Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
H2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell Organelles
Enviado por
SefLRhoDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
H2 Biology - Notes On Cell Structure - Cell Organelles
Enviado por
SefLRhoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
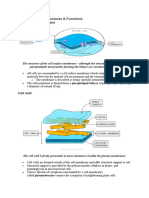
Notes on cell structure Cell theory o States that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells
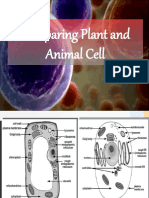
s o States that cells are Basic structural and functional units Have membranes which regulate movements in and out Contain various organelles Contain hereditary information Units of conversion o 1 cm = 10-2m o 1 um = 10-6 m o 1 nm = 10-9 m Upper and lower limits of cells o Upper limit determined by surface are to vol. ratio diffusion distance nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio Name the typical animal and plant cells as seen under electron microscope and light microscope Light microscope Nucleus Cell surface membrane Cytoplasm Vacuole Nucleolus Chloroplast Tonoplast Cellulose cell wall Electron microscope All under light microscope Grana in chloroplast Chromatin Mitochondria Glogi apparatus Centrioles Lysosome Microvillus Microtubule Free ribosomes rER, sER Identify the different organelles under electron microscope (refer to notes) Describe the structure of the common cell organelles and relate to their functions components Structure Largest organelle ~10-20 um in diameter Found in all eukaryotic cells except mature phloem sieve-tube elements and rbc Double membrane Fluid filled space of 25 nm Outer membrane continuous with rER Has nuclear pores lined by protein octet Function Control centre for activities of the cell Contain DNA Essential for cell division
Cell organelles Nucleus
Nuclear envelope
Allow exchange of substances Selective in proteins
1|Page Created by SefLRho (2012) DHS
Nucleoplasm
Gel-like matrix of nucleus
Euchromatin
Heterochromatin
Nucleolus Endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER
Lightly packed Unfolded Allows gene regulatory protein and RNA polymerase complexes to bind Lighter staining Genetically inactive Tightly coiled Located at the peripheral of nucleus Darkly stained spherical body inside nucleus Extensive 3D network of membranous tubules and sacs known as cisternae internal compartment known as cisternae space smooth without bound ribosomes consists of meshwork of fine tubules continuous with rER Presence of ribosomes System of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cistarnae Continuous with nucleus envelope
Serve as medium for diffusion of metabolites and large macromolecules Actively transcribed
Site of synthesis of ribosomal ribonucleic acid
Rough ER
Golgi Apparatus Stack of smooth surfaced, flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae System of associated Golgi vesicles Cis face (receive) and trans face (punches off)
Lysosomes
Contains hydrolytic enzymes Acidic in nature
Lipid synthesis Detoxification of drugs and poisons in the liver Storage and release of Ca2+ Secrete HCl Site of protein synthesis o Proteins formed will enter cisternal space o Fold into native config. o Bud off to Golgi Serves as intracellular transport network Stores secretions such as hormones Finishing factory chemically modifies them such as maturation by added short carbohydrate chains Sorts and package Formation of lysosomes Formation of cellulose cell walls in plant Phagocytosis Autophagy digestion of worn out organelles Autolysis suicide
2|Page Created by SefLRho (2012) DHS
Peroxisomes
Contain oxidative enzymes that catalyze reactions
Mitochondria
Plastids
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Plant vacuole
Occur in all eukaryotic cells Large numbers Contain 70S ribosomes and circular DNA Double membrane o Smooth outer: highly permeable to small solutes o Inner convoluted (cristae): irregular series of partitions Intermembrane space Biconvex discs Double membrane Contain a system of flattened membranous sacs known as thylakoids Thylakoids form stacks known as grana Surrounding fluid: stroma Contain circular DNA, 70S ribosomes Enclosed by tonoplast Large permanent central vacuole
Break down fats in small molecules Store in liver to detoxify compounds Involved in cellular respiration Formation of ATP
Site of photosynthesis Contain chlorophyll Light dependent: thylakoid Light independent: stroma
Animal vacuole
Much smaller Temporary
Ribosome
Found in all cells Free ribosomes suspended in the cytosol Bound ribosomes attached to rER Usually occurring in clusters polyribosomes Size: 20 nm Made up of large subunit and a smaller subunit (40S +
Stores and reserves important organic compounds Stores inorganic compounds Contain pigments that colour the cells Plant growth by absorbing water and elongating cell Food vacuoles: formed by phagocytosis Contractile vacuole: amoeba pump excess water out of cell Site of protein synthesis Free ribo: make proteins for internal use Bound ribo: make proteins for exocytosis Structurally identical, ribosomes can alternate between roles
3|Page Created by SefLRho (2012) DHS
Centrioles
Cytoskeleton
Microtubules
Microfilament
60S) Edist as pair Positioned with their longitudinal axis at right angles to each other 9 triplets of microtubules Located close to nucleus Straight, hollow fibers 25 nm Occur singly or in bundles Solid structure 5-7 nm Occur as bundles
Form spindle fibers during cell division
Intermediate filaments Cytosol
Made up of diverse protein Gel-like matrix
Cellulose cell wall
Consists of cellulose fibres embedded Permeable to small solutes
Cellular support Tracks for organelle movement Cytoplasmic streaming through contraction and relaxation to move cell organelles within cytoplasm Fixes location of certain organelles eg nucleus Store vital chemicals Site of certain metabolic pathways Act as filter Provide mechanical support Provides turgidity
Ultrastructure of prokaryotes Nucleoid region No nucleus Bacterial chromosome is located in a region of the cell called the nucleoid region Contain 70s ribosomes Needed for protein synthesis Where nutrients and reserves may be stored Primary function: ensure survival of bacteria through periods of environmental stress Layer of polysaccharides that protects the cell from environmental dangers Often present in pathogenic bacteriab Partially permeable May have mesosome (infoldings) May have photosynthetic
In the cytoplasm
Ribosomes
Storage granules Endospores
Surface structures
Capsule
Murein cell wall Cell plasma membrane
4|Page Created by SefLRho (2012) DHS
Appendages
Pili (singular: pilus) Flagella
membranes Allow bacteria to attach to other cells For motility Rotates Cork screw motion (in eukaryotes, it is in wave form)
5|Page Created by SefLRho (2012) DHS
Você também pode gostar
- H2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesDocumento15 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesSefLRho100% (5)
- A Level Biology Essay Model AnswersDocumento4 páginasA Level Biology Essay Model AnswersKFCStadivari100% (1)
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryDocumento8 páginasBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryJulian WolfgangAinda não há avaliações
- 2014 JC 1 Promos Revision Package - H1 - Revision Package 2 - ANS (Final)Documento19 páginas2014 JC 1 Promos Revision Package - H1 - Revision Package 2 - ANS (Final)Wesley TanAinda não há avaliações
- !. Sffi51tffiiDocumento48 páginas!. Sffi51tffiiaggogogogAinda não há avaliações
- Family - General PaperDocumento5 páginasFamily - General PaperDeclan RajAinda não há avaliações
- H3 Molecular BiologyDocumento17 páginasH3 Molecular BiologyTerrence LiAinda não há avaliações
- We Cannot Save The Environment Without Fighting Poverty.' Do You AgreeDocumento4 páginasWe Cannot Save The Environment Without Fighting Poverty.' Do You Agreeh1generalpaperAinda não há avaliações
- H2 A Level Chemistry Transition Elements Notes Part 1Documento19 páginasH2 A Level Chemistry Transition Elements Notes Part 1Peng Jia XinAinda não há avaliações
- 2011 GP Prelim p1 CompilationDocumento5 páginas2011 GP Prelim p1 CompilationjjnaseemAinda não há avaliações
- Ecology 6th Edition Molles Test BankDocumento4 páginasEcology 6th Edition Molles Test BankmejavAinda não há avaliações
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDocumento8 páginasBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDana PorterAinda não há avaliações
- Admission Test For The Degree Course in Medicine and Surgery Academic Year 2018/2019Documento44 páginasAdmission Test For The Degree Course in Medicine and Surgery Academic Year 2018/2019Umberto PrincipeAinda não há avaliações
- Control and Co-Ordination 2021-2022 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADDocumento21 páginasControl and Co-Ordination 2021-2022 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADADEEL AHMADAinda não há avaliações
- Can Terrorism Ever Be Eradicated? SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Eradicating TerrorismDocumento3 páginasCan Terrorism Ever Be Eradicated? SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Eradicating TerrorismValNovel100% (1)
- All JCs H2 Econs Prelim 2011Documento19 páginasAll JCs H2 Econs Prelim 2011Clarion TanAinda não há avaliações
- Biology: Cell StructuresDocumento12 páginasBiology: Cell Structurescarl gamingAinda não há avaliações
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocumento10 páginasEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25Ainda não há avaliações
- lecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjkDocumento12 páginaslecture_1_-_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanismssdfkgjktanique.nembhard1022Ainda não há avaliações
- Bio ASDocumento189 páginasBio ASNgu War KhinAinda não há avaliações
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento51 páginas2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocumento35 páginasChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangAinda não há avaliações
- Cell & Intercellular JunctionsDocumento35 páginasCell & Intercellular JunctionsDikpal BikramAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento70 páginasFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- CELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsDocumento6 páginasCELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsAli WarisAinda não há avaliações
- Completely Compiled BiologyDocumento236 páginasCompletely Compiled BiologyKyu9930100% (1)
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocumento12 páginasThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsShakera ReidAinda não há avaliações
- The Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocumento12 páginasThe Structure and Components of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsAlix AliAinda não há avaliações
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesDocumento8 páginasProkaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesnabilahAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular OrganizationDocumento102 páginasCellular OrganizationMellyAinda não há avaliações
- Cell TheoryDocumento146 páginasCell TheoryGynewAinda não há avaliações
- BiochemDocumento108 páginasBiochemJangAinda não há avaliações
- Cell BiologyDocumento68 páginasCell Biologyleanavill100% (2)
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Documento8 páginas11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Structure and FunctionsDocumento72 páginasStructure and FunctionsSha AkoAinda não há avaliações
- Botany ReviewerDocumento14 páginasBotany ReviewerTherese EspinosaAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Science CellsDocumento12 páginasNotes Science CellsHina SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: Structures and FunctionsDocumento6 páginasCells: Structures and Functionsakash kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Structure/ Mitosis & Meiosis: SE Shirley Dept of PathologyDocumento36 páginasCell Structure/ Mitosis & Meiosis: SE Shirley Dept of PathologyJohn M. HemsworthAinda não há avaliações
- Cells Structure FunctionDocumento8 páginasCells Structure FunctionRameesha RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant CellsDocumento10 páginasCell Organelles: The Structures that Power Plant Cellsjhariesargente05Ainda não há avaliações
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocumento30 páginasLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Exam 2 Study GuideDocumento6 páginasBio Exam 2 Study GuidekecordovaAinda não há avaliações
- Module IDocumento18 páginasModule IAdvith A JAinda não há avaliações
- CellDocumento28 páginasCellJanvi SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Comparison ChartDocumento3 páginasCell Comparison ChartJake BryantAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocumento68 páginasCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- 1 Cell Structure FunctionDocumento124 páginas1 Cell Structure FunctionIntoy, Stephanie Mae100% (1)
- Cell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADDocumento44 páginasCell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADJason RobinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in BiologyDocumento8 páginasReviewer in BiologyMikaela EvangelistaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction CellDocumento48 páginasIntroduction CellabdAinda não há avaliações
- 2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)Documento7 páginas2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)rastete195Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell. Prikaryotic and Euk.Documento30 páginasCell. Prikaryotic and Euk.avneeshraj100% (1)
- Cells Structure and FunctionDocumento56 páginasCells Structure and FunctionAnnisa DiyanabilaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento29 páginasChapter 4skywalkerAinda não há avaliações
- The Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDocumento49 páginasThe Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDaezel DeuxAinda não há avaliações
- Biology RevisionDocumento29 páginasBiology RevisionelsybelsyAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles NotesDocumento2 páginasCell Organelles Notesoriel blountAinda não há avaliações
- Cells - Basic Unit of LifeDocumento45 páginasCells - Basic Unit of Lifeapi-202349222Ainda não há avaliações
- The CellDocumento36 páginasThe CellSam MumoAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Biology - Notes On Nervous ControlDocumento7 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On Nervous ControlSefLRhoAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesDocumento10 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of VirusesSefLRhoAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Biology - Notes On EnzymesDocumento4 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On EnzymesSefLRhoAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Biology - Notes On Cell and Nuclear DivisionsDocumento8 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On Cell and Nuclear DivisionsSefLRhoAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaDocumento10 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaSefLRho0% (1)
- H2 Biology - Notes On BiomoleculesDocumento9 páginasH2 Biology - Notes On BiomoleculesSefLRho100% (1)
- H2 Biology - Water PropertiesDocumento2 páginasH2 Biology - Water PropertiesSefLRhoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocumento78 páginasChapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeRoboAinda não há avaliações
- Final MC1 Laboratory ManualDocumento18 páginasFinal MC1 Laboratory ManualKrison Jake ArticuloAinda não há avaliações
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5Documento6 páginasNcert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5ppusapatiAinda não há avaliações
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONDocumento7 páginasCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONChhaya GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Class 9 Science Chapter 0 Revision NotesDocumento9 páginasClass 9 Science Chapter 0 Revision NotesMr CrownAinda não há avaliações
- Amc Past PapersDocumento26 páginasAmc Past PapersDr. Ameer HamzaAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeDocumento8 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in PeroxisomeKeannoAinda não há avaliações
- Genyo Learning Plan March10Documento5 páginasGenyo Learning Plan March10Gia Carla RecioAinda não há avaliações
- Long TestDocumento5 páginasLong TestEmmanuel LouiseAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21Documento16 páginasCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/21Malak ShokryAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocumento22 páginasUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Lysosomes IntroductionDocumento13 páginas1 Lysosomes IntroductionJojo LomoAinda não há avaliações
- My Answer in Our LaboratoryDocumento4 páginasMy Answer in Our LaboratoryKris Marie DelaCruz DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- Inbo 2009Documento42 páginasInbo 2009BenjaminVasileniucAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocumento35 páginasPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test Bankpithlessriverp4d6100% (31)
- Kcse 2012 Biology p1Documento7 páginasKcse 2012 Biology p1Urex ZAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem Practice ExamDocumento8 páginasBiochem Practice ExamLouie Bello50% (2)
- The Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyDocumento30 páginasThe Cell: Cytoplasmic Organelles: Prepared By: Lenor M. Tunac MAED-BiologyLenor TunacAinda não há avaliações
- Zoology (Book)Documento26 páginasZoology (Book)sme olaplAinda não há avaliações
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomesDocumento20 páginasCell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomescbseiscAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento6 páginasCell Structure and FunctionasyuraAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Lecture AssignmentDocumento16 páginasInteractive Lecture AssignmentIpulCool100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocumento2 páginasCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartCyril Mae MagallanesAinda não há avaliações
- Comparing Plant and Animal CellDocumento38 páginasComparing Plant and Animal CellRegie G. GalangAinda não há avaliações
- FLGX113 SU3.3 and SU 3.4Documento60 páginasFLGX113 SU3.3 and SU 3.4Jason Van Den HeeverAinda não há avaliações
- Class IX biology cell organelles MCQsDocumento2 páginasClass IX biology cell organelles MCQsGREEN HEARTAinda não há avaliações
- Khan Academy Eukaryotic Cells QuestionsDocumento3 páginasKhan Academy Eukaryotic Cells QuestionsLoraAinda não há avaliações
- Mobilizzazione LipidicaDocumento21 páginasMobilizzazione LipidicaLuca PellaAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocumento13 páginasBiochemistry ReviewerGienelle Susana San Juan FerrerAinda não há avaliações
- Color The Animal CellDocumento6 páginasColor The Animal Cellyuefen tohAinda não há avaliações