Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Transport System
Enviado por
gnana87Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Transport System
Enviado por
gnana87Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Transport System
-
Transport system present in the bodies are essential to keep the cells alive and healthy. - Transport system consists of heart, blood vessels and blood. 1. What is the need of Transport System? Transport System - Functions: 1. It helps in transport of O2 from lungs to various parts of the body. 2. It requires to transport digested food from small intestine to various parts of the body. 3. It requires to transport of nutrients to various parts of the body. 4. It helps in the collection of CO2 from various parts of the body to lungs and then it is expelled out. 5. It helps in transport of hormones from different endocrine glands to various parts of the body. 2.
In amphibians heart in associated with sac like structure called sinus venosus.
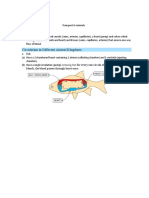
4. Write brief note on sinus venosus? Sinus venosus: It is a sac like structure formed by union of caval veins. It is a centre for collecting deoxygenated blood. It opens into right auricle. - Sinus venosus is present in pisces (fish) amphibians, and reptiles and it is absent in "Aves and mammals". - Process of circulation:
2 All. B.P Veins Blood DeO
Sinus venosus Right Auricle Ventricle
Mixed Blood Ventricle Left Auricle Lungs
How many types of circulatory system are there? give example? Circulatory systems are of two types. They are 1. Open type circulation 2. Closed type circulation Open type circulation consist of heart, blood sinuses and blood. Eg: Insects Closed type circulation consist of heart, blood vessels and blood. The main difference between open type and closed type circulation is blood vessels. Blood vessels are present in closed type circulation. Blood vessels are absent in open type circulation.
- Deoxygenated (DeO2) blood collected from all the body (All B.P) parts and send to sinus venosus, from sinus venosus blood goes to right auricle; from here blood goes to ventricle and it goes to lungs through pulmonary arteries. In lung blood gets oxygenated and send to left auricle, from here oxygenated blood goes to ventricle. In ventricle blood gets mixed (pure blood + impure blood) and sent to various part of the body.
5. What is double circuit circulation? Give Examples: (V.V.Imp) Double circuit circulation: - The blood passes through the heart twice in a circulation is called double circuit circulation. (1. Heart - Lungs 2. Heart - Body parts) Eg: Amphibians, Reptiles, Aves and Mammals. 6. What is single circuit circulation? Give Examples? Single circuit circulation: - The blood passes through the heart only once in a circulation is called single circuit circulation. Eg: Fish 7. What is pulmonary heart? Give Examples? - Pulmonary heart: The heart pumps blood to the lungs for purification is called pulmonary heart. Eg: Amphibians - Mammals 8. What is Branchial Heart? Give Examples. - Branchial Heart: The heart pumps blood to the
3. Explain the Transport System in Amphibians or Frog? (V.V.Imp) - Circulatory system in Frog: - Circulatory system of Frog consists of heart, blood vessels and blood. Hence it comes under closed type circulation. - Frog's heart consists of '3' chambers. They are two auricles and 'one' ventricle. - Auricle (left and right) are present side by side and are separated with inter auricular septum. - Behind the auricles a chamber is present called ventricle.
gills for purification is called Branchial heart. Eg: Fish
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM IN MAN
1. Write short note on pericardium? Pericardium: - Heart is enclosed in a double thin transparent sac like structure called pericardium. The space present between two membranes is called pericardial space which is filled with pericardial fluid. - Pericardium and pericardial fluid protect the heart from physical shocks or blows. 2. Give an account of valves present in human heart? - Valves present in the human heart: There are four types of valves present in human heart. They are 1. Tricuspid valves 2. Bicuspid valves 3. Pulmonary valves 4. Aortic valves - Tricuspid valves: It is present between right auricle and right ventricle, and it allows blood from right auricle to right ventricle. It has three flaps or cups. - Bicuspid valve: It is present between left auricle and left ventricle. It allows blood from left auricle to left ventricle. It has two flaps. - Pulmonary valves: It is present at the origin of pulmonary aorta in the right ventricle. It has 3 half moon shaped or semilunar valves. - Aortic valves: It is present at the origin of aorta in the left ventricle. It allows blood to flow from left ventricle into the aorta. 3. What is B.P or hypertension? What are the causes and write preventive measures? Hypertension or high blood pressure or High B.P: - The pressure with which the blood flows in the blood vessels is called blood pressure. - The normal blood pressure is 120/80. The numerator- '120' is called systolic pressure. The denominator- '80' is called diastolic pressure. - If B.P is more than 120/80 is called high B.P or hypertension. - Causes for B.P:
1. Increasing the levels of cholesterol in the blood. 2. Constant stress and strain for a long time. 3. Improper functions of kidneys. 4. Smoking and consumption of alcohol. Preventive measures: 1. Diet control. 2. Avoid stress and strain. 3. Avoid consumption of alcohol and smoking. 4. Doing regular moderate exercises. 5. Taking appropriate medicines.
Fill up the blanks:
1. Blood vessels are absent in ______ circulatory system. 2. Example for open type circulatory system is ______ 3. Sinus venosus is absent in ______ 4. Incompletely divided ventricle is found in______ animals. 5. In man caval veins opens into ______ 6. Bicuspid valve is also known as ______ 7. Pulmonary circuit is present between ______and______ 8. Systemic aorta carries ______ blood. 9. Superior venacava is also know as ______ 10. Pericardium is associated with ______
KEY
1. Open type 2. Insects 3. Aves and Mammals 4. Reptile 5. Right Auricle 6. Mitral valve 7. Heart and Lungs, Lungs to Heart 8. Oxygenated 9. Pre caval vein 10. Heart
Você também pode gostar
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartAinda não há avaliações
- Notes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals ObjectivesDocumento36 páginasNotes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals Objectivespraneeth satishAinda não há avaliações
- Ch-9 Transport in AnimalsDocumento23 páginasCh-9 Transport in Animalsdaveymilan36Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7. CirculationDocumento54 páginasChapter 7. CirculationankurbiologyAinda não há avaliações
- Class 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Documento12 páginasClass 9 - Biology Lesson-7-Circulatory System 2Shlok JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- B2U3 CirculationNotesDocumento15 páginasB2U3 CirculationNotesVanusha Azzriel100% (1)
- The Anatomy of HeartDocumento46 páginasThe Anatomy of HeartPrincess NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- HeartDocumento6 páginasHeartAhmed OmaarAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento21 páginasCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezAinda não há avaliações
- A and P NoteDocumento4 páginasA and P Notebibisha hadidjaAinda não há avaliações
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocumento62 páginasAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyAinda não há avaliações
- CH-9 - Transport in AnimalsDocumento45 páginasCH-9 - Transport in Animalsjihen chouchenAinda não há avaliações
- Elesson 10 Bio 14mayDocumento4 páginasElesson 10 Bio 14mayArchanaGuptaAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart Lies in The Thorax Behind The Chest BoneDocumento10 páginasThe Heart Lies in The Thorax Behind The Chest BoneclinoAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocumento9 páginasPregnancy Induced HypertensionRiazell Antonio DungcaAinda não há avaliações
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocumento12 páginasFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizAinda não há avaliações
- Blood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyDocumento4 páginasBlood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyMisterBlueSky89% (9)
- Circulatory SystemDocumento11 páginasCirculatory SystemAhmad S AlkarmyAinda não há avaliações
- The Circulatory System in Man: A Concise Guide to the Heart and Blood FlowDocumento54 páginasThe Circulatory System in Man: A Concise Guide to the Heart and Blood FlowStudent ResearchAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 9 Notes CardioDocumento8 páginasTopic 9 Notes Cardioapi-388956899Ainda não há avaliações
- TM 8 TM 8only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishDocumento66 páginasTM 8 TM 8only Clinical Exam of Heart and Circulatory System AGWEnglishcellin rubianti azzharaAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocumento94 páginasCardiovascular DisordersLui Andrei AnilaAinda não há avaliações
- The Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemDocumento29 páginasThe Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With Othe Organs in The SystemAngela VirayAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDocumento13 páginasCardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDavid GoliathAinda não há avaliações
- heart grade 10Documento18 páginasheart grade 10amulyajadhav119Ainda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System Biology ChapterDocumento27 páginasCirculatory System Biology ChapterPranati SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- How Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemDocumento8 páginasHow Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemRoszana RafliaAinda não há avaliações
- Online Session 18Documento10 páginasOnline Session 18addy 05Ainda não há avaliações
- Closed Circulatory System EvolutionDocumento8 páginasClosed Circulatory System Evolutionfardhu91Ainda não há avaliações
- TRANSPORTATIONDocumento9 páginasTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento39 páginasCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaAinda não há avaliações
- DomingoDocumento3 páginasDomingoMikaellah DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- Body Fluids and CirculatoinDocumento34 páginasBody Fluids and CirculatoinPrasmita BeheraAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System IIDocumento13 páginasCirculatory System IIsmbdy tbhhhAinda não há avaliações
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocumento10 páginasBody Fluids and CirculationArjun ChristopherAinda não há avaliações
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocumento20 páginasW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996Ainda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesDocumento62 páginasIGCSE Biology Transport in Animals NotesSir AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory SystemDocumento21 páginasCirculatory SystemSaadAinda não há avaliações
- Animal PhysiologyDocumento104 páginasAnimal PhysiologyClara MaeAinda não há avaliações
- CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY NOTESDocumento20 páginasCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY NOTESVivek ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Case StudyDocumento15 páginasAnatomy Case StudyHazreen HazwanyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter9 Transport in AnimalsDocumento77 páginasChapter9 Transport in Animalsyuuu32716Ainda não há avaliações
- 9 Transport in AnimalssDocumento59 páginas9 Transport in AnimalssFathmath JameelAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System PlanDocumento95 páginasCirculatory System Plankirsten23Ainda não há avaliações
- 2.2 Cardiovascular SystemDocumento49 páginas2.2 Cardiovascular SystemPratham ChopraAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento43 páginasTransport in AnimalsEdwins MaranduAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation 1 PDFDocumento9 páginasTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalAinda não há avaliações
- BookDocumento8 páginasBookmohamed aweys abuukarAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Structure and Function GuideDocumento27 páginasHeart Structure and Function GuideAb AbAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDocumento16 páginasGrade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDane Gian Angelo TanAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio SystemDocumento1 páginaCardio SystemMarean NicholeAinda não há avaliações
- The Circulatory System: Mark Anthony R. Peralta Science TeacherDocumento38 páginasThe Circulatory System: Mark Anthony R. Peralta Science TeacherMark Anthony R. PeraltaAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 6 Lessons on the Heart, Circulatory System & BloodDocumento18 páginasGrade 6 Lessons on the Heart, Circulatory System & Bloodniel justin lakerAinda não há avaliações
- Circulatory System Sci 6Documento26 páginasCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart: Basis of Life .?Documento94 páginasThe Heart: Basis of Life .?Diksha AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento6 páginasTransport in Animals2027dpatel.studentAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction For The Cardiovascular System 1Documento7 páginasIntroduction For The Cardiovascular System 1Abdallah Essam Al-ZireeniAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy Hypertension CaseDocumento7 páginasPregnancy Hypertension CaseRalph Emerson RatonAinda não há avaliações
- System Is An: ArteriesDocumento4 páginasSystem Is An: ArteriesPinasti Aprilia PutriAinda não há avaliações
- HypertensionDocumento9 páginasHypertensionEdmr SlzarAinda não há avaliações
- Rectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyDocumento28 páginasRectal Cancer,: Clinical Practice Guidelines in OncologyRaíla SoaresAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Assessment FormDocumento14 páginasPhysical Assessment FormHedda Melriz DelimaAinda não há avaliações
- PMO - Pasteurized Milk OrdinanceDocumento340 páginasPMO - Pasteurized Milk OrdinanceTato G.k.Ainda não há avaliações
- - - - - شاهينDocumento101 páginas- - - - شاهينDdsa FaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 10Th Edition Raven Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasBiology 10Th Edition Raven Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlewis.barnes1000100% (12)
- Far Eastern University: Module #3 - Oxygenation (Oxygen Therapy)Documento28 páginasFar Eastern University: Module #3 - Oxygenation (Oxygen Therapy)aaaaaAinda não há avaliações
- Viral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinDocumento200 páginasViral and Bacterial Infections of The SkinKarla Jane100% (1)
- The Decline and Fall of Pax Americana, by DesertDocumento200 páginasThe Decline and Fall of Pax Americana, by DesertDHOBO0% (1)
- MCQs 08Documento39 páginasMCQs 08api-3736493100% (2)
- Headache - 2001 - Jacome - Transitional Interpersonality Thunderclap HeadacheDocumento4 páginasHeadache - 2001 - Jacome - Transitional Interpersonality Thunderclap HeadacheactualashAinda não há avaliações
- Causes, Signs, and Treatment of HyponatremiaDocumento65 páginasCauses, Signs, and Treatment of HyponatremiaFaryalBalochAinda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases: Obstructed AlveoliDocumento3 páginasPathophysiology of Respiratory Diseases: Obstructed AlveoliApril Dianne ParungaoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 Mendilan and Genetics Study GuideDocumento16 páginasChapter 10 Mendilan and Genetics Study GuideKing AllanAinda não há avaliações
- Upper FINAL 2Documento5 páginasUpper FINAL 2Анна КоноваловаAinda não há avaliações
- IMCI child health strategyDocumento11 páginasIMCI child health strategyIvy100% (2)
- Modified Double Glove TechniqueDocumento1 páginaModified Double Glove TechniqueSohaib NawazAinda não há avaliações
- Assessments of Newborn NewDocumento15 páginasAssessments of Newborn NewYashoda Satpute100% (1)
- Book of Vile DarknessDocumento25 páginasBook of Vile Darknessv0idless100% (2)
- Dangers of Excess Sugar ConsumptionDocumento2 páginasDangers of Excess Sugar ConsumptionAIDEN COLLUMSDEANAinda não há avaliações
- Diane Pills Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDiane Pills Drug StudyDawn EncarnacionAinda não há avaliações
- ICMIDocumento4 páginasICMIKim MingyuAinda não há avaliações
- VSL TB Workplace Policy ProgramDocumento3 páginasVSL TB Workplace Policy ProgramAlexander John AlixAinda não há avaliações
- Word Parts Dictionary, Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots and Combining FormsDocumento237 páginasWord Parts Dictionary, Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots and Combining Formslaukings100% (9)
- Hendra - EKGDocumento34 páginasHendra - EKGRINAAinda não há avaliações
- International Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsDocumento5 páginasInternational Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsLilian Rahma AnandaAinda não há avaliações
- Joint Mobilization EnhancesDocumento12 páginasJoint Mobilization EnhancesDavid BrunoAinda não há avaliações
- Anti-Inflammatory and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Beta Blocker in A Rat Model of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento14 páginasAnti-Inflammatory and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Beta Blocker in A Rat Model of Rheumatoid ArthritisKndratAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Living Therapeutics With Synthetic BiologyDocumento20 páginasEngineering Living Therapeutics With Synthetic BiologyGabriel LohnAinda não há avaliações
- Wet Cell and Radial DeviceDocumento21 páginasWet Cell and Radial DeviceChava Chavous100% (1)
- Nina Rajan Pillai & Ors. Vs Union of India and Ors. On 13 May, 2011Documento33 páginasNina Rajan Pillai & Ors. Vs Union of India and Ors. On 13 May, 2011Sanjayan KizhakkedathuAinda não há avaliações