Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Question Bank, BE
Enviado por
KaniniAnbazhaganDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Question Bank, BE
Enviado por
KaniniAnbazhaganDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
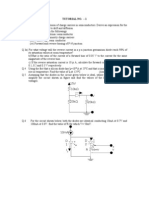
Write the definition of Diode? Explain the V-I characteristics of PN junction diode? Explain forward and reverse biasing of PN junction diode with proper diagram? Explain the Zener breakdown and Avalanche mechanism? Write down the effect of temperature the reverse current?
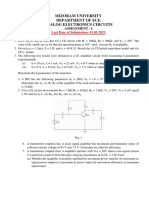
6. A Silicon diode has a saturation current of 1pA at 20oC. Find Diode bias voltage when diode current is 3mA. Diode bias current when the temperature is 100OC assuming the diode voltage to be constant. 7. Find the static and dynamic resistance of a p-n junction germanium diode if the temperature is 27OC and IO=1A for an applied forward bias of 0.2V. 8. Explain the transistor operation of PNP and NPN? 9. Write down the input and output characteristics of Common emitter and common base configuration? 10. A Ge transistor with = 100 has base-to-collector leakage current of 5 A. If the transistor is connected in common-emitter operation, find the collector current for base current (a) 0 and (b) 40 A. 11. In a transistor circuit, when the base current is increased from 0.32 mA to 0.48 mA, the emitter current increases from 15 mA to 20 mA. Find ac and ac values. 12. A transistor with = 0.98 and ICBO = 5 A has IB = 100 A. Find IC and IE. 13. Explain the operation of LED? 14. Write down the application of LED? 15. Explain the VI characteristics of Zener diode? 16. In a zener voltage regulator if Vz=10V, Rs=1K, RL-2K. If the input voltage Vin varies from 22 to 40 V, find the maximum and minimum values of zener current. 17. Write down the advantage , disadvantage of self bias and fixed bias? 18. For a fixed bias circuit using Si transistor, RB = 500 k, RC = 2 k, VCC = 15 V, ICBO = 20 A and = 70. Find the Q-point collector current ICQ. 19. For a fixed bias circuit, VCC = 12 V and RC = 4 k. The Ge transistor used is characterized by = 50, ICEO = 0 and VCE sat = 0.2 V. Find the value of RB that just results in saturation. 20. A fixed bias circuit has VCC = 20 V, RC = 5 k, RE = 4 k and RB = 300 k. The Si transistor has ICBO = 0 and = 50. Find ICQ and VCEQ. 21. Define OPAMP? 22. Write down the characteristics of an ideal diode? 23. Define the following: Slew rate, CMRR, input offset current, input bias current.
24. Derive the gain of Inverting and Non inverting amplifier? 25. Derive output voltage of the Differentiator and Integrator apamp ? 26. Design an OPAMP circuit such that output is given by vo=(0.5v1+0.75v2) where v1 and v2 are input voltages. Choose RF=10K 27. Explain the block diagram of Communication system? 28. Write down the advantage, disadvantage, application of optical fiber and co-axial cable. 29. Explain the need for modulation? 30. Prove that 66.67% of total power is wasted in transmitting carrier signal ? 31. An audio signal 10sin (21000t) amplitude modulates a carrier of 40sin (22000t). Find i. Modulation index ii. Sideband frequencies. iii. Bandwidth. iv. Total power delivered if RL = 1K. v. Amplitude of each side band components. 32. The antenna current of an AM transmitter is 8A when only carrier is transmitted, but increases to 8.93A when carrier is modulated by a single sine wave. Find the percentage modulation. Determine the antenna current when the depth of modulation changes to 0.8A. 33. A certain transmitter radiates 9KW with carrier unmodulated and 10.125KW when carrier is sinusoidally modulated. Calculate modulation index. If another sine wave corresponding to 40% modulation is transmitted simultaneously, determine the total power radiated. 34. Write the application of SSB,DSB and VSB? 35. Write down the advantage of VSB over SSB and DSB? 36. Given a FM equation VFM(t) = 10 cos [ 2 108t + 5 sin(2 15000t) ] , Calculate i. Carrier frequency. ii. Modulating frequency. iii. Frequency deviation. iv. Bandwidth using Carsons rule.
Você também pode gostar
- Edc - Assignment Questions - NbaDocumento5 páginasEdc - Assignment Questions - Nbagunda manasaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 EE6303 ReviewquestionsDocumento4 páginas4 EE6303 ReviewquestionsKapildev KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocumento5 páginasModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantAinda não há avaliações
- PDC 1Documento3 páginasPDC 1Sravya LakshmiAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento12 páginasElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Sheet Analog ElectronicsDocumento7 páginasTutorial Sheet Analog ElectronicsPraney KalraAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics RefresherDocumento2 páginasElectronics RefresherPaolo Steven PolintanAinda não há avaliações
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocumento19 páginas4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrAinda não há avaliações
- E-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMDocumento6 páginasE-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMkartik.doye2005Ainda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics 102409025108 1Documento7 páginasPower Electronics 102409025108 1sushil4056Ainda não há avaliações
- PDC Assignment IDocumento4 páginasPDC Assignment IathomeAinda não há avaliações
- Ies 11980 Only BJTDocumento7 páginasIes 11980 Only BJTGaurav ShrimaliAinda não há avaliações
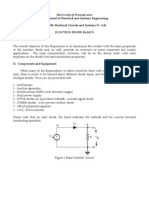
- Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab Junction Diode Basics I. PurposeDocumento6 páginasDepartment of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab Junction Diode Basics I. Purposekstu1112Ainda não há avaliações
- EdcqbDocumento10 páginasEdcqbPranveer Singh PariharAinda não há avaliações
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocumento6 páginasEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Sem 3 Module 3Documento5 páginasSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Edc Unit Wise QuestionsDocumento2 páginasEdc Unit Wise QuestionsMuppala Chiranjeevi0% (1)
- Assignment I PDFDocumento1 páginaAssignment I PDFRam SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Principle of Electronics EnggDocumento47 páginasPrinciple of Electronics EnggNilabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices & Circuits SyllabusDocumento4 páginasElectronic Devices & Circuits SyllabusShareef KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADocumento8 páginasElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanAinda não há avaliações
- Semiconductor Devices - Sample QuestionsDocumento3 páginasSemiconductor Devices - Sample QuestionsJohn Idun EssumanAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUDocumento11 páginasBasic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUShrishail Bhat100% (1)
- Assignment 01Documento6 páginasAssignment 01Z S PlaysAinda não há avaliações
- Ece 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Documento2 páginasEce 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Deepanshu SehgalAinda não há avaliações
- EN1802 Tutorial 2 PDFDocumento4 páginasEN1802 Tutorial 2 PDFHashan ErandaAinda não há avaliações
- PTEE-7402 April-2021Documento2 páginasPTEE-7402 April-2021imman46920Ainda não há avaliações
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Documento45 páginasMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250Ainda não há avaliações
- Sem 3 Module 1Documento3 páginasSem 3 Module 1fczeroAinda não há avaliações
- Pe Course File 9 198Documento190 páginasPe Course File 9 198Dr ADITYA VORAAinda não há avaliações
- EDS - Question BankDocumento21 páginasEDS - Question BankAnkita PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Documento7 páginasPower Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Herbert DeepakAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank AECDocumento5 páginasQuestion Bank AECChandra SekharAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSDocumento1 páginaQuestion Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSShubhang CharantimathAinda não há avaliações
- Edctutorial BctII IDocumento3 páginasEdctutorial BctII INeelesh MrzAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics AssignmentsDocumento7 páginasElectronics AssignmentsSoumyaranjan PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulse Digital CircuitsDocumento5 páginasPulse Digital CircuitsnaveenAinda não há avaliações
- TB Chapter33Documento18 páginasTB Chapter33qvrlenarasegtAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank - Principles of ElectronicsDocumento13 páginasQuestion Bank - Principles of ElectronicsADDELYN CYNTHIA ANAK TONYAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 13Documento2 páginasTutorial 13Aayush RastogiAinda não há avaliações
- 電子學 (一) 許恒壽Documento12 páginas電子學 (一) 許恒壽qw3rtytr3wqAinda não há avaliações
- EC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsDocumento6 páginasEC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsAshish KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices Model Question PapersDocumento2 páginasElectronic Devices Model Question Papersk_kunarajAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical 02Documento10 páginasElectrical 02Hary Kriz33% (3)
- ES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 1: NPN Common-Emitter AmplifierDocumento7 páginasES330 Laboratory Experiment No. 1: NPN Common-Emitter AmplifierAhmed SalehAinda não há avaliações
- EdcDocumento3 páginasEdcSandy RonaldoAinda não há avaliações
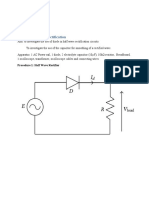
- Experiment 7: Procedure 1: Half Wave RectifierDocumento4 páginasExperiment 7: Procedure 1: Half Wave Rectifiertashy richardsAinda não há avaliações
- EDC - Question BankDocumento7 páginasEDC - Question BankSwaum KisAinda não há avaliações
- 9A02405 Analog Electronic CircuitsDocumento4 páginas9A02405 Analog Electronic CircuitssivabharathamurthyAinda não há avaliações
- EE Important QuestionsDocumento6 páginasEE Important QuestionsLE-1 BhargaviAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics: June/July, 2010Documento7 páginasElectronics: June/July, 2010Prasad C MAinda não há avaliações
- Special ExamDocumento4 páginasSpecial ExamPerol YuuzouAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocumento19 páginasAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarAinda não há avaliações
- Eee 2202 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasEee 2202 AssignmentEnock OmariAinda não há avaliações
- 22ESC141 Basic ElectronicsDocumento2 páginas22ESC141 Basic Electronicszwq4rrkkq8Ainda não há avaliações
- Subject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Documento4 páginasSubject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Mihir JainAinda não há avaliações
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1No EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsNo EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Datasheet PDFDocumento2 páginasDatasheet PDFBarkat HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Rohini 74049417647Documento5 páginasRohini 74049417647Aakash SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Niko - p07d03lvgDocumento5 páginasNiko - p07d03lvgTininha MachadoAinda não há avaliações
- Guided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 30 Q. (3 M (-1) )Documento8 páginasGuided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 30 Q. (3 M (-1) )Ice WaterAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento3 páginasElectronic Devices and CircuitsShaik Faizan 23Ainda não há avaliações
- CatalogueDocumento29 páginasCatalogueAnonymous CPmZqMAinda não há avaliações
- GE Transistor Manual 6th 1962 PDFDocumento465 páginasGE Transistor Manual 6th 1962 PDFjgrisi065757100% (1)
- Abraham 1986Documento16 páginasAbraham 1986vndjndfvAinda não há avaliações
- Process Variation of MOSFET and MESFETDocumento1 páginaProcess Variation of MOSFET and MESFETArvindGovaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 13Documento4 páginasExperiment 13Karla Alberto TorresAinda não há avaliações
- Re Transistor ModelDocumento15 páginasRe Transistor ModelUmar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 27 - Pocket Money ProjectsDocumento77 páginasChapter 27 - Pocket Money ProjectsRaymond BonehillAinda não há avaliações
- How To Repair Dell E153Fpc LCD Monitor With Display Shutdown ProblemDocumento7 páginasHow To Repair Dell E153Fpc LCD Monitor With Display Shutdown ProblemRamiro Prieto0% (1)
- Module 1 - Computer ConceptsDocumento6 páginasModule 1 - Computer ConceptsJong Suk LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Sensor Pendeteksi Gempa Atau Pemeriksa ArusDocumento17 páginasSensor Pendeteksi Gempa Atau Pemeriksa ArusBianAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Field Effect Transistors (FETs)Documento39 páginas2 Field Effect Transistors (FETs)July ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- ElectronicDocumento214 páginasElectronicprithvirajAinda não há avaliações
- TV Radar PJDocumento55 páginasTV Radar PJShiv Narayan AhirwarAinda não há avaliações
- SMD Power Mosfet Transistor (N-Channel)Documento7 páginasSMD Power Mosfet Transistor (N-Channel)Rodolfo LaraAinda não há avaliações
- Us4691336 PDFDocumento9 páginasUs4691336 PDFhernandez.josedomingo6804Ainda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocumento23 páginasBasic Electronic ComponentsNilesh Jadhav100% (4)
- Yaesu DMU-2000 ServDocumento21 páginasYaesu DMU-2000 ServlarsAinda não há avaliações
- D009 C3L A1 9493Documento4 páginasD009 C3L A1 9493patrikosgnachAinda não há avaliações
- Vtu Lab Manuals VlsiDocumento79 páginasVtu Lab Manuals VlsisrikanthuasAinda não há avaliações
- NanoData ReportDocumento203 páginasNanoData ReportGary Ryan DonovanAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics and Instrumentation Syla PDFDocumento134 páginasElectronics and Instrumentation Syla PDFchetanAinda não há avaliações
- 40A Power Supply UnitDocumento6 páginas40A Power Supply Unitrsira2001100% (3)
- Subj:Digital Design: R K TiwaryDocumento31 páginasSubj:Digital Design: R K Tiwaryrktiwary256034Ainda não há avaliações
- Infineon TLE8110EE DS v01!03!01 enDocumento74 páginasInfineon TLE8110EE DS v01!03!01 enEduardo FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - Vi Field Effect TransistorDocumento16 páginasUnit - Vi Field Effect TransistorBhavaniPrasadAinda não há avaliações