Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
AD
Enviado por
nanduslns070 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações6 páginasADER
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoADER
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações6 páginasAD
Enviado por
nanduslns07ADER
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 6
Fundamentals of Compressible Flow
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Fluid Flow
1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Conservation of mass 1 1.3 Particle paths, streamlines and streaklines in 2-D steady flow 5 1.4 Particle paths in three dimensions 18 1.5 The substantial derivative 18 1.6 Momentum transport due to convection 21 1.7 Momentum transport due to molecular motion at microscopic scales 26 1.8 Conservation of energy 33 1.9 Summary - the equations of motion 38 1.10 Problems 39
Chapter 2 - Thermodynamics of Dilute Gases
2.1 Introduction 1 2.2 Thermodynamics 1 2.3 The Carnot Cycle 5 2.4 Enthalpy 9 2.5 Heat capacities 12 2.6 Ideal gases 13 2.7 Constant specific heat 16 2.8 The entropy of mixing 18 2.9 Isentropic expansion 25 2.10 Some results from statistical mechanics 31 2.11 Enthalpy - diatomic gases 33 2.12 Speed of sound 33 2.13 Atmospheric models 34 2.14 The third law of thermodynamics 36 2.15 Problems 38
bjc
TOC.1
9/12/11
Chapter 3 - Control Volumes, Vector Calculus
3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Control volume definition 1 Vector calculus 2 Gauss theorem 6 Stokes theorem 8 Problems 9
Chapter 4 - Kinematics of Fluid Motion
4.1 Elementary flow patterns 1 4.2 Rate-of-strain and rate-of-rotation tensors 8 4.3 Problems 9
Chapter 5 - The Conservation Equations
5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 Leibniz rule for differentiation of integrals 1 Conservation of mass 5 Conservation of momentum 6 Conservation of energy 9 Summary - differential form of the equations of motion 11 Integral form of the equations of motion 12 Applications of control volume analysis 15 Stagnation enthalpy, temperature and pressure 21 Problems 29
Chapter 6 - Several Forms of the Equations of Motion
6.1 The Navier-Stokes equations 1 6.2 The momentum equation in terms of vorticity 2 6.3 The momentum equation in terms of the entropy and vorticity 4 6.4 Inviscid, irrotational, homentropic flow 6 6.5 The velocity potential 8 6.6 The vorticity equation 11 6.7 Fluid flow in three dimensions, the dual stream function 13 6.8 The vector potential 14 6.9 Incompressible flow with mass and vorticity sources 16 6.10 Turbulent flow 17 6.11 Problems 20
9/12/11
TOC.2
bjc
Chapter 7 - Entropy Generation and Transport
7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 Convective form of the Gibbs equation 1 The kinetic energy equation 1 Internal energy 3 Viscous dissipation of kinetic energy 4 Entropy 5 Problems 8
Chapter 8 - Viscous Flow Along a Wall
8.1 The no-slip condition 1 8.2 Equations of motion 3 8.3 Plane, compressible Couette flow 4 8.4 The viscous boundary layer on a wall 12 2 8.5 The laminar boundary layer in the limit M ! 0 19 8.6 Compressible laminar boundary layers 24 8.7 Mapping a compressible to an incompressible boundary layer 27 8.8 Turbulent boundary layers 41 8.9 Transformation between flat plate and curved wall boundary layers 47 8.10 Problems 50
Chapter 9 - Quasi-One-Dimensional Flow
9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Control volume and integral conservation equations 1 Area averaged flow 5 Normal shock waves 12 Shock wave thickness 25 Problems 32
Chapter 10 - Gasdynamics of Nozzle Flow
10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Area-Mach number function 1 A simple convergent nozzle 6 Converging-diverging nozzle 9 Examples 15 Problems 22
bjc
TOC.3
9/12/11
Chapter 11 - Area Change, Wall Friction and Heat Transfer
11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Control volume 1 Stagnation pressure and entropy 2 Velocity, density, temperature, pressure 4 The Mach number 5 Mass flow, area-mach-number function 6 Integrated relations 7 Detonations and deflagrations 17 Problems 24
Chapter 12 - Steady Waves in Compressible Flow
12.1 12.2 12.3 12.5 Oblique shock waves 1 Weak oblique waves 7 The Prandtl-Meyer expansion 11 Problems 14
Chapter 13 - Unsteady Waves in Compressible Flow
13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 13.7 13.8 Governing equations 1 The acoustic equations 1 Propagation of acoustic waves in one space dimension 4 Isentropic, finite amplitude waves 7 Centered expansion wave 10 Compression wave 12 The shock tube 13 Problems 20
Chapter 14 - Thin Airfoil Theory
14.1 Compressible potential flow 1 14.2 Similarity rules for high speed flight 16 14.3 Problems 25
Appendix 1 - Some Results From the Kinetic Theory of Gases
A1.1 Distribution of molecular velocities in a gas 1 A1.2 Mean molecular velocity 7 A1.3 Distribution of molecular speeds 9
9/12/11
TOC.4
bjc
A1.4 Pressure 10 A1.5 The mean free path 13 A1.6 Viscosity 14 A1.7 Heat conductivity 15 A1.8 Specific Heats, the law of equipartition 16 A1.9 Diatomic gases 17 A1.10 Energy levels in a box 25
Appendix 2 - Equations in cylindrical and spherical coordinates
A2.1 A2.2 A2.3 A2.4 A2.5 A2.6 A2.7 A2.8 Coordinate systems 1 Transformation of vector components 2 Summary of differential operations 2 Continuity 6 Momentum 7 Energy equation 9 Components of the stress tensor 11 Energy dissipation function 12
bjc
TOC.5
9/12/11
9/12/11
TOC.6
bjc
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- AI Skills Taxonomy JuneDocumento6 páginasAI Skills Taxonomy JunePradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Isit437 L01Documento8 páginasIsit437 L01Pradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
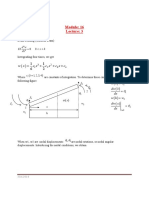
- Approximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Documento7 páginasApproximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Pradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Total DerivativeDocumento8 páginasTotal DerivativePradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Fig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsDocumento4 páginasFig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- WX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXDocumento6 páginasWX CX CX CXC: DW EI X H DXPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- m16l41 PDFDocumento4 páginasm16l41 PDFPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
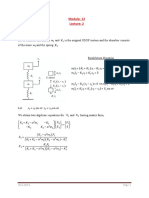
- Module: 12 Lecture: 1: MX MX CX CX KX KX FT MX MX CX CX KX KX FTDocumento4 páginasModule: 12 Lecture: 1: MX MX CX CX KX KX FT MX MX CX CX KX KX FTPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Approximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Documento7 páginasApproximate Methods: Module: 15 Lecture: 1Pradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- m15l38 PDFDocumento3 páginasm15l38 PDFPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Fig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsDocumento4 páginasFig. 1 Airfoil Model Mounted in Bending and Torsional SpringsPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Module: 13 Lecture: 3: Rigid Body ModeDocumento4 páginasModule: 13 Lecture: 3: Rigid Body ModePradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- With Viscous Damping (Under Damped)Documento6 páginasWith Viscous Damping (Under Damped)Pradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- m14l31 PDFDocumento7 páginasm14l31 PDFPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Beat Phenomenon: O, RespectivelyDocumento5 páginasBeat Phenomenon: O, RespectivelyPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- m11l23 PDFDocumento7 páginasm11l23 PDFPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration Absorber:: M and K Is The Original SDOF System and The Absorber Consists M and The Spring KDocumento2 páginasVibration Absorber:: M and K Is The Original SDOF System and The Absorber Consists M and The Spring KPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Laplace Transformation: T F KX X C X MDocumento3 páginasLaplace Transformation: T F KX X C X MPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- m7l13 PDFDocumento10 páginasm7l13 PDFPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- System With Two DOF: Free Undamped VibrationDocumento4 páginasSystem With Two DOF: Free Undamped VibrationPradip GuptaAinda não há avaliações