Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Leadership, Case Analysis and Decision Making
Enviado por
Gerrely Dela CruzDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Leadership, Case Analysis and Decision Making
Enviado por
Gerrely Dela CruzDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
LEADERSHIP SKILLS - Learned through experience, including adverse experiences.
Leader the one who leads Leadership is a process of guiding, teaching, motivating, and directing the activities of others toward attaining goals. 1. Setting goals-sharing vision 2. Developing motivation 3. Decision making 4. Empowering others 5. Teaching staff 6. Using feedback 7. Managing time 8. Managing resources 9. Advocating 10. Managing conflict 11. Using research CASE ANALYSIS - is a description of an actual administrative situation involving a decision to be made or a problem to be solved. It can a real situation that actually happened just as described, or portions have been disguised for reasons of privacy. I keep six honest serving men (They taught me all I knew); Their names are What and Why and When; And How and Where and Who. Rudyard Kipling DECISION MAKING - Critical nursing skills that helps nurses shape their actions. It is also an essential element in handling change, working with conflict, managing resources, evaluating care and performances - Is also a selection and implementing a course of action from a group of alternatives. It may or may not involve a problem. 1. CRITICAL THINGKING IS NECESSARY TO MAKE GOOD DECISIONS 2. EVERYTHING THAT IS DONE INVOLVES A DECISION 3. ALL DECISIONS ARE ETHICAL DECISIONS 1. Types of Decision: + Programmed-Non programmed a. Programmed- most decision are programmed meaning anticipated and routing examples: guidelines, policies or procedures that can be followed. b. Non-programmed- unexpected, unique and more complex. + Ends-Means c. Ends- deals with the determination of desired individual or organizational results to be achieved d. Means- decisions deal with strategic or operational programmed activities that will accomplish desired results. These usually occur during managerial planning processes, strategy and objective formulation processes + Administrative-Operational e. Administrative- made by senior management which have significant throughout the organization. Usually this type of decision is concerned with policy, resource allocation and utilization f. Operational- are generally made by mid level and first line managers and address day to day operational activities of a particular organizational.
2. The Process of Decision Making - Is the same process you have been using as the nursing process. Although the nursing process is a decision-making process for the purpose of planning patient care, the elements transfer to other situations, such as those in which you are making decisions for groups of patients, for staff, and in regard to collaboration with others. To make effective decisions, you will need to assess an entire situation through gathering appropriate data, analyze the data and come to conclusions, plan desired outcomes and actions, implement actions and evaluate the result. The nursing action process is not simple line from one step to another, but rather is constantly moving back and forth from one aspect to another as the situation evolves. Similarly an effective decision-making process is active and flexible. Decision Making and Problem-Solving Models and Nursing Process Decision Making 1. identify the problems and analyze the solution 2. explore the alternatives 3.choose the most desirable alternatives 4. implement the decision 5. evaluate the results Problem Solving 1.assess: define the problem 2.plan: generate a list of alternatives and evaluate for cost, feasibility and risk 3. choose the best solution 4. implement the apparent best solution 5. evaluate the effectiveness Nursing Process 1.assess 2.select nursing diagnosis 3.plan care 4.implement the care plan 5. evaluate the outcomes
3. Decision-Making tools help visualize option to facilitate evaluation of the option. a. Algorithms- precise set of process that leads to specific outcome. In health care, we see algorithms as a series of questions to ask that can be answered by yes or no. In our field we often use or designed for critical or emergency care decision. Pictured out. Example: Basic CPR is an algorithm in which 1st question is does the person respond? if yes CPR not needed, if no, check for breathing? b. Six Thinking Hats- strategy encourages you to look at a situation from multiple perspectives. De Bono(2000) suggested set of hats that help address different attitudes or approaches to the problem. He designated them with different colors. >white hat- viewpoint considers facts and data. >yellow hat- viewpoint looks at the positive ideas and takes the optimistic viewpoint >black hat- viewpoint is the pessimist and looks at all the problems and considers what you might have to do in relationship to those problems. >red hat- position tries to examine the feelings and gut reactions associated with the situation. >green hat- viewpoint is the creative one. >blue hat- is for the leader of a group who tries to get each of the other viewpoints on the table. c. Decision trees- help you to decide between several courses of actions. The decision is written in a box on left side of a paper. Each possible strategy is written on a line drawn out from that box. At the end of each line, positive and negatives effects are written in different circles. If other decisions are needed along the branches, then these are drawn in boxes. Example:
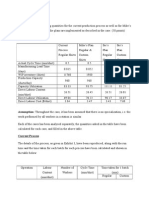
d. Gantt chart- named after their developer, Henry Gantt are highly developed schedules that allow one to visualize multiple tasks that have to be done. Task Collect information Type report Revise report Submit Report Responsible ME Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
ME ME
ME
4. Group Decision-Making/ Participative Decision-Making - means a group of individuals make the decision rather than a single individual Types: Consensus- a general agreement that the members of the group will support a specific strategy even if was not their most preferred strategy. Majority Rule- a simple vote is taken and the strategy preferred by the majority is adopted Brainstorming- lets brain storm that problem for a while. Is also a way to gather as many alternatives as possible. A good brainstorming session may last 2 or 3 days. Later, a group will sit down and begin to identify the feasibility and usefulness of the various ideas. Everything is written down for future consideration. Quality Circles- bring together persons who are working in the same area and have common concerns.
Nominal Group Technique- involves 7-10 individuals selected by the manager. The manager presents the problem to the group, and each participant writes down what he or she sees as the best solution without discussing it with others. The leader then shares the ideas with the group and writes them on a chalk board. There is no discussion until all ideas are written down. Then each solution is analyzed. Participants are asked to rank the solutions privately and individually from most acceptable to least acceptable. The solution that receives the highest overall ranking is then presented as the first alternative. This process allows for consideration of a number of approaches without the members of the group being pressured toward particular approach. The Delphi Method- is similar to nominal group technique. The person initiating the Delphi process choose participants. Participants may be polled for suggested alternatives, which are then complied and distributed to the participants. The manager may add alternatives to the list. Participants then select their preferred alternative and return the written information to the organizer. The membership of the group is anonymous, with only the manger knowing whom he or she has sent the information and /or questionnaires. The fact that the participants do not meet together prevents one person fro influencing the decision of another. Because the participants are never identified by name, they are free to approach the problem and suggested solutions creatively and objectively without fear of repercussions. 5. Ethical Decision Making -deals with concerns about right and wrong or good and evil. 1. Beneficence- refers to the commitment to do or bring about good 2. Non-maleficence- which means to do no harm 3. Autonomy- refers to the right of each individual to make personal decisions about those things that affect themselves. 4. justice- related to the obligation we have to be fair to all aspect. 5. fidelity- refers to the obligation to carry out the agreements and responsibilities one has undertaken. 6. Veracity- refers to the obligation to tell the truth.
Prepared by: DELA CRUZ, GERRELY D.C 4-A
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Storage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Floating RoofDocumento32 páginasStorage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Floating RoofhgagAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- SIP Project ProposalDocumento2 páginasSIP Project ProposalDeep SutariaAinda não há avaliações
- Vernacular in Andhra PradeshDocumento1 páginaVernacular in Andhra PradeshNandyala Rajarajeswari DeviAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Description: Super Thoroseal Is A Blend of PortlandDocumento2 páginasDescription: Super Thoroseal Is A Blend of Portlandqwerty_conan100% (1)
- Wbuhs PG ThesisDocumento7 páginasWbuhs PG Thesisgbx272pg100% (2)
- Additional Material On CommunicationDocumento15 páginasAdditional Material On CommunicationSasmita NayakAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Adsa Ka SyllabusDocumento3 páginasAdsa Ka SyllabusHacker RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Prestressed Concrete ProblemDocumento9 páginasPrestressed Concrete ProblemPrantik Adhar SamantaAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A705F Schematic Circuit Diagram HALABTECHDocumento11 páginasA705F Schematic Circuit Diagram HALABTECHbcscneg0% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Prescriptions For Closing The Seven Service Quality GapsDocumento1 páginaPrescriptions For Closing The Seven Service Quality GapsReema NegiAinda não há avaliações
- Imarest 2021 Warship Development 1997Documento43 páginasImarest 2021 Warship Development 1997nugrohoAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Lesson 2 - Reflection PaperDocumento2 páginasLesson 2 - Reflection PaperkristhelynAinda não há avaliações
- Stearic Acid MSDSDocumento6 páginasStearic Acid MSDSJay LakhaniAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Remote Sensing: Carbon Stocks, Species Diversity and Their Spatial Relationships in The Yucatán Peninsula, MexicoDocumento18 páginasRemote Sensing: Carbon Stocks, Species Diversity and Their Spatial Relationships in The Yucatán Peninsula, MexicoSara EspinozaAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Executive Shirt CompanyDocumento6 páginasExecutive Shirt CompanyPramod kAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- BUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation ScheduleDocumento7 páginasBUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation SchedulePaulina Arti WilujengAinda não há avaliações
- Brittan Bradford ResumeDocumento2 páginasBrittan Bradford Resumeapi-574584381Ainda não há avaliações
- Final PaperDocumento12 páginasFinal PaperReikooAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Translated Copy of Jurnal B.inggris 41117110162 Aditya NurfajriDocumento16 páginasTranslated Copy of Jurnal B.inggris 41117110162 Aditya Nurfajriaditya estimatorAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Project Report: MES Dental College and HospitalDocumento28 páginasProject Report: MES Dental College and HospitalAnurtha AnuAinda não há avaliações
- Job No. 25800: Quebrada Blanca Fase 2Documento1 páginaJob No. 25800: Quebrada Blanca Fase 2Benjamín Muñoz MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- Faculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian UniversityDocumento59 páginasFaculty of Civil Engineering and Planning Civil Engineering Department Petra Christian Universitykenny lieAinda não há avaliações
- COCapplication08rev Working SampleDocumento34 páginasCOCapplication08rev Working SampleTanya HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Unit 8 - A Closer Look 2Documento3 páginasUnit 8 - A Closer Look 2Trần Linh TâmAinda não há avaliações
- Pricing and Marketing Strategy: Rahul Mishra, Narendra Singh, Dinesh KumarDocumento12 páginasPricing and Marketing Strategy: Rahul Mishra, Narendra Singh, Dinesh KumarGaurav ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Vishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENDocumento3 páginasVishay Load Cell Calibration System - ENSarhan NazarovAinda não há avaliações
- G120D Getting Started 0418 en-USDocumento94 páginasG120D Getting Started 0418 en-USHamadi Ben SassiAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- ECON 304 Course ContentDocumento2 páginasECON 304 Course ContentAanand JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Excel VBA Programming For Solving Chemical Engineering ProblemsDocumento42 páginasExcel VBA Programming For Solving Chemical Engineering ProblemsLeon FouroneAinda não há avaliações
- Al Kindi AssingmentDocumento9 páginasAl Kindi AssingmentMuhammad Sirajuddin MazlanAinda não há avaliações