Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Closing Checklist
Enviado por
presidente2008Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Closing Checklist
Enviado por
presidente2008Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
St.
Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
St. Marys University of Minnesota
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session 9
Project Closing and Examination 2
Monday, June 18
Dr. Gary L. Jurek
Summer Semester 2007
Initiate Monitor and Control
Plan Execute Close
PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine Welcome! Questions, Concerns, Expectations, and Issues PMP/Reading Questions Project Closing Work on Team Presentations What did you learn today? Exam Two
Initiate Monitor and Control
Plan Execute Close
9-1
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Questions, Concerns, Expectations, and Issues
PRM600
Project Management / Reading Questions
Lets test your PMBOK reading comprehension!
9-2
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
Project Closing
Initiate Monitor and Control
Plan
Execute
Close
Definition: Closing Processes Formalizes acceptance of the project, service or result and brings the project or a project phase to an orderly end.
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition. P. 41.
PRM600
Project Closing Processes Topics
Gaining project acceptance and bringing the project to an orderly end
9-3
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
So - am I done Yet?
Your product has been accepted and signed off by your stakeholder, are you done yet?
NO!
Why Not? Whats left to do? Remember: You need to meet both product development requirements and project management requirements!
High Level Summary of Process Groups Interactions
Enterprise Environmental Factors
Organizations culture Project management information system Human resource pool Policies, procedures standards, processes Defined processes Historical information Lessons learned
Initiating Process Group
Statement of Work Contract
Project Initiator or Sponsor
Organizational Process Assets
Project Charter Preliminary Project Scope Statement Planning Process Group Project Management Plan Executing Process Group
Recommended corrective actions Recommended preventive actions Performance Reports Recommended defect repair Forecasts Validated defect repair Approved deliverables Organizational process assets (updates) Customer
Final product, Service, results
Monitoring and Controlling Process Group
Deliverables Requested changes Implemented change requests Implemented corrective actions Implemented preventive actions Implemented defect repair Work performance information Approved change requests Rejected change requests Approved corrective actions Approved preventive actions Approved defect repair Project Management Plan (updates) Project Scope Statement (updates) Administrative closure procedure Contract closure procedure A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition. p. 42.
Closing Process Group
9-4
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Project Integration Management
1. Develop Project Charter 2. Develop Preliminary Project Scope Statement 3. Develop Project Management Plan 4. Direct and Manage Project Execution 5. Monitor and Control Project Work 6. Integrated Change Control 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
PRM600
Project Scope Management
Scope Planning Scope Definition Create WBS Scope Verification Scope Control 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Project Time Management
Activity Definition Activity Sequencing Activity Resource Estimating Activity Duration Estimating Schedule Development Schedule Control
7. Close Project
Project Cost Management
1. Cost Estimating 2. Cost Budgeting 3. Cost Control
Project Quality Management
1. Quality Planning 2. Perform Quality Assurance 3. Perform Quality Control
Project Human Resource Management
1. Human Resource Planning Planning 2. Acquire Project Team 3. Develop Project Team 4. Manage Project Team
Project Communications Management
1. 2. 3. 4. Communications Planning Information Distribution Performance Reporting Manage Stakeholders 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Project Risk Management
Risk Management Planning Risk Identification Qualitative Risk Analysis Quantitative Risk Assessment Risk Response Planning Risk Monitoring and Control 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Project Procurement Management
Plan Purchases and Acquisitions Plan Contracting Request Seller Responses Select Sellers Contract Administration
6. Contract Closure
Overview of Project Management Knowledge Areas and Project Management Processes (PMBOK Third Edition, p. 11)
Closing Process Group
Monitoring and Controlling Process Group
Close Project Planning Process Group Contract Closure
Executing Process Group
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition. p. 60.
9-5
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Suggested Project Management Deliverables by Life Cycle Process Group
Initiation
(High Level) Project Charter Preliminary Project Scope Statement Project Calendar Project Directory Start Requirements capture
Planning
(Detail Level) Project Management Plan Project Scope statement List of Milestones List of Deliverables (with features and requirements) WBS with Activities Network Diagram Estimates and forecasts OBS Responsibility Matrix Responsibility Assignment Matrix Project Schedule Budget/Cost Management Plan Quality Plan Project Standards
Executing
Work Performance Reports Deliverables Gantt Chart Progress Measurement Change Management Risk Management Defect Management Meeting Management, Minutes, and Action Items
Monitoring and Controlling
Performance Reports Corrective actions Preventive actions Defect Repair Change actions Forecasts Approved Deliverables Project Management plan (updates) Project Scope Statement (updates)
Closing
Final Product, Service, Results Acceptance Final Status Report Administrative Closing Checklist Contract Closing Procedures Lessons Learned Summaries: Defect, Risk, Corrective and Change Organizational Process Assets (updates) Project Archiving
PRM600
Closing Processes Tools and Techniques
Project Management Methodology (CMM 3+) Project Management Information System (CMM 3+) Expert judgment (CMM Levels 1-2)
Initiating Process
Planning Processes
Controlling Processes
Executing Processes
Closing Processes
Always check for organizational standards!
9-6
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Closing Processes Outputs/Deliverables
1. Administrative Closure Procedure: activities, roles and responsibilities Deliverables: Stakeholder approval requirements (changes and deliverables) Processes: Confirmation, verification, and validation actions and activities (legal, financial, administrative) Project: completion of action and activities to satisfy project completion or exit criteria Contract Closure Procedure Final Product, Service, or Result Formal acceptance and handover Organizational Process Assets (Updates) Formal acceptance documentation Project files Project closure documents Historical information: historical information and lessons learned
2. 3. 4.
Big Question: Who Needs To Sign Off!
PRM600
Close Project
Close Project
This is the process necessary to finalize all activities across all of the Process Groups to formally close the project or a project phase.
Inputs
Project management plan Contract documentation Enterprise environmental factors Organization process assets Work performance information Deliverables
Outputs
Administrative closure procedure Contract closure procedure Final product, service, or result Organizational process assets (updates)
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition. pp. 67.
9-7
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Contract Closure
Contract Closure
This is the process necessary for completing and settling each contract, including the resolution of any open items, and closing each contract applicable to the project or a project phase.
Inputs
Procurement management plan Contract management plan Contract documentation Contract closure procedure
Outputs
Closed contracts Organizational process assets (updates)
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) Third Edition. pp. 67.
PRM600
What are three project situations where you may need communications administrative closure?
1. When a project ends 2. When a project (or contract) is terminated before the work is completed 3. At the end of each project phase
All projects must be closed! If a project involves contracts, contract closeout should occur before administrative closure!
Source: The Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, 2000 Edition.
9-8
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Short List for Closing a Project
Final Status Report Closing Checklist Autopsy / After Action Report Change Request Analysis Lessons Learned Project Archiving Smart Idea: Develop a RAM for each activity
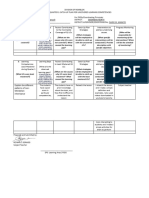
Example: Checklist for Closing a Large Project
Description Needed? Yes No Required Date Responsible Person Notes
Identify Remaining Work Closing/Terminating Plan Personal Evaluations Close-out Work Orders Audit Final Changes Pay all Vendors Close-Out Books/Audit Final Delivery Instructions Customer Training Notify Purchasing of Completion Equipment Redeployed Materials Returned to Inventory Staff Reassigned Close-Down Procedures Engineering Documentation Final Staff Meeting Final Report and Review Meeting Celebration and bonuses?
Baker, Baker, and Campbell, The Complete Idiots Guide to Project Management (Third Edition), p. 357
9-9
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Example from Gantt Head
Examples: Project Completion Questions Is there a system in place for evaluating and cataloging all useful information collected at the completion of the project? Low 1 2 3 4 5 High
Will reusable components be captured and catalogued for future projects? Is there an audit process to determine project success/failure and document recommended process improvements?
Low
High
Low
High
Is there a formal administrative process for closing down the project upon completion? Is all project source code and documentation stored in permanent format?
Low
High
Low
High
PRM600
Exercise:
Individual Project.
Develop a Closing Checklist!
Develop a master project closing checklist for one of your projects. If you already have one help a friend in class.
9-10
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Release the Resources
Thank your contributors! Is a formal assessment required? Note in their files? Notify resource managers (well before closing) Protect core project contributors if possible
PRM600
Change Requests as Deliverables
1. Put together a list of items that were asked for by your client. List separately those that were not put into this project. 2. Where did the change requests come from? 3. List change impacts (projected or real). 4. List new products/projects that would support the clients business. 5. Share project Lessons Learned summary to aid in improving what was effective and correct what was ineffective for future projects.
9-11
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
Evaluation of Effective and Ineffective Activities (Formal Critique Method)
The purpose of Formal Critique Method to accurately describe what actually took place and implement processes (best practices) that improve on what was effective and correct what was ineffective. 1. Bring together all team members (project, management, and client / stakeholder, contractor, suppliers, etc.) Each individual needs to think through events of the project to identify specific behaviors (both positive and negative) that impacted the production efficiency of the project. Examples of what took place need to be in the form of descriptions, not just vague generalities, opinions or impressions. Ask each to individually list what they remember as being effective and ineffective in the project. Even if everyone agrees, it is important to have individuals share the specific examples because often no one person remembers everything. After collecting data, rank items, discuss what can be done to improve effective areas and what can be done to eliminate/correct ineffective areas. Incorporate these Best Practices" into the next project
PRM600
2.
3. 4.
PRM600
Lessons Learned
What categories would you review in a projects lessons learned session?
9-12
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Final Project Report
Does your group have a Final Report template? CMM Levels 2+ have this If not, ask the major stakeholders what they require May be as simple as a one paragraph executive summary or as complex as long-term impact analysis Final Report may include reviews of: Scope, deliverables, changes requests, corrective actions, risk/preventive actions, defect repair, forecasts, and performance reports
PRM600
Archive the Project
Archiving refers to long term storage of project related materials Project materials are needed for the following reasons: Future changes or enhancements to the original project Legal protection Marketing Reference for future similar projects See Organization Standards
9-13
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
Project Closing Processes Topics
Gaining project acceptance and bringing the project to an orderly end
PRM600
Case Study Exam Two ??? Enterprises
Follow your instructors directions. Good Luck!
9-14
St. Marys University of Minnesota - PRM600
Fundamentals of Project Management
Session Nine
PRM600
What did you learn today?
9-15
Você também pode gostar
- Communication Plan TemplateDocumento6 páginasCommunication Plan TemplateHussain ElarabiAinda não há avaliações
- Project Control Stages A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo EverandProject Control Stages A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management Proj - LifecycleDocumento5 páginasProject Management Proj - LifecycleSohini DasAinda não há avaliações
- Requirements Management Plan A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo EverandRequirements Management Plan A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Schedule Management PlanDocumento6 páginasSchedule Management PlanPaul AshtonAinda não há avaliações
- Project Charter: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Case July 5, 2020Documento2 páginasProject Charter: Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Case July 5, 2020i love you babyyAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Project Plan and Scope Management PDFDocumento17 páginas3-Project Plan and Scope Management PDFMuhamad BrilliantAinda não há avaliações
- C M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMEDocumento7 páginasC M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMERoqaia AlwanAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Metrics Project ManagementDocumento8 páginasQuality Metrics Project Managementselinasimpson1501Ainda não há avaliações
- Project Quality ManagementDocumento53 páginasProject Quality Managementatularvin231849168Ainda não há avaliações
- Communication Plan TemplateDocumento18 páginasCommunication Plan TemplateWael Khalil Pmp100% (1)
- Communications PlanDocumento7 páginasCommunications PlanoliverapopovicAinda não há avaliações
- Change Request Process Flowchart PDFDocumento1 páginaChange Request Process Flowchart PDFtigrotAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Project ExecutionDocumento16 páginasChapter 4 Project ExecutionczuberekAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management PlanDocumento114 páginasProject Management PlanसागरऊमळकरAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management Plan TemplateDocumento17 páginasProject Management Plan TemplateburumoiseAinda não há avaliações
- CDC Up Project Management Plan TemplateDocumento30 páginasCDC Up Project Management Plan TemplateMohmmed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Stakeholder Analysis: Project Name Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Project Project Phase InitiationDocumento18 páginasStakeholder Analysis: Project Name Wilmont's Pharmacy Drone Project Project Phase Initiationkani gargAinda não há avaliações
- Project Plan TemplateDocumento16 páginasProject Plan TemplateAnonymous e8wpeGnEJAinda não há avaliações
- Project Quality ManagementDocumento64 páginasProject Quality ManagementKelvin Ting100% (1)
- Project Closing - Project Review and Close ReportDocumento9 páginasProject Closing - Project Review and Close ReportMegat Zainurul Anuar bin Megat JohariAinda não há avaliações
- Communication Matrix: Project: ID: Objective User Responsibility TimeDocumento3 páginasCommunication Matrix: Project: ID: Objective User Responsibility TimeDaniel Socorro RamirezAinda não há avaliações
- Requirements Management PlanDocumento20 páginasRequirements Management Planguddu9388Ainda não há avaliações
- Time & Cost PlanningDocumento35 páginasTime & Cost Planninghoda sawanAinda não há avaliações
- PMO-1.8 Monthly Status-Reporting PDFDocumento6 páginasPMO-1.8 Monthly Status-Reporting PDFbakbakAinda não há avaliações
- SITE VISIT REPORT - Alexa Tower ProjectDocumento6 páginasSITE VISIT REPORT - Alexa Tower ProjectMohtadyAinda não há avaliações
- Project Monitoring PlanDocumento2 páginasProject Monitoring PlanharithaAinda não há avaliações
- Change Management PlanDocumento7 páginasChange Management PlanHaseebAinda não há avaliações
- Project Closing Report: Templat Pengurusan Projek ICT Sektor Awam Versi 2Documento7 páginasProject Closing Report: Templat Pengurusan Projek ICT Sektor Awam Versi 2Basyiroh SaadAinda não há avaliações
- PMP Project Quality Management PMBOK V4.0Documento70 páginasPMP Project Quality Management PMBOK V4.0Mohammad Mizanur Rahman NayanAinda não há avaliações
- Monitoring ControllingDocumento22 páginasMonitoring ControllingGio BattadAinda não há avaliações
- Project Closeout Report InstructionsDocumento2 páginasProject Closeout Report InstructionstohemaAinda não há avaliações
- Study GuideDocumento329 páginasStudy GuideWarren DyckmanAinda não há avaliações
- 09-Close-Out Phase PDFDocumento18 páginas09-Close-Out Phase PDFChowKC03100% (1)
- Quality: To Meet Product or Service Specifications and ExpectationsDocumento13 páginasQuality: To Meet Product or Service Specifications and ExpectationsmaelikahAinda não há avaliações
- Project Integration ManagementDocumento18 páginasProject Integration ManagementNikita JainAinda não há avaliações
- Project PlanDocumento12 páginasProject Planapi-3705824100% (1)
- Project Charter: This Project Charter Was Created For The Corporate Employee Recognition FrameworkDocumento3 páginasProject Charter: This Project Charter Was Created For The Corporate Employee Recognition FrameworkVaisakhAinda não há avaliações
- Projectmanagement 2 PDFDocumento45 páginasProjectmanagement 2 PDFancynaveenAinda não há avaliações
- PPMP20008 Quality Management Plan TemplateDocumento8 páginasPPMP20008 Quality Management Plan TemplateXuhy Ximuoi NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Organizational Breakdown StructureDocumento25 páginasOrganizational Breakdown StructureAnni Lou BordiosAinda não há avaliações
- W10 ProjectCommunicationManagementDocumento30 páginasW10 ProjectCommunicationManagementabdul hannanAinda não há avaliações
- Schedule Management PlanDocumento3 páginasSchedule Management PlanGeeta RamsinghAinda não há avaliações
- P N B B: Procurement Management PlanDocumento26 páginasP N B B: Procurement Management PlanFabian GamboaAinda não há avaliações
- F4-40-03 Context & Interested Parties RegisterDocumento3 páginasF4-40-03 Context & Interested Parties RegisterGerritAinda não há avaliações
- Project Monitoring ChecklistDocumento2 páginasProject Monitoring ChecklistribijiAinda não há avaliações
- Date: Project Manager: Karrar Haider: Role Stakeholder NameDocumento14 páginasDate: Project Manager: Karrar Haider: Role Stakeholder NameSyed Haider50% (2)
- Change Request FlowDocumento1 páginaChange Request Flowyash shahAinda não há avaliações
- Drone Case Project Schedule Rev 02 Date 2 May 2020Documento1 páginaDrone Case Project Schedule Rev 02 Date 2 May 2020Nasim MammadovAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management HandbookDocumento8 páginasProject Management HandbookEvans MandinyanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Training Project PlanDocumento8 páginasTraining Project PlangolfohAinda não há avaliações
- Project Charter DocumentDocumento8 páginasProject Charter DocumentPranjeet Chakravarty100% (1)
- SAHAJ - 701 - GP AssignmentDocumento3 páginasSAHAJ - 701 - GP AssignmentsalmanAinda não há avaliações
- Xaydung360.Vn - Project Management PlanDocumento15 páginasXaydung360.Vn - Project Management PlanHoang Vien Du100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Chapter 3 CHE620 Project ManagementDocumento42 páginasLecture Notes Chapter 3 CHE620 Project ManagementFizaAinda não há avaliações
- Planning A ProjectDocumento33 páginasPlanning A ProjectLjuba SindzirevicAinda não há avaliações
- Sample CloseoutDocumento6 páginasSample CloseoutArpita GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Project Budget: Budget Actual Under (Over) Total Labor Materials Budget Actual Under (Over)Documento4 páginasProject Budget: Budget Actual Under (Over) Total Labor Materials Budget Actual Under (Over)Juridic nortekAinda não há avaliações
- 2010-06-14 1300 Project Management Broad Spectrum Overview WikibookDocumento522 páginas2010-06-14 1300 Project Management Broad Spectrum Overview WikibookKits Sri100% (1)
- Math-Magic: Textbook in Mathematics For Class IIIDocumento6 páginasMath-Magic: Textbook in Mathematics For Class IIISundeep GargAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 Rizal 1Documento6 páginasLesson 1 Rizal 1Anne Maerick Jersey OteroAinda não há avaliações
- JNTUK DAP B.tech Regulations R10 Batch StudentsDocumento6 páginasJNTUK DAP B.tech Regulations R10 Batch StudentsmadhueeAinda não há avaliações
- Preface of The Course File Lab-1 NewDocumento7 páginasPreface of The Course File Lab-1 Newtheeppori_gctAinda não há avaliações
- Career Counseling Intake InterviewDocumento30 páginasCareer Counseling Intake InterviewSachin ManjalekarAinda não há avaliações
- DLL - English 4 - Q1 - W8Documento6 páginasDLL - English 4 - Q1 - W8Rhadbhel PulidoAinda não há avaliações
- UTS Character StrengthsDocumento3 páginasUTS Character StrengthsangelaaaxAinda não há avaliações
- Music6 - Q2 - Mod1 - C, G, F MajorDocumento40 páginasMusic6 - Q2 - Mod1 - C, G, F MajorJohn Lorenz G. FaltiqueraAinda não há avaliações
- Resume - Jason PopeDocumento2 páginasResume - Jason Popeapi-232853914Ainda não há avaliações
- MUSIC 7 Q3 W1D1 MoroIslamic Vocal MusicDocumento2 páginasMUSIC 7 Q3 W1D1 MoroIslamic Vocal MusicAires Ichon100% (1)
- (FO-L) Script - ColDocumento32 páginas(FO-L) Script - ColMuhammad Revaldi AkbarAinda não há avaliações
- SPA Daily Lesson Log g8 Nov. 21 25Documento2 páginasSPA Daily Lesson Log g8 Nov. 21 25Chudd LalomanAinda não há avaliações
- Aparchit 1st August English Super Current Affairs MCQ With FactsDocumento27 páginasAparchit 1st August English Super Current Affairs MCQ With FactsVeeranki DavidAinda não há avaliações
- CPHRM Healthcare BrouchureDocumento10 páginasCPHRM Healthcare BrouchureHanan AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- B. Ed Final Prospectus Autumn 2019 (16-8-2019) PDFDocumento41 páginasB. Ed Final Prospectus Autumn 2019 (16-8-2019) PDFbilal1294150% (4)
- Blue Print XiiDocumento1 páginaBlue Print XiiJayasarathiAinda não há avaliações
- Coping Mechanism of SHS Students in Transitioning Adm To F2F Mode ClassesDocumento5 páginasCoping Mechanism of SHS Students in Transitioning Adm To F2F Mode ClassesPomelo Tuquib LabasoAinda não há avaliações
- Shs Class RecordDocumento62 páginasShs Class RecordMae Sheilou Conserva PateroAinda não há avaliações
- Accomplishment Report in Psych SocDocumento34 páginasAccomplishment Report in Psych SocJeffrey ManzanoAinda não há avaliações
- MapehDocumento8 páginasMapehBilly Jane MadrigalAinda não há avaliações
- Educating Individuals With Diverse Learning Need1Documento8 páginasEducating Individuals With Diverse Learning Need1George OpokuAinda não há avaliações
- CV - Hendro FujionoDocumento2 páginasCV - Hendro FujionoRobert ShieldsAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Labor Economics: Inequality in EarningsDocumento37 páginasModern Labor Economics: Inequality in EarningssamuelAinda não há avaliações
- Planning and Sequence of LearningDocumento24 páginasPlanning and Sequence of LearningPax GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Writing Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasWriting Lesson Planapi-252918385Ainda não há avaliações
- Catch Up Plan Template Division of Romblon1Documento12 páginasCatch Up Plan Template Division of Romblon1MICHELLE RAFAELAinda não há avaliações
- 8th International Conference On Learning, Education and Pedagogy (LEAP)Documento20 páginas8th International Conference On Learning, Education and Pedagogy (LEAP)Global Research and Development ServicesAinda não há avaliações
- Cadets Admission FormDocumento4 páginasCadets Admission Formfarhan9125Ainda não há avaliações
- Teaching Creativity Skills in Primaryuagc2013Documento6 páginasTeaching Creativity Skills in Primaryuagc2013Iancu CezarAinda não há avaliações
- Jamila Joy ResumeDocumento2 páginasJamila Joy ResumeJamila TaguiamAinda não há avaliações
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionNo Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeNo EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (99)
- Project Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.No EverandProject Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeNo EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (36)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeNo EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialNo EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (240)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionNo EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (18)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationAinda não há avaliações
- The Power of the Other: The startling effect other people have on you, from the boardroom to the bedroom and beyond-and what to do about itNo EverandThe Power of the Other: The startling effect other people have on you, from the boardroom to the bedroom and beyond-and what to do about itNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (9)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesNo EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (6)
- PMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersNo EverandPMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsNo EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (16)
- The PMP Project Management Professional Certification Exam Study Guide - PMBOK Seventh 7th Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the PMP Exam With Confidence - Complete Practice Tests With AnswersNo EverandThe PMP Project Management Professional Certification Exam Study Guide - PMBOK Seventh 7th Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the PMP Exam With Confidence - Complete Practice Tests With AnswersNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Managing Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)No EverandManaging Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (47)
- The Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsNo EverandThe Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (48)
- Crossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersNo EverandCrossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (19)
- Scrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementNo EverandScrum: Understanding Scrum at a Deeper Level and Mastering Agile Project ManagementNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Lean Six Sigma: A Practical Guide for Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma along with How It Can Be Integrated with Agile and ScrumNo EverandLean Six Sigma: A Practical Guide for Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma along with How It Can Be Integrated with Agile and ScrumNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (30)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialNo EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (114)
- Project Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessNo EverandProject Control Methods and Best Practices: Achieving Project SuccessAinda não há avaliações
- Agile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNo EverandAgile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (34)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamNo EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)