Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
SWOT Analysis R&D
Enviado por
Sampath RajDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SWOT Analysis R&D
Enviado por
Sampath RajDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Master of Business Administration- Semester 2 MB0046 Marketing Management - 4 Credits (Book ID: B1135) Assignment Set- 1 (60 Marks)
Q.1 Explain the various stages involved in new product development Ans: 1.Idea Generation is often called the "fuzzy front end" of the NPD process Ideas for new products can be obtained from basic research using a SWOT analysis (Strengths,
Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats), Market and consumer trends, company's R&D department, competitors, focus groups, employees, salespeople, corporate spies, trade shows, or Ethnographic discovery methods (searching for user patterns and habits) may also be used to get an insight into new product lines or product features. Lots of ideas are being generated about the new product. Out of these ideas many ideas are being
implemented. The ideas use to generate in many forms and their generating places are also various. Many reasons are responsible for generation of an idea. Idea Generation or Brainstorming of new product, service, or store concepts - idea generation
techniques can begin when you have done your OPPORTUNITY ANALYSIS to support your ideas in the Idea Screening Phase (shown in the next development step). 2. Idea Screening The object is to eliminate unsound concepts prior to devoting resources to them. The screeners should ask several questions: Will the customer in the target market benefit from the product? What is the size and growth forecasts of the market segment/target market? What is the current or expected competitive pressure for the product idea? What are the industry sales and market trends the product idea is based on? Is it technically feasible to manufacture the product? Will the product be profitable when manufactured and delivered to the customer at the
target price? 3. Concept Development and Testing Develop the marketing and engineering details Investigate intellectual property issues and search patent data bases Who is the target market and who is the decision maker in the purchasing process? What product features must the product incorporate?
What benefits will the product provide? How will consumers react to the product? How will the product be produced most cost effectively? Prove feasibility through virtual computer aided rendering, and rapid prototyping What will it cost to produce it?
Testing the Concept by asking a sample of prospective customers what they think of the idea. Business Analysis
Usually via Choice Modelling. 4. 5.
Estimate likely selling price based upon competition and customer feedback Estimate sales volume based upon size of market and such tools as the Fourt-Woodlock equation Estimate profitability and break-even point Beta Testing and Market Testing Produce a physical prototype or mock-up Test the product (and its packaging) in typical usage situations Conduct focus group customer interviews or introduce at trade show Make adjustments where necessary Produce an initial run of the product and sell it in a test market area to determine customer Technical Implementation
acceptance 6. 7.
New program initiation Finalize Quality management system Resource estimation Requirement publication Publish technical communications such as data sheets Engineering operations planning Department scheduling Supplier collaboration Logistics plan Resource plan publication Program review and monitoring Contingencies - what-if planning Commercialization (often considered post-NPD) Launch the product
8.
Produce and place advertisements and other promotions Fill the distribution pipeline with product Critical path analysis is most useful at this stage New Product Pricing Impact of new product on the entire product portfolio Value Analysis (internal & external) Competition and alternative competitive technologies Differing value segments (price, value, and need) Product Costs (fixed & variable) Forecast of unit volumes, revenue, and profit
These steps may be iterated as needed. Some steps may be eliminated. To reduce the time that the NPD process takes, many companies are completing several steps at the same time (referred to as concurrent engineering or time to market). Most industry leaders see new product development as a proactive process where resources are allocated to identify market changes and seize upon new product opportunities before they occur (in contrast to a reactive strategy in which nothing is done until problems occur or the competitor introduces an innovation). Many industry leaders see new product development as an ongoing process (referred to ascontinuous development) in which the entire organization is always looking for opportunities.
Q.2 Discuss the importance of SWOT analysis to develop effective marketing mix. Ans: SWOT analysis (alternately SLOT analysis) is a strategic planning method used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses/Limitations, Opportunities, and Threats involved in a project or in a business venture. It involves specifying the objective of the business venture or project and identifying the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieve that objective. The technique is credited to Albert Humphrey, who led a convention at Stanford University in the 1960s and 1970s using data from Fortune 500 companies. Setting the objective should be done after the SWOT analysis has been performed. This would allow achievable goals or objectives to be set for the organization. Strengths: characteristics of the business, or project team that give it an advantage over others Weaknesses (or Limitations): are characteristics that place the team at a disadvantage relative to
others Opportunities: external chances to improve performance (e.g. make greater profits) in the
environment Threats: external elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project
Identification of SWOTs is essential because subsequent steps in the process of planning for achievement of the selected objective may be derived from the SWOTs. First, the decision makers have to determine whether the objective is attainable, given the SWOTs. If the objective is NOT attainable a different objective must be selected and the process repeated. Users of SWOT analysis need to ask and answer questions that generate meaningful information for each category (strengths, opportunities, weaknesses, and threats) in order to maximize the benefits of this evaluation and find their competitive advantage. Marketing In many competitor analyses, marketers build detailed profiles of each competitor in the market, focusing especially on their relative competitive strengths and weaknesses using SWOT analysis. Marketing managers will examine each competitor's cost structure, sources of profits, resources and competencies, competitive positioning and product differentiation, degree of vertical integration, historical responses to industry developments, and other factors. Marketing management often finds it necessary to invest in research to collect the data required to perform accurate marketing analysis. Accordingly, management often conducts market research (alternately marketing research) to obtain this information. Marketers employ a variety of techniques to conduct market research, but some of the more common include: Qualitative marketing research, such as focus groups Quantitative marketing research, such as statistical surveys Experimental techniques such as test markets Observational techniques such as ethnographic (on-site) observation Marketing managers may also design and oversee various environmental scanning and
competitive intelligence processes to help identify trends and inform the company's marketing analysis. Below is an example SWOT analysis of a market position of a small management consultancy with specialism in HRM.
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
Reputation in marketplace Shortage of consultants at Well established position partner level niche
Large consultancies
operating level rather than with a well defined market operating at a minor level
Expertise at partner level in Unable to deal with multi- Identified market for
Other small consultancies
HRM consultancy
disciplinary assignments because of size or lack of ability
consultancy in areas other looking to invade the than HRM marketplace
Q.3 Briefly explain the major external and uncontrollable factors that influence an organization decision making, performance and strategies Ans:
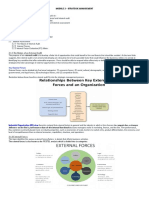
1) Demographic Environment : A business and its forces in its micro environment operate in larger macro
environment of forces that shape opportunities and pose threats to the business. It refers the major external and uncontrollable factors that influence an organization's decision making, and affect its performance and strategies. These factors include the economic factors; demographics; legal, political, and social conditions; technological changes; and natural forces. The important environmental factors are; (1) Economic Environment (2) Political and Governmental Environment (3) Socio-cultural Environment (4) Natural Environment (5) Demographic Environment (6) Technological Environment (7) International Environment.
2) Political and Governmental Environment: - Political environment refers to the influence exerted by the
three political institutions they are; Legislature, Executive, Judiciary etc. The legislature decides on a particular course of action. Government is the executive and its job is to implement whatever was decided by parliament. The judiciary has ensure that both the legislature and executive function in public interest and within the boundaries of constitution. Legal and political environment provides a framework within the business is to function and its existence depends on the success with which it can face the various challenges constructed out of political and legal framework.
3) Socio-cultural Environment : Changes in social trends can impact on the demand for a firm's products
and the availability and willingness of individuals to work. Social class and caste of a person goes a long way in deciding the business activities in relation to its production and marketing activities. Tradition, customs and social attitudes have changed the attitude and beliefs of the persons which have their effect on organizational environment. Class and caste are influencing the purchasing pattern. Socio-cultural
environment may include expectations of the society from business, attitudes of society towards business and its management, views towards achievement of work, views towards structure, responsibility and organizational positions, views towards customs, traditional and conventional, class structure and labour mobility and level of education.
4) Technological Environment: In order to survive in today's competitive world, a business has to adopt
technological changes from time to time. New technologies create new products and new processes. Technology can reduce costs, improve quality and lead to innovation. These developments can benefit consumers as well as the organizations providing the products. MP3 players, computer games, online gambling and high definition TVs are all new markets created by technological advances. Online shopping, bar coding and computer aided design are all improvements to the way we do business as a result of better technology.
Q.4 Discuss the potential benefits associated with MIS. Ans: A marketing information system (MIS) is a set of procedures and methods designed to generate, analyze, disseminate, and store anticipated marketing decision information on a regular, continuous basis. An information system can be used operationally, managerially, and strategically for several aspects of marketing.
1) Helps to recognize market trends: MIS helps managers to recognize market trends, in respect of price, designs of products, fashions, etc. timely information of the market trend enables the firm to follow the right course of action.
2) Facilitates marketing planning and control: effective marketing planning is required in terms of product planning, pricing, promotion and distribution. Such planning will be possible only if the company is possessing adequate and relevant information. this is also possible through MIS.
3) Quick supply of information: today a firm has to take quick decisions. for this purpose it requires fast flow of information which is facilitated by a properly designed MIS.
4) Improves quality of decision making: a properly designed MIS supplies reliable and relevant information. with the help of computers and other data processing equipments, the marketing managers can make the right
decisions at the right time.
Q.5 Describe five interdependent levels of basic human needs (motivators) as propounded by Abraham Maslow Ans: Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology, proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, all of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. Maslow use the terms Physiological, Safety, Belongingness and Love, Esteem, and Self-Actualization needs to describe the pattern that human motivations generally move through
1)Self-actualization Maslow's hierarchy of needs is often portrayed in the shape of a pyramid, with the largest and most fundamental levels of needs at the bottom, and the need for self-actualization at the top. While the pyramid has become the de facto way to represent the hierarchy, Maslow himself never used a pyramid to describe these levels in any of his writings on the subject.
2)Physiological needs For the most part, physiological needs are obvious they are the literal requirements for human survival. If these requirements are not met, the human body simply cannot continue to function.
Physiological needs are the most pre potent of all the other needs. Therefore, the human that lacks food, love, esteem, or safety would consider the greatest of his/her needs to be food. Air, water, and food are metabolic requirements for survival in all animals, including humans. Clothing and shelter provide necessary protection from the elements. The intensity of the human sexual instinct is shaped more by sexual competition than maintaining a birth rate adequate to survival of the species. 3) Safety needs With their physical needs relatively satisfied, the individual's safety needs take precedence and dominate behavior. In the absence of physical safety due to war, natural disaster, or, in cases of family violence, childhood abuse, etc. people experience post-traumatic stress disorder and trans-generational trauma transfer. In the absence of economic safety due to economic crisis and lack of work opportunities these safety needs manifest themselves in such things as a preference for job security, grievance procedures for protecting the individual from unilateral authority, savings accounts, insurance policies, reasonable disability accommodations, and the like. This level is more likely to be found in children because they have a greater need to feel safe. 4) Love and belonging After physiological and safety needs are fulfilled, the third layers of human needs is interpersonal and involve feelings of belongingness. The need is especially strong in childhood and can over-ride the need for safety as witnessed in children who cling to abusive parents. Deficiencies with respect to this aspect of Maslow's hierarchy due to hospitalize, neglect, shunning, ostracism etc. can impact individual's ability to form and maintain emotionally significant relationships in general. 5) Esteem All humans have a need to be respected and to have self-esteem and self-respect. Esteem presents the normal human desire to be accepted and valued by others. People need to engage themselves to gain recognition and have an activity or activities that give the person a sense of contribution, to feel self-valued, be it in a profession or hobby. Imbalances at this level can result in low self-esteem or an inferiority complex. People with low self-esteem need respect from others. They may seek fame or glory, which again depends on others. Note, however, that many people with low self-esteem will not be able to improve their view of themselves simply by receiving fame, respect, and glory externally, but must first accept themselves internally. 6)Self-actualization This level of need pertains to what a person's full potential is and realizing that potential. Maslow describes this desire as the desire to become more and more what one is, to become everything that one is capable of becoming. This is a broad definition of the need for self-actualization, but when applied to individuals the need is specific. For example one individual may have the strong desire to become an ideal parent, in another it may be expressed athletically, and in another it may be expressed in painting, pictures, or inventions. As mentioned before, in order to reach a clear understanding of this level of need one must first not only achieve the previous needs, physiological, safety, love, and esteem, but master these needs.
Q.6 List the important differences between Consumer market and business markets Ans: Business Marketing is the practice of individuals, or organizations, including commercial businesses, governments and institutions, facilitating the sale of their products or services to other companies or organizations that in turn resell them, use them as components in products or services they offer, or use them to support their operations. Also known as industrial marketing, business marketing is also called business-to-business marketing, or B2B marketing, for short. Business marketing v/s consumer marketing although on the surface the differences between business and consumer marketing may seem obvious, there are more subtle distinctions between the two with substantial ramifications. Dwyer and Tanner (2006) note that business marketing generally entails shorter and more direct channels of distribution. While consumer marketing is aimed at large demographic groups through mass media and retailers, the negotiation process between the buyer and seller is more personal in business marketing. According to Hutt and Speh (2001), most business marketers commit only a small part of their promotional budgets to advertising, and that is usually through direct mail efforts and trade journals. While that advertising is limited, it often helps the business marketer set up successful sales calls. Marketing to a business trying to make a profit (Business-to-Business marketing) as opposed to an individual for personal use (Business-to-Consumer, or B2C marketing) is similar in terms of the fundamental principles of marketing. In B2C, B2B and B2G marketing situations, the marketer must always: successfully match the product/service strengths with the needs of a definable target market; position and price to align the product/service with its market, often an intricate balance; and Communicate and sell it in the fashion that demonstrates its value effectively to the target market.
Você também pode gostar
- The SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyNo EverandThe SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (10)
- Communication Style InventoryDocumento6 páginasCommunication Style Inventoryapi-358787203Ainda não há avaliações
- BIMAS 2 Teacher Standard Form From Tim Simmons WCPSSDocumento2 páginasBIMAS 2 Teacher Standard Form From Tim Simmons WCPSSA.P. Dillon50% (2)
- Framework For Marketing PlanningDocumento16 páginasFramework For Marketing PlanningDK CresendoAinda não há avaliações
- Active Listening Techniques HandoutDocumento2 páginasActive Listening Techniques HandoutJane Limsan Paglinawan100% (6)
- Strategic Analysis OF MICROSOFTDocumento7 páginasStrategic Analysis OF MICROSOFTAmandeep Singh GujralAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- An Enemy of The People IbsenDocumento23 páginasAn Enemy of The People IbsenadadanAinda não há avaliações
- Situational ScrumDocumento15 páginasSituational ScrumsrimkbAinda não há avaliações
- The Gnostic Book of Changes Chapter Five: Consulting the Oracle GuideDocumento11 páginasThe Gnostic Book of Changes Chapter Five: Consulting the Oracle GuideKenneth Anderson100% (2)
- Strategic MarketingDocumento52 páginasStrategic MarketingAnkit Sharma 028Ainda não há avaliações
- MB0046Documento13 páginasMB0046sumit86Ainda não há avaliações
- SWOT AnalysisDocumento49 páginasSWOT AnalysisvikasAinda não há avaliações
- The Eight Stages of New Product DevelopmentDocumento3 páginasThe Eight Stages of New Product DevelopmentJasmene KachrooAinda não há avaliações
- Major Stage S in NPD: "The "Fuzzy Front End" of The New Product Development Process"Documento5 páginasMajor Stage S in NPD: "The "Fuzzy Front End" of The New Product Development Process"Karthik RameshAinda não há avaliações
- The Process: New Product Development ProcessDocumento9 páginasThe Process: New Product Development ProcessDhananjay SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6 - Foundation For Market Strategy Selection and AnalysisDocumento13 páginasModule 6 - Foundation For Market Strategy Selection and Analysisalma agnasAinda não há avaliações
- Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDocumento5 páginasEntrepreneurship DevelopmentAsadul HoqueAinda não há avaliações
- 5 C Analysis PEST Analysis SWOT AnalysisDocumento4 páginas5 C Analysis PEST Analysis SWOT Analysisavisekghosh2015Ainda não há avaliações
- Hoe To Download From ScribdDocumento42 páginasHoe To Download From ScribdSurya ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- History of Swot AnalysisDocumento42 páginasHistory of Swot Analysiscreation toolsAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT AnalysisDocumento53 páginasSWOT Analysisdivjn367% (6)
- The Process: Business Engineering ProductDocumento12 páginasThe Process: Business Engineering Producthemu22Ainda não há avaliações
- New Product Development: The ProcessDocumento6 páginasNew Product Development: The ProcessFathmath XaaAinda não há avaliações
- Fourth Quarter Module 2 Part 2Documento4 páginasFourth Quarter Module 2 Part 2Ljane Agabin CarbonelAinda não há avaliações
- Product DevelopmentDocumento6 páginasProduct DevelopmentDeonald Barcena TamodraAinda não há avaliações
- New Product Development ProcessDocumento3 páginasNew Product Development ProcessDasari Chandra Kanth ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Industrial ManagementDocumento10 páginasIndustrial ManagementHimanshu GautamAinda não há avaliações
- The Process: Business Engineering ProductDocumento7 páginasThe Process: Business Engineering ProductAmiya MahatoAinda não há avaliações
- Analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats with a SWOT analysisDocumento5 páginasAnalyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats with a SWOT analysisLya HellenAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing MixDocumento11 páginasMarketing Mixketan chavanAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Task and New Product Development Process & The Product Life Cycle (PLC) and Marketing Strategies at Different StageDocumento10 páginasMarketing Task and New Product Development Process & The Product Life Cycle (PLC) and Marketing Strategies at Different StageTonoy RoyAinda não há avaliações
- Swot Analysis PROJECTDocumento52 páginasSwot Analysis PROJECTDipanjan Das100% (2)
- NPD and VMSDocumento4 páginasNPD and VMSK V S MadaanAinda não há avaliações
- S&T Unit # 2Documento30 páginasS&T Unit # 2Arsene MawejaAinda não há avaliações
- The Process: Business Engineering Product Product Design Marketing AnalysisDocumento4 páginasThe Process: Business Engineering Product Product Design Marketing AnalysisShahzadyaqoob SagarAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2 - Strat ManDocumento4 páginasModule 2 - Strat ManElla MaeAinda não há avaliações
- New Product Development ProcessDocumento6 páginasNew Product Development Processsomebodystopme21Ainda não há avaliações
- The Stages: SWOT Analysis R&DDocumento2 páginasThe Stages: SWOT Analysis R&DUmmed SinghoyaAinda não há avaliações
- Strategy - What Is Strategy?: Overall DefinitionDocumento14 páginasStrategy - What Is Strategy?: Overall DefinitionSyed DidarAinda não há avaliações
- 152-71-812-068 Md. Abu Zafar Samsuddin PDFDocumento18 páginas152-71-812-068 Md. Abu Zafar Samsuddin PDFmiraj hossenAinda não há avaliações
- Swot AnalysisDocumento19 páginasSwot AnalysisDipanjan DasAinda não há avaliações
- Market ResearchDocumento9 páginasMarket ResearchAnkit G SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Competitor AnalysisDocumento12 páginasCompetitor AnalysiskiranaishaAinda não há avaliações
- MB0046 - Marketing ManagementDocumento9 páginasMB0046 - Marketing ManagementArun Mishra100% (1)
- Swot AnalysisDocumento6 páginasSwot AnalysisnatashaaAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT AnalysisDocumento25 páginasSWOT AnalysisChor Chan0% (1)
- SWOT Analysis I-WPS OfficeDocumento11 páginasSWOT Analysis I-WPS OfficebrightrexpondaniAinda não há avaliações
- Marketing Research ProcessDocumento5 páginasMarketing Research ProcessBare SharmakeAinda não há avaliações
- Business Enterprise SimulationDocumento12 páginasBusiness Enterprise SimulationCha Eun WooAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT analysis guideDocumento6 páginasSWOT analysis guidenaifudeenAinda não há avaliações
- Class 7Documento83 páginasClass 7Abhishek ShrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Environment: Environment May Refer ToDocumento53 páginasEnvironment: Environment May Refer ToPrincess SubeenAinda não há avaliações
- SWOT Analysis: Ibrahim M. RihanDocumento7 páginasSWOT Analysis: Ibrahim M. RihanJeetin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Module L Tool, Techniques, Frameworks of Market and Industry AnalysisDocumento8 páginasModule L Tool, Techniques, Frameworks of Market and Industry AnalysisCasey AbelloAinda não há avaliações
- The Process of Strategic PlanningDocumento4 páginasThe Process of Strategic Planningyaasir_7868868Ainda não há avaliações
- Business Studies Notes MR RajabDocumento57 páginasBusiness Studies Notes MR RajabsmmaabzAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento22 páginasChapter 2omarel5ter2002Ainda não há avaliações
- Department of Food & Nutritional Sciences Sri Satya Sai Institute of Higher Learning Anantapur CampusDocumento31 páginasDepartment of Food & Nutritional Sciences Sri Satya Sai Institute of Higher Learning Anantapur Campuschaitanya bhagavathiAinda não há avaliações
- Conduct Strategic SWOT AnalysisDocumento8 páginasConduct Strategic SWOT AnalysisJo Ann RamboyongAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Marketing ResearchDocumento5 páginasRole of Marketing ResearchRupesh Chaube100% (1)
- Smu MBA 0046 SEM 2 Assignments - NjoyeeeeeDocumento11 páginasSmu MBA 0046 SEM 2 Assignments - NjoyeeeeeSumit Singh100% (1)
- SLHT - Applied Economics Week3 Q2 With Page NumberDocumento10 páginasSLHT - Applied Economics Week3 Q2 With Page NumberPëàrl Ragasajo100% (1)
- Marketing Research as Input for Decision MakingDocumento56 páginasMarketing Research as Input for Decision MakingDolly ParhawkAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5Documento8 páginasChapter 5Elijah IbsaAinda não há avaliações
- 8 stages product developmentDocumento3 páginas8 stages product developmentSarah MehrAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic Consulting Frameworks: Consulting PreparationNo EverandStrategic Consulting Frameworks: Consulting PreparationAinda não há avaliações
- Om 0018Documento187 páginasOm 0018praveen4_4Ainda não há avaliações
- Financial Management Set 2Documento25 páginasFinancial Management Set 2Sampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- MB0053Documento7 páginasMB0053garima bhatngar100% (1)
- MB0050 SET - 2.odtDocumento10 páginasMB0050 SET - 2.odtSampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- MB0044 Set-1Documento14 páginasMB0044 Set-1garima bhatngarAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Management Set 2Documento25 páginasFinancial Management Set 2Sampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Management Set 2Documento25 páginasFinancial Management Set 2Sampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- OM0012 Set 2.odtDocumento4 páginasOM0012 Set 2.odtSampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- Management Information System Set 2Documento8 páginasManagement Information System Set 2Sampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- MB0043 Human Resource Management Assignments Feb 11Documento2 páginasMB0043 Human Resource Management Assignments Feb 11AnilkumarsanctumAinda não há avaliações
- MBA Assignment on Management Functions and Learning TheoriesDocumento27 páginasMBA Assignment on Management Functions and Learning TheoriesSalim KottayilAinda não há avaliações
- Q.1 Explain The Different Types of Communication With Relevant Examples?Documento12 páginasQ.1 Explain The Different Types of Communication With Relevant Examples?Uttam SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial EconomyDocumento3 páginasManagerial EconomySampath RajAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 (Assumptions About Art)Documento19 páginasChapter 1 (Assumptions About Art)Ivy Mojado100% (1)
- Done Eapp q1 Module2-CDocumento12 páginasDone Eapp q1 Module2-CMishal NoroñaAinda não há avaliações
- Planning An Ergonomically Sound Office EnvironmentDocumento15 páginasPlanning An Ergonomically Sound Office EnvironmentDanTot BarcebalAinda não há avaliações
- mghb02 Chapter 1 NotesDocumento1 páginamghb02 Chapter 1 NotesVansh JainAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Introduction To ArtDocumento9 páginasModule 1 Introduction To ArtPatricia Diego FlorescaAinda não há avaliações
- Global Marketing SyllabusDocumento15 páginasGlobal Marketing SyllabusDence Cris RondonAinda não há avaliações
- Instant Help For Teens - Bulimia Workbook For TeensDocumento128 páginasInstant Help For Teens - Bulimia Workbook For TeensMariana SantalhaAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Division Primary Classes of AJK Text Book Board by Husses Ul Hassan B.Ed (Hons) Govt P/S Nagyal Tehsil &distt MirpurDocumento48 páginasSyllabus Division Primary Classes of AJK Text Book Board by Husses Ul Hassan B.Ed (Hons) Govt P/S Nagyal Tehsil &distt MirpurMuhammad NoveedAinda não há avaliações
- Protect Young Minds How To Talk To Kids About Pornography A Quick Start Guide 2019Documento15 páginasProtect Young Minds How To Talk To Kids About Pornography A Quick Start Guide 2019Tadeu Montenegro100% (1)
- A Compelling CollectionDocumento2 páginasA Compelling CollectionroshniprasaiAinda não há avaliações
- DOLE-GIP Application FormDocumento6 páginasDOLE-GIP Application FormjoemariAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Strand 4 Life and Career Skills: Decision Making Comprehensive Sexuality EducationDocumento7 páginasLearning Strand 4 Life and Career Skills: Decision Making Comprehensive Sexuality EducationBernie SarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Overview of Lesson (100-150 Words)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan: Overview of Lesson (100-150 Words)api-572580540Ainda não há avaliações
- Oral Presentations RubricDocumento1 páginaOral Presentations RubricMohd Idris Shah IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: "Pete The Cat-Rocking in My School Shoes" by Eric Litwin (Documento9 páginasLesson Plan: "Pete The Cat-Rocking in My School Shoes" by Eric Litwin (FranciscoDiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Robbins - Eob13ge - 01 - What Is OBDocumento33 páginasRobbins - Eob13ge - 01 - What Is OBDung Nguyễn MinhAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Answer Key A: GrammarDocumento6 páginas2 Answer Key A: GrammarCoralza SacAinda não há avaliações
- Monsters, Madmen and Myths A Critical Review of The Serial Killing Literature by Joshua Stuart-BennettDocumento35 páginasMonsters, Madmen and Myths A Critical Review of The Serial Killing Literature by Joshua Stuart-BennettSalvador Murlà AlluéAinda não há avaliações
- 300 Project Manager Interview QuestionsDocumento7 páginas300 Project Manager Interview Questionsbhaveshkumar78Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity 2Documento4 páginasActivity 2ДашаAinda não há avaliações
- Course OutlineDocumento2 páginasCourse OutlinerabiaAinda não há avaliações
- SAN JOSE Health Officer RecommendationDocumento5 páginasSAN JOSE Health Officer RecommendationSample BakeshopAinda não há avaliações
- David Wilcock 23-10-2017Documento94 páginasDavid Wilcock 23-10-2017Daniel EscobarAinda não há avaliações