Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Hydro Cep Hal Us
Enviado por
Mamam CaemDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Hydro Cep Hal Us
Enviado por
Mamam CaemDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
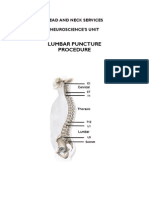
Hydrocephalus
What is hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus (also called water on the brain) occurs when there is extra cerebrospinal fluid (also called CSF) surrounding the brain. Normally, CSF surrounds the brain and spinal cord; CSF helps cushion the brain and spinal cord, as well as delivers nutrients to the brain and removes waste. Excess CSF results in dilation (opening) of the four ventricles (spaces around the brain) and increases the pressure on the brain.
Normal brain
Brain
Hydrocephalus
Compressed brain tissue
Ventricles Enlarged ventricles
Spinal cord
Diagrams courtesy of Cincinnati Childrens Hospital Medical Center
There are several different types of hydrocephalus. Communicating hydrocephalus occurs when CSF is blocked after leaving the ventricles. Non-communicating (or obstructive) hydrocephalus occurs when CSF is blocked somewhere between the ventricles.
What causes hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (develops at or after birth). Congenital hydrocephalus may be caused by genetic conditions or environmental factors during the babys development. One of the most common causes of hydrocephalus is aqueductal stenosis (narrowing of the path between the third and fourth ventricles). Other possible causes of hydrocephalus include neural tube defects (NTD, an opening along the neck or spine), certain viruses, a tumor, or hemorrhage (bleeding) near the brain. For some babies with hydrocephalus, an exact cause may not be identified. Acquired hydrocephalus may be caused by injury or disease. Approximately 1 out of every 500 babies born each year have hydrocephalus.
How is hydrocephalus treated?
Hydrocephalus is most often treated by surgically placing a shunt near the brain or spinal cord. The shunt allows the extra CSF to flow from the brain to another part of the body (such as the abdomen), where it is naturally absorbed back into the bodys circulation. Your childs doctor(s) will discuss appropriate treatment options with you.
For more information
Cincinnati Childrens Hospital http://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/info/neurology/diagnose/hydrocephalus.htm Hydrocephalus Association - http://www.hydroassoc.org MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia - http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/hydrocephalus.html National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/hydrocephalus/detail_hydrocephalus.htm Sources: Hydrocephalus Association, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Gapuz Communicable Disease NursingDocumento62 páginasGapuz Communicable Disease NursingKaeNiel Doctolero78% (9)
- NEURODIAGNOSISDocumento17 páginasNEURODIAGNOSISRohit kumar Saravana kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Tuberculous meningitis: many questions, too few answersDocumento11 páginasTuberculous meningitis: many questions, too few answersGustavo MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- Bio621 MindmapDocumento3 páginasBio621 MindmapMizahAinda não há avaliações
- Lumbar PunctureDocumento23 páginasLumbar Puncturemamoon100% (2)
- Myelography Procedure and Indications ExplainedDocumento12 páginasMyelography Procedure and Indications ExplainedDiana CharaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrocephalus IDocumento52 páginasHydrocephalus IVlad Alexandra50% (2)
- Test QuestionsDocumento28 páginasTest QuestionsJerson CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Neuroanatomy MCQDocumento7 páginasNeuroanatomy MCQi can always make u smile :D78% (9)
- Assessment of Hydrocephalus in Children Based On Digital Image Processing and AnalysisDocumento14 páginasAssessment of Hydrocephalus in Children Based On Digital Image Processing and Analysissamsul8149Ainda não há avaliações
- Lumbar PunctureDocumento9 páginasLumbar PunctureLeang KarichakAinda não há avaliações
- CSFDocumento40 páginasCSFDrNaveen Singh Rajpurohit KaduAinda não há avaliações
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocumento5 páginasIncreased Intracranial PressureLorelyn Santos CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- LP Procedure NoteDocumento2 páginasLP Procedure NoteDaisy MugaAinda não há avaliações
- Examination and Clinical Care of The Patient With NeuropathyDocumento10 páginasExamination and Clinical Care of The Patient With NeuropathyFelipe Palma UrrutiaAinda não há avaliações
- Meningoencephalocele of The Temporal Bone-A Case Report: DR.B.V.N Muralidhar Reddy, DR K.V.V.RamjiDocumento6 páginasMeningoencephalocele of The Temporal Bone-A Case Report: DR.B.V.N Muralidhar Reddy, DR K.V.V.RamjiNityaAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Tumor in ChildrenDocumento42 páginasBrain Tumor in ChildrenKryztalGhail Llanora75% (4)
- Meningitis (Physical Exam)Documento6 páginasMeningitis (Physical Exam)MohammadAwitAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrocephalus PPT SSMC RewaDocumento60 páginasHydrocephalus PPT SSMC RewaAbhishek Mishra100% (3)
- Meningitis Pathophysiology PDFDocumento59 páginasMeningitis Pathophysiology PDFpaswordnyalupa100% (1)
- DD of CP Angle TumorDocumento43 páginasDD of CP Angle TumorBayarbaatar BoldAinda não há avaliações
- Aneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocumento9 páginasAneurysmal Subarachnoid HemorrhageAlejandra Pinillos RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Neuro Post TestDocumento6 páginasNeuro Post Testmarlon armamentoAinda não há avaliações
- Nervous System OverviewDocumento29 páginasNervous System OverviewDarla Mitu100% (2)
- Comparison of Pre Procedural and Real Time Ultrasound Guided Spinal Anesthesia For Traumatic Lower Limb InjuryDocumento7 páginasComparison of Pre Procedural and Real Time Ultrasound Guided Spinal Anesthesia For Traumatic Lower Limb InjuryIJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- Atlas of Neurosurgery Anatomy PDFDocumento213 páginasAtlas of Neurosurgery Anatomy PDFbalica silvia100% (1)
- Boyles TH Et Al. Guidelines For The Management of Acute Meningitis in Children and Adults in South AfricaDocumento11 páginasBoyles TH Et Al. Guidelines For The Management of Acute Meningitis in Children and Adults in South AfricaBilly Shan LastKagerooboroAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 10 - Nervous SystemDocumento5 páginasUnit 10 - Nervous Systemlola.konjevicAinda não há avaliações
- The Ventricular System of The BrainDocumento35 páginasThe Ventricular System of The BrainBaguma MichaelAinda não há avaliações
- Gatehouse Report PDFDocumento978 páginasGatehouse Report PDFTauseek RangrejAinda não há avaliações