Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Notes For Biology PDF
Enviado por
phapalla101Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes For Biology PDF
Enviado por
phapalla101Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Notes for Biology The Need for Energy Cells are constantly active doing what three things?
1. 2. 3. What are the two ways organisms obtain energy? 1. 2. Give the term for both definitions: _________________- The process that converts the radiant energy of sunlight into chemical energy. _________________- the process that releases chemical energy for use in the cell. Give the definitions for both terms: Autotroph-________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Heterotroph-________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ The ultimate source of energy for all living things is: A. Oxygen B. Sunlight C. Biosynthesis D. ATP *Photosynthesis is the major way that autotrophs produce chemical energy {Radiant energy + CO2+H2O Glucose + O2}
*All organisms use some form of respiration to obtain energy {Glucose + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy}
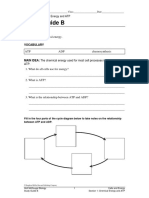
Adenosine Triphosphate What is a series of reactions from process that involve are biochemical reactions (respiration and photosynthesis)? __________________________ What the three parts of ATP? 1. 2. 3.
Energy is stored in the __________ between ____________ groups in ATP. _____________- The enzyme that breaks bonds between the second and third phosphate groups ADP is formedA- P ~ P ~ P A- P ~ P + P + Energy AMP is formedA- P ~ P + Energy A- P + P + Energy Phosphorylation: A. The building of ATP from ADP and a free phosphate group B. The transfer of a phosphate group to another molecule C. The breakdown of ATP to ADP and a phosphate group D. The collection of a phosphate group from another molecule *Whatever picks up the phosphate picks up the energy Explain the meaning of the chemical representation A- P ~ P ~ P
What is the difference between ATPase and ATP Synthase? ________________________________
*Photosynthesis, respiration, the formation of ATP, and the breakdown of ATP form a fundamental biological cycle Photosynthesis stores energy in the glucose molecules, ________________ releases that energy. There are two main types of respiration, both begin with: A. Krebs Cycle B. Oxidative Phosphorylation C. Glycolysis D. Anaerobic respiration The two types of respiration are: A. Fermentation and oxidative phosphorylation B. Metabolic reception and aerobic respiration C. Anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration D. Fermentation and aerobic respiration
How does the cell release energy stored in an ATP molecule? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________
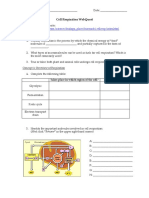
Glycolysis Where does Glycolysis occur? ____________________ Glycolysis requires oxygen T / F How many ATP are produced by the end of Glycolysis? ___________________ How many NADH+ are produced by the end of Glycolysis? __________________ What is the net number of ATP at the end of Glycolysis? ___________________ How many pyruvic acid molecules are generated by the end of Glycolysis? __________________ Glucose is an unstable energy molecule T / F Ten Steps of Glycolysis Number Step One Step Two Step Three Step Four Step Five Step Six Step Seven Step Eight Step Nine Step Ten Begin Enzyme Product
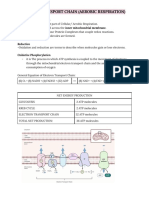
Ten Steps of Glycolysis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Cellular Respiration Diagram Fill in the Diagram with the needed terms and words. The answer diagram in on the next page.
Aerobic Respiration The result of Glycolysis and aerobic respiration (ATP totals may vary slightly). Glycolysis- C6H12O6+ 6O2 Aerobic Respiration- 6H2O + 6CO2 + 38 ATP (may vary)
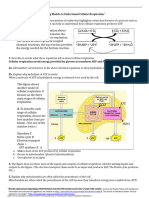
Most organisms do not carry out aerobic respiration T / F Where do these two processes occur? GlycolysisAerobic RespirationEnzymes associated with Krebs Cycle occur in the ______? A. Outer membrane and inner membrane B. Inner membrane and matrix C. Cytoplasm and outer membrane D. Matrix and the cytoplasm Matrix- the dense solution enclosed by the inner membrane The inner membrane also contains the molecules of the (three words) ______________________ and ATP synthase enzymes. (Answer to Diagram)
Three beginning steps of aerobic respiration (conversion process): 1. 2. 3. During this transformation pyruvic acid loses ____________. Three carbon- pyruvic acid molecule loses what molecule to become a two-carbon acetyl group? A. H2O B. CO2 C. PGAL D. O2 What picks up that molecule, and what does it become? (ex. Phosphorus; PGAL) __________________; __________________ Pyruvic acid + CoA + NAD+ becomes Acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH+ Acetyl CoA now enters the Krebs Cycle Each molecule of glucose produces how many pyruvic acid? A. 2 B. 4 C. 3 D. 6 Therefore, how many molecules of acetyl-CoA enter the Krebs Cycle? A. 1 B. 3 C. 2 D. 4 Explain in terms of cellular respiration why we need oxygen and why we exhale carbon dioxide. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Krebs CycleKrebs Cycle- _____________________________________________________________________ Also known as:
Carbon Cycle (hint and spelling: oxaloacetae): 1. 2. 3. Citric acid is immediately oxidized by enzymes in the mitochondria ____ carbon atoms are removed in the form of CO2, and 8 ___________ atoms are released in the Krebs Cycle. A. Two; carbon B. Four; hydrogen C. Three; oxygen D. Two; hydrogen Two molecules pick up these atoms: 1. NAD+ 2. What are the products of the Krebs Cycle from one acetyl-CoA molecule (name and number)? 1. 2. 3. When asked for the number of products from glucose the numbers: A. Double B. Triple C. Divide in half D. Stay the same Explain the roles of Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle in the biosynthesis of organic molecules: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Electron Transport ChainGlycolysis +
Conversion of pyruvic acid Acetyl-CoA + Krebs Cycle Write the number of each compound in the blank, and to the side, make note of where each compound came from. Also note, these totals are the combined NET product, not the number produced. _____ new ATP molecules + ___ NADH + ____ FADH2 These molecules carry ______________ to the electron transport chain and therefore carry energy. Electrons move down the electron transport chain, with ___________as the final electron acceptor. Water is formed in the process (oxygen combines with hydrogen to form water). What is another one word name for electron transport chain? ________________________ What is another two-word name for electron transport chain? ___________________________ Hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane into the _________________________? These ions make the space very _______________ charged? A. Positively B. Negatively C. Neutrally D. Ninjas The energy given up by electrons as they move through the electron transport chain is used to: A. break down glucose B. make NADH and FADH2 C. pump H1 through the membrane D. oxidize water E. Manufacture glucose When the poison cyanide blocks the electron transport chain, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. Why do you think they stop? A. They both run out of ATP B. Unused O2 interferes with cellular respiration C. They run out of NAD+ and FAD D. Electrons are no longer available E. They run out of ATP
On the back of this page, draw the electron transport chain beginning with NADH from glycolysis. An electrochemical gradient forms and hydrogen ions diffuse through channels that contain ATPase T / F Positive ions repel- so they have/make potential energy Back in the matrix- as it goes through the membrane during the electron transport chain, ATP synthase uses energy to make ATP. The energy generated by the _______________ of hydrogen ions is used by ATP synthase to make ATP. *Each molecule of NADH yields 2 ATP *Each molecule of FADH2 yields 2 ATP Therefore, electron transport chain yields a maximum of 34 molecules of ATP? T / P At the end of the electron transport, oxygen is the final _____________ and _____________ acceptor. Water forms in the process: O2 + 2H2O Energy Yield Glycolysis - ____ ATP Krebs____ ATP ETC____ ATP (min) ____ ATP (max) *Number of ATP may vary depending on the area of the body. Aerobic respiration is 19 times more efficient than anaerobic respiration. ATP produced represents only the total energy stored in a molecule of glucose. Fermentation FermentationAnaerobic respirationFermentation has nothing to do with ATP. T / F Function of fermentation- to break down ____________ and regenerate _______ for reuse in Glycolysis, NOT the production of ATP. {NAD+ needed for glycolysis. However when pyruvic acid is formed NAD+ is used to form NADH} Fermentation occurs in two forms: 1. 2. *Alcoholic fermentation- 6-10 in glycolysis
Lactic Acid FermentationLactic acid fermentation1. 2. Lactic acid forms which pyruvic acid accepts ________________ from NADH. Pyruvic acid + NADH Lactic Acid + NAD+ When no _________ is available, NADH donates is hydrogen atom to pyruvic acid. Lactic acid makes muscles: A. Firm B. Pretty sexy C. Sore D. Tighten Lactic acid is transported to the _______ where it is converted into glucose. A. Stomach B. Liver C. Heart D. That boom boom POW Fill in the chart below. The answers are on the last page.
Alcoholic Fermentation Alcoholic fermentationIn alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid is converted into isopropyl alcohol T / F ____________ accumulates during alcoholic fermentation: A. Ethanol B. Isopropyl C. Ethyl D. Ethel Pyruvic acid + NADH ethyl alcohol + CO2 + NAD Lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation do not supply cells with any additional ______ molecules. Compare and contrast fermentation as it occurs in human muscle cells and as it occurs in yeast cells. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Fill in the diagram below. Answers on the last page.
Você também pode gostar
- Photosynthesis Review WorksheetDocumento9 páginasPhotosynthesis Review Worksheetbrianjay.codillaAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT - : Aerobic Respiration: NameDocumento9 páginasUNIT - : Aerobic Respiration: NameTanishq SimonAinda não há avaliações
- Aerobic Respiration RevisionDocumento10 páginasAerobic Respiration RevisionJenny JanssonAinda não há avaliações
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetDocumento8 páginasCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review WorksheetMhai MontanoAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration Guided NotesDocumento4 páginasCellular Respiration Guided NotesRangerbackAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration ReviewDocumento27 páginasPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration ReviewBarry SeeboAinda não há avaliações
- Aerobic Respiration Power PointDocumento35 páginasAerobic Respiration Power PointJeremy WongAinda não há avaliações
- Aerobic RespirationDocumento10 páginasAerobic RespirationAnnarose HilhorstAinda não há avaliações
- A. Readings and DiscussionsDocumento9 páginasA. Readings and DiscussionsChristian Jay R. LanuriasAinda não há avaliações
- Kristine Tigley GENBIO1 WEEK 3 PDFDocumento9 páginasKristine Tigley GENBIO1 WEEK 3 PDFVivian giducosAinda não há avaliações
- TEST I. Refer To Google Forms. TEST II. Fill in The Blanks. Write Your Answer Before Each NumberDocumento3 páginasTEST I. Refer To Google Forms. TEST II. Fill in The Blanks. Write Your Answer Before Each NumberDacks WangAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Quarter Gen Bio 1 Week 2Documento12 páginas2nd Quarter Gen Bio 1 Week 2Jonela BesaresAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Summary: Cell RespirationDocumento5 páginasChapter Summary: Cell Respirationsarah parkAinda não há avaliações
- Unlock SGCh07Documento7 páginasUnlock SGCh07SilaxAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 Week 6 Answer Sheet: EvaluateDocumento4 páginasGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 Week 6 Answer Sheet: EvaluateSamantha MedranoAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Respiration WorksheetDocumento3 páginasCell Respiration WorksheetTim DAVISAinda não há avaliações
- GB1 Q2 Week-3bDocumento10 páginasGB1 Q2 Week-3bAnnejhel Mae PoralanAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Respiration WorksheetDocumento3 páginasCell Respiration Worksheetcristian gonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Respiration WebQuest 2015Documento3 páginasCell Respiration WebQuest 2015Haley HaunAinda não há avaliações
- CellularRespiration REVIEWDocumento4 páginasCellularRespiration REVIEWLoren TejonesAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide For QuestDocumento4 páginasStudy Guide For Questapi-352384491Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Practice TestDocumento13 páginasChapter 9: Cellular Respiration Practice TestDaniel ClementsAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration Review WorksheetDocumento7 páginasCellular Respiration Review WorksheetJJ AlmagroAinda não há avaliações
- Key Photosynthesis Respiration Review WorksheetDocumento3 páginasKey Photosynthesis Respiration Review WorksheetShilpa Kantaria50% (2)
- Microbial Metabolism Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCDocumento30 páginasMicrobial Metabolism Microbiology Lecture PowerPoint VMCDrAmit VermaAinda não há avaliações
- BScie 104 - Laboratory Exercise 3Documento2 páginasBScie 104 - Laboratory Exercise 3Cherry Joy SalcedaAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration Webquest DBBBBDocumento5 páginasCellular Respiration Webquest DBBBB....Ainda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: K A L E BDocumento7 páginasPhotosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Review: K A L E BDestiny DunkleyAinda não há avaliações
- Autotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular RespirationDocumento7 páginasAutotrophs and Heterotrophs: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respirationapi-319819727Ainda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCellular Respiration Worksheetapi-26388972Ainda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration WebquestDocumento3 páginasCellular Respiration WebquestHaley HaunAinda não há avaliações
- Using Models To Understand Cellular Respiration ShortDocumento3 páginasUsing Models To Understand Cellular Respiration ShortgithaigaedithAinda não há avaliações
- Bio 10 Chapter 8 Study Test 10-11: Multiple ChoiceDocumento11 páginasBio 10 Chapter 8 Study Test 10-11: Multiple Choicegeorge linAinda não há avaliações
- Photosynthesis Lecture Notes PDF RevisedDocumento5 páginasPhotosynthesis Lecture Notes PDF Revisedapi-479879206Ainda não há avaliações
- hssb0400s StudygdaDocumento18 páginashssb0400s StudygdaMohamed HassaneinAinda não há avaliações
- RESPIRATION (Chapter 11)Documento4 páginasRESPIRATION (Chapter 11)Mia MistypuffAinda não há avaliações
- Ch. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDocumento8 páginasCh. 7 Pre Reading QuestionsDJ ISAACS25% (4)
- Jamal Hassan - Photosynthesis BookletDocumento51 páginasJamal Hassan - Photosynthesis BookletJamal HassanAinda não há avaliações
- HANDOUT - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review Sheet 2017Documento3 páginasHANDOUT - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review Sheet 2017ezraburrosAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration Study GuideDocumento4 páginasCellular Respiration Study GuideLana50% (2)
- Aerobic Respiration Quiz 2 2019 (Final Version)Documento6 páginasAerobic Respiration Quiz 2 2019 (Final Version)KHANSAAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On RespirationDocumento4 páginasBio Factsheet: Answering Exam Questions On Respirationapi-213276898Ainda não há avaliações
- Essentials of The Living World 4th Edition Johnson Test Bank DownloadDocumento17 páginasEssentials of The Living World 4th Edition Johnson Test Bank DownloadKathleen Salinas100% (21)
- Gen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedDocumento37 páginasGen Bio 1 Second QTR Module RevisedMichaela CasabaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Respiration Worksheet KEYDocumento3 páginasCell Respiration Worksheet KEYerikabeltranAinda não há avaliações
- AP Bio Chapter 9 Study GuideDocumento4 páginasAP Bio Chapter 9 Study GuidelilyhcyAinda não há avaliações
- Ellular Espiration: Big PictureDocumento3 páginasEllular Espiration: Big PicturehomamunfatAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 5 Reading WorksheetDocumento3 páginasChap 5 Reading WorksheetSarahAinda não há avaliações
- hssb0400s StudygdbDocumento12 páginashssb0400s StudygdbMohamed HassaneinAinda não há avaliações
- AP Biology Cellular RespirationDocumento47 páginasAP Biology Cellular RespirationJ15Ainda não há avaliações
- Electron Transport ChainDocumento4 páginasElectron Transport ChainBonilla, Alicia Mae B.Ainda não há avaliações
- BozemanATPGuided NotesDocumento4 páginasBozemanATPGuided NotesedeceAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 6 WorksheetDocumento6 páginasUnit 6 WorksheetMarta YantiAinda não há avaliações
- Module 7 RationaleDocumento2 páginasModule 7 RationaleG IAinda não há avaliações
- Ap Biology PhotosynthesisDocumento7 páginasAp Biology PhotosynthesisMinh Triet LyAinda não há avaliações
- (Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration) : What I Know (Pre Test)Documento16 páginas(Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration) : What I Know (Pre Test)Maricar Feb MaturanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2No EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Ainda não há avaliações
- Production of Clean Hydrogen by Electrochemical Reforming of Oxygenated Organic CompoundsNo EverandProduction of Clean Hydrogen by Electrochemical Reforming of Oxygenated Organic CompoundsAinda não há avaliações
- Bioenergetics: A Novel Theory for Atp SynthesisNo EverandBioenergetics: A Novel Theory for Atp SynthesisAinda não há avaliações
- Northern Renaissance ArtDocumento69 páginasNorthern Renaissance Artphapalla101Ainda não há avaliações
- AP Preparing To Write Your Concentration StatementDocumento1 páginaAP Preparing To Write Your Concentration Statementphapalla101Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Write UpDocumento6 páginasLab Write Upphapalla10150% (2)
- AP European History 2004 MC ExamDocumento18 páginasAP European History 2004 MC Examresilientnight100% (4)
- Biology Notes Chapter Four CompleteDocumento22 páginasBiology Notes Chapter Four Completephapalla101Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary Fatty Alcohols LFRMIDocumento2 páginasSummary Fatty Alcohols LFRMILuis Fernando Ramos Méndez IrisAinda não há avaliações
- Hormones and Metabolic RegulationDocumento40 páginasHormones and Metabolic RegulationEka HabinaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 151 - Syllabus - 1st Sem 2014-2015Documento4 páginasCH 151 - Syllabus - 1st Sem 2014-2015hybridizemeAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Exam Syll Rev 2010 IITDDocumento5 páginasComprehensive Exam Syll Rev 2010 IITDswjaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Inborn Errors of CHO MetabolismDocumento30 páginasInborn Errors of CHO Metabolismwaleedemad649Ainda não há avaliações
- Heat and LifeDocumento7 páginasHeat and LifeAbeer FatimaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Test N EappDocumento5 páginasDiagnostic Test N Eappcherish mae oconAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Plant NutritionDocumento35 páginas1 Plant NutritionAbbie UgotAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook PDF General Organic Biological Chemistry 4th EditionDocumento61 páginasEbook PDF General Organic Biological Chemistry 4th Editionjohn.le742100% (46)
- STPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: SulitDocumento14 páginasSTPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: Sulitrevathy varatharajahAinda não há avaliações
- BiochemistryDocumento10 páginasBiochemistryArjayle Airobail LlevadoAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Microbial Growth and ControlDocumento13 páginas3 Microbial Growth and Controlwarren delizoAinda não há avaliações
- Bio ChemistryDocumento16 páginasBio ChemistryDamini MandhoryaAinda não há avaliações
- Carbohydrate Metabolism-1Documento27 páginasCarbohydrate Metabolism-1RESHMA I MBAAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Cellular RespirationDocumento47 páginasChapter 7 Cellular Respirationwickedbiology101Ainda não há avaliações
- Plant Physiology Part IIDocumento33 páginasPlant Physiology Part IIamitAinda não há avaliações
- The Metabolism Reset Diet - Dr. Alan Christianson (2019)Documento2 páginasThe Metabolism Reset Diet - Dr. Alan Christianson (2019)Jules1998Ainda não há avaliações
- Niara Baksh and Selina Beharry - Ketoacidosis ProjectDocumento7 páginasNiara Baksh and Selina Beharry - Ketoacidosis ProjectSelina BeharryAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Metabolism: Horton Chapters 10.1 & 10.3Documento26 páginasIntroduction To Metabolism: Horton Chapters 10.1 & 10.3sabweedAinda não há avaliações
- ECOSYSTEMDocumento10 páginasECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyAinda não há avaliações
- Reactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaDocumento7 páginasReactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaBetina PAinda não há avaliações
- Active Principle: Lecture 10 Pharm Sci/Chem 177, University of California, IrvineDocumento52 páginasActive Principle: Lecture 10 Pharm Sci/Chem 177, University of California, IrvineVivian PhamAinda não há avaliações
- METABÓLITOS SECUNDÁRIOS para TRATAMENTO DE DIABETESDocumento67 páginasMETABÓLITOS SECUNDÁRIOS para TRATAMENTO DE DIABETESNathalia CibelleAinda não há avaliações
- MT202 Unit5Documento52 páginasMT202 Unit5Nurul Balqish Abdul WahabAinda não há avaliações
- Week 7 - Answer Sheet - BioenergeticsDocumento4 páginasWeek 7 - Answer Sheet - BioenergeticsアーロンクリスチャンAinda não há avaliações
- Life Sciences Part 1 Csir JRF Net Gate DBTDocumento132 páginasLife Sciences Part 1 Csir JRF Net Gate DBTmakerk82100% (1)
- Worksheets On PRDocumento3 páginasWorksheets On PRPrince KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 PhotosynthesisDocumento18 páginasChapter 6 PhotosynthesisDaniel ChrysAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional Management of The Critically Ill.29Documento16 páginasNutritional Management of The Critically Ill.29Ririn Muthia ZukhraAinda não há avaliações
- MDCAT 2022 Biology Bioenergetics MCQsDocumento36 páginasMDCAT 2022 Biology Bioenergetics MCQsSalman AhmedAinda não há avaliações