Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Intercompany Sales Processing Stages
Enviado por
pankajsri684149Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Intercompany Sales Processing Stages
Enviado por
pankajsri684149Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Intercompany Sales Intercompany sales processing consists of the following three stages: Processing sales orders Processing deliveries
ies Billing
The sales organization and the plant are assigned to different company codes and have the following responsibilities: Sales organization: Processes the sales order Bills the customer Plant: Delivers goods to the customer Bills the ordering company code (sales organization) - this is intercompany billing. Intercompany billing uses SAP EDI to carry out posting to vendor account for the ordering company code. Company Structure Company code 0001 0002 Condition Record A condition record specifies that plant 0002 bills sales organization 0001 for goods at 80% of the net invoice value. Sales orders Sales organization 0001 receives the following sales order from customer XYZ: Item 10 Product A 20 pcs (Plant 0001) USD 200 Item 20 Product B 50 pcs (Plant 0002) USD 500 The second item requires intercompany sales processing, since product B must be delivered from a different company (company code 0002). Intercompany Sales Processing The intercompany sales functions are carried out as follows: o Pricing for customer invoice: Sales organization 0001 Sales organization 0001 Plant 0001 0002
o o
delivery: Plant 0002 billing: Sales organization 0001 bills the customer for USD 500
Sales organization 0002 bills sales organization 0001 for USD 400 (with an intercompany billing document) o Financial accounting: In company code 0001, SAP EDI is used to carry out posting to vendor account
Relationship to Pricing
The system processes intercompany pricing elements in exactly the same way as other pricing elements. The data for intercompany sales is stored in condition records. Pricing for intercompany billing is controlled by condition types, pricing procedures, and access sequences. Intercompany billing itself is controlled in a separate menu point in Customizing. This control data is defined in Customizing for Sales by your system administrator. See also: Working with Intercompany Sales Orders Working with Intercompany Deliveries Working with Intercompany Billing For further information, see Conditions and Pricing.
Given that the competitive landscape for business is being expanded to a global playing field, it is increasingly necessary to represent and support the global organization in your Enterprise system. Not only must the appropriate organization structures be represented, but also the business processes that utilize these structures must be flexible enough to support your legal and business reporting requirements. This article will review the organization structures necessary to support a global enterprise, as well as reviewing the sales processes that rely on these structures. In particular, we will focus on the Inter-company sales process. Organization Structures In order to establish the organization structures necessary to support global business processes, it is necessary to review the organizational structures in SAP ECC, and relate them to your Enterprise. The organization structures are represented in three functional areas: Financial, Sales and Distribution, and Logistics. All allowable organizational structures must first be defined in customizing, and then can be assigned relationships to other organizational structures. The Financial organizational structure represented in SAP ECC is the Company Code. It is the organizational structure that identifies the legal financial entity from a reporting perspective. A company code must be established for each country where financial transactions are to be reported. It is the level of financial integration for all SAP business transactions. All business transactions that post to general ledger accounts do so at the company code level. All postings to the general ledger from subsidiary applications are created automatically. Therefore, the company code must be determined automatically in that application. The Sales and Distribution organizational structure is called the Sales Area. The sales area is a combination of three individual organizational structures: the sales organization, the distribution channel, and the division. The sales
area is used for capturing sales data, it helps establish the pricing strategy for the sales document, and it can be used to determine default master data for the sales order. The sales organization is the highest level for reporting sales information. It represents the selling companys legal responsibilities. It defines the customers rights of recourse for product liability. It answers the question: Who did the selling? In configuration, a sales organization is uniquely linked to one company code. This is how the SAP ECC system determines the company code used to post general ledger accounts at billing time. The distribution channel identifies how our sales efforts reach our customers. It answers the question: How did we sell? Examples of distribution channels may be wholesale, retail and direct marketing. For global enterprises, you may define a separate distribution channel for international and domestic sales, for example. For each sales organization, we configure the valid distribution channels that can be used. The division identifies the product categories that we sell. It answers the question: What did we sell? The division is a part of the sales area, and as such helps define reporting, pricing, and master data default data. It is also a field that can be stored in the material master, and can be configured to be defaulted to the line item level of the sales order. Therefore, it can be used for product line sales reporting. The Logistics structure necessary to support global business processes is the Plant. The Plant is the highest level in the Materials Management application and is used to track inventory. Examples of plants can be distribution centers and manufacturing facilities. The plant is related to the Company code in SAP ECC to determine financial ownership of the inventory. Although it represents where the inventory is located, it may be necessary to define multiple Plant codes to represent inventory that is stored in one physical location but owned by different Company codes. This relationship is used at the time the goods issue is recorded. It determines the company code that is used to financially record the reduction in the inventory General Ledger account, and post the offset typically to the cost of goods sold account. The plant code is also related to Sales organization structures. We must configure allowable combinations of Sales organizations and Distribution channels that can sell from a specific plant. For example, the US Sales organizations for domestic wholesale distribution channels can sell from US plants that are distribution centers, while the US Sales organization for international wholesale distribution channels can sell from both Domestic and International Distribution channels located throughout the world. In both cases, we may establish that, in general, we are not allowed to source a sales order directly from a manufacturing facility. Manufacturing plants only transfer inventory to distribution center plants. This is merely an example of how to use the relationship of plant to sales organization and distribution channel, not a recommendation or limitation of the SAP ECC system. The plant code is determined automatically for each sales order line. The SAP ECC system uses a specific sequence of master records to default the delivering plant into the sales order item. We first check the Customer Material Information master record. This record is stored based on the combination of sales organization, distribution channel, sold-to customer and material. This means different combinations of sales organizations and distribution channels can propose different delivering plants for the same sold to customer and material. If this record is found, we will check to see if a delivering plant is stored in this record. If so, the search is ended, and the delivering plant is returned to the sales order line. If no Master record exists, or a delivering plant is not found, we continue to the Ship-to customer master. The delivering plant on the Ship-to customer master is stored based on the sales area. Therefore, different sales areas can propose a different delivering plant for the same ship to customer. The delivering plant is stored on the shipping tab of the customer master. Once again, if found, the search ends, and the delivering plant is returned to the sales order item. If not found, we proceed to the material master. The delivering plant is stored on the material master, based on the combination of sales organization and distribution channel. Once again, different combinations of sales organizations and distribution channels can propose a different delivering plant for the same material. When the delivering plant is determined, it is also checked to make sure we are allowed to sell from that plant based on the sales organization and distribution channel on the order. Inter-Company Sales The definition of inter-company sales in SAP ECC is when the company code that is determined by the delivering plant at goods issue time differs from the company code determined by the sales organization at billing time. In essence, inventory was sold that belonged to a different legal entity. In order to balance the books, after posting goods issue from the delivering plant, two billing documents need to be generated. The first billing document, which is issued to the customer, is used to record the revenue and accounts receivable in the company code that is related to
the sales organization of the sales order. The second billing document is used to record the intercompany sales. That is, the company code related to the plant that provided the inventory bills the company code related to the sales organization that received credit for the sale. Let us review each billing document to see how they are used to post an intercompany sale. In the customer, the billing document type is defaulted from the order type. Order type OR defaults billing document type F2 in the standard system. The sales area is determined from the sales order. The payer customer is defaulted from the sales order. The pricing procedure is determined using these influencing factors. In this billing document, pricing procedure RVAA01 is provided. Revenue is posted using the standard pricing condition type PR00. The cost however, is determined with an intercompany condition type PI01 intercompany price. It is defined at the level of the sales org and the delivering plant. This means that the same product can have a different intercompany price, or cost, based on which sales organization is selling the product, and which plant it is being delivered from. This allows flexibility in recording profitability for the sale to the customer. In the second invoice, which is used to record the intercompany sale, the sales area is determined based on the delivering plant. The payer customer is determined based on the sales organization of that sales area. The perspective is that the sales organization is buying the inventory from the delivering plant to support the sale. Therefore, the sales organization is providing the customer, and the delivering plant provides the sales area for the intercompany invoice. The intercompany invoice also defaults the billing document type from the sales order type. Order type OR defaults billing document type IV. Using the intercompany sales area, internal customer and billing document type IV, a different pricing procedure is determined. Pricing procedure ICAA01is determined. The revenue is posted using condition type IV01, which references the pricing data from condition type PI01. The reason different condition types are used is due to financial controlling. Basically, a condition type can be mapped as either revenue or cost, but not both. The cost on the intercompany invoice uses the standard condition type VPRS, which determines the cost form the material master. It is logical that we use the same data as condition type PI01, as the cost on the customer invoice is actually the cost on the intercompany invoice.
INTER COMPANY BILLING
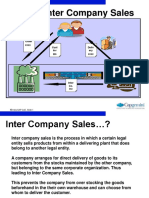
Definition: A company arranges direct delivery of the goods to the customer from the stocks of another company belonging to the same corporate group. To put in simple terms, Company code A orders goods through its sales organization A from Plant B belonging to Company code B. It is imperative that both Plants A & B should have the material. In other words, the material is created for both the Plants A & B + their respective storage locations. Sales Organizations and Plants are uniquely assigned to Company codes. It is not possible to assign either a plant or a sales organization to more than one company code. Sales organizations and plants assigned to each other need not belong to the same company code. In other terms, a plant belonging to Company code A & assigned to Sales Organization A can also be assigned to Sales Organization B of Company Code B. This enables cross company sales. PARTIES INVOLVED
1) End Customer 2) Ordering Company code 3) Supplying Company Code. End customer: Customer who orders goods from the ordering company code. Ordering Company Code: Which orders goods from Plant belonging to Supplying Company code through its sales organization and bills the end customer? Supplying Company Code: Supplies goods from its plant to the end customer specified by the ordering company code and bill the ordering company code. CONFIGURATION SETTINGS Assign Delivery Plant of the supplying company code to Sales Org + Distribution channel of the Ordering company code in the Enterprise Structure. DEFINE ORDER TYPES FOR INTERCOMPNY BILLING: Menu path: IMG/ SD/Billing/Intercompany Billing/Define Order Types for Intercompany billing Assign Organizational units by Plant: Menu Path: IMG/ SD/Billing/Intercompany Billing/Assign Organizational units by Plant. Define Internal Customer Number By Sales Organization: Menu Path: IMG/ SD / Billing/ Intercompany Billing/ Define Internal Customer Number By Sales Organization: Creating / Showing Ordering Sales Organization as Internal Customer for Supplying Company code: Transaction Code: XD01 The ordering sales organization is represented as internal customer of Supplying company code. We need to create customer master in Account Group - Sold to Party and maintain minimum required financial & Sales Area data. This internal customer number has to be assigned to the ordering sales organization. Hence, the system automatically picks up this internal customer number whenever there is Intercompany billing. PRICING:
We need to maintain two pricing procedures RVAA01 & ICAA01. Pricing procedure RVAA01 represents condition type PR00 & any other discounts or surcharges that are meant for end customer. We assign Pricing procedure RVAA01 to combination of Sales area (Of Ordering company code) + Customer Pricing Procedure + Document Pricing Procedure of Sales document type. This pricing Procedure (RVAA01) is determined both at Sales Order level & Billing processing for the end customer. We maintain PR00 condition type to represent the ordering company code's price to the end customer. Condition records for PR00 are maintained using organizational elements of Ordering company code, end customer & the Material. Eg: Sales Org. of Ordering company code + End customer + Material. We also need to maintain PI01 condition type to represent costs to Ordering company code (in other words revenue to supplying company code). It is statistical condition type & meant for information purpose only.
Condition records for PI01 are created Ordering sales Org + Supplying Plant + Material
with
the
following
key
combination:
Pricing Procedure ICAA01 is determined at Intercompany billing processing level. 1. Pricing Procedure ICAA01 - Pricing Procedure for Inter Company billing is assigned to the combination of: Sales Area (of supplying company code) + Document pricing Procedure of Billing document type IV + Customer Pricing Procedure of the internal customer. Pricing Procedure ICAA01 has condition type IV01 that represents revenues for Supplying company code in the intercompany billing. 2. PR00 condition type also appears in Intercompany billing document. It is for information purposes only and does not have bearing on the value of the document. 3. PI01 represented under pricing procedure RVAA01 is reference condition type for IV01 and the same is defined in the condition type IV01. Due to this these two condition types represent same value.
4. The condition type IV01 in intercompany billing document represents revenue to the Supplying Company. But its corresponding condition type PI01 in the billing document to the end customer is shown as a statistical item meant for information purposes. Condition Type VPRS in the intercompany-billing document indicates cost to the supplying company code. The use of two different condition types in Intercompany billing is necessary to ensure that data is transmitted correctly to the financial statement (Component CO-PA).
ILLUSTRATION: STEP 1: Create Sales Order Manually Enter the Delivery Plant of the Supplying Company Code: OBSERVE CONDITIONS SCREEN FOR ITEM: PR00 represents Price to the end customer (in other words, revenue for the ordering company). PI01 represents cost to ordering company (in other words, revenue for the supplying company). It is represented as statistical item only. DELIVERY: Delivery is carried out from the supplying point & hence we can observe that it is done from shipping point assigned to the supplying plant. Subsequently, Picking & PGI are carried out. BILLING TO END CUSTOMER:
T-Code: VF01 Create Intercompany Billing: T-code: VF01 OBSERVE THE CONDITIONS SCREEN OF THE INTERNAL INVOICE: IV01 Condition type represents revenue for the supplying company code. VPRS condition type represents cost to the supplying company code. PR00 in intercompany billing document displays amount billed to the end customer. It serves as just an information item and is inactive. If the ordering company enters the incoming invoice manually, the delivering company can print out an invoice document with the help of output type RD00, which is then sent to the Payer. If automatic invoice receipt has been agreed, we must use the SD output control functions to ensure that output type RD04 is found in internal billing. In R/3 system, output determination procedure V40000, which includes this output type, is assigned to Intercompany billing type IV. The automatic posting to the vendor account is initiated when output type RD04 is processed. The system uses the EDI output type INVOIC in the FI variant. To ensure that payables are posted in financial accounts of the ordering company, the delivery company must be created as a vendor.
Você também pode gostar
- SAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsNo EverandSAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (11)
- SAP SD Frequently Asked Questions - ERP Operations - SCN WikiDocumento6 páginasSAP SD Frequently Asked Questions - ERP Operations - SCN WikiNeeraj JainAinda não há avaliações
- Intercompany SalesDocumento7 páginasIntercompany SalesSiva Ud67% (3)
- Invoice List in ERP SAPDocumento13 páginasInvoice List in ERP SAPbalashowryraju100% (8)
- Inter-Company Billing Process - SAP BlogsDocumento20 páginasInter-Company Billing Process - SAP BlogsquyenhuynhhaAinda não há avaliações
- SAP SD - Copy ControlsDocumento27 páginasSAP SD - Copy ControlsRamachandra100% (2)
- Sap-Sd Pricing Condition Technique & Pricing Procedure DetermniationDocumento33 páginasSap-Sd Pricing Condition Technique & Pricing Procedure DetermniationLaxmi Narsimha Rao Mamidala100% (1)
- SAP BL Billing PlanDocumento29 páginasSAP BL Billing PlanSoma KiranAinda não há avaliações
- Define Pricing Procedure StepsDocumento3 páginasDefine Pricing Procedure Stepsashokkumar1979Ainda não há avaliações
- Set up inter-company sales in SAP SDDocumento1 páginaSet up inter-company sales in SAP SDrafay12350% (2)
- Cross Company Sales ConfigurationDocumento70 páginasCross Company Sales Configurationnelsondarla1275% (4)
- Sap SDDocumento87 páginasSap SDSatya Bulusu100% (2)
- Packing in SAPDocumento9 páginasPacking in SAPAnupa Wijesinghe75% (4)
- Shipping Point DeterminationDocumento10 páginasShipping Point DeterminationAnupa Wijesinghe80% (5)
- Transportation Scheduling in SAPDocumento29 páginasTransportation Scheduling in SAPAnupa Wijesinghe96% (27)
- BOM Process in SDDocumento6 páginasBOM Process in SDshajeelkhan100% (1)
- Intercompany Billing For STOsDocumento10 páginasIntercompany Billing For STOsMalith Tharaka Perera75% (4)
- Rebates ConfigurationDocumento35 páginasRebates ConfigurationS Joseph RajAinda não há avaliações
- Inter Company SaleDocumento40 páginasInter Company SaleSUSMITAAinda não há avaliações
- SAP SD Third Party SalesDocumento28 páginasSAP SD Third Party Salesramesh B50% (2)
- Sales & Distribution User ExitsDocumento12 páginasSales & Distribution User ExitsRamesh Balaji100% (2)
- Material Determination Process in Sap SDDocumento26 páginasMaterial Determination Process in Sap SDAnitha Chowdary KommiAinda não há avaliações
- Availability Check ConfigurationDocumento8 páginasAvailability Check ConfigurationshajeelkhanAinda não há avaliações
- Intercompany STO ProcessDocumento19 páginasIntercompany STO ProcessMalith Tharaka Perera93% (44)
- SAP SD ECC 5.0 - Billing Document Structure and ProcessingDocumento236 páginasSAP SD ECC 5.0 - Billing Document Structure and Processinggl_sudhir765386% (7)
- SD GuideDocumento116 páginasSD GuidevenkatAinda não há avaliações
- Subcontracting ProcessDocumento2 páginasSubcontracting ProcessparavaiselvamAinda não há avaliações
- Zero Confirmed Quantity When Insufficient Stock in SAPDocumento35 páginasZero Confirmed Quantity When Insufficient Stock in SAPbiswajitAinda não há avaliações
- Determination Rule in SD For Quick Reference: SL.N o Determination Object Rules For DeterminationDocumento4 páginasDetermination Rule in SD For Quick Reference: SL.N o Determination Object Rules For DeterminationRajanikanth AnnaluruAinda não há avaliações
- Season Processing in SAP (is-AFS)Documento23 páginasSeason Processing in SAP (is-AFS)Anupa Wijesinghe89% (19)
- Create Customer Hierarchy Node (MarketingDocumento28 páginasCreate Customer Hierarchy Node (Marketingsap_my100% (3)
- SD Revenue Account Determination SetupDocumento10 páginasSD Revenue Account Determination SetupkarthikbjAinda não há avaliações
- Inter-Company STO With SD Delivery, Billing & LIV - SAP BlogsDocumento37 páginasInter-Company STO With SD Delivery, Billing & LIV - SAP BlogsASHOK NAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Rollout - SD Module ConfigurationDocumento15 páginasSAP Rollout - SD Module Configurationaayush_nigam100% (6)
- SD User exits overviewDocumento15 páginasSD User exits overviewVky VeeraAinda não há avaliações
- Sap Pricing Configuration and End User ManualDocumento35 páginasSap Pricing Configuration and End User Manualdeepiiitbhu100% (5)
- SAP Services and Organizational UnitsDocumento9 páginasSAP Services and Organizational UnitssharathmscAinda não há avaliações
- Inter-Company Resource Related BillingDocumento3 páginasInter-Company Resource Related BillingAnnapureddy Srinivasa Reddy100% (1)
- Contract in Sap SDDocumento53 páginasContract in Sap SDrekhagoleyAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Third Party Sales ProcessDocumento18 páginasStandard Third Party Sales ProcessRam KLAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of SAP SD PricingDocumento13 páginasFundamentals of SAP SD Pricingrajendrakumarsahu100% (3)
- Release Procedure For Pricing ConditionsDocumento14 páginasRelease Procedure For Pricing ConditionsAnupa Wijesinghe95% (22)
- SAP SD Third-party sales process overviewDocumento13 páginasSAP SD Third-party sales process overviewsumit patilAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Sales Document TypesDocumento30 páginasSAP Sales Document TypesSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Intercompany NLCCDocumento19 páginasIntercompany NLCCrespinosamillaAinda não há avaliações
- SAP LE Shipment Cost ProcessingDocumento21 páginasSAP LE Shipment Cost ProcessingashahmednAinda não há avaliações
- The Up & Away Advisors’ Guide to Implementing and Executing Sap’s Vehicle Management SystemNo EverandThe Up & Away Advisors’ Guide to Implementing and Executing Sap’s Vehicle Management SystemAinda não há avaliações
- Uncover the Secrets of SAP Sales and DistributionNo EverandUncover the Secrets of SAP Sales and DistributionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- SAP Variant Configuration: Your Successful Guide to ModelingNo EverandSAP Variant Configuration: Your Successful Guide to ModelingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNo EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Enterprise StructureDocumento9 páginasSAP Enterprise StructurePriyabrata Ray0% (1)
- European Vacancy and Recruitment Report 2012Documento200 páginasEuropean Vacancy and Recruitment Report 2012Joaquín Vicente Ramos RodríguezAinda não há avaliações
- PSP, Modern Technologies and Large Scale PDFDocumento11 páginasPSP, Modern Technologies and Large Scale PDFDeepak GehlotAinda não há avaliações
- Soal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISDocumento59 páginasSoal Ulangan Harian Smester 1 Kelas 8 SMP BAHASA INGGRISsdn6waykhilauAinda não há avaliações
- Subsurface Sewage DisposalDocumento174 páginasSubsurface Sewage DisposalSanthi KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Var, CaR, CAR, Basel 1 and 2Documento7 páginasVar, CaR, CAR, Basel 1 and 2ChartSniperAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Documento4 páginasUnit 3 Test A Test (Z Widoczną Punktacją)Kinga WojtasAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocumento10 páginasLesson 3 Lymphatic System and Body DefensesJulio De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- Vol 98364Documento397 páginasVol 98364spiveynolaAinda não há avaliações
- The Voice of PLC 1101Documento6 páginasThe Voice of PLC 1101The Plymouth Laryngectomy ClubAinda não há avaliações
- E.Coli Coliforms Chromogenic Medium: CAT Nº: 1340Documento2 páginasE.Coli Coliforms Chromogenic Medium: CAT Nº: 1340Juan Manuel Ramos ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Course Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Documento20 páginasCourse Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Tanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Fish Culture Y4Documento136 páginasFish Culture Y4KèlǐsītǎnKǎPáng100% (1)
- Affect of CRM-SCM Integration in Retail IndustryDocumento8 páginasAffect of CRM-SCM Integration in Retail IndustryRajeev ChinnappaAinda não há avaliações
- SKILLS TRANSFER PLAN FOR MAINTENANCE OF NAVAL EQUIPMENTDocumento2 páginasSKILLS TRANSFER PLAN FOR MAINTENANCE OF NAVAL EQUIPMENTZaid NordienAinda não há avaliações
- An Empirical Study of Car Selection Factors - A Qualitative & Systematic Review of LiteratureDocumento15 páginasAn Empirical Study of Car Selection Factors - A Qualitative & Systematic Review of LiteratureadhbawaAinda não há avaliações
- KG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Documento2 páginasKG Technologies Inc Metric: K119X-DX024P-1AT-90A-C399Bhushan PAwarAinda não há avaliações
- Music Literature (Western Music)Documento80 páginasMusic Literature (Western Music)argus-eyed100% (6)
- 02-Procedures & DocumentationDocumento29 páginas02-Procedures & DocumentationIYAMUREMYE EMMANUELAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study 1Documento2 páginasCase Study 1Diana Therese CuadraAinda não há avaliações
- Trends Interiors Architecture Fashion Lifestyle: 6 Spring 2013 Collector's EditionDocumento116 páginasTrends Interiors Architecture Fashion Lifestyle: 6 Spring 2013 Collector's EditionFernanda RaquelAinda não há avaliações
- Bluetooth® (SAP) Telephone Module, Version 4Documento2 páginasBluetooth® (SAP) Telephone Module, Version 4Željko BokanovićAinda não há avaliações
- Jamaica's Unemployment Aims, Causes and SolutionsDocumento23 páginasJamaica's Unemployment Aims, Causes and Solutionsnetzii300067% (3)
- Credit Card Statement: Payment Information Account SummaryDocumento4 páginasCredit Card Statement: Payment Information Account SummaryShawn McKennanAinda não há avaliações
- Concept of Intestate SuccessionDocumento9 páginasConcept of Intestate SuccessionBodhiratan BartheAinda não há avaliações
- ExpressionismDocumento16 páginasExpressionismRubab ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Mar 2021Documento2 páginasMar 2021TanAinda não há avaliações
- Angel Turns 18 Debut ScriptDocumento2 páginasAngel Turns 18 Debut ScriptChristian Jorge Lenox100% (1)
- ControllingDocumento8 páginasControllingAnjo Pasiolco Canicosa100% (2)
- Limiting and Excess Reactants Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasLimiting and Excess Reactants Lesson Planapi-316338270100% (3)
- Alberta AwdNomineeDocs Case Circle BestMagazine NewTrailSpring2016Documento35 páginasAlberta AwdNomineeDocs Case Circle BestMagazine NewTrailSpring2016LucasAinda não há avaliações