Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Aieee - 2012
Enviado por
OP GuptaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Aieee - 2012
Enviado por
OP GuptaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
By OP GUPTA
[Elect.&Comm.Engg.]
(+91-9650350480)
Visit at:
www.scribd.com/theopgupta,
www.theopgupta.blogspot.com
K
P
S
AIEEE 2012
Solutions Of
MATHEMATICS
This document belongs to.....................................................................
Batch Timings.......................... School ..........................................
AIEEE 2012 2
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
PART A: HATHEHATICS
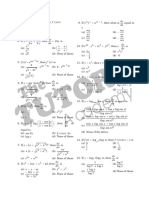
1. The equation e
sin x
e
sin x
4 = 0 has
(1) infinite number of real roots (2) no real roots
(3) exactly one real root (4) exactly four real roots
1. 2
Sol. e
sin x
e
sin x
= 4 e
sin x
= t
t
1
t
= 4
t
2
4t 1 = 0 t =
4 16 4
2
+
t =
4 2 5
2
t = 2 5
e
sin x
= 2 5 1 sin x 1
1
e
e
sin x
e
e
sin x
= 2 + 5 not possible
e
sin x
= 2 5 not possible hence no solution
2. Let
a and b be two unit vectors. If the vectors
c a 2b and d 5a 4b = + =
are perpendicular to each other,
then the angle between
a and b is
(1)
6
(2)
2
(3)
3
(4)
4
2. 3
Sol. c d 0 =
2
2
5 a 6a b 8 b 0 + =
1
6a b 3 a b
2
= =
( )
a b
3
3. A spherical balloon is filled with 4500 cubic meters of helium gas. If a leak in the balloon causes the gas
to escape at the rate of 72 cubic meters per minute, then the rate (in meters per minute) at which the
radius of the balloon decreases 49 minutes after the leakage began is
(1)
9
7
(2)
7
9
(3)
2
9
(4)
9
2
3. 3
Sol. v =
2
4
r
3
After 49 minutes volume = 4500 49 (72) = 972
4
3
r
3
= 972 r
3
= 729 r = 9
v =
4
3
r
3
2
dv 4 dr
3r
dt 3 dt
= 72 = 4
2
dr
r
dt
dr 72 2
dt 4 9 9 9
= =
4. Statement 1: The sum of the series 1 + (1 + 2 + 4) + (4 + 6 + 9) + (9 + 12 + 16) + ...... + (361 + 380 +
400) is 8000.
Statement 2: ( )
( )
n
3
3 3
k 1
k k 1 n
=
=
for any natural number n.
(1) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
(2) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
(3) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
AIEEE 2012 3
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
(4) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
4. 2
Sol. Statement 1 has 20 terms whose sum is 8000
And statement 2 is true and supporting statement 1.
k
th
bracket is (k 1)
2
+ k(k 1) + k
2
= 3k
2
3k + 1.
5. The negation of the statement If I become a teacher, then I will open a school is
(1) I will become a teacher and I will not open a school
(2) Either I will not become a teacher or I will not open a school
(3) Neither I will become a teacher nor I will open a school
(4) I will not become a teacher or I will open a school
5. 1
Sol. ~(~p q) = p ~q
6. If the integral
5tanx
tanx 2
}
dx = x + a ln |sin x 2 cos x| + k, then a is equal to
(1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 1 (4) 2
6. 4
Sol.
5tanx 5sinx
dx dx
tanx 2 sinx 2cosx
=
} }
( ) ( ) 2 cosx 2sinx sinx 2cosx
dx
sinx 2cosx
( + +
(
(
}
=
cosx 2sinx
2 dx dx k
sinx 2cosx
+ | |
+ +
|
\ .
} }
= 2 log |sin x 2 cos x| + x + k a = 2
7. Statement 1: An equation of a common tangent to the parabola y
2
=16 3x and the ellipse 2x
2
+ y
2
= 4 is
y = 2x + 2 3 .
Statement 2: If the line y = mx +
4 3
m
, (m 0) is a common tangent to the parabola
y
2
= 16 3x and the ellipse 2x
2
+ y
2
= 4, then m satisfies m
4
+ 2m
2
= 24.
(1) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
(2) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
(3) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
(4) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
7. 2
Sol. y
2
= 16 3x
2 2
x y
1
2 4
+ =
y = mx +
4 3
m
is tangent to parabola
which is tangent to ellipse c
2
= a
2
m
2
+ b
2
2
48
m
= 2m
2
+ 4 m
4
+ 2m
2
= 24 m
2
= 4
8. Let A =
1 0 0
2 1 0
3 2 1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
. If u
1
and u
2
are column matrices such that Au
1
=
1
0
0
| |
|
|
|
\ .
and Au
2
=
0
1
0
| |
|
|
|
\ .
, then u
1
+ u
2
is
equal to
(1)
1
1
0
| |
|
|
|
\ .
(2)
1
1
1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
(3)
1
1
0
| |
|
|
|
\ .
(4)
1
1
1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
8. 4
AIEEE 2012 4
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
Sol. A =
1 0 0
2 1 0
3 2 1
| |
|
|
|
\ .
Let u
1
=
a
b
c
(
(
(
(
; u
2
=
d
e
f
(
(
(
(
Au
1
=
1
1 1
0 u 2
0 1
( (
( (
=
( (
( (
Au
2
=
0
1
0
(
(
(
(
u
2
=
0
1
2
(
(
(
(
u
1
+ u
2
=
1
1
1
(
(
(
(
9. If n is a positive integer, then
( ) ( )
2n 2n
3 1 3 1 + is
(1) an irrational number (2) an odd positive integer
(3) an even positive integer (4) a rational number other than positive integers
9. 1
Sol.
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
n n
2n 2n 2 2 n n
3 1 3 1 3 1 3 1 4 2 3 4 2 3
( (
+ = + = +
( (
=
( ) ( )
n n
n
2 2 3 2 3
(
+
(
=
{ }
n n n n n 1 n n 2 n n n n 1 n n 2
0 1 2 0 1 2
2 C 2 C 2 3 C 2 3 C 2 C 2 3 C 2 3
( (
+ + + +
=
n 1 n n 1 n n 3 n 1
1 3
2 C 2 3 C 2 3 3 2 3
+ +
(
+ + =
(some integer)
Which is irrational
10. If 100 times the 100
th
term of an AP with non zero common difference equals the 50 times its 50
th
term,
then the 150
th
term of this AP is
(1) 150 (2) 150 times its 50
th
term
(3) 150 (4) zero
10. 4
Sol. 100(T
100
) = 50(T
50
) 2[a + 99d] = a + 49d a + 149d = 0 T
150
= 0
11. In a PQR, if 3 sin P + 4 cos Q = 6 and 4 sin Q + 3 cos P = 1, then the angle R is equal to
(1)
5
6
(2)
6
(3)
4
(4)
3
4
11. 2
Sol. 3 sin P + 4 cos Q = 6 ...... (1)
4 sin Q + 3 cos P = 1 ...... (2)
From (1) and (2) P is obtuse.
(3 sin P + 4 cos Q)
2
+ (4 sin Q + 3 cos P)
2
= 37
9 + 16 + 24 (sin P cos Q + cos P sin Q) = 37
24 sin (P + Q) = 12
sin (P + Q) =
1
2
P + Q =
5
6
R =
6
12. An equation of a plane parallel to the plane x 2y + 2z 5 = 0 and at a unit distance from the origin is
(1) x 2y + 2z 3 = 0 (2) x 2y + 2z + 1 = 0
AIEEE 2012 5
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
(3) x 2y + 2z 1 = 0 (4) x 2y + 2z + 5 = 0
12. 1
Sol. Equation of plane parallel to x 2y + 2z 5 = 0 is x 2y + 2z + k = 0 ...... (1)
perpendicular distance from O(0, 0, 0) to (1) is 1
k
1 4 4 + +
= 1 |k| = 3 k = 3 x 2y + 2z 3 = 0
13. If the line 2x + y = k passes through the point which divides the line segment joining the points (1, 1) and
(2, 4) in the ratio 3 : 2, then k equals
(1)
29
5
(2) 5 (3) 6 (4)
11
5
13. 3
Sol. Point p =
6 2 12 2
,
5 5
+ + | |
|
\ .
p =
8 14
,
5 5
| |
|
\ .
8 14
p ,
5 5
| |
|
\ .
lies on 2x + y = k
16 14
k
5 5
+ = k =
30
5
= 6
14. Let x
1
, x
2
, ......, x
n
be n observations, and let x be their arithematic mean and
2
be their variance.
Statement 1: Variance of 2x
1
, 2x
2
, ......, 2x
n
is 4
2
.
Statement 2: Arithmetic mean of 2x
1
, 2x
2
, ......, 2x
n
is 4x .
(1) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
(2) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
(3) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
(4) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
14. 4
Sol.
2
=
2
2
i i
x x
n n
| |
|
\ .
Variance of 2x
1
, 2x
2
, ....., 2x
n
=
( )
2
2
i
i
2x
2x
n n
| |
|
\ .
=
2
2
i i
x x
4
n n
(
| |
(
|
( \ .
= 4
2
Statement 1 is true.
A.M. of 2x
1
, 2x
2
, ......, 2x
n
=
1 2 n 1 2 n
2x 2x 2x x x x
2 2x
n n
+ + + + + + | |
= =
|
\ .
Statement 2 is false.
15. The population p(t) at time t of a certain mouse species satisfies the differential equation
dp(t)
dt
= 0.5 p(t)
450. If p(0) = 850, then the time at which the population becomes zero is
(1) 2 ln 18 (2) ln 9 (3)
1
ln18
2
(4) ln 18
15. 1
Sol.
d(p(t)) 1
dt 2
= p(t) 450
d(p(t)) p(t) 900
dt 2
=
d(p(t))
2 dt
p(t) 900
=
} }
AIEEE 2012 6
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
2 ln |p(t) 900| = t + c
t = 0 2 ln 50 = 0 + c c = 2 ln 50
2 ln |p(t) 900| = t + 2 ln 50
P(t) = 0 2 ln 900 = t + 2 ln 50
t = 2 (ln 900 ln 50) =
900
2ln
50
| |
|
\ .
= 2 ln 18.
16. Let a, b R be such that the function f given by f(x) = ln |x| + bx
2
+ ax, x 0 has extreme values at x = 1
and x = 2.
Statement 1: f has local maximum at x = 1 and at x = 2.
Statement 2: a =
1
2
and b =
1
4
(1) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
(2) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
(3) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
(4) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
16. 2
Sol. f(x) =
1
x
+ 2b x + a
f has extremevalues and differentiable
f(1) = 0 a 2b = 1
f(2) = 0 a + 4b =
1
2
a =
1
2
, b =
1
4
f(1), f(2) are negative. f has local maxima at 1, 2
17. The area bounded between the parabolas x
2
=
y
4
and x
2
= 9y, and the straight line y = 2 is
(1) 20 2 (2)
10 2
3
(3)
20 2
3
(4) 10 2
17. 3
Sol. Required area
A =
2 2
0 0
y 5 y
2 3 y dy 2 dy
2 2
(
| |
( = |
|
(
\ .
} }
=
2
3 / 2
3 / 2
0
y 10 20 2
5 2 0
3/ 2 3 3
(
(
= =
(
(
O
y = 2
x
2
=
9
4
x
2
= 9y
18. Assuming the balls to be identical except for difference in colours, the number of ways in which one or
more balls can be selected from 10 white, 9 green and 7 black balls is
(1) 880 (2) 629 (3) 630 (4) 879
18. 4
Sol. Number of ways of selecting one or more balls from 10 white, 9 green, and 7 black balls
= (10 + 1)(9 + 1)(7 + 1) 1 = 11 10 8 1 = 879.
19. If f: R R is a function defined by f(x) = [x]
2x 1
cos
2
| |
|
\ .
, where [x] denotes the greatest integer
function, then f is
(1) continuous for every real x (2) discontinuous only at x = 0
(3) discontinuous only at non-zero integral values of x (4) continuous only at x = 0
19. 1
AIEEE 2012 7
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
Sol. f(x) =
2x 1 1
x cos x cos x
2 2
| | | |
= ( (
| |
\ . \ .
= [x] sin x is continuous for every real x.
20. If the lines
x 1 y 1 z 1 x 3 y k z
and
2 3 4 1 2 1
+
= = = = intersect, then k is equal to
(1) 1 (2)
2
9
(3)
9
2
(4) 0
20. 3
Sol. Any point on
x 1 y 1 z 1
2 3 4
+
= = = t is (2t + 1, 3t 1, 4t + 1)
And any point on
x 3 y k z
1 2 1
= = = s is (s + 3, 2s + k, s)
Given lines are intersecting t =
3
2
and s = 5 k =
9
2
21. Three numbers are chosen at random without replacement from {1, 2, 3, ...... 8}. The probability that their
minimum is 3, given that their maximum is 6, is
(1)
3
8
(2)
1
5
(3)
1
4
(4)
2
5
21. 2
Sol. Let A be the event that maximum is 6.
B be event that minimum is 3
P(A) =
5
2
8
3
C
C
(the numbers < 6 are 5)
P(B) =
5
2
8
3
C
C
(the numbers > 3 are 5)
P(A B) =
2
1
8
3
C
C
Required probability is
2
1
5
2
C B P(A B) 2 1
P
A P(A) 10 5
C
| |
= = = =
|
\ .
.
22. If z 1 and
2
z
z 1
is real, then the point represented by the complex number z lies
(1) either on the real axis or on a circle passing through the origin
(2) on a circle with centre at the origin
(3) either on the real axis or on a circle not passing through the origin
(4) on the imaginary axis
22. 1
Sol. Let z = x + iy ( x 1 as z 1)
z
2
= (x
2
y
2
) + i(2xy)
2
z
z 1
is real its imaginary part = 0
2xy (x 1) y(x
2
y
2
) = 0
y(x
2
+ y
2
2x) = 0
y = 0; x
2
+ y
2
2x = 0
z lies either on real axis or on a circle through origin.
AIEEE 2012 8
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
23. Let P and Q be 3 3 matrices with P Q. If P
3
= Q
3
and P
2
Q = Q
2
P, then determinant of
(P
2
+ Q
2
) is equal to
(1) 2 (2) 1 (3) 0 (4) 1
23. 3
Sol. P
3
= Q
3
P
3
P
2
Q = Q
3
Q
2
P
P
2
(P Q) = Q
2
(Q P)
P
2
(P Q) + Q
2
(P Q) = O
(P
2
+ Q
2
)(P Q) = O |P
2
+ Q
2
| = 0
24. If g(x) =
x
0
cos4t dt
}
, then g(x + ) equals
(1)
g(x)
g( )
(2) g(x) + g() (3) g(x) g() (4) g(x) . g()
24. 2 or 4
Sol. g(x) =
x
0
cos4t dt
}
g(x) = cos 4x g(x) =
sin4x
k
4
+ g(x) =
sin4x
4
[ g(0) = 0]
g(x + ) = g(x) + g() = g(x) g() ( g() = 0)
25. The length of the diameter of the circle which touches the x-axis at the point (1, 0) and passes through
the point (2, 3) is
(1)
10
3
(2)
3
5
(3)
6
5
(4)
5
3
25. 1
Sol. Let (h, k) be centre.
(h 1)
2
+ (k 0)
2
= k
2
h = 1
(h 2)
2
+ (k 3)
2
= k
2
k =
5
3
diameter is 2k =
10
3
k
k
(h, k)
(2, 3)
(1, 0)
26. Let X = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}. The number of different ordered pairs (Y, Z) that can be formed such that Y X, Z
X and Y Z is empty, is
(1) 5
2
(2) 3
5
(3) 2
5
(4) 5
3
26. 2
Sol. Y X, Z X
Let a X, then we have following chances that
(1) a Y, a Z
(2) a Y, a Z
(3) a Y, a Z
(4) a Y, a Z
We require Y Z =
Hence (2), (3), (4) are chances for a to satisfy Y Z = .
Y Z = has 3 chances for a.
Hence for five elements of X, the number of required chances is 3 3 3 3 3 = 3
5
27. An ellipse is drawn by taking a diameter of the circle (x 1)
2
+ y
2
= 1 as its semiminor axis and a
diameter of the circle x
2
+ (y 2)
2
= 4 as its semi-major axis. If the centre of the ellipse is the origin and
its axes are the coordinate axes, then the equation of the ellipse is
AIEEE 2012 9
Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29 A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, Ph: 46106000, 26569493, Fax: 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com
(1) 4x
2
+ y
2
= 4 (2) x
2
+ 4y
2
= 8 (3) 4x
2
+ y
2
= 8 (4) x
2
+ 4y
2
= 16
27. 4
Sol. Semi minor axis b = 2
Semi major axis a = 4
Equation of ellipse =
2 2
2 2
x y
a b
+ = 1
2 2
x y
16 4
+ = 1
x
2
+ 4y
2
= 16.
28. Consider the function f(x) = |x 2| + |x 5|, x R.
Statement 1: f(4) = 0
Statement 2: f is continuous in [2, 5], differentiable in (2, 5) and f(2) = f(5).
(1) Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
(2) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
(3) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
(4) Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false
28. 2
Sol. f(x) = 7 2x; x < 2
= 3; 2 x 5
= 2x 7; x > 5
f(x) is constant function in [2, 5]
f is continuous in [2, 5] and differentiable in (2, 5) and f(2) = f(5)
by Rolles theorem f(4) = 0
Statement 2 and statement 1 both are true and statement 2 is correct explanation for statement 1.
29. A line is drawn through the point (1, 2) to meet the coordinate axes at P and Q such that it forms a
triangle OPQ, where O is the origin. If the area of the triangle OPQ is least, then the slope of the line PQ
is
(1)
1
4
(2) 4 (3) 2 (4)
1
2
29. 3
Sol. Equation of line passing through (1, 2) with slope m is y 2 = m(x 1)
Area of OPQ =
2
(m 2)
2 m
=
2
m 4 4m
2m
+
=
m 2
2
2 m
+
is least if
m 2
2 m
= m
2
= 4 m = 2 m = 2
30. Let ABCD be a parallelogram such that AB q, AD p = =
and BAD be an acute angle. If r
is the vector
that coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B to the side AD, then r
is given by
(1)
( )
( )
3 p q
r 3q p
p p
(2)
p q
r q p
p p
| |
= +
|
\ .
(3)
p q
r q p
p p
| |
=
|
\ .
(4)
( )
( )
3 p q
r 3q p
p p
= +
30. 2
AIEEE201210
2
Sol. AE vector component of q on p
(p.q) (p.q)
AE p p
p
p
ABE; AB BE AE
(p.q) (p.q)
q r p r q p
(p.q) (p.q)
=
+ = =
*This solution module has been prepared by OP Gupta. He can be approached on his
mobile +91-9650350480 and mail-id: theopgupta@gmail.com.
Please visit: www.scribd.com/theopgupta, www.theopgupta.blogspot.com
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Class 11 SA2Documento23 páginasClass 11 SA2OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Value Based XIIDocumento18 páginasPhysics Value Based XIIOP Gupta100% (1)
- Assignment SA 1Documento1 páginaAssignment SA 1OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Mathematics - Value Based Question - 12Documento10 páginasMathematics - Value Based Question - 12OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- IIT JEE - 2012 Paper 1 & 2Documento18 páginasIIT JEE - 2012 Paper 1 & 2OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Chemistry Value Based XIIDocumento11 páginasChemistry Value Based XIIOP Gupta100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- CH 10Documento1 páginaCH 10OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Grant Me The Strength To Accept Those Things I Can Not ChangeDocumento1 páginaGrant Me The Strength To Accept Those Things I Can Not ChangeOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- M Cover PageDocumento2 páginasM Cover PageOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Ch08 - 13Documento1 páginaCh08 - 13OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Calender 2012Documento1 páginaCalender 2012OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocumento3 páginasLinear Equations in Two VariablesOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Objective TestDocumento1 páginaObjective TestOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch10 11Documento1 páginaCh10 11OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Multiple Choice Questions For Science & English, Class XDocumento62 páginasMultiple Choice Questions For Science & English, Class XOP Gupta88% (24)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Test 6Documento1 páginaTest 6OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Test 7Documento1 páginaTest 7OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Message To AllDocumento1 páginaMessage To AllOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- I'm Indebted ToDocumento1 páginaI'm Indebted ToOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Maths GeneralliDocumento5 páginasMaths GeneralliOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Senior Class FormulaeDocumento8 páginasSenior Class FormulaeOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Similar TrianglesDocumento4 páginasSimilar TrianglesOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Test 4Documento1 páginaTest 4OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematicia Hots SeriesDocumento5 páginasMathematicia Hots SeriesOP Gupta100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- PolynomialsDocumento3 páginasPolynomialsOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Real Numbers & Number SystemDocumento4 páginasReal Numbers & Number SystemOP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- CT 02Documento1 páginaCT 02OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- CT 01Documento2 páginasCT 01OP GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Sample Paper MathsDocumento14 páginasSample Paper MathsRavi KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Mesl Problems Set 2Documento5 páginasMesl Problems Set 2Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoAinda não há avaliações
- P.5 MTC NotesDocumento137 páginasP.5 MTC NotesSamuel OloyaAinda não há avaliações
- Speech FormatDocumento4 páginasSpeech FormatNik Razin Azim Ismail100% (3)
- Quantitative Aptitude - Simplification - Free Aptitude PracticeDocumento9 páginasQuantitative Aptitude - Simplification - Free Aptitude PracticeRaJu SinGhAinda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Methods For AlgebraDocumento40 páginasIntermediate Methods For AlgebraAnup SaravanAinda não há avaliações
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2024Documento6 páginasMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2024kothandan muthuAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Moons The SeriesDocumento39 páginas2 Moons The SeriesShifa Fauziah0% (1)
- R16a PDFDocumento66 páginasR16a PDFสฮาบูดีน สาและAinda não há avaliações
- Chemeketa Community College 2012 Graduation Ceremony ProgramDocumento36 páginasChemeketa Community College 2012 Graduation Ceremony ProgramStatesman JournalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter1 Basics A1 LevelDocumento303 páginasChapter1 Basics A1 Levelvarshasdm1987100% (1)
- Impressions 1112 Issue1Documento11 páginasImpressions 1112 Issue1Singapore International School (Hong Kong)Ainda não há avaliações
- 2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnDocumento30 páginas2010 NJC MA H2 P1 Prelim SolnloposhAinda não há avaliações
- TCS Latest Pattern Questions - 29Documento5 páginasTCS Latest Pattern Questions - 29Arnab DasAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Quarter ExamDocumento3 páginas2nd Quarter ExamSarah SaraelAinda não há avaliações
- 6-Introduction To PolygonsDocumento4 páginas6-Introduction To PolygonsAymenAinda não há avaliações
- Portfolio 2 Triangles EditedDocumento3 páginasPortfolio 2 Triangles Editedapi-312004413Ainda não há avaliações
- 2nd Grading Classifying Learners Grades Per Learning AreasDocumento8 páginas2nd Grading Classifying Learners Grades Per Learning Areasemelyn tumpagAinda não há avaliações
- Budgeted Lesson in Math CutDocumento2 páginasBudgeted Lesson in Math CutWilma Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- 08 Practice Tests Set 17 - Paper 2H-3H Mark SchemeDocumento15 páginas08 Practice Tests Set 17 - Paper 2H-3H Mark SchemeKenneth SorraAinda não há avaliações
- Basis2 Steel enDocumento107 páginasBasis2 Steel enNguyen HaiAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative and Qualitative Aptitude ProblemsDocumento21 páginasQuantitative and Qualitative Aptitude ProblemslembdaAinda não há avaliações
- Xii - CH-1 - Relation & Function - MCQSDocumento5 páginasXii - CH-1 - Relation & Function - MCQSraghuAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveDocumento12 páginasLesson 2-09 Areas Under A Standard Normal CurveJamiefel PungtilanAinda não há avaliações
- Differentiation For TelegramDocumento3 páginasDifferentiation For TelegramAkash SAinda não há avaliações
- Number TheoryDocumento85 páginasNumber TheoryArjunRanaAinda não há avaliações
- Writing A SpeechDocumento2 páginasWriting A SpeechMelissa Rosila Mohamad MahfuzAinda não há avaliações
- Rethinking HomeworkDocumento6 páginasRethinking Homeworkapi-202412886Ainda não há avaliações
- Topic: Further Mathematics SLDocumento58 páginasTopic: Further Mathematics SLDavid Mosquera LoisAinda não há avaliações
- Finland School Education MethodsDocumento3 páginasFinland School Education MethodsArvind RanganathanAinda não há avaliações
- Amc2015 Junior PDFDocumento7 páginasAmc2015 Junior PDFLe Huu HaiAinda não há avaliações