Nursing ReviewergilpogsAinda não há avaliações
- CHNDocumento8 páginasCHNAziil LiizaAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDocumento2 páginasConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadAinda não há avaliações
- Ex LapDocumento42 páginasEx LapOmar Khalif Amad PendatunAinda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersDocumento5 páginasThis Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersdanceAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular AberrationDocumento14 páginasCellular AberrationjinahyangAinda não há avaliações
- AtireviewDocumento163 páginasAtireviewGlory Mimi0% (1)
- TFN Chapter 1Documento167 páginasTFN Chapter 1MC Lopez Aguilar100% (1)
- Digestive System 2Documento32 páginasDigestive System 2Johnmer AvelinoAinda não há avaliações
- 18 Cellular AberrationsDocumento70 páginas18 Cellular AberrationsBea Bianca CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityDocumento1 páginaBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoAinda não há avaliações
- Cholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESDocumento52 páginasCholelithiasis GRAND CASE PRESKyle Cholo CholoAinda não há avaliações
- Iv Fluid Sheet: Bautista A 58 2021-0000025 Milagros F Medical Ward-207Documento1 páginaIv Fluid Sheet: Bautista A 58 2021-0000025 Milagros F Medical Ward-207Renea Joy ArruejoAinda não há avaliações
- Moral Principles ExerciseDocumento1 páginaMoral Principles ExerciseGerome Isaiah RabangAinda não há avaliações
- MyelomeningoceleDocumento7 páginasMyelomeningocelemavefigAinda não há avaliações
- Family Caseload Presentation Barangay BalagbagDocumento6 páginasFamily Caseload Presentation Barangay BalagbagCharmae NaveaAinda não há avaliações
- Course Audit Professional AdjustmentDocumento9 páginasCourse Audit Professional Adjustmentshenric16Ainda não há avaliações
- Predisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryDocumento2 páginasPredisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryChloé Jane HilarioAinda não há avaliações
- EndocrinedisorderDocumento3 páginasEndocrinedisorderDyan LazoAinda não há avaliações
- Application of Nursing Standards Is A Must in Community Health Nursing. To Whom of The Following Do These Standards Apply?Documento27 páginasApplication of Nursing Standards Is A Must in Community Health Nursing. To Whom of The Following Do These Standards Apply?L1NEDS DAinda não há avaliações
- Cancer and Oncology Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz ANSDocumento5 páginasCancer and Oncology Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz ANSyanyan cadizAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Documento4 páginasNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torAinda não há avaliações
- FNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Documento4 páginasFNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Aaron EspirituAinda não há avaliações
- CHN Quiz Compilation FinalsDocumento20 páginasCHN Quiz Compilation FinalsFayeann Vedor LoriegaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiogenic Shock NCLEX Review QuizDocumento6 páginasCardiogenic Shock NCLEX Review QuizRegie Marie EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Community Health Nursing Review NotesDocumento12 páginasCommunity Health Nursing Review NotesISICLE GTAinda não há avaliações
- Uterine Rupture: Mariano Marcos StateDocumento10 páginasUterine Rupture: Mariano Marcos StateSalvaje CaballeroAinda não há avaliações
- Transcultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodDocumento5 páginasTranscultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodeuLa-mayzellAinda não há avaliações
- Cop Lec - Unit Iv - Physical Care of OlderDocumento3 páginasCop Lec - Unit Iv - Physical Care of Oldercayla mae carlosAinda não há avaliações
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Documento3 páginasSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelAinda não há avaliações
- And Standards of Practice EmphasizesDocumento15 páginasAnd Standards of Practice EmphasizesKrizia R. PingkeAinda não há avaliações
- Study Questions 2Documento10 páginasStudy Questions 2CGAinda não há avaliações
- CMCQDocumento31 páginasCMCQJim Christian EllaserAinda não há avaliações
- What Is CancerDocumento23 páginasWhat Is CancerSamatha MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular AberrationsDocumento94 páginasCellular AberrationsridzkhaAinda não há avaliações
- When Cancer Spreads: EnlargeDocumento5 páginasWhen Cancer Spreads: EnlargeAlfrien Ivanovich LarchsonAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Cancer What Is Cancer and Types of CancerDocumento6 páginasUnderstanding Cancer What Is Cancer and Types of CancerPatrisha KerrAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of Physical Activity On Primary Dysmenorrhea of Female University StudentsDocumento21 páginasThe Effect of Physical Activity On Primary Dysmenorrhea of Female University StudentsIntan AyuAinda não há avaliações
- WarfarinDocumento10 páginasWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Threatened AbortionDocumento3 páginasThreatened Abortionjay5ar5jamorabon5torAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Documento154 páginasAcute Myeloid Leukemia: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Krisha Marie BadilloAinda não há avaliações
- UK Info & LabelDocumento28 páginasUK Info & LabelJenn LamAinda não há avaliações
- Bahir Dar University Institute of TechnologyDocumento26 páginasBahir Dar University Institute of Technologytazeb AbebeAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment-Tool-For-Ambulance 2018 PDFDocumento12 páginasAssessment-Tool-For-Ambulance 2018 PDFDerrick ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- Facial Fillers Relevant Anatomy Injection TechniquDocumento9 páginasFacial Fillers Relevant Anatomy Injection TechniquMasoud Rahimi100% (1)
- Angina PectorisDocumento12 páginasAngina Pectorismardsz93% (14)
- Trauma-Informed Care For Schools Presentation 508CDocumento41 páginasTrauma-Informed Care For Schools Presentation 508Cemptychair_nelAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Exam NCM 145Documento17 páginasComprehensive Exam NCM 145Adrian Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- FinalsDocumento9 páginasFinalsCathy PhongAinda não há avaliações
- Autism Spectrum Disorder GeneDocumento8 páginasAutism Spectrum Disorder GeneMichelle2Ainda não há avaliações
- CPG - Whiplash Associated DisordersDocumento74 páginasCPG - Whiplash Associated DisordersGumDropAinda não há avaliações
- DpcoDocumento41 páginasDpcodrugdrugAinda não há avaliações
- Calcium HoaxDocumento40 páginasCalcium HoaxpuravAinda não há avaliações
- Inservice Education Plan On GlutenDocumento3 páginasInservice Education Plan On GlutenchandlerAinda não há avaliações
- Consumer Chemistry: Quarter 4 - Module 3Documento22 páginasConsumer Chemistry: Quarter 4 - Module 3wetlog lolololimAinda não há avaliações
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410Documento6 páginasChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410PromagEnviro.comAinda não há avaliações
- Wintobootic2mockboard Exam - Social Work CounselingDocumento4 páginasWintobootic2mockboard Exam - Social Work CounselingATLASAinda não há avaliações
- NCP-DP NCM112LecDocumento4 páginasNCP-DP NCM112LecShane CabucosAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormal Psych Question 1Documento10 páginasAbnormal Psych Question 1Ronald Jacob Picorro100% (1)
- Introduction To PedodonticsDocumento33 páginasIntroduction To PedodonticsKhushboorana A Scientist100% (1)
- Summer Internship ReportDocumento103 páginasSummer Internship ReportChandan Srivastava100% (4)
- Silver Hill Hospital Chronic Pain and Recovery CenterDocumento8 páginasSilver Hill Hospital Chronic Pain and Recovery CenterSilver Hill HospitalAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook CoreDocumento38 páginasEbook CoreDiana GoldAinda não há avaliações
- MedDocumento76 páginasMedRazvanPopAinda não há avaliações
- Nicotine: How Does Nicotine Deliver Its Effect?Documento6 páginasNicotine: How Does Nicotine Deliver Its Effect?jmolaecheaAinda não há avaliações
- Wall Color of Patients RoomDocumento80 páginasWall Color of Patients RoomHadži Olivera NikolićAinda não há avaliações
- Compartment ModelsDocumento67 páginasCompartment ModelsGhadeer M HassanAinda não há avaliações