Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
IUPAC Nomenclature
Enviado por
Nitesha MadhuDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
IUPAC Nomenclature
Enviado por
Nitesha MadhuDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nomenclature of Alkanes, Alkene, and Alkynes
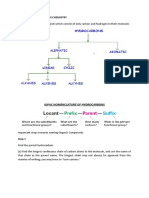
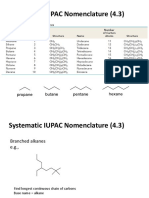
1. What type of molecule is it? If straight chain, go to number 2. If branched chain go to number 3. If cyclic go to number 4. 2. Straight-chain alkane are named by counting the number of C atoms in the backbone and adding the family name -ane (if only single bonds). If a double bond is present add the family name -ene. If a triple bond is present add the family name -yne (Refer to Table 12.3 for the list of parent names) When naming a straight chain alkene or alkyne, you must number the carbon that the double/triple bond is on. For example 2-heptene.
3. Branched chain hydrocarbons can be named in the following 4 steps. ! ! ! ! i. Name the main chain. Find the longest continuous chain of carbons, and name the chain according to the number of carbon atoms it contains. The longest chain may not be immediately obvious because it is not always written !on one line; you may have to turn corners to nd it. Always begin counting the number of carbons in the carbon backbone from an end carbon (primary carbon)
! ! ! !
II. Number the carbon atoms in the main chain. Begin at the end nearer the rst branch point for alkanes (or the end closest to a double/triple bond for alkenes and alkynes). You may begin numbering from the left or the right to see which direction will allow your substituents have the lowest number possible (always begin numbering from a primary carbon)
Nomenclature of Alkanes, Alkene, and Alkynes
! ! ! ! III. Identify the branching substituents, and number each according to its point of attachment to the main chain. (For a list of substituents refer to Table 12.4) -If there are two substituents on the same carbon, assign the same! number to both. There must always be as many numbers in the name as there are substituents. a. If the branched points have the different numbering from the left and the right, you want to number the chain based on the lowest number priority to the branched groups regardless of alphabetical priority. (For alkanes only) !
b. If the branched points have the same number numbering from the left and the right, you want to number the chain based on alphabetical priority of the branched groups. (For alkanes only)
! ! !
! ! !
c. For alkenes and alkynes, the branch point does not matter as much as the location of the double/ triple bonds. Remember to start numbering the carbon backbone at the end closest to the double triple bond, and then allow the substituents to have the lowest number possible.
! ! ! ! ! ! ! !
VI. Write the name as a single word, using hyphens to separate the numbers from the different prexes and commas to separate numbers if necessary. If two or more different substituent groups are present, cite them in alphabetical order. -If two or more identical substituents are present (doesn't need to be on the same carbon, the substituents can be on any carbon), use one of the prexes di-, tri-, tetra-, and so forth, ! but do not use these prexes for alphabetizing purposes. -Remember if there are double or triple bonds, the sufx changes to -ene or -yne, and you are required to number the carbon that the double/triple bond is on.
Nomenclature of Alkanes, Alkene, and Alkynes
4. Cycloalkanes are named by a straightforward extension of the rules for naming open-chain alkanes. In most cases, only two steps are needed. ! ! ! ! I. Use the cycloalkane name as the parent. Be sure to count only the number of carbons in the ring, not the longest chain of carbons! If there is only one substituent on the ring, it is not even necessary to assign a number because all ring positions are identical. If the ring contains a double bond it is called a cycloalkene, if it contains a triple bond, it is called a cycloralkyne
! !
! II. Identify and number the substituents. a. For cycloalkanes with only 2 substituents. Identify and number the substituents. Start numbering at the group that has alphabetical priority, and proceed around the ring in the direction that gives the second substituent the lower possible number.
b. For cycloalkanes with 3 or more substituents. You want to number the carbons in the ring based on the lowest number priority regardless of alphabetical priority.
Nomenclature of Alkanes, Alkene, and Alkynes
c. If you are naming a cycloalkene or cycloalkyne, the carbons with the double or triple bond is always numbered 1,2. You will number the carbons clockwise or counterclockwise to allow for the substituent to have the smallest number possible.
Você também pode gostar
- Naming Alkanes: Iupac Rules For Alkane NomenclatureDocumento4 páginasNaming Alkanes: Iupac Rules For Alkane NomenclatureRUZCHEMISTRYAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature 1Documento35 páginasNomenclature 1Anchal ChadhaAinda não há avaliações
- CA Lesson 2 AlkanesDocumento31 páginasCA Lesson 2 AlkanesAlbaraaAliAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Assignment 1Documento4 páginasChem Assignment 1Protikal GamerAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC RulesDocumento14 páginasIUPAC RulesIce BoyAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesDocumento9 páginasNomenclature Organic IUPAC RulesSkyla DavisAinda não há avaliações
- Naming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesDocumento34 páginasNaming of Alkanes, Alkenes and AlkynesArt Caresosa-FernandoAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Documento5 páginasAlkanes and Cycloalkanes: Hybridized and Tetrahedral, With All Bond Angles of 109.5°Alecs Elinor AmoguisAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento55 páginasOrganic ChemistryKim Taeha BTSAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC rules organic compound namingDocumento10 páginasIUPAC rules organic compound namingJuan Carlos SihotangAinda não há avaliações
- Classifying and Naming of Functional GroupsDocumento30 páginasClassifying and Naming of Functional GroupsAlthea Buenavista TayobongAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC rules for naming organic compoundsDocumento6 páginasIUPAC rules for naming organic compoundsK S RayuduAinda não há avaliações
- Alkyne Naming Rules: A Guide to Naming Alkyne Functional GroupsDocumento4 páginasAlkyne Naming Rules: A Guide to Naming Alkyne Functional GroupsDyaharra AgangAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 21Documento31 páginasCHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 21kush chaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocumento12 páginasOrganic Chemistry HydrocarbonsAlshaimaa SolimanAinda não há avaliações
- Alkane NomenclatureDocumento1 páginaAlkane NomenclatureRhian Geena VelasquezAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 - HydrocarbonsDocumento3 páginas1.2 - HydrocarbonskiranAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes 2Documento30 páginasAlkanes 2Jaymarie ZabateAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Alkanes NomenclatureDocumento29 páginas10 Alkanes Nomenclaturesomayya waliAinda não há avaliações
- Orgo Naming RulesDocumento7 páginasOrgo Naming Ruleskirtmartinreyes14Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Functional Groups in Organic ChemistryDocumento115 páginasChapter 1 Functional Groups in Organic ChemistryZedo AnberbirAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes - Naming Organic MoleculesDocumento18 páginasAlkanes - Naming Organic MoleculesinayahviAinda não há avaliações
- 14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamDocumento21 páginas14-04-20 - Nomenclature - Alkanes, AlkenesmamArthiAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Rules For Alkane NomenclatureDocumento8 páginasIUPAC Rules For Alkane NomenclatureLance Eubert MarcellanaAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocumento11 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesPablo KamgneAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC organic chemistry nomenclatureDocumento26 páginasIUPAC organic chemistry nomenclatureYa seen khanAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry Compound NamingDocumento35 páginasOrganic Chemistry Compound NamingRENE N. RAMILOAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocumento19 páginasAlkanes and CycloalkanesHanna GalatiAinda não há avaliações
- Carbon-Electronegative BondsDocumento36 páginasCarbon-Electronegative BondsShalou Beth FlorendoAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryDocumento21 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryKanika BakhaiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Organic ChemistryMoya-Dean Walcott100% (2)
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesDocumento17 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Basic PrinciplesSUBHENDU5174124Ainda não há avaliações
- CHEM 105L bioChemistry LABDocumento24 páginasCHEM 105L bioChemistry LABFaith BernadetteAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Rules for Naming Alkanes, Cycloalkanes, Alkenes and Other Organic CompoundsDocumento16 páginasIUPAC Rules for Naming Alkanes, Cycloalkanes, Alkenes and Other Organic CompoundsfebriAinda não há avaliações
- EGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALDocumento75 páginasEGF2042 Chapter 2 (Naming Organic Compound) ORIGINALhanis izzatiAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaDocumento63 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - WikipediaAnonymous BB82lXF0m2Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Study Guide PDFDocumento57 páginasChapter 4 Study Guide PDFkAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsDocumento40 páginas1.2 Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsElina NaberezhnovaAinda não há avaliações
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryDocumento10 páginasIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic ChemistryYashwanth SrinivasaAinda não há avaliações
- 02 - Detailed Naming Hydrocarbons PowerpointDocumento24 páginas02 - Detailed Naming Hydrocarbons Powerpoint1jerryzhouAinda não há avaliações
- AlkanesDocumento61 páginasAlkanesFrancis LaoAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature 02Documento8 páginasNomenclature 02bbrajenAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrocarbons: ObjectivesDocumento29 páginasHydrocarbons: Objectivesjohn ryan piolAinda não há avaliações
- Nomenclature of HydrocarbonsDocumento7 páginasNomenclature of HydrocarbonsIsioma MmeniAinda não há avaliações
- Systematic IUPAC Nomenclature (4.3)Documento22 páginasSystematic IUPAC Nomenclature (4.3)Jennifer PatrickAinda não há avaliações
- Iupac Nomenclature OrganicDocumento14 páginasIupac Nomenclature Organicaj619624Ainda não há avaliações
- A. Alkana (Parafin) : 1.B Reaksi Kimia AlkanaDocumento16 páginasA. Alkana (Parafin) : 1.B Reaksi Kimia Alkanamaria stefaniAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes 2Documento25 páginasAlkanes 2Esther OgelekaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 1814 Review SheetsDocumento14 páginasChem 1814 Review SheetsLinda Appiah OfosuheneAinda não há avaliações
- Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2Documento57 páginasAlkanes and Cycloalkanes - PPTX 2eysabelagwenAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento11 páginasOrganic Chemistryapi-546066323Ainda não há avaliações
- An Shul Article 2Documento9 páginasAn Shul Article 2Education via Blogging NSS IITmAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 10 Organic ChemistryDocumento51 páginasUNIT 10 Organic ChemistryTristan PereyAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocumento4 páginasOrganic Chemistry HydrocarbonsRizza Mae CaninoAinda não há avaliações
- AlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio StudentsDocumento23 páginasAlkenesAlkynes-nomenclature-and-properties-for - College-Bio Studentshixevab276Ainda não há avaliações
- Saturated HydrocarbonsDocumento12 páginasSaturated HydrocarbonsRielle JaliqueAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento46 páginasUntitled양우경Ainda não há avaliações
- Triazoles 1, 2, 4No EverandTriazoles 1, 2, 4Carroll TempleAinda não há avaliações
- Concerning Amines: Their Properties, Preparation and ReactionsNo EverandConcerning Amines: Their Properties, Preparation and ReactionsNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (2)
- Day1 - 07 - Gorkem Yusuf Topcu - Energy Market Regulatory AuthorityDocumento29 páginasDay1 - 07 - Gorkem Yusuf Topcu - Energy Market Regulatory Authorityaegean227Ainda não há avaliações
- SPE-97856-MS Unlocking The Value in West Sak Heavy Oil - Field DevelopmentDocumento14 páginasSPE-97856-MS Unlocking The Value in West Sak Heavy Oil - Field DevelopmentGilbert OmittaAinda não há avaliações
- Exploration PDFDocumento19 páginasExploration PDFMarilyn Garzón AguirreAinda não há avaliações
- E CombusDocumento2 páginasE CombusalexAinda não há avaliações
- QatarEnergy Annual Review 2020 - EnglishDocumento174 páginasQatarEnergy Annual Review 2020 - Englishnunya businessAinda não há avaliações
- Garp Erp Study NotesDocumento71 páginasGarp Erp Study Notesjohn smith100% (2)
- Locations & Operators: April 24, 2015 A Weekly Report of Working LocationsDocumento18 páginasLocations & Operators: April 24, 2015 A Weekly Report of Working LocationsmarkanapierAinda não há avaliações
- Edible Oil Import Feb-2020Documento5 páginasEdible Oil Import Feb-2020Usman MahmoodAinda não há avaliações
- SUNISO - Cross Reference TableDocumento2 páginasSUNISO - Cross Reference TableMassimiliano Vola100% (2)
- British Petroleum Exam For Geologist StudentDocumento6 páginasBritish Petroleum Exam For Geologist StudentShakeel AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Box Color Guide: Motorcycle Engine OilDocumento2 páginasBox Color Guide: Motorcycle Engine OilAndi Septian Eka SetiawanAinda não há avaliações
- Antoine Coefficient TableDocumento14 páginasAntoine Coefficient Tablenafaluck0% (1)
- Angola Concessions PDFDocumento1 páginaAngola Concessions PDFPedro G Morais100% (1)
- Q Names1 PDFDocumento4 páginasQ Names1 PDFClement Charles100% (1)
- Olefix UOP PDFDocumento2 páginasOlefix UOP PDFEmadAinda não há avaliações
- CV - Id.enDocumento4 páginasCV - Id.enNandaKresnaApriantoAinda não há avaliações
- Two (2) Usa Sellers Oil & Gas - Updated May 2022Documento4 páginasTwo (2) Usa Sellers Oil & Gas - Updated May 2022AlanAinda não há avaliações
- Project Reference ArmaGelDocumento2 páginasProject Reference ArmaGelĐạo NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 30 Science Chapter 5 Coal and PetroleumDocumento3 páginasNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 30 Science Chapter 5 Coal and PetroleumSamarth KatariyaAinda não há avaliações
- Natural GasDocumento86 páginasNatural GasNikhil TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 1 Importance of PetrochemicalDocumento40 páginasCHAPTER 1 Importance of PetrochemicalSyahmiAinda não há avaliações
- Palm Oil Specifications GuideDocumento1 páginaPalm Oil Specifications GuideAndi crasherAinda não há avaliações
- Enhanced Oil Recovery MethodsDocumento14 páginasEnhanced Oil Recovery MethodsSuleiman BaruniAinda não há avaliações
- Guyana University final exam petroleum geologyDocumento12 páginasGuyana University final exam petroleum geologyswf svAinda não há avaliações
- Coal and CokeDocumento2 páginasCoal and Cokeapi-3764139100% (3)
- API Gravity PDFDocumento225 páginasAPI Gravity PDFAnurag RayAinda não há avaliações
- First and Last Names of Over 40 IndividualsDocumento45 páginasFirst and Last Names of Over 40 IndividualsTamal SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview of The World LNG Market and Canada's Potential For Exports of LNGDocumento44 páginasAn Overview of The World LNG Market and Canada's Potential For Exports of LNGJoel Lim Min SheuAinda não há avaliações
- BusinessAssociate CodesDocumento1.014 páginasBusinessAssociate Codeselaine gamerAinda não há avaliações
- Hydroulics Calculation and Gas PropertiesDocumento3 páginasHydroulics Calculation and Gas PropertiesSteve WanAinda não há avaliações