Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Science Year 5 - Unit 2 Survival of The Species (Notes and Exercise)
Enviado por
kheshin80Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Science Year 5 - Unit 2 Survival of The Species (Notes and Exercise)
Enviado por
kheshin80Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
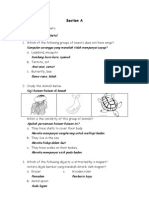
Science Year 5 Unit 2 Survival of the Species
Mammoths and dinosaurs are examples of animals that no longer exist. Is it because of their gigantic size? Elephants look similar to mammoths. Why are they still surviving? Rafflesia is an example of a plant species found in Malaysia that is facing extinction. Why? How do animals and plants ensure the survival of their species? 1. Animals take care of their eggs and young to ensure the survival of their species. 2. Plants disperse seeds and fruits to ensure survival of their species. 3. Shortage of food can cause extinction of species. How the animals take care of their eggs and young: 1. Animals that give birth to their young nurture and care for their babies. 2. Their mothers suckle their young 3. They have their own ways to protect their young from danger. Examples: Cow- protects its young with its horns.
Cat fights off attackers with claws
Kangaroo carries young in its pouch
Whale- stays to its calves
4. All birds such as sparros , eagle and ducks reproduce by laying eggs. 5. This is what a typical bird will do to ensure the safety of its eggs and young. 6. Some animals lay large numbers of eggs in selected spots which are safe and cannot be detected by predators. 7. Some animals take care of theirs eggs while others donot. Example: Turtle lays hundreds of eggs at night and buries the eggs in the sand.
Snake it will coils round the eggs
Butterfly lays the eggs on the undersides of leaves
Survival of plants Seed and fruit dispersal: 1. plants disperse their seeds and fruits by scattering them far away from the parent plants. 2. Dispersal of fruits and seeds (a )reduces competition between the parent plant and the seeds (b ) reduces overcrowding (c ) enables seeds to grow healthily (d) provides opportunities to spread the species to new places 3.some plants disperse their fruits that contain seeds while others disperse The seeds themselves Various ways plants disperse their seeds and fruits 1. The seeds and fruits of plants have special characteristics which help the agent to disperse them. 2. Seeds and fruits can be dispersed by *water *wind *animals *an explosive mechanism Example: water
wind
Animals
an explosive mechanism
Exercise: To classify the plants in the column: Pong-pong fruit rambutan angsana balsam durian coconut lotus guava mangrove tree rubber fruit Water Wind Animals
ladies finger mimosa meranti
an explosive mechanism
Você também pode gostar
- Circle The Correct Answer Diagram Shows An Apparatus Used in Science Room. 2. Diagram Shows Three Types of AnimalDocumento17 páginasCircle The Correct Answer Diagram Shows An Apparatus Used in Science Room. 2. Diagram Shows Three Types of AnimalNorhafizah AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- UPT Matematik Tahun 4 K1 MEI 2019Documento14 páginasUPT Matematik Tahun 4 K1 MEI 2019skdkbpAinda não há avaliações
- Monthly Year 5 Science 2014Documento12 páginasMonthly Year 5 Science 2014Ksnithiya GthavanAinda não há avaliações
- Plant ReproductionDocumento5 páginasPlant ReproductionFaizan ElahiAinda não há avaliações
- End-Of-Year Test: Name: - Class: - DateDocumento15 páginasEnd-Of-Year Test: Name: - Class: - Dateniezma2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Soalan Matematik Tahun5 Kertas1sekolah Rendah Ujian MarchDocumento6 páginasSoalan Matematik Tahun5 Kertas1sekolah Rendah Ujian Marchkeris_keras95% (22)
- Classifying Living Things: The Five KingdomsDocumento17 páginasClassifying Living Things: The Five KingdomsMuhammad MuneebAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Science NotesDocumento16 páginasIntegrated Science NotesannmarieAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Sains - Year 5 (Module 1)Documento19 páginasSoalan Sains - Year 5 (Module 1)ZAZOLNIZAM BIN ZAKARIA67% (3)
- Plant Needs & Microorganisms IdentificationDocumento17 páginasPlant Needs & Microorganisms IdentificationValar RamanAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4Documento3 páginasSoalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4ika_nikan0% (1)
- Name:: Read The Questions Carefully and Choose The BEST Answer. Then Circle in Your Question Paper and Answer SheetDocumento22 páginasName:: Read The Questions Carefully and Choose The BEST Answer. Then Circle in Your Question Paper and Answer SheetNORAIHAN BINTI JAMALI MoeAinda não há avaliações
- Breathing Organs of Animals DiagramDocumento7 páginasBreathing Organs of Animals DiagramDevaky_Dealish_182Ainda não há avaliações
- Science Year 4 Paper 1Documento15 páginasScience Year 4 Paper 1NormaAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics TEST 2, Year 2, August 2010Documento6 páginasMathematics TEST 2, Year 2, August 2010norizan bt awang100% (2)
- Science Quarter 2 Module 5Documento13 páginasScience Quarter 2 Module 5Zerreitug Elppa100% (2)
- Topical Exercises Year 4: Chapter 1: Investigating Living ThingsDocumento6 páginasTopical Exercises Year 4: Chapter 1: Investigating Living ThingsHusna Zakaria80% (5)
- Exam Sains Final THN 4Documento17 páginasExam Sains Final THN 4mohdyusAinda não há avaliações
- Question 1 To 5. Read The Passage and Circle The Correct AnswerDocumento5 páginasQuestion 1 To 5. Read The Passage and Circle The Correct AnswerdzulfikharAinda não há avaliações
- FINAL YEAR SCIENCE EXAMDocumento18 páginasFINAL YEAR SCIENCE EXAMLin100% (1)
- Soalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 4Documento20 páginasSoalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 4sasauball75% (4)
- Bi 1 Tahun 3 PatDocumento7 páginasBi 1 Tahun 3 PatRafik ArifAinda não há avaliações
- Sains THN 3-Section ADocumento13 páginasSains THN 3-Section AMohd Izwan OthmanAinda não há avaliações
- Soalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 2Documento27 páginasSoalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 2sasauball75% (8)
- Year 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWDocumento9 páginasYear 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWMariayee PerumalAinda não há avaliações
- Ujian Bulanan Ogos Matematik Tahun 4 Kertas 1Documento7 páginasUjian Bulanan Ogos Matematik Tahun 4 Kertas 1Anbu Arasu100% (1)
- Science Year 3Documento3 páginasScience Year 3Long En LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Science Year 5 Unit 2 Survival of The Species Notes and ExerciseDocumento4 páginasScience Year 5 Unit 2 Survival of The Species Notes and ExerciseRiaz MohideenAinda não há avaliações
- Year 3scienceDocumento10 páginasYear 3sciencenshyAinda não há avaliações
- Matematik Kertas 2 Tahun 3 Math Paper 2 Year 3Documento11 páginasMatematik Kertas 2 Tahun 3 Math Paper 2 Year 3kusingbarAinda não há avaliações
- SN T3 Final ExamDocumento11 páginasSN T3 Final ExamZULFAHAMI ZAinda não há avaliações
- Ujian Sains Tingkatan 2Documento15 páginasUjian Sains Tingkatan 2SITI ZAIDAH AHMAD75% (12)
- Modul Sains Tahun 4 PKP (DLP)Documento15 páginasModul Sains Tahun 4 PKP (DLP)why da100% (1)
- Soalan Matematik Penilaian 3 Tahun 2Documento5 páginasSoalan Matematik Penilaian 3 Tahun 2norizan bt awang83% (6)
- Science Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYDocumento1 páginaScience Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYNrhfzhjrzfzAinda não há avaliações
- Mind Map Science Upsr Year 4Documento37 páginasMind Map Science Upsr Year 4ramziby88% (25)
- Soalan Sains Tahun 4 BHG A B Dan JawapanDocumento15 páginasSoalan Sains Tahun 4 BHG A B Dan Jawapanmytaste056119100% (2)
- Tahun5 Kertas2Documento4 páginasTahun5 Kertas2keris_keras100% (2)
- Soalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1Documento5 páginasSoalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1norizan bt awang100% (2)
- SJKT Ladang Senawang, 71450 SG - Gadut: Mid Term Examination Science Year 5 1 Hour 15 MinutesDocumento27 páginasSJKT Ladang Senawang, 71450 SG - Gadut: Mid Term Examination Science Year 5 1 Hour 15 MinutesNadarajahAinda não há avaliações
- Science Year 5unit 3 Food Chain and Food WebDocumento2 páginasScience Year 5unit 3 Food Chain and Food Webkheshin80Ainda não há avaliações
- Latihan Sains UPSRDocumento6 páginasLatihan Sains UPSRAlia AminAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 Year 3 Sumatif 1Documento9 páginasPaper 2 Year 3 Sumatif 1Izzan Fatihin100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions 1.Documento2 páginasChapter 7 Algebraic Expressions 1.cikguanuar89% (9)
- Year 5 Science Notes SasbadiDocumento11 páginasYear 5 Science Notes SasbadiVira HashimAinda não há avaliações
- Mid Year Exam Year 1Documento7 páginasMid Year Exam Year 1nurhafizaramdzanAinda não há avaliações
- Corn pests and natural enemies guideDocumento43 páginasCorn pests and natural enemies guideAdrian Mausig100% (3)
- BIRDS ActivityDocumento13 páginasBIRDS ActivityMudasir SalikAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Life Cycles: Turtles, Birds and ButterfliesDocumento7 páginasAnimal Life Cycles: Turtles, Birds and ButterfliesAinun NikmahAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Life Processes: Human BreatheDocumento7 páginasChapter 2: Life Processes: Human BreatheKavitha RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- C5 - CH 1 - Plant Reproduction - Notebook Work 22-23Documento6 páginasC5 - CH 1 - Plant Reproduction - Notebook Work 22-23Abhit Rao RaiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Biodiversity: 3.1 Diversity of Living OrganismsDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 Biodiversity: 3.1 Diversity of Living OrganismsWJ LooAinda não há avaliações
- G-11 PPT P-2Documento126 páginasG-11 PPT P-2etsubtarekegn87Ainda não há avaliações
- Spark Science 5 KeybookDocumento53 páginasSpark Science 5 Keybookmaryam arshad100% (1)
- Individual Worksheet - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocumento3 páginasIndividual Worksheet - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsHarmanjot KaurAinda não há avaliações
- Seed and Fruit DispersalDocumento2 páginasSeed and Fruit DispersalryZzAinda não há avaliações
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Documento11 páginasHow Do Organisms Reproduce - Notes-Class 10Varshini PeraAinda não há avaliações
- Stages of Cockroach and Housefly CompletedDocumento14 páginasStages of Cockroach and Housefly CompletedJerin JacobAinda não há avaliações
- Seeds and Seeds Class 5 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 5 (PDF)Documento6 páginasSeeds and Seeds Class 5 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 5 (PDF)krishna GAinda não há avaliações
- Zoo CC305 Parental Care in AmphibiansDocumento28 páginasZoo CC305 Parental Care in AmphibiansAnshuman PandaAinda não há avaliações