Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bio 101 Finals (Reviewer)
Enviado por
Gwen CaubangDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bio 101 Finals (Reviewer)
Enviado por
Gwen CaubangDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Animal Organ Systems (Part 1) How do animal structures well suited to specific functions come about?
Natural selection favors the most functional structures for a particular environment.
Which of the following ideas is not consistent with our understanding of animal structure?
-
Different animals contain fundamentally different categories of tissues.
Which of the following is true of interstitial fluid?
-
It provides for the exchange of materials between blood and body cells.
In a typical multicellular animal, the circulatory system interacts with various specialized surfaces in order to exchange materials with the exterior environment. Which of the following is not an example of such an exchange surface?
-
Muscle
Which statement best links the group of tissues known as connective tissue? A connective tissue will have
-
relatively few cells and a large amount of extracellular matrix.
If you gently twist your ear lobe it does not remain distorted because it contains
-
elastin fibers.
What holds bones together at joints?
-
Ligaments
Matrices of connective tissue include all of the following except
-
actin and myosin of muscle.
The functional unit of nervous tissue
-
neuron
Which of the following traits is characteristic of all types of muscle tissue?
-
cells that contain actin and myosin
Which of the following describes cardiac muscle?
-
striated and branched
The most significant single factor in preventing you from being able to run for a full 24 hours without stopping is the
-
lack of sustainable levels of cellular respiration
The body's automatic tendency to maintain a constant internal environment is termed
-
homeostasis.
How does positive feedback differ from negative feedback?
-
In positive feedback, the effector's response is in the same direction as the initiating stimulus rather than opposite to it.
Where is the thermostat of vertebrates located?
-
Hypothalamus
Animal Organ Systems (Part 2)
In which animal does blood flow from the pulmocutaneous circulation to the heart before circulating through the rest of the body? - Frog A human red blood cell in an artery of the left arm is on its way to deliver oxygen to a cell in the thumb. From this point in the artery, how many capillary beds must this red blood cell pass through before it returns to the left ventricle of the heart?
-
Two
Through how many capillary beds must a human red blood cell travel if it takes the shortest possible route from the right ventricle to the right atrium?
-
Two
Which sequence of blood flow can be observed in either a reptile or a mammal?
-
vena cava right atrium ventricle pulmonary circuit
Average blood pressure is lowest in which structure(s)?
-
venae cavae
Which of the following is correct for a blood pressure reading of 130/80? I. The systolic pressure is 130. II. The diastolic pressure is 80. III. The blood pressure during heart contraction is 80.
-
I and II only
What can be expected to happen to the blood pressure of a healthy individual during inhalation?
-
There will be a transient decrease in blood pressure.
If, during protein starvation, the osmotic pressure on the venous side of capillary beds drops below the hydrostatic pressure, then
-
fluids will tend to accumulate in tissues.
If a person were suffering from edema, which of the following conditions would help to reduce the accumulation of interstitial fluid?
-
decrease of the systolic blood pressure
Cyanide acts as a mitochondrial poison by blocking the final step in the electron transport chain. What will happen to human red blood cells if they are placed in an isotonic solution containing cyanide?
-
The cells will probably be unaffected.
high blood pressure - Hypertension defect in one or more of the valves of the heart - heart murmur plaque formation by infiltration of lipids into arterial smooth muscles - atherosclerosis Why is the velocity of blood flow the lowest in capillaries?
-
The total surface area of the capillaries is larger than the total surface area of the arterioles.
To adjust blood pressure independently in the capillaries of the gas-exchange surface and in the capillaries of the general body circulation, an organism would need a(n)
-
four-chambered heart.
Animal Organ Systems (Part 3)
Why is gas exchange more difficult for aquatic animals with gills than for terrestrial animals with lungs? Water is denser than air. Water contains much less O2 than air per unit volume.
Which of the following is an example of countercurrent exchange? the flow of water across the gills of a fish and that of blood within those gills
Tracheal systems for gas exchange are found in which organism? Insect
All of the following respiratory surfaces are associated with capillary beds except the tracheae of insects.
The blood level of which gas is most important in controlling human respiration rate? carbon dioxide
The Bohr shift on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve is produced by changes in pH.
How is most of the carbon dioxide transported by the blood in humans? bicarbonate ions in the plasma
When you hold your breath, which of the following blood gas changes first leads to the urge to breathe? rising CO2
In negative pressure breathing, inhalation results from contracting the diaphragm.
A decrease in the pH of human blood caused by exercise would increase heart rate.
Prokariotic and Eukariotic Cell Differences The cell has true nucleus, consisting of nuclear membrane and nucleoli e Which has larger ribosomes? Membrane enclosed organelles are absent p This is an external structure of a prokariotic cell that may protect pathogens from phagocytosis and it enable adherence to surfaces, prevent desiccation and may provide nutrients. Cells usually involves mitosis during cell division. Which statement is not correct: E Lysosomes and peroxisomes are absent in these cells. P Prokariotic cells have chloroplasts. Capsules or Glycocalyx E Prokaryotes are usually much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Yes
You cannot find cytoskeleton in these cells p
Vesicles are present in prokariotic and eukariotic cells. Yes
Bonds Quiz A chemical bond in which one atom loses an electron to form a positive ion and the other atom gains an electron to form a negative ion Ionic Bond
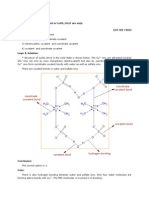
Hydrogen bond is a chemical bond formed between an electropositive atom (typically hydrogen) and a strongly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the bonding of water molecules in liquid and solid states, and are weaker than covalent and ionic bonds True
Covalent bond is used to describe the bonds in compounds that result from the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons True
A bond between 2 nonmetal atoms that have different electronegativities and therefore have unequal sharing of the bonding electron pair Polar Covalent Bond
A bond between 2 nonmetal atoms that have the same electronegativity and therefore have equal sharing of the bonding electron pair Non-Polar Covalent bond
Você também pode gostar
- Law On Mass MediaDocumento11 páginasLaw On Mass MediaGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Sing For A PennyfinalDocumento13 páginasSing For A PennyfinalGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Speaking Across The CurriculumDocumento264 páginasSpeaking Across The CurriculumGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Caubang Gwena Dale CaubangDocumento4 páginasCaubang Gwena Dale CaubangGwen Caubang100% (3)
- Charles Dickens - A Tale of Two CitiesDocumento670 páginasCharles Dickens - A Tale of Two CitiesnegrutzzzAinda não há avaliações
- The Digestive SystemDocumento5 páginasThe Digestive SystemGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- A Case Study On DwarfismDocumento6 páginasA Case Study On DwarfismGwen Caubang0% (1)
- Class LegacyDocumento2 páginasClass LegacyGwen Caubang100% (1)
- Continuing Rizal's WorksDocumento2 páginasContinuing Rizal's WorksGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Fallen Cyber AngelDocumento1 páginaFallen Cyber AngelGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Class HistoryDocumento3 páginasClass HistoryGwen Caubang100% (2)
- The Beauty of Her SuperiorityDocumento1 páginaThe Beauty of Her SuperiorityKent CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Facts About FacebookDocumento2 páginasFacts About FacebookGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Interesting FactsDocumento2 páginasInteresting FactsGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- The ArtDocumento1 páginaThe ArtGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Thank YouDocumento1 páginaThank YouGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Living Without YouDocumento1 páginaLiving Without YouGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Through The Signs of Times - TermPaper in SocioDocumento2 páginasReading Through The Signs of Times - TermPaper in SocioGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- My Life's QuotationDocumento2 páginasMy Life's QuotationGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- My MargauxDocumento2 páginasMy MargauxGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- Living Without YouDocumento1 páginaLiving Without YouGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- My Best BuddyDocumento2 páginasMy Best BuddyGwen CaubangAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Class 12 P Block Elements by Bharat PanchalDocumento34 páginasClass 12 P Block Elements by Bharat PanchalHardik Gaur100% (2)
- "Connecting Chemistry To Life": Grade 12 Learning Module First Quarter - First Semester 2020-2021Documento28 páginas"Connecting Chemistry To Life": Grade 12 Learning Module First Quarter - First Semester 2020-2021RJ AcepcionAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise - I: (Conceptual Problems)Documento3 páginasExercise - I: (Conceptual Problems)Siddharth RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Periodic Trends Resource 1Documento8 páginasPeriodic Trends Resource 1anitAinda não há avaliações
- Solution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryDocumento18 páginasSolution 1:: Class X Chapter 2 - Chemical Bonding ChemistryvikasAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic ReactionsDocumento10 páginasChapter 6 An Overview of Organic ReactionsRen Liew Jia QingAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - Page 2 of 5 - ICSEHELPDocumento9 páginasChemical Bonding ICSE Class-10 Concise Chemistry Selina Solutions - Page 2 of 5 - ICSEHELPlionelkenethAinda não há avaliações
- LESSON PLAN IN GRADE TrendsDocumento7 páginasLESSON PLAN IN GRADE TrendsPedrosa Nard100% (5)
- 1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 MainDocumento9 páginas1 s2.0 S0167732220370549 Maintuangsiong ShuAinda não há avaliações
- IIT-JAM Entrance Exam Practice QuestionsDocumento18 páginasIIT-JAM Entrance Exam Practice QuestionsRams ChanderAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction & The Chemistry of LifeDocumento39 páginasIntroduction & The Chemistry of Life林芸妡Ainda não há avaliações
- 10+2 Chem P-Block ElementsDocumento44 páginas10+2 Chem P-Block ElementsArjun PasrichaAinda não há avaliações
- Nagar Et Al 2023Documento34 páginasNagar Et Al 2023Ricardo Amorocho-ParraAinda não há avaliações
- 11th Standard Chemistry Materials GuideDocumento77 páginas11th Standard Chemistry Materials GuideSARMA PRESS SARMA PRESSAinda não há avaliações
- CH 11 PDFDocumento13 páginasCH 11 PDFkrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Exam QuestionsDocumento14 páginasScience Exam Questionsvedanth rajAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 6 Exercise QuestionsDocumento19 páginasICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 6 Exercise QuestionsLisa SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- JDLee Inorganic Chemistry Book PDF How ToDocumento28 páginasJDLee Inorganic Chemistry Book PDF How ToSunil Pandey35% (26)
- SCH 300 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF S - P - BLOCK ELEMENTS 2003Documento70 páginasSCH 300 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF S - P - BLOCK ELEMENTS 2003wafula kennedyAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry by Ashwani Ohri: Electronegativity and Miscl. QuestionsDocumento3 páginasChemistry by Ashwani Ohri: Electronegativity and Miscl. QuestionsSavvy GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- As Chemistry Notes All in OneDocumento230 páginasAs Chemistry Notes All in OneMildred MunatsiAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Chemistry and Periodic Table GuideDocumento10 páginasInorganic Chemistry and Periodic Table Guidedebraj sethi100% (1)
- Chemistry Major SyllabusDocumento27 páginasChemistry Major Syllabuseuroheritage20Ainda não há avaliações
- Polarity and Intermolecular Forces Lab SheetDocumento9 páginasPolarity and Intermolecular Forces Lab SheetLama AshiAinda não há avaliações
- CHE 413N Problem Set 1: Materials Science ConceptsDocumento1 páginaCHE 413N Problem Set 1: Materials Science ConceptsLouie G NavaltaAinda não há avaliações
- PORTFOLIO IN GENERAL CHEMISTRYDocumento31 páginasPORTFOLIO IN GENERAL CHEMISTRYAmira B TarusanAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 1Documento23 páginasGrade 11 Chemistry Study Guide Chapter 1Aung LayAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Bonding McqsDocumento6 páginasChemical Bonding McqsSumera SarwarAinda não há avaliações
- Electronegativity Elements PPT SlidesDocumento3 páginasElectronegativity Elements PPT SlidesAlejandro GuibaoAinda não há avaliações
- Acetic Acid C-O Bond Order TestDocumento8 páginasAcetic Acid C-O Bond Order Testd anjilappaAinda não há avaliações