Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Polygon Vocabulary. Triangle Vocabulary
Enviado por
Bill LauloDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Polygon Vocabulary. Triangle Vocabulary
Enviado por
Bill LauloDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Polygon Vocabulary. You will be given a set of geometry cards.
With your partner group these cards in any way you want to. One table at a time will be asked to come to the board and add to a list of the properties that an be used to group the cards. In geometry the shapes are usually named using the number of sides and the types of angles. See the h t S th sheets called ll d Geometry Vocabulary Bingo Geometry terms handout Geometry terms flash cards Make a list of the vocabulary you dont know or print the sheets from the blog and use them.
Triangle Vocabulary: Triangle Names Using Sides: No equal sides: Two equal sides: Three equal sides: Scalene triangle Isosceles triangle Equilateral triangle
Triangle Names Using Angles: All angles less than 90 One angle equals 90 One angle more than 90 Acute triangle Right triangle Obtuse triangle
Give the name for the following triangles
Bisectors?
If an object is divided in half we say it has been bisected. Describe the following: A
BD bi sec ts ABC segment BD bisects angle ABC
B D
FH is the perpendicular bisector of EG
See page 413 for extra practice
Polygon Properties.
If you dont want to write all the vocabulary you can print the sheet Quadrilateral Definitions which is on the blog.
Polygons are closed figures with three or more sides.
Vocabulary: Names of polygons:
4 sides 5 sides id 6 sides 7 sides 8 sides 9 sides 10 sides
Parallelogram A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
quadrilateral
pentagon hexagon heptagon
octagon
nonagon
decagon
Rectangle. A quadrilateral with four 900 angles.
Square. A quadrilateral with four 900 angles and four equal sides.
Rhombus. A quadrilateral with four equal sides.
Trapezoid. A quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides.
Kite.
A quadrilateral with two pairs of equal sides the pairs have different lengths the sides with equal lengths are next to each other.
Concave and convex Polygons
C
Concave polygons have at least one point going in.
A B
Convex polygons have all points going out
B C
Questions using properties of quadrilaterals:
See the sheet QuadrilateralComparisonChart to help with these questions.
A rectangle is a trapezoid. True or False Look at the second shape mentioned. What properties are needed for a polygon to be a trapezoid? Only one pair of parallel sides? Does a rectangle have only pair of parallel sides? No. Therefore: False because a rectangle does not have only one pair of parallel sides. OR False because a rectangle has more than one pair of parallel sides
A square is a rectangle. True or False Look at the second shape mentioned. What properties are needed for a polygon to be a rectangle? Four 900 angles? Does a square have four 900 angles? Yes. Therefore: True because a square has four 900 angles.
Is every square a rhombus. What properties are needed for a polygon to be a rhombus? A quadrilateral with four equal sides? Is a square a quadrilateral with four equal sides? Yes. Therefore: Yes because a square has four equal sides.
A parallelogram is a kite. True or False What properties are needed for a polygon to be a kite? two pairs of equal sides the pairs have different lengths the sides with equal lengths are next to each other.? Does a parallelogram have all those things? D ll l h ll th thi ? No. Therefore: False because a parallelogram does not have the equal sides next to each other.
Fill in this chart to help you practice these questions.
is always a A parallelogram square rectangle rhombus trapezoid kite
Parallel Lines Vocabulary.
F a ls e F a ls e
parallelogram
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
square
T ru e
T ru e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
rectangle
T ru e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
Corresponding Angles: Are in matching positions compared to the parallel lines and the transversal.
A and E d
G and B d
F and C d
rhombus
T ru e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
Alternate Interior Angles: Are between the parallel lines and diagonally opposite.
D and F
trapezoid
E and B
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
Alternate Exterior Angles: Are outside the parallel lines and diagonally opposite.
kite
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
F a ls e
H and C
A and G
See the sheet geometry concepts polygons for more practice.
Parallel Lines Vocabulary.
Sum of Angles Vocabulary.
Vertical Angles: Are opposite each other on a pair of crossed lines
Supplementary Angles: Have a sum of 180
A and B
G and E
F and H
A and B
C and D
Same side interior angles: Are between the parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal.
Complementary Angles: Have a sum of 90.
D and E
F and B
B and C
Same side exterior Angles: Are outside the parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal.
A and H
G and C
Lines Concepts. Lines have no end points they extend forever in two directions.
Intersection of Lines, Segments and Rays. The intersection of two lines is? A point draw a diagram if you are unclear.
The symbol is AB. In words - line AB.
Rays have one end point they extend forever in one direction.
The symbol is AB In words - ray AB. AB. AB
Segments have two end points they have ends in two directions.
The symbol is AB. In words - segment AB.
The intersection of two rays?
Plane Concepts. Planes have no edges they extend forever in two directions.
A point or a segment draw a diagram if you are unclear.
The symbol is P. In words - plane P.
How many points are needed to exactly define a plane? Three non-collinear points define a plane.
Intersections with Planes. What is the intersection of two planes? A line draw a diagram if you are unclear
What is the intersection of a line and a plane? A line or a point draw a diagram if you are unclear.
What is the intersection of three planes? A point or a line draw diagrams or give examples using the planes in the classroom.
Intersections Summary: Fill this chart in to help you with questions such what is the intersection of a line and a segment.
Line Line Ray Segment Plane
point
ray point
segment line point point
ray point i t
Ray
ray segment segment g point i point
Segment
segment segment point point
line
Plane
For extra practice see the sheet Geometry Concept Lines and Planes
Quadrilateral summary: After doing the Geometer Sketchpad project you should be able to fill in this chart on the properties of quadrilaterals.
Parallelogram Rectangle Rhombus Isosceles Trapezoid
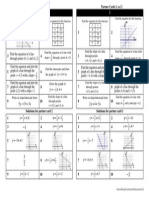
The sum of the angles in a triangle is 1800 The sum of the angles making up a straight line is 1800 Find the values for A and B
A B 115
Side properties
Opposite sides equal.
Adjacent pairs Adj t i sum 180 Opposite pairs are equal
Opposite sides equal.
All sides equal.
Non-parallel sides equal
Always start with something you are told and find another angle
Angle properties
All are 90
Adjacent pairs Base pairs sum 180 are equal Opposite pairs Non-base pairs are equal sum 180
32
B 115 180 B 65
The use the new angle to find another angle
Diagonal properties
Bisect each other
Bisect each other Same length
Bisect each other Bisect the angles Are perpendicular
Same length
65 A 32 180 A 83
See page 414 and sheet Triangle Questions for extra practice
For practice see the sheet GSP project: Quadrilateral and Polygon questions.
Z 110 180 z 70 xy 2x 70 180 2x 110
xy
y 32 78 180 y 110 180
y 70 x 70
2x 52 180 2x 128 x 64
Note that the angles may not be accurately drawn.
x 55
Calculations for Quadrilaterals based on the GSP project.
Parallel Lines Angle Calculations.
ABC 650 BAD 1050
length AC 14
ADC 650 length AB 20
In parallel lines a pair of angles will always be either congruent (equal) or supplementary (sum of 180)
ABC 1300 BCD 500 ADC 500 length DE 13 length M 11
length AC 20
EAB 320 0 ABE 58 BCD 640 ADC 1160 length AB 6
A and B are A and H are G and B are C and H are E and B are
congruent sup plementary congruent congruent congruent
Parallel Lines Angle Calculations.
A = 120 F = 60
Starting from the angles you are told you should be able to find every other angle. The angle may not be accurate on the diagram.
G = 120
Starting from the angles you are told you should be able to find every other angle. The angle may not be accurate on the diagram.
Similar Triangles:
1. Look at the triangle with the unknown. 2. Identify pairs of sides that have matching positions in the two triangles look at the angles to identify the positions. 3. Set up proportions with the unknown on the top.
x matches up with ? 12 4 matches up with ? 7
x 12 4 7
multiply both sides by 4
x
See page 414 and sheet Parallel Lines Questions for extra practice
48 7
See the Khan Academy video Similar Triangles
1. Look at the triangle with the unknown. 2. Identify pairs of sides that have matching positions in the two triangles look at the angles to identify the positions. 3. Set up proportions with the unknown on the top.
Calculate the sum of the angles in a polygon: Think of the polygons divided into triangle What is the connection between the number of sides and the number of triangles? The number of triangles equals =
P matches up with ? 14 6 matches up with ? 8
P 14 6 8
multiply both sides by 6
14 6 21 8 2
Each triangle equals 1800 Therefore what is the sum of all the angles in the polygon
The sum of angles in a polygon (number of sides 2) 180
Calculate the size of each interior angles in a regular polygon:
Think of the polygon divided into triangle You know how to find the sum of all the angles in the polygon Therefore how do we find the size of each interior angles in a regular polygon?
interior angle
(number of sides 2) 180 number of sides
Você também pode gostar
- Coordinate Algebra FormulasheetDocumento1 páginaCoordinate Algebra Formulasheetapi-322806742Ainda não há avaliações
- Teaching Work Sample 2020-3Documento45 páginasTeaching Work Sample 2020-3api-427644091Ainda não há avaliações
- J3 Solving Linear Inequalities in One VariableDocumento18 páginasJ3 Solving Linear Inequalities in One VariableWilma Arnedo SalinasAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ArithmeticDocumento5 páginasBasic ArithmeticKamil KAmikaziAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge International A & AS LevelDocumento37 páginasCambridge International A & AS LevelzsureshAinda não há avaliações
- Math 9 - Chapter 2Documento21 páginasMath 9 - Chapter 2yyanan1118Ainda não há avaliações
- GEOMETRY Chapter 1 Test ADocumento5 páginasGEOMETRY Chapter 1 Test AStephanie NielsenAinda não há avaliações
- Angle Relationships in CirclesDocumento7 páginasAngle Relationships in CirclesPristine CharlesAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry Chapter 1 TestDocumento3 páginasGeometry Chapter 1 TestWillSchulzeAinda não há avaliações
- Algebraic Expressions and IdentitiesDocumento21 páginasAlgebraic Expressions and IdentitiesPranav SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Questions: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics 0580Documento37 páginasPractice Questions: Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics 0580Hayaa KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Geometrical ShapesDocumento31 páginasGeometrical ShapesAlanie Grace Beron Trigo100% (1)
- 5.3 Year 9 Algebra Question and NotesDocumento20 páginas5.3 Year 9 Algebra Question and Notesprimalp6105Ainda não há avaliações
- Form 4 Chapter 5 Straight LineDocumento23 páginasForm 4 Chapter 5 Straight LineGaryBong100% (1)
- CC2 CH 6 TVDocumento122 páginasCC2 CH 6 TVngyncloud100% (2)
- Grade 9 Cirlce Geometry Unit Test For MeganDocumento5 páginasGrade 9 Cirlce Geometry Unit Test For Meganapi-2731665380% (3)
- GR 9-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21Documento7 páginasGR 9-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21George JeniferAinda não há avaliações
- Radical Unit CompiledDocumento27 páginasRadical Unit Compiledapi-494459090Ainda não há avaliações
- Revision Guide 2018Documento63 páginasRevision Guide 2018api-375411758100% (2)
- Percentage PDFDocumento0 páginaPercentage PDFAnkur Gupta0% (1)
- MathDocumento5 páginasMathkhae villanoAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra techniquesDocumento13 páginasAlgebra techniquesLorcanBautistaAinda não há avaliações
- 041 Maths PDFDocumento193 páginas041 Maths PDFAnsh SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Student Application DocumentsDocumento24 páginasStudent Application DocumentsAngelo PizarroAinda não há avaliações
- 9-Trigonometry and Area PDFDocumento4 páginas9-Trigonometry and Area PDFMark Abion ValladolidAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement and number conversions explainedDocumento1 páginaMeasurement and number conversions explainedGarden BeautyAinda não há avaliações
- 5/3/1 Overhead Press & Deadlift LogDocumento2 páginas5/3/1 Overhead Press & Deadlift LogffpedroAinda não há avaliações
- Flowchart and Paragraph ProofsDocumento25 páginasFlowchart and Paragraph ProofsVexegicAinda não há avaliações
- Find the Equation of a Straight LineDocumento18 páginasFind the Equation of a Straight LineJiaJia LauAinda não há avaliações
- 17 NCM7 2ed SB ANS Chapter 1 AnswersDocumento57 páginas17 NCM7 2ed SB ANS Chapter 1 AnswersAlex Dong Nyuk KimAinda não há avaliações
- Batdangthuc DDTHDocumento40 páginasBatdangthuc DDTHTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- Tenambit PS Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 T1Documento3 páginasTenambit PS Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 T1S TANCRED100% (1)
- Class 5 Scholarship Test QuestionsDocumento6 páginasClass 5 Scholarship Test QuestionssunnyiitkgpAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - Basic CryptarithmsDocumento12 páginas3 - Basic CryptarithmskevinAinda não há avaliações
- Set 5 AnswersDocumento80 páginasSet 5 AnswersThanmay ShajinAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 ReviewDocumento10 páginasChapter 7 Reviewales8806Ainda não há avaliações
- Bloom S Taxonomy of QuestionsDocumento20 páginasBloom S Taxonomy of QuestionsDivina Gracia Barrion Cuya100% (1)
- Unit 3 Quiz Review Triangle ProofsDocumento5 páginasUnit 3 Quiz Review Triangle ProofsDeyb KubyoAinda não há avaliações
- Maths - Positive and Negative Integers Chapter 12Documento36 páginasMaths - Positive and Negative Integers Chapter 12api-320846565Ainda não há avaliações
- Maths Extension 2 Assessment AnswersDocumento23 páginasMaths Extension 2 Assessment AnswersThanh NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Reducing The Fraction Answer: Example 2Documento8 páginasReducing The Fraction Answer: Example 2Dave100% (2)
- Grade 7 Fractions Test Draft 2Documento3 páginasGrade 7 Fractions Test Draft 2Keturah CathnottAinda não há avaliações
- Washington's Newburgh AddressDocumento3 páginasWashington's Newburgh AddressPhDJAinda não há avaliações
- Set-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsDocumento19 páginasSet-A Test Series: JEE Main Full Test - 4 Hints & Solutions MathematicsMohammed Aftab AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Polynomials:: X y X XyDocumento2 páginasPolynomials:: X y X XyIolanda FelixAinda não há avaliações
- Shore 2012 Year 10 Commerce YearlyDocumento13 páginasShore 2012 Year 10 Commerce YearlyMusab AlbarbariAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Probabilities Using a Spinner WorksheetDocumento1 páginaCalculating Probabilities Using a Spinner Worksheetwizard guy100% (1)
- 2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 3-5 PDFDocumento28 páginas2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 3-5 PDFWong Kah Kei JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 3 4Documento7 páginas10 Maths NcertSolutions Chapter 3 4kumar harshAinda não há avaliações
- Quadrilaterals - PropertiesDocumento20 páginasQuadrilaterals - PropertiesShraddha SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Fifth Grade - Individual Test #1: - Please Turn OverDocumento2 páginasFifth Grade - Individual Test #1: - Please Turn OverElnathan Delos ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Permutation and Combination PDFDocumento10 páginasPermutation and Combination PDFBinoy PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Operations With Whole NumbersDocumento5 páginasOperations With Whole NumbersIreen JamayoAinda não há avaliações
- Student Workbook - Unit 8 - Transformations InvestigationDocumento11 páginasStudent Workbook - Unit 8 - Transformations Investigationapi-232099327100% (2)
- Saxon Research 1Documento16 páginasSaxon Research 1api-478596695Ainda não há avaliações
- Area & Volume FormulasDocumento2 páginasArea & Volume FormulasMohammed AltafAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004Documento16 páginasMathematics (2 Unit) : Based On 1983 Syllabus, Written in 2004PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocumento39 páginasGeometry EOC Review PacketVale MejiaAinda não há avaliações
- Beginning Algebra - Basic Geometry2Documento22 páginasBeginning Algebra - Basic Geometry2Zarah Jane Rull NateAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry Study GuideDocumento6 páginasGeometry Study GuideMelodee PetersAinda não há avaliações
- Water ResourcesDocumento1 páginaWater ResourcesBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Propaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleDocumento4 páginasPropaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- AFC Outline Part 2Documento2 páginasAFC Outline Part 2Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Resources From EBSCO - WATERDocumento1 páginaResources From EBSCO - WATERBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Skills 3 Review 1Documento2 páginasBasic Skills 3 Review 1Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- ReviewCubes BasicSkills3Documento4 páginasReviewCubes BasicSkills3Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary: Simplifying Radical TermsDocumento5 páginasVocabulary: Simplifying Radical TermsBill Laulo100% (1)
- Sources For PovertyDocumento2 páginasSources For PovertyBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- AFC Outline Part 2Documento2 páginasAFC Outline Part 2Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Propaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleDocumento4 páginasPropaganda Poster Paragraph Organizer ExampleBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- AFC OutlineDocumento2 páginasAFC OutlineBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- ReviewCubes Ma8IntroToFunctions2Documento1 páginaReviewCubes Ma8IntroToFunctions2Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- AFC Outline IIDocumento2 páginasAFC Outline IIBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Radicals HomeworkDocumento1 páginaUnderstanding Radicals HomeworkBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Review Partner Cards Functions Part 2Documento1 páginaReview Partner Cards Functions Part 2Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Political Brief Sentence Frames 2014Documento2 páginasPolitical Brief Sentence Frames 2014Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- PPR IntroDocumento1 páginaPPR IntroBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Political Propaganda Poster 2014Documento1 páginaPolitical Propaganda Poster 2014Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Review Partner Cards 1-Intro To Functions Part 1Documento6 páginasReview Partner Cards 1-Intro To Functions Part 1Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Energy CalculationsDocumento18 páginasEnergy CalculationsBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Sample People Power Revolution EssayDocumento3 páginasSample People Power Revolution EssayBill Laulo85% (13)
- PPR ConclusionDocumento1 páginaPPR ConclusionBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- PPR Body P1Documento1 páginaPPR Body P1Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary Transitional Words Transitional PhrasesDocumento1 páginaVocabulary Transitional Words Transitional PhrasesBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- SI Organizing Sheet For PPR EssayDocumento2 páginasSI Organizing Sheet For PPR EssayBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- PPR Essay OrganizerDocumento5 páginasPPR Essay OrganizerBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Who Done It - Performance TaskDocumento2 páginasWho Done It - Performance TaskBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Intorduction Paragraph OrganizerDocumento5 páginasIntorduction Paragraph OrganizerBill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Functions Review Questions For Assessment Part 1Documento7 páginasIntroduction To Functions Review Questions For Assessment Part 1Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Adapted Ma8ConceptCheck#28Documento2 páginasAdapted Ma8ConceptCheck#28Bill LauloAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6 Polygon PacketDocumento6 páginasUnit 6 Polygon Packetfruity pebblesAinda não há avaliações
- Math G9: Quarter 3 - Week 2Documento21 páginasMath G9: Quarter 3 - Week 2Jaden BanzonAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Test 4.1-4.5 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function IndicatedDocumento3 páginasPractice Test 4.1-4.5 - NO CALC: Find The Value of The Trig Function Indicatedrust accAinda não há avaliações
- Geometric Inequalities: Hayk Sedrakyan Nairi SedrakyanDocumento454 páginasGeometric Inequalities: Hayk Sedrakyan Nairi SedrakyanEmmanuel Cornejo Apaza100% (2)
- TipsDocumento5 páginasTipsShivara ShivarajAinda não há avaliações
- Advance Math PDFDocumento2 páginasAdvance Math PDFhallelAinda não há avaliações
- Plane Geometry Practice Problems Part1 2015Documento11 páginasPlane Geometry Practice Problems Part1 2015mekeleweng100% (1)
- IMO Problems - 1959 PDFDocumento1 páginaIMO Problems - 1959 PDFOctavian TonicăAinda não há avaliações
- Congruence of Triangles 29Documento25 páginasCongruence of Triangles 29Lalit DudheriaAinda não há avaliações
- Angles of Elevation and Depression ExplainedDocumento15 páginasAngles of Elevation and Depression Explainedsherdan0% (2)
- Solid Mensuration Chapter 1Documento76 páginasSolid Mensuration Chapter 1216435964Ainda não há avaliações
- QUADRILETARALSDocumento9 páginasQUADRILETARALSMasuma M RemtullaAinda não há avaliações
- The Art of Problem Solving Vol 2 SolutionsDocumento188 páginasThe Art of Problem Solving Vol 2 SolutionsRahulKumar100% (4)
- Angles, Voltages and RadiansDocumento42 páginasAngles, Voltages and RadiansJoshua Anthony LimantoAinda não há avaliações
- Proves Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram (Rectangle, Rhombus, Square) M9Ge-Iiic-1Documento3 páginasProves Theorems On The Different Kinds of Parallelogram (Rectangle, Rhombus, Square) M9Ge-Iiic-1Lenlyn SalvadorAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Parallelograms, Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Their RelationshipsDocumento4 páginasProperties of Parallelograms, Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Their Relationshipsanushika sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Documento3 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7Maribel LuisAinda não há avaliações
- Shape Dictionary PDFDocumento47 páginasShape Dictionary PDFOrlando MotaAinda não há avaliações
- Mtap g9Documento4 páginasMtap g9Eric de GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- The Olympic Mathematical Marathon Grades 7-12 Vol.1 - George ApostolopoulosDocumento5 páginasThe Olympic Mathematical Marathon Grades 7-12 Vol.1 - George ApostolopoulosAndrei346Ainda não há avaliações
- Geometry WorksheetsDocumento11 páginasGeometry WorksheetsJassim MagallanesAinda não há avaliações
- HM Point PropertiesDocumento9 páginasHM Point PropertiesChaitanya GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Learn Octagon Construction MathDocumento16 páginasLearn Octagon Construction MathDr-Salah JaradatAinda não há avaliações
- Mensuration Formulas For CAT SSC CGL and Other Exams EditedDocumento8 páginasMensuration Formulas For CAT SSC CGL and Other Exams EditedRaj Kumar YadavAinda não há avaliações
- UCEED 2018 Final Answer Keys PDFDocumento1 páginaUCEED 2018 Final Answer Keys PDFAnshumanmodiAinda não há avaliações
- Bingo รูปทรงDocumento16 páginasBingo รูปทรงsatanghisoAinda não há avaliações
- Miracles of Pascal Triangle Revealed in 40 CharactersDocumento2 páginasMiracles of Pascal Triangle Revealed in 40 CharactersKrishna prasad EAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise 1: Find The Area of The Following TrapezoidDocumento11 páginasExercise 1: Find The Area of The Following TrapezoidChristian M. MortelAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge Primary Ready To Go Lessons For Maths Stage 6 Answers To Photocopiable PagesDocumento12 páginasCambridge Primary Ready To Go Lessons For Maths Stage 6 Answers To Photocopiable PagesRicco ChettAinda não há avaliações
- Mtap Questions Team OralsDocumento6 páginasMtap Questions Team OralsLinart Seprioto100% (1)