Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
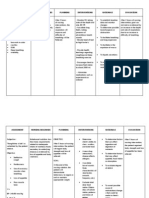
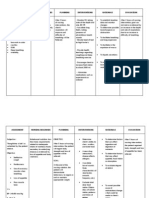
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis / Inference Planning Intervention / Rationale Evaluation
Enviado por
Mon ManguilinDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis / Inference Planning Intervention / Rationale Evaluation
Enviado por
Mon ManguilinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NURSING CARE PLAN
Patients Name: Diagnosis: Patient EG Cardiac Dysrhythmias Secondary to DM Type II NURSING ANALYSIS / ASSESSMENT PLANNING DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE
Ineffective breathing pattern related to decreased respiratory depth secondary to pain as manifested by the respiratory rate of 25 bpm. Spontaneous Depolarization Triggers extra beas Altered automacity Dysrhythmia Short-term: After 15 minutes of nursing intervention, the client will demonstrate understanding of the ways on how to improve breathing pattern. Long-term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention, the client will establish a normal, effective respiratory pattern.
Age: Religion:
51 y/o Gender: Dating Daan
Male
INTERVENTION / RATIONALE
Independent: Strictly monitor V/S. Auscultate chest R: To evaluate presence/character of breath sounds and secretions. Note rate and depth of breath sounds, type of breathing pattern. Monitor pulse oximetry. R: To verify maintenance/improvement of oxygen saturation. Review lab data such as the ABG. R: To determine degree of oxygenation. Elevate the head of bed. R: To promote maximum lung expansion. Encourage slower/deeper respirations and use of pursed-lip technique. R: To promote deep breathing. Encourage adequate rest periods. R: To limit fatigue. Assess for pain/discomfort. R: This may restrict respiratory effort. Assist the client in using relaxation techniques. R: To minimize anxiety. Keep calm attitude while dealing with the client. R: To minimize anxiety.
EVALUATION
Goals were met. After 15 minutes of nursing intervention, the client demonstrated understanding of the ways on how to improve breathing pattern. After 1 hour of nursing intervention, the client established a normal, effective respiratory pattern.
Subjective: Pag humihinga ako, parang ang bigat, hindi ako masyado makahinga ng maayos. Objective: V/S : T 36.8; PR 103; RR 25: BP 120/80 Use of accesory muscle in breathing (trapezius) Restlessness
Dependent: Administer oxygen at lowest concentration indicated and prescribed respiratory medications. R: For management of underlying respiratory condition. Collaborative: Maintain emergency equipments readily accessible. R: For easy access in case of emergency situation. Advise regular medical evaluation with primary care provider R: To determine effectiveness of current therapeutic regimen and to promote general well-being.
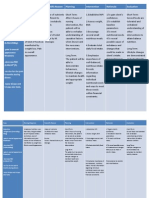
NURSING CARE PLAN Patients Name: Diagnosis: ASSESSMENT
Subjective: Hindi ko nasusunod yung tamang pag-inom ng gamut ko. Objective: V/S : T 36.8; PR 103; RR 25; BP 120/80 CBG: 161 mg/dL (12pm; 06/25/12) Dry skin Restlessness
Patient EG Cardiac Arrhythmias NURSING DIAGNOSIS
Unstable blood glucose level related to lack of medication adherence as manifested by CBG level of 161 mg/dL.
Age: Religion: ANALYSIS / INFERENCE
51 y/o Dating Daan PLANNING
Short-term: After 20 minutes of nursing intervention, the client will: Acknowledge factors that may lead to unstable glucose level. Verbalize understanding of body and energy needs. Verbalize understanding of importance of healthy lifestyle in stabilizing glucose level. Long-term: After 4 hours of nursing intervention, the client will maintain blood
Gender: INTERVENTION / RATIONALE
Male EVALUATION
Goals were met. After 20 minutes of nursing intervention, the client: Acknowledged the factors that may lead to unstable glucose level. Verbalized understanding of body and energy needs. Verbalized understanding of importance of healthy lifestyle in stabilizing glucose level. After 4 hours of nursing intervention, the client maintained blood glucose level in a satisfactory range.
Independent: Review clients dietary program and usual pattern; compare with recent intake. R: This identifies deficits and deviations from therapeutic plan, which may precipitate unstable glucose and uncontrolled hyperglyc emia. Weigh daily or as indicated. R: This assesses adequacy of nutritional intakeboth absorption and utilization. Identify food preferences, including ethnic and cultural needs. R: This increases clients cooperation. Observe for signs of hypoglycemia changes in LOC, cool & clammy skin, rapid
glucose level in a satisfactory range.
pulse, hunger, irritability, anxiety, headache, lightheadedness, and shakiness. R: Once CHO metabolism resumes, blood glucose level will fall, and as insulin is being adjusted, hypoglycemia may occur. Strictly monitor clients CBG levels. R: To check effectiveness of the above interventions. Review lab results such as the FBS. Dependent: Administer hypoglymic drugs as prescribed by the physician. Collaborative: Consult with dietician about specific dietary needs based on clients condition.
Você também pode gostar
- Meeting the American Diabetes Association Standards of CareNo EverandMeeting the American Diabetes Association Standards of CareAinda não há avaliações
- Intermittent Fasting For Women: A Beginner’s Transformation Made EasyNo EverandIntermittent Fasting For Women: A Beginner’s Transformation Made EasyAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- NCP MiDocumento8 páginasNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento10 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationLean Ashly Tuddao Macarubbo0% (1)
- NCP CKDDocumento9 páginasNCP CKDDanica Salinas100% (1)
- NCP FinalDocumento18 páginasNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Which It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToDocumento8 páginasWhich It Is A Process Whereby Pancreatic Enzymes Destroy Its Own Tissue Leading ToAriane-Gay Cristobal DuranAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento10 páginasNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocumento7 páginasNursing Care Plan PediaYvonne Niña Aranton100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care PlanAl RizkyAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study and NCP!Documento8 páginasDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- NCPDocumento7 páginasNCPBeverLyAinda não há avaliações
- R: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyDocumento4 páginasR: This Provides Baseline Measurement For Future Evaluation and Guides TherapyTyron ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- ACSDocumento21 páginasACSchris_arc90100% (1)
- ACS Nursing Care PlanDocumento21 páginasACS Nursing Care Planchris_arc90100% (6)
- Scolio, Heart FailureDocumento12 páginasScolio, Heart FailureArjay AvesAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento11 páginasNCPJaziel Remo100% (1)
- Fdar NonieDocumento3 páginasFdar NonieDana LabusonAinda não há avaliações
- Part XI - NCPDocumento6 páginasPart XI - NCPjeslergarciachioAinda não há avaliações
- Actual Nursing Care Plan GT DisorderDocumento3 páginasActual Nursing Care Plan GT DisordermandzkievonnieAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento9 páginasNursing Care PlanjmichaelaAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento9 páginasNCPLeolene Grace BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP EndoDocumento8 páginasNCP EndoJan Rainier Carlos BalariaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP FinalDocumento7 páginasNCP FinalAkira MizukamiAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento11 páginasNursing Care PlanKevin John ReaLubit SaLisi100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAdelaine LorestoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP CaseDocumento34 páginasNCP CaseIsobel Mae JacelaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For CipDocumento22 páginasNCP For CipBing DayaoAinda não há avaliações
- GastroenteritisDocumento8 páginasGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento7 páginasNursing Care PlantinnnnnnnnnnnnnAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento10 páginasAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Diarrhea Crampy Abdominal Pain Nausea VomitingDocumento2 páginasDiarrhea Crampy Abdominal Pain Nausea VomitingLiezl Ann BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Script Part B Mental Health Mid170014Documento6 páginasAnswer Script Part B Mental Health Mid170014knj210110318Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP GrandcaseDocumento5 páginasNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloAinda não há avaliações
- CHF Concept MapDocumento4 páginasCHF Concept MapLisaSanders99Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento14 páginasNursing Care PlanMaria Pina Barbado PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Care of Unconscious PatientDocumento15 páginasCare of Unconscious PatientAejaz AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento10 páginasNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezAinda não há avaliações
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocumento5 páginasDiabetic KetoacidosisJamie IllmaticAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento1 páginaImpaired Gas ExchangeAdelaine LorestoAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationLP BenozaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP and Problems FinalDocumento8 páginasNCP and Problems FinalRina CebreroAinda não há avaliações
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento5 páginasMyocardial InfarctionDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaAinda não há avaliações
- Laryngeal Cancer - DanDocumento12 páginasLaryngeal Cancer - DanRoldan VidadAinda não há avaliações
- RNCPDocumento5 páginasRNCPReymon Jan RodadoAinda não há avaliações
- Conceptmaptext For EpDocumento9 páginasConceptmaptext For Epapi-272402391Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP Laryngeal CancerDocumento10 páginasNCP Laryngeal CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (2)
- DM NCPDocumento7 páginasDM NCPMichael Anthony Cardenas Macaballug67% (3)
- Nursing Care ManagementDocumento40 páginasNursing Care ManagementɱΘΟθ CuasitoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento3 páginasNCPJoevelyn LaynoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP Crohn'sDocumento2 páginasNCP Crohn'sJanice Marco100% (1)
- Membantu Pasien Dengan Gejala Dan Membawaa Produk ObatDocumento13 páginasMembantu Pasien Dengan Gejala Dan Membawaa Produk ObatMisgi Candra DasaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlansDocumento6 páginasNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map - Abby !Documento3 páginasConcept Map - Abby !Franklin A. Salaum III0% (2)
- Fdar Charting 3 Oct12Documento2 páginasFdar Charting 3 Oct12Aziil LiizaAinda não há avaliações
- Phase 3 HCG Diet: Successful Stabilization Plan RevealedNo EverandPhase 3 HCG Diet: Successful Stabilization Plan RevealedAinda não há avaliações
- Gastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2No EverandGastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2Ainda não há avaliações
- A Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Oxygen Therapy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Description of Equipment Arterial LineDocumento5 páginasDescription of Equipment Arterial LineMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- Mind MappingDocumento2 páginasMind MappingMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Gordon's - NikkiDocumento2 páginas5 Gordon's - NikkiMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Course in The WardDocumento2 páginas6 Course in The WardMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- 4 GenogramDocumento1 página4 GenogramMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Nursing History + GordonsDocumento2 páginas3 Nursing History + GordonsMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- Cystoscopy WordDocumento4 páginasCystoscopy WordMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- 08 2008 Solaiman SampleDocumento10 páginas08 2008 Solaiman SampleMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- Retrograde PyelogramDocumento12 páginasRetrograde PyelogramMon ManguilinAinda não há avaliações
- Marijuana and Treatment of Drug Addiction in The Philippines - Nathaniel Dela CruzDocumento38 páginasMarijuana and Treatment of Drug Addiction in The Philippines - Nathaniel Dela CruzJek RicoAinda não há avaliações
- What Are Mucous CystsDocumento10 páginasWhat Are Mucous CystsNena TamaraAinda não há avaliações
- Case Management: AssessmentDocumento97 páginasCase Management: AssessmentgitaAinda não há avaliações
- MedDocumento76 páginasMedRazvanPopAinda não há avaliações
- Chemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410Documento6 páginasChemicals Zetag MSDS Powder Magnafloc 919 - 0410PromagEnviro.comAinda não há avaliações
- Pan and Chu - 2017 - Fate of Antibiotics in Soil and Their Uptake by EdDocumento13 páginasPan and Chu - 2017 - Fate of Antibiotics in Soil and Their Uptake by EdDaniel BañónAinda não há avaliações
- Mcdonalds Diet ActivityDocumento2 páginasMcdonalds Diet Activityapi-246304404Ainda não há avaliações
- VaccinationDocumento22 páginasVaccinationFareed KhanAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 4 - DIAGNOSIS Part 1Documento3 páginasUNIT 4 - DIAGNOSIS Part 1Anonymous Wfl201YbYoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study CADocumento8 páginasDrug Study CAAna Marie Besa Battung-ZalunAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment-Tool-For-Ambulance 2018 PDFDocumento12 páginasAssessment-Tool-For-Ambulance 2018 PDFDerrick ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- NNSC (Northumbria Nutrition Score Chart) : Health and Clinical Excellence) Berdasarkan Reproduktifitas Dan KemudahanDocumento4 páginasNNSC (Northumbria Nutrition Score Chart) : Health and Clinical Excellence) Berdasarkan Reproduktifitas Dan KemudahanYoky AlamsyahAinda não há avaliações
- BehaviourismDocumento9 páginasBehaviourismVijeyachandhar DorairajAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Food and ExerciseDocumento4 páginasRole of Food and ExerciseShanmugasundaram M Shanmugasundaram MAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Service CavitadorDocumento29 páginasManual Service CavitadorErik Sanchez HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Removable AppliancesDocumento32 páginasRemovable AppliancesmegamarwaAinda não há avaliações
- Imaging Infections Jain 2017Documento263 páginasImaging Infections Jain 2017johnalan100% (2)
- Solution Focussed ApproachDocumento30 páginasSolution Focussed Approach08brad02Ainda não há avaliações
- Sports Vision G. JanssenDocumento35 páginasSports Vision G. Janssenphilip davisAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Care Nursing A Holistic Approach 11th Edition Morton Fontaine Test Bank PDFDocumento335 páginasCritical Care Nursing A Holistic Approach 11th Edition Morton Fontaine Test Bank PDFSami Atawi100% (1)
- Katalog Pavna ANG Siebec-03-WEBDocumento24 páginasKatalog Pavna ANG Siebec-03-WEBzanjan98Ainda não há avaliações
- Overt Agitation Severity ScaleDocumento8 páginasOvert Agitation Severity ScaleSD100% (1)
- Compartment ModelsDocumento67 páginasCompartment ModelsGhadeer M HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Surgical Treatment For Inguinoscrotal Hernia With.2Documento10 páginasSurgical Treatment For Inguinoscrotal Hernia With.2carlos.alberto.palacios.serratAinda não há avaliações
- Preventive Drug Education Resource Package For TeachersDocumento97 páginasPreventive Drug Education Resource Package For TeachersHwsAPhangAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To STYEDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To STYESumit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Children's Depression Inventory CDI™Documento2 páginasChildren's Depression Inventory CDI™ManickaSaravanan27% (11)
- Fluids and Electrolytes NCM 101Documento142 páginasFluids and Electrolytes NCM 101France John Evangelista Torres100% (2)
- AnticholinergicsDocumento34 páginasAnticholinergicskityamuwesiAinda não há avaliações
- Chaibasa Master Plan - 2040 Draft Report EnglishDocumento241 páginasChaibasa Master Plan - 2040 Draft Report EnglishArvind S.100% (3)