Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
NCP
Enviado por
Jonathan LiscanoTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
NCP
Enviado por
Jonathan LiscanoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CUES
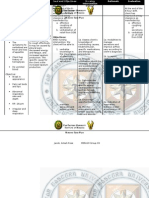
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Self-Care Deficit: bathing/ hygiene, dressing/ grooming, feeding, toileting
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION
OBJECTIVES (PLANNING)
NURSING INTERVENTIONS > promote pt./ SO participation in problem identification and decision making
RATIONALE
EXPECTED OUTCOME SHORT TERM >After 4 hours of NI, the pt. shall have been able to verbalize knowledge of health care practices.
S> O > pt. may manifest inability to: - prepare food for ingestion; open containers - handle utensils; get food onto utensil safely; bring food from a receptacle to mouth - wash body or body parts - get in and out of the bathroom/ tub - dry body > pt. may manifest inability to
Self-care deficit is the SHORT TERM impaired ability to >After 4 hours perform feeding, of NI, the pt. will bathing or hygiene, be able to dressing and verbalize grooming, or knowledge of toileting activities for health care oneself [on a practices. temporary, permanent, or progressing basis]. LONG TERM > After 2 days of NI, the pt. will demonstrate techniques/ lifestyle changes to meet selfcare needs
> enhances commitment to plan, optimizing outcomes
> plan time for > to discover listening to the pt./ barriers to SO participation in regimen > review safety concerns > review/ modify program periodically to accommodate changes in clients abilities > assist with necessary adaptations to accomplish ADLs; begin with familiar, easily accomplished > to reduce risk of injury > assists client to adhere to plan of care to fullest extent
LONG TERM > After 2 days of NI, the pt. shall have demonstrated techniques/ lifestyle changes to meet self-care needs
> to encourage pt. and build on successes
put on or take off necessary items of clothing; fasten locks/ zippers; put on socks/ shoes >pt. may manifest inability to get to toilet/ commode; carry out proper toilet hygiene
tasks > review instructions from other members of the health care team and provide written copy
> provides clarification, reinforcement, and periodic review by pt./ caregivers
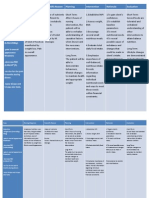
H Y P E R T H E R M I A ASSESSMENT S> NURSING DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVE EXPLANATION Fever is not an Short term: illness and it is an O> the patient important part of the bodys After 4 INTERVENTIONS Monitor record VS RATIONALE EXPECTED OUTCOME obtain Short term: After the NI, the pts To pts
and To
baseline data
hours of NI, the pts Assess general condition
manifested:
defense against infection
determine temperature shall decreased have to
temperature will be able to decrease to
current status
normal range Determine precipitating Identifying the underlying cause essential recovery is to Long term: After the NI, the pt shall
Hyperthermia Pain Infection Albumin trace on urinalysis
Antigens
or
normal range
microorganisims causes inflammation and the release of which substance After 2 days Long term:
factors
pyrogens of NI, the pt is a will be able to that be free of complications Control environmental
have been free of
Removing
complications
source of heat and
Vs: 39.8 20 cpm 86 bpm 110/70 mmHg
induces fever
and core
maintain
tempereature
can begin the maintained cooling process core and core temperature reduce temperature within normal range.
temperature within normal range
This decreases warmth Remove excess clothing and covers increases evaporative cooling and
To Provide TSB temp
decrease y
conduction
These measure help promote Provide cooling
additional cooling mechanisms like the use of fan and local ice packs To like
Administer analgesics
promote in core
decrease body
Paracetamol as ordered
temperature
A C U T E
P A I N EXPECTED OUTCOME Short term: Goal Met. After 2-3 hours of
ASSESSMENT S>
SCIENTIFIC NURSING EXPLANATIO DIAGNOSIS N Ascariasis in the hepatobiliary tract can cause acute cholecystitis, acute cholangitis, obstructive
OBJECTIVE Short term:
INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
Masakit Acute Pain
yung sa may bandang balakang ko. Sa likod chaka lalo na kapag umiihi
O> patient
the
jaundice, acute pancreatitis and hepatic
manifested: Observed evidence of pain Grimaces,
liver abscess. After gaining entry from the ampulary
Document location, Helps evaluate the site duration, intensity, of obstruction and and radiation. Note progress. Flank pain After 2-3 hours of nonverbal signs such may be suggestive that nursing as elevated BP, pulse, presence of renal restlessness, moaning, stones are already in interventions, and guarding the kidney area. patient will be able behaviors. This will provide timely to verbalize non administration of analgesia pharmacologic and alerts care givers to Explain cause of pain the possibility of passing means of pain and importance of stone / developing notifying health care complications. management and providers of the identify positions changes in pain occurrence and that may Promotes relaxation, characteristics. contribute to reduces muscle tension, and enhances muscle relaxation coping. Provide comfort Long term: measures and encourage deep Relieves muscle breathing exercises. After 3-4 days of tension and may
nursing interventions, patient was able to verbalize non pharmacologic means of pain
management and identify positions that contribute may to
muscle relaxation
easily distracted Positionin g relieve pain Diaphores is Narrowed attention span to
orifice the worms can
nursing interventions,
reduce reflex spasms
freely move in patient will be able Apply warm compress Pain may worsen in to back and out of the to report a marked supine position, vigorous hydration biliary tree reduction in pain promotes passing of and they can sensation. stone, prevents urinary stasis, and aids in cause Encourage with prevention of further frequent ambulation abdominal stone formation as indicated and pain in the increased fluid intake patient. Note reports of increased / persistent Complete obstruction abdominal pain of ureter may cause perforation and extravasation of urine into perirenal space. This may represent an acute surgical emergency. Administer medications as ordered: Narcotics, NSAIDS, Ibuprofen This is to reduce renal colic and promote muscle relaxation
Long term: Goal Met. After 3-4 days of
nursing interventions, patient was able to report a
marked reduction in pain sensation as evidenced by a relaxed appearance appropriate resting and and
sleeping patterns.
Risk for injury Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Expected Outcomes
S> O> patient manifested: >left-sided body weakness >inability to perform ADLs >patient is being assisted by SOs in doing ADLs patient may manifest: > inability to adapt to environmental conditions >frequent muscle spasms
Risk for injury
The risk for injury continues throughout recovery from hepatobiliary ascariasis. It may also extend into the home environment, where patients attempt to perform former activities, such as walking, cooking or dressing. Factors that increase the risk for injury include decreased level of consciousness, weakness, flaccidity, spasticity, impulsive behavior, altered thought processes and
Short term: After 5 hours of nursing interventions, the patient will demonstrate behaviors to reduce risk factors and to protect self from injury.
> Establish rapport
> To establish nurse-patient relationship.
Short term:
> Monitor vital signs. > Note age and sex of the patient.
Long term: After 4 days of nursing interventions, the patient will remain free from injury as evidenced by an absence of abrasions, burns or falls.
> Evaluate developmental level, decisionmaking ability, level of cognition and competence.
> Assess mood, coping capabilities and personality styles like temperament, aggression and impulsive behavior.
The patient shall have >To establish demonstrated baseline data. behaviors to reduce risk >Elderly persons factors and to are at greater protect self risk of injury. from injury after 5 hours of > To determine nursing the technique to interventions. use in educating the patient on Long term: how to reduce or eliminate risk The patient factors. shall have remained free > These may from injury as result in evidenced by an carelessness or absence of increased risk abrasions, burns taking without or falls after 4 consideration of days of nursing consequences. interventions. > May enhance disregard for own or others
motor, visual and spatialperceptual impairments.
safety. > Evaluate patients response to violence > To determine in surroundings. the severity of body weakness and to be able > Assess muscle to perform strength, gross and appropriate fine motor interventions. coordination. > To promote safe physical environment and individual safety. > Identify interventions and safety devices such > Impulsive as asking for behaviors may assistance in increase the risk performing ADLs. of the patient to injury. > Encourage use of techniques to > To enhance reduce stress and self-esteem and vent emotions such sense of worth. as anger and hostility. > Encourage participation in self> to make the patient be self-
help programs such as assertiveness training and positive self-image. > Discuss to patient/SO importance of selfmonitoring of conditions/emotions that can contribute to occurrence of injury. > Encourage patient to prevent doing things beyond what her body can perform. > Instruct SO to assist client in performing her activities of daily living. > Instruct SO to understand the patient especially when she is in distress.
reliant and be responsible of her own safety.
> To reduce the occurrences of injury.
> To reduce risk for injury.
> The understanding and support of people who are close to the patient may increase the wellness of the patient.
Você também pode gostar
- Super Final NCPDocumento16 páginasSuper Final NCPNessaly Jane PrestoAinda não há avaliações
- NICU Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNICU Nursing Care Planlorence_cachoAinda não há avaliações
- Long Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeDocumento18 páginasLong Term: PT Will Demonstrate Increased Tolerance To Activity by DischargeMary Ann Ebol0% (1)
- NCP PTBDocumento2 páginasNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Cerebral Palsy Nursing DiagnosesDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan: Cerebral Palsy Nursing Diagnosesrusnani100% (1)
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocumento4 páginasNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentThomas FarrishAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Somera Case 1928Documento68 páginasSomera Case 1928jrkalbo75% (4)
- NCP PediaDocumento2 páginasNCP PediaJoey JoseAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPjoyce_albertoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Clear Airway GoalDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plan for Clear Airway GoalSkyerexAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - CaDocumento3 páginasDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ReliefDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Pain ReliefAdelaine LorestoAinda não há avaliações
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocumento7 páginasAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkAinda não há avaliações
- NCP CSDocumento7 páginasNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocumento5 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaAinda não há avaliações
- Seizure NCPDocumento2 páginasSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Jacildo LT Module 6 TCNDocumento2 páginasJacildo LT Module 6 TCNMeryville JacildoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing ManagementDocumento16 páginasNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaAinda não há avaliações
- Azithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento2 páginasAzithromycin Nursing ConsiderationsKristine YoungAinda não há avaliações
- Guaifenesin Drug CardDocumento1 páginaGuaifenesin Drug CardJessie JenningsAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study TableDocumento14 páginasDrug Study TableAl-Mujib TanogAinda não há avaliações
- Ethical BrochureDocumento2 páginasEthical Brochureapi-414703292100% (1)
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case StudyDocumento38 páginasIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case Studygiadda100% (9)
- Running Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1Documento11 páginasRunning Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1api-546355462Ainda não há avaliações
- Pneumo HemothoraxDocumento126 páginasPneumo HemothoraxLyra Jan Roo100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 páginasIneffective Tissue PerfusionStephanie Louisse Gallega Hisole100% (2)
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocumento2 páginasStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisChristian Remetio100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento13 páginasNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocumento1 páginaAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocumento8 páginasNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliAinda não há avaliações
- ClubfootDocumento9 páginasClubfootLorebell100% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento6 páginasNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaAinda não há avaliações
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Documento32 páginasN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Ainda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Plan for a Child with IntussusceptionCharina Aubrey100% (1)
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 páginasActivity Intoleranceayra_alegreAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map FinalDocumento6 páginasConcept Map Finalapi-314827222Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP BleedingDocumento3 páginasNCP Bleedingapi-316491996Ainda não há avaliações
- Diabetes InsipidusDocumento48 páginasDiabetes InsipidusAhmed Fraz MamoonAinda não há avaliações
- Case Group Work #2 CHAPTER 6 Learning Exercise 6.4 L&M 03-03-2021 SituationDocumento3 páginasCase Group Work #2 CHAPTER 6 Learning Exercise 6.4 L&M 03-03-2021 SituationZunnel CortesAinda não há avaliações
- Augmentin drug classification, dosage, indications, contraindications and nursing interventionsDocumento2 páginasAugmentin drug classification, dosage, indications, contraindications and nursing interventionsCherubim Lei DC FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Tranexamic AcidDocumento2 páginasTranexamic AcidIrish Ivy VibethAinda não há avaliações
- BSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoDocumento2 páginasBSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoAlliahkherzteen LagoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCP 4Documento1 páginaNCP 4marohunkAinda não há avaliações
- Discharge PlanDocumento5 páginasDischarge PlanDenise Louise PoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPMarielle SorianoAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan-1idealDocumento30 páginasNursing Care Plan-1idealSheila Mae PanisAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPNaidin Catherine De Guzman-AlcalaAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired MobilityDocumento3 páginasImpaired MobilityYeana AlonAinda não há avaliações
- 4 NCP's FinalDocumento9 páginas4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- GastroenteritisDocumento8 páginasGastroenteritistanlimdania100% (3)
- NCP FinalDocumento18 páginasNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento9 páginasNursing Care PlanjmichaelaAinda não há avaliações
- NCP GrandcaseDocumento5 páginasNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloAinda não há avaliações
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Nursing Management of CVA and NIDDMDocumento12 páginasNursing Management of CVA and NIDDMKaloy KamaoAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento2 páginasNCPJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- JournalDocumento9 páginasJournalJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- A Framework For Independent Prescribing of Intravenous FluidsDocumento1 páginaA Framework For Independent Prescribing of Intravenous FluidsJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- Bell S PalsyDocumento21 páginasBell S PalsyJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- Pneumonia Is Also The Most Common Fatal Infection Acquired by Already Hospitalized PatientsDocumento14 páginasPneumonia Is Also The Most Common Fatal Infection Acquired by Already Hospitalized PatientsAshlee ShepherdAinda não há avaliações
- JournalDocumento9 páginasJournalJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- TuberculosisDocumento4 páginasTuberculosisJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento20 páginasAnatomy and PhysiologyJonathan LiscanoAinda não há avaliações
- ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers: Standard Specification ForDocumento64 páginasASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers: Standard Specification ForAnonh AdikoAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional Assessment Form of ChildrenDocumento6 páginasNutritional Assessment Form of ChildrenBisakha Dey100% (2)
- Shree Pa and Uranga Ash Tak AmDocumento5 páginasShree Pa and Uranga Ash Tak AmDowlutrao GangaramAinda não há avaliações
- ANGLICISMSDocumento14 páginasANGLICISMSManuel Jorquera100% (1)
- The Liver in Systemic Disease A Clinician's Guide To Abnormal LiverDocumento285 páginasThe Liver in Systemic Disease A Clinician's Guide To Abnormal Liveroleksandra.bilotkachAinda não há avaliações
- Aerobic BodybuilderDocumento38 páginasAerobic Bodybuildercf strength80% (5)
- Numerical Reasoning Practice Test Answers: de Roza Education and Research 2016Documento2 páginasNumerical Reasoning Practice Test Answers: de Roza Education and Research 2016johnAinda não há avaliações
- Rotex Brochure PDFDocumento4 páginasRotex Brochure PDFestramilsolutionAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles of Erp RecordingDocumento14 páginasBasic Principles of Erp Recordingkeihoina keihoinaAinda não há avaliações
- The Dynamics of BreathingDocumento5 páginasThe Dynamics of BreathingChris McCulloch100% (1)
- Efektivitas Penggunaan Komposit Polimer Yang Diperkuat Serat Untuk Perbaikan Pipa Baja Bawah AirDocumento15 páginasEfektivitas Penggunaan Komposit Polimer Yang Diperkuat Serat Untuk Perbaikan Pipa Baja Bawah Air31Hanif ArdhioAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter I - The Research Problem: Introduction/Background of The StudyDocumento4 páginasChapter I - The Research Problem: Introduction/Background of The StudyCha LinsengAinda não há avaliações
- NTS Test 02 (ANS REQ)Documento6 páginasNTS Test 02 (ANS REQ)talal hussainAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal 10Documento11 páginasJurnal 10Atika DelianaAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Review - KEDRABDocumento97 páginasClinical Review - KEDRABcoolchapAinda não há avaliações
- Bureau Corrections ManualDocumento55 páginasBureau Corrections ManualEugene UCAinda não há avaliações
- Kids' Classic Readers SummaryDocumento17 páginasKids' Classic Readers SummaryRatilal M JadavAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Membrane TransportDocumento37 páginasCell Membrane TransportMaya AwadAinda não há avaliações
- ARSA 2010 International Conference Proceeding - Volume IIDocumento540 páginasARSA 2010 International Conference Proceeding - Volume IICholnapa AnukulAinda não há avaliações
- Bladder StonesDocumento20 páginasBladder StonesRiean AuliaAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation For Organic Synthesis 2001 2Documento747 páginasHandbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation For Organic Synthesis 2001 2Purna Bhavnari75% (4)
- Flood Risk Mitigation Adis Ababa UNI PDFDocumento100 páginasFlood Risk Mitigation Adis Ababa UNI PDFshucayb cabdiAinda não há avaliações
- Where Your Tax Money Goes: Essential ServicesDocumento37 páginasWhere Your Tax Money Goes: Essential ServicesPOC MMPA17Ainda não há avaliações
- ONGC - Internship - Report Please Don't Edit Directly Make A Copy of This FileDocumento65 páginasONGC - Internship - Report Please Don't Edit Directly Make A Copy of This File19024 Fenil PatelAinda não há avaliações
- SerieventilacionDocumento37 páginasSerieventilacionCaexvenAinda não há avaliações
- Charles LawDocumento12 páginasCharles LawLerr Real RelleAinda não há avaliações
- ATEX Guidelines for the Valve IndustryDocumento49 páginasATEX Guidelines for the Valve Industryio1_roAinda não há avaliações
- I-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910Documento94 páginasI-WEB - Com.vn Manual 498031910IBJSC.comAinda não há avaliações
- Brake Accumulator Test and ChargeDocumento8 páginasBrake Accumulator Test and ChargeBarzola Soto Omar100% (1)
- Pectin-Based Bioplastics from Passion Fruit RindDocumento3 páginasPectin-Based Bioplastics from Passion Fruit RindDyna Lou Jane CatanAinda não há avaliações