Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Network Configuration Tool: Operation Manual
Enviado por
Khaled El-RayesDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Network Configuration Tool: Operation Manual
Enviado por
Khaled El-RayesDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ROI-S03671-053E 021105
Network Configuration Tool
Operation Manual
NEC Corporation
Copyright 2002
ROI-S03671
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 NETWORK CONFIGURATION TOOL ...................................................................................... 1 1.1 PURPOSE ........................................................................................................................................ 1 1.2 DEFINITIONS, ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ............................................................................ 1 2 NETCFGTOOL OPERATION ..................................................................................................... 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 NETCFGTOOL COMMAND MENU STRUCTURE ........................................................................... 2 STARTING NETCFGTOOL ........................................................................................................... 3 CLOSING NETCFGTOOL ............................................................................................................ 4 CREATING A NEW NETWORK CONFIGURATION WORKSPACE. ..................................................... 4 OPENING AN EXISTING WORKSPACE (*.NCT).............................................................................. 4 NETWORK PROPERTIES: NAMING THE INDIVIDUAL NETWORKS IN A WORKSPACE ..................... 6 NETWORK PROPERTIES: NETWORK ADDRESS AND SUBNET SETTING ....................................... 7 EDITING WORKSPACE. ............................................................................................................... 9
2.9 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 3
2.8.1 2.8.2 2.8.3 2.8.4 2.8.5 2.8.6 2.8.7 2.8.8 2.8.9 2.8.10
2.12.1 2.12.2
CREATING CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................... 59 CHANGED NE LIST .............................................................................................................. 62 VIEWING THE SUBNET INFORMATION.................................................................................. 63 EXPORTING NETWORK CONFIGURATION FILES. .................................................................. 64 SAVING CURRENT WORKSPACE. .......................................................................................... 66 PRINTING CURRENT NETWORK ........................................................................................... 67 ABOUT NETWORK CONFIGURATION TOOL ........................................................................... 69
Adding a new Network Element (NE). ........................................................................... 9 Adding back-to-back line (cable) ..................................................................................... 9 Back-to-Back Line Color Codes .....................................................................................10 Deleting a Network Element (NE). ...............................................................................11 Deleting a line (cable) ....................................................................................................11 Setting Pasolink V3 and Pasolink -S Properties..........................................................12 Setting Pasolink + Properties........................................................................................23 MIU (Line Concentrator) Properties ..........................................................................36 MIU (Hop) Properties ...................................................................................................47 Setting line (cable) Properties. ................................................................................58
Exporting Network Configuration files for PNMS.......................................................64 Exporting Network Configuration Files for PM Card .................................................65
MULTIPLE CPMC WORKSPACE............................................................................................ 70
APPENDIX A: MIU SETTINGS....................................................................................................... 72 APPENDIX B: SUBNETS................................................................................................................. 73
-i -
ROI-S03671
Network Configuration Tool
The Network Configuration Tool (NetCfgTool) is an optional application tool for the Pasolink Network Management System, which provides an easy to use graphical interface in building NEC PASOLINK networks. It is a powerful tool used to generate configuration files for the Pasolink Management Cards (PMC) and network connection data files for the Pasolink Network Management System (PNMS).
1.1 Purpose
This document illustrates the use of the NetCfgTool. The explanation focuses on the common functions of the NetCfgTool and therefore is for general-purpose operation use. Moreover, the NEC PNMS is also described in passing for the users to have a general idea of the NEC PASOLINK NMS.
1.2 Definitions, Acronyms and Abbreviations
PNMS PMC/CTRL PNMT CPMC / CPM Pasolink Network Management System. Also alternatively referred to as Central Computer in this manual. Pasolink Management Card. (for Pasolink only.) Control Module (CTRL) for Pasolink+ only. Pasolink Network Maintenance Terminal Central PMC. The PMC located on the central station's IDU and is directly connected to the PNMS. Acts as the master in the HDLC chain and are responsible for polling other PMC in its network. Remote PMC. The PMC located on the remote sites that are configured as slaves. Sub-Central PMC. A PMC located in the remote site and is configured as slave to the CPMC but is a master to the sub-network below it. Network Element. Node. Outdoor Unit Indoor Unit High-level Data Link Control protocol Digital Service Channel Point to Point Protocol Simple Network Time Protocol
RPMC / RPM SCPMC / SCPM
NE ODU IDU HDLC DSC PPP SNTP
-1 -
ROI-S03671
2
2.1
NetCfgTool Operation
NetCfgTool Command Menu Structure
File New Close Open Save Save As Print Area Print Export Changed NE List Exit Application File for PNMS Configuration Files for PM Card
Setting Clear
Main Menu File Edit Network Tools Window Help
Edit Delete
Network New Delete Properties
Tools Create Configuration Performance Subnet Information
Window Cascade Tile
Help Help About NetConfigTool
-2 -
ROI-S03671
2.2
Starting NetCfgTool
To start NetCfgTool: 1. Go to Programs -> NetCfgTool -> NetCfgTool from the Windows 98/NT/2000 Start menu.. 2. NetConfig Tool main window will be displayed.
-3 -
ROI-S03671
2.3
Closing NetCfgTool
To close the NetCfgTool application: 1. Go to File -> Exit Application in the main menu.
2.4
Creating a New network configuration workspace
To start creating new workspace: 1. Go to File -> New on the main menu. 2. A blank workspace will be displayed. 3. If a workspace is currently loaded, a pop-up message will appear to remind the user to save the current workspace before opening a new one. Click on Cancel button and save the current workspace and repeat step 1. 4. Start creating and editing network configuration workspace.
2.5
Opening an existing workspace (*.nct)
NetCfgTool allows you to save a workspace in *.nct file format so that you can open and modify the current network configuration. Once you load an existing/current workspace you will be able to modify, delete or add NEs on the network. (See also 2.12 Saving the Current Workspace.)
-4 -
ROI-S03671
To open an existing workspace: 1. Click on File -> Open at the main menu of the main window.
2. Select the *.nct file of the workspace from the list. 3. Click on Open button.
4. Verify that the correct workspace is opened in the main menu.
-5 -
ROI-S03671
2.6
Network Properties: Naming the individual networks in a workspace
Since one workspace can contain a number of networks, the NetCfgTool allows you to provide useful names to each of the networks. By default, Network-x, where x is the network number, is assigned. To set the network name: 1. Click on Network -> Properties from the main menu or right click anywhere on the current Network window.
2. Enter the name you want to be associated to this workspace/network in the Network Name box. 3. Click on [OK] button to apply the new setting.
-6 -
ROI-S03671
2.7
Network Properties: Network Address and Subnet Setting
The IP addresses assigned by the NetCfgTool to Pasolink network depends on the assigned Network Address and Subnet mask in the Network Properties window. (Please refer to the PNMS Engineering Manual for the network-sizing rule and IP addressing scheme.) To set the subnet of the selected network: 1. Click on Network -> Properties from the main menu. 2. Click on Subnet Tab on the ensuing window.
3. By default the NetCfgTool will utilize the private network address 172.18.0.0 with subnet mask 255.255.254.0. This subnet allocates 512 IP addresses to the selected network. You can modify this subnet by selecting the default subnet and clicking on [Modify] button. In cases wherein the network was initially assigned a smaller subnet, you can add another subnet when the IP address runs out. Click on [Add] button to assign a new subnet to the selected network. **For example, network address 10.10.10.0 with subnet mask 255.255.255.192 was initially assigned to the selected network. This means only 64 address are allocated initially. If the number of NEs exceeds 62, then a new subnet must be assigned to the network to allocate new IP addresses on the new NEs. NOTE: The maximum number of NEs per CPMC network is 416 NEs regardless to whether more than 416 IP addresses are assigned to the network. (See PNMS Engineering Manual)
-7 -
ROI-S03671
4. The ensuing window, Network Address window, allows you to modify the default subnet by either changing the Network Address or the Subnet mask that will be used by the selected network. You can increase or decrease the allocated IP address on the selected network by modifying the subnet mask and the network address on this window. (Refer to Appendix A: Subnets to see the available subnets in the Pasolink network.) In the example shown below, where the network address 172.18.0.64 with subnet mask 255.255.255.192 was given to the selected network, NetCfgTool will allocate IP addreses 172.18.0.65-126 to this network. Note that in this example 62 IP addresses were assigned and 2 were assigned for network address (172.18.0.64) and broadcast address (172.18.0.127). Click on [OK] to apply the new subnet.
When the [Add] button was clicked in step.3, the ensuing window enables you to define another subnet that will be added to the existing subnet. Click on [Add] button to apply the new subnet.
5. Click on [OK] button to apply the new settings.
-8 -
ROI-S03671
2.8 2.8.1
Editing workspace. Adding a new Network Element (NE).
The NetConfig Tool supports Pasolink V3, Pasolink-S , MIU and Pasolink+ network configurations. Therefore a network element can either be a Pasolink V3 or Pasonlik S , MIU or Pasolink+. Note that Pasolink-S and Pasolink V3 share the same configuration. To add a new NE: icon to add a network element. Select the type of NE that you would 1. Click on like to add from the pull-down list. Pasolink V3 is selected by default.
2. Click on the location on the current workspace where you want to add the NE. 3. Arrange the newly added hop according to desired position in the workspace. The Pasolinks can be moved around the workspace by clicking on it and dragging it to the desired location in the workspace
2.8.2
Adding back-to-back line (cable)
To add a back-to-back line (cable): 1. Click on the icon.
2. Click on one of the Pasolink to be connected. Then click on the other Pasolink to be connected with back-to-back line (cable) to the previously selected Pasolink. Refer to the example given below. Example: Connecting Pasolink No.002 with Pasolink No.008 Step 1. Click on icon. Click on Pasolink No. 002.
Step 2. Click on Pasolink No. 008 Step3. Set line properties. (Refer to 2.6.6 Setting Line (cable) Properties.)
Note: Multi-drop or branching Line (B-B) cannot be connected to the output or the NMS signal source -No.001 in this example. PMC NMS port splits only the input signal but not the output signal. This is a hardware limitation of the PMC.
-9 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.3
Back-to-Back Line Color Codes
The NMS back-to-back connection between NEs varies according to the type of NEs connected, speed, synchronization, the port used and the type of protocol used. To allow the network designer to differentiate the various types of connection the NetCfgTool uses color-coded lines.
The following lists the color codes used by the NetCfgTool to represent the different backto-back connection types. Black: represents the common RS-485/RS-232C/9600bps/ASYNC multi-drop line between Pasolink, Line Concentrator, MIU and Pasolink-S NEs. Red: represents the 64kbps/RS-422/SYNC connections between NE1 and NE1 of Pasolink+ NEs. Violet: represents the RS485/19200bps/ASYNC connections NE2 and NE1 of Pasolink+ NE or RS485/19200bps/ASYNC connection between Pasolink+ and Pasolink V3/Pasolink-S/MIU NE. Blue: represents the LAN (Ethernet) back-to-back connection between Pasolink+ NE.
- 10 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.4
Deleting a Network Element (NE).
To remove an NE: 1. Right-click on the NE to bring up the context menu.
2. Click on Delete in the context menu to remove the NE.
2.8.5
Deleting a line (cable)
To remove a line: 1. Right click on the line to bring up the context menu.
2. Click on Line Delete in the context menu to continue removing the line.
- 11 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6
Setting Pasolink V3 and Pasolink -S Properties.
To modify Pasolink properties: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu.
2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will be displayed as shown below.
- 12 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6.1
Editing Pasolink General Parameters
To change the Pasolink General configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
4. In this window, Equipment Type, Pasolink Name, Area Name, Note, PMC Type, Pasolink Name Position, and Antenna Direction can be defined and modified. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.1.
- 13 -
ROI-S03671
Table 5.1: Pasolink General Properties
Parameter Equipment Type Network Element Name Area Name Note PMC Type Name Position Antenna Direction Definition Specifies the type of Pasolink equipment of the target NE. (Pasolink V3 or Pasolink-S) Defines the station or site name of the Pasolink. Maximum number characters allowed is 32. Defines the name of the area where the Pasolink is located. (Optional). Maximum number characters allowed is 80. Optional note used to describe the selected Pasolink. Maximum number characters allowed is 80. Defines the role of the Pasolink in the network. It can either be a CPM, RPM or Sub-CPM Defines the position where the Pasolink Name will be displayed in relation to the Pasolink bitmap in the workspace Defines the direction where the Pasolink is facing in the workspace.
- 14 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6.2
Editing the Network Parameters
To change the Pasolink Network Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. Click on Network Tab to display the Network Parameter window.
a) Network tab of CPMC
b) Network tab of SCPMC
4. In this window, the IP Address, Opposite Pasolink IP Address, NMS IP Address for Dual, IP Address for SCPM, Parent Pasolink Master, NetMask and Gateway can be viewed. Network Name and Network Name (Secondary) can be modified. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.2.
- 15 -
ROI-S03671
Table 5.2: Pasolink Network Properties
Parameter Primary IP Address Subnet Mask Definition Defines the assigned IP Address of the selected Pasolink Defines which part of the PMC IP Address will be masked and be defined as its subnet. This also, defines what class of IP addressing is used. (i.e. Class A, Class B, Class C, etc.) Defines the IP Address of the gateway Defines the name of the primary sub-network Defines the IP Address of the opposite station This IP address is only assigned to the NMS port of the CPM with dual-master mode. IP address of the SCPMC in the multi-drop or multibranch network. Not used in RPMC. No entry if the NE is RPMC
Gateway IP Address Network Name Opposite Network Element Secondary* IP Address of NMS (for CPMC with dualmaster mode only) IP Address of SCPM (for SCPMC only) IP Address Network Name
Defines the name of the second sub-network, if there are any, that the selected Pasolink is connected. * In this field, the available information depends on the role of the target NE.
- 16 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6.3
Editing Port Configuration Parameters
To change the Port Configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. Click on Port Tab to display the Port Parameter window.
4. In this window, baud rate of the DPU Port and NMS Port can be modified. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.3.
Table 5.3: Port Configuration Parameter
Parameter DPU Port Action Mode Baud Rate NMS Port Action Mode Baud Rate Definition Defines the role of the DPU Port of Pasolink. * The possible modes are Master, Slave, and Repeater. Defines the speed of the DPU Port in bits-per-second (bps). Defines the role of the NMS Port of Pasolink.* The possible modes are Master, Slave, Repeater and Disabled. Defines the speed of the NMS Port in bits-per-second (bps).
Defines the wiring (interface) protocol used Mode * This item will not be defined until Create Configuration is done.
- 17 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6.4
Editing HDLC Configuration Parameter
To change the HDLC Configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. Click on HDLC Tab to display the Port Parameter window.
4. In this window, the Master Timeout, Master Interval, Slave Timeout, Auto Roll Change, Roll Change and High BER DPU Inhibit can be defined and changed. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.4.
- 18 -
ROI-S03671
Table 5.4: HDLC Properties
Parameter Master Timeout Master Interval Slave Timeout Auto Role Change Definition The time in seconds wherein the PMC will assume that it has lost communication link with the master PMC. The time in seconds where in the PMC will check for the polling signal from the master PMC. The time in seconds wherein the master PMC will assume that the link with its slave PMC is lost. If enabled, the PMC will automatically change its role from slave to master PMC, once it has lost its link with the master PMC in the upper network. It will also automatically change back to slave once the link with the master is restored. This is normally set to "Enable". The elapsed time in seconds that the slave PM card waits for the polling message from the CPMC before it changes itself to assume the role of the CPMC. If High BER DPU Inhibit is set to Enable, Hi BER alarm is inhibited. This means that it will not be activated even if the DPU port receives degraded data.
Role Change Timeout
High BER DPU Inhibit
2.8.6.5
Editing Other Pasolink Parameters
To change the Other Pasolink Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. Click on Others Tab to display the Port Parameter window.
- 19 -
ROI-S03671
4. In this window, the Auto Set Time, Set Time Interval, Auto Write Back, and Write Back Interval can be changed. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.5.
Table 5.5: Other Properties
Parameter Auto Set Time Set Time Interval Auto Writeback Write Back Interval Definition If enabled, the PMC automatically sets its time to match that of the PNMS or the CPMC. The time interval before the PMC periodically synchronizes its time to the PNMS or CPMC. If enabled, the PMC automatically writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM. The time interval before the PMC writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM.
- 20 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.6.6
Editing Pasolink PNMS Parameters ( for CPMC only )
This parameter is relevant only to the NE that is assigned as CPMC. To change the Pasolink V3 or Pasolink-S PNMS Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. Click on PNMS Tab to display the PNMS Parameter window.
4. In this window, the IP address and subnet mask information of the PNMS port is defined. As the connection type, LAN or RS232/RS422 is selected, the corresponding parameters in the ensuing box are applied. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 5.6.
- 21 -
ROI-S03671
Table 5.6: PNMS Properties
Parameter PNMS Connection Definition Defines the type of connection used by the CPMC to the PNMS. The Pasolink CPMC can connect to the PNMS PC / Workstation either thru RS232C/RS422 (Dial-Up) or LAN (IP) connection. Pasolink V3: RS232C/RS422/LAN Pasolink-S : RS232C/RS422 LAN IP address Net Mask Default Gateway RS232C/RS422 Connection Type IP address of LAN port of the target Pasolink. Subnet mask of LAN port mentioned above. IP address of Default Gateway. Normally the IP address of the PNMS PC. Defines the type of connection used by the CPMC to the PNMS. The Pasolink CPMC can connect to the PNMS PC either thru Direct connection (Dial-Up) or Router connection. When the RS232C or RS422 PNMS connection is selected, the fields are sensitive. The IP address defines that is used by the RS232C or RS422 port of the Pasolink IDU. Subnet Mask of the RS232C or RS422 port mentioned above.
IP Address
Net Mask
- 22 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7
Setting Pasolink + Properties.
To modify Pasolink+ properties: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink to bring up the context menu
2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink+ Properties window will be displayed as shown below
- 23 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.1
Editing Pasolink+ General Parameters
To change the Pasolink+ General configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
4. In this window, Pasolink Name, Area Name, Note, PMC Type, Pasolink Name Position, and Antenna Direction can be changed. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 6.1.
- 24 -
ROI-S03671
Table 6.1: Pasolink+ General Properties
Parameter System Equipment Type Network Element Name Area Name Note PMC Type PMC Type Root NE Definition The type of Pasolink+ equipment: STM-1, STM-0 and PDH. The name of the NE in the network. The area where the NE is located (optional). Additional description, or remark on the NE. (optional) Role of the PMC in the network. CPMC, SCPMC or RPMC. Checked when selected NE is CPMC. This is automatically checked by the NetCfgTool for every Pasolnk + CPMC. Automatically or Manually set the subnet of the DPU/Radio port and the NE1 port. When the Subnet Separation mode is set to manual, this parameter can be customized. Either the DPU/NE1 is separated or in the same subnet. The position of the text in the workspace can be customized here. The antenna icon in the workspace can be customized to face either Right or Left. This provides the IP information of the available port in the Pasolink+ NE. The IP address that the port uses and its subnet mask can be viewed in this section.
Subnet Separation Mode Radio/NE1 Interface
Position/Direction
Name Position Antenna Direction
Port Information
- 25 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.2
Editing Pasolink+ Mode Parameters
In Pasolink+ network, the number of NEs per sub-network is selectable: 1, 5,13, 29, or 61 NE/subnetwork. To select the number of NEs per subnetwork, you can manual set the assigned Netmask in this tab. Also the IP address assignment on the selected NE can be manually assigned by enabling it in this tab (Warning!!!: Please proceed with caution when manually assigning IP addresses) To change the Pasolink+ Mode Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the Mode tab to display the Mode parameters.
4. In this window, the IP address and Netmask assignment mode can be selected. The default and recommended setting of this parameter is Auto or automatic IP address assignment of the NetConfig Tool.
- 26 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.3
Editing Pasolink+ Radio/NE1 Parameters
To change the Pasolink+ Radio/NE1 Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the Radio/NE1 tab to bring up the Pasolink+ port information.
4. In this window, the IP Address information of the Pasolink+ ports are defined. If Radio/NE1 interface from the General tab is set to The Same Subnet, the IP address under Bridge is used. On the other hand, if Different subnet is set, the IP addresses under Separate Interface are used. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 6.2. NOTE: The IP addresses, Net Masks can only be manually set if it is set to Manual in Mode tab. (See 2.8.7.2 Editing Pasolink+ Mode Parameters)
- 27 -
ROI-S03671
Table 6.2: Pasolink Radio/NE1 Properties
Parameter IP Address Bridge IP Address Bridge Netmask IP Address of Radio Netmask of Radio IP Address of NE1 Netmask of NE1 Port Setting Radio /Speed Radio /Opposite IP Address NE1 /Speed NE1 /Mode Definition IP address of the Bridge or LAN port of the Pasolink+ IDU Subnet mask of the LAN port IP address of the DPU/Radio port. Subnet mask of the DPU/Radio Port IP address of NE1 port Subnet mask of NE1 port Speed of the DPU port of the Pasolink+ radio IP address of the opposite Pasolink+ radio (DPU port). Speed of the NE1 port of the target Pasolink+ The HDLC mode of NE1 port. Enabled only when NE1 (64000 bps is used). The possible modes are Master, Slave and Disabled.
- 28 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.4
Editing Pasolink+ NE2 Parameters
To change the Pasolink+ NE2 Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the NE2 tab to bring up the Pasolink+ NE2 port information.
4. In this window, the IP Address information of the Pasolink+ NE2 port is defined. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 6.3.
- 29 -
ROI-S03671
Table 6.3: Pasolink NE2 Properties
Parameter Common Data Link Definition Type of data link protocol used by NE2. This is always set at HDLC when connected in multi-drop with another Pasolink+. The data link will be set to PPP when connected to a Pasolink V3/PasolinkS/MIU CPMC. IP address of NE2. Subnet mask of NE2 port. Speed of NE2 port. Specifies if the NE2 port is used in HDLC. The NE2 port can either be Master, Slave or blank. Automatically allow the NetConfig tool to terminate the HDLC connection of the selected NEs NE2 port, if it is the last port in the HDLC line. (Recommended) If Terminal Auto Assign is set to Manual, the termination on the NE2 port can be set to On or Off.
IP Address Net Mask Speed HDLC Mode Terminal Auto Assign
Terminate
- 30 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.5
Editing Pasolink+ LAN (B-B) Parameters
To change the Pasolink+ LAN (B-B) Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the LAN (B-B) tab to display the LAN (BB) parameters.
4. The IP address and Netmask of the LAN port is defined in this window. It is shown only if the back to back connection is set to LAN.
- 31 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.6
Editing Pasolink+ PNMS Parameters (for CPMC only)
This parameter is relevant only to the NE that is assigned as CPMC. To change the Pasolink+ PNMS Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the PNMS tab to bring up the Pasolink+ PNMS parameter.
4. In this window, the IP Address and subnet mask information of the PNMS port is defined. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 6.4. (See also 2.7 Network Properties: Setting-up the PNMS Connection.)
- 32 -
ROI-S03671
Table 6.4: Pasolink NE2 Properties
Parameter PNMS Connection Definition Defines the type of connection used by the CPMC to the PNMS. The Pasolink+ CPMC can connect to the PNMS PC either thru V.11 (Dial-UP) connection or LAN (IP) connection. IP Address When the Ethernet connection is selected, the LAN fields are sensitive. The IP address defines that that is used by the LAN port of the Pasolink+ IDU. Note that is only used when the LAN port is used for PNMS connection IP address of LAN port of the Pasolink+. This is only set if the selected NE is a CPMC. Net Mask V.11 (Default) IP Address Subnet mask of LAN port mentioned above. When the Dial-Up connection is selected, the V.11 fields are sensitive. The IP address defines that that is used by the V.11 port of the Pasolink+ IDU. Note that is only used when the V.11 port is used for PNMS connection. Subnet Mask of the V.11 port mentioned above. Connection speed used by the dial-up.
LAN
Net Mask Speed
- 33 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.7
Editing Pasolink+ Routing Parameters
To change the Pasolink+ Routing Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the Routing tab to display the routing parameters.
4. The IP address of the Default Gateway can be set in this window. The Default Gateway IP address is normally the IP address of the PNMS PC / Workstation or the associated router of the PNMS.
- 34 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.7.8
Editing Pasolink+ SNTP Parameters
Pasolink+ support Simple Network Time Protocol, used to synchronize its internal clock to a defined Time-server in the network. To change the Pasolink+ SNTP Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Pasolink+ to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Pasolink+ Properties window. 3. The Pasolink Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration. Click on the SNTP tab to display the SNTP parameters.
4. The Time Synchronization mode can be set in this window. The time on the Pasolink+ CRTL module can either be synchronized to the PNMS PC / Workstation, a time-server with SNTP in the network or set to None or no time synchronization. The IP address of the time-server as well as the Refresh Interval- the time in seconds that has elapsed before the NE will try to synchronize its internal clock to a specified time-server can be set in this window.
- 35 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8
MIU (Line Concentrator) Properties
Line Concentrator is a Stand-alone MIU that is used as a CPMC to poll other NEs in its sub-network. To modify MIU (Line Concentrator) properties: 1. Right click on the selected MIU (Line Concentrator) to bring up the context menu.
2. Click on Properties to open the Properties window of the selected Line concentrator.
3. The Properties window of the Line Concentrator contains the parameters shown and defined in Table 7.1 below:
- 36 -
ROI-S03671
Table 7.1: Line Concentrator Properties Parameter System Equipment Redundancy Total PMC Definition In Line Concentrator this field will display Line Concentrator and will be grayed-out/not selectable. Not Applicable. The total number of PMCs needed to monitor the selected equipment. NOTE: In case of Line concentrator, ONLY 1 PMC is allowed. DO NOT set the Total PMC to a value greater than 1. Type Repeater Type Bit Rate ID FASYNC Alarm Active Symbol Name Not Applicable. Not Applicable. Not Applicable. Not Applicable. The name that will be associated with the selected Line concentrator symbol. NOTE: This is the primary name NE in the workspace. This name will NOT be associated to the configuration file for this NE. To set the name for the configuration file see section 2.6.8.1.1 Editing the Line Concentrator NE General Tab, Table 7.2) Name Position Line Direction MIU CPMC Normal The position where the name of the selected Line concentrator will be displayed. Defines which side the NMS line will be added to the Line concentrator. This button contains the NE properties of the Line concentrator. This contains the network, HDLC, port and other parameters connected to the NMS setting of the MIU. (See Appendix A: MIU Setting)
4. Click on [OK] button after completing the Line concentrator properties setup.
- 37 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8.1
CPMC Normal
To set the NE properties of the MIU (Line Concentrator): 1. Right-click on the target Line Concentrator. 2. Select Properties from the context menu. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button on the ensuing window.
4. The NE properties of the Line concentrator will be displayed. Click on [OK] button to apply the save and close the window. [Cancel] button will close the window without saving the changes.
- 38 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8.1.1
Editing the Line Concentrator NE Properties General Tab
To change the Line Concentrator General configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Line Concentrator to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the line concentrator Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button. 4. The NE Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. In this window, the NE Name, Area Name, Note, Equipment Type and A/D Convert Type can be changed. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 7.2.
- 39 -
ROI-S03671
Table 7.2 General MIU (Line Concentrator) Properties
Parameter System NE Name Area Name Note PMC Usage Equipment Type Performance Monitor Input A/D Convert Type Definition The name that will be associated to the target NE. This name will be applied in the configuration files The area where the NE is located (optional). Additional description of the NE (optional). Not Available Displayed as Line Concentrator (not selectable). Not Available. The number of Analog-to-Digital conversions used in the MIU. The MIU is capable of processing a maximum of two (2) A/D conversions. Set as CPMC for line concentrators cannot be modified.
PMC Type
2.8.8.1.2
Editing the MIU Network Properties
(See 2.8.6.2 Editing the Network Parameters.)
- 40 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8.1.3
Editing the Line Concentrators HDLC Properties
To change the HDLC configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Line concentrator to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button. 4. The NE Properties window will appear. The default is the HDLC Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The HDLC properties window contains the parameters concerning the HDLC settings of the target Line Concentrator. Note that the HDLC default values are the optimum (recommended) settings. The definition of the HDLC parameters is shown in Table 7.3.
- 41 -
ROI-S03671
Table 7.3 HDLC Properties
Parameters HDLC Timer Master Timeout Master Interval Slave Timeout Role Change Auto Role Change Definition The time in seconds wherein the PMC will assume that it has lost communication link with the master PMC. The time in seconds where in the PMC will check for the polling signal from the master PMC. The time in seconds wherein the master PMC will assume that the link with its slave PMC is lost. If enabled, the PMC will automatically change its role from slave to master PMC, once it has lost its link with the master PMC in the upper network. It will also automatically change back to slave once the link with the master is restored. This is normally set to "Enable". The elapsed time in seconds that the slave PM card waits for the polling message from the CPMC before it changes itself to assume the role of the CPMC. If High BER DPU Inhibit is set to Enable, Hi BER alarm is inhibited. This means that it will not be activated even if the DPU port receives degraded data.
Role Change Timeout
HDLC Relay
High BER DPU Inhibit
2.8.8.1.4
Editing the Line Concentrator Port Properties
To change the Port configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Line Concentrator to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button.
- 42 -
ROI-S03671
4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the Port Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The Port properties window contains the parameters defining the port settings of the target Line Concentrator. The definition of the Port parameters is shown in Table 7.4.
Table 7.4 Port Properties
Parameters DPU Port* Action Mode Baud Rate Mode NMS Port Action Mode Baud Rate Mode Terminal Control Definition Defines the role of the DPU Port of MIU. Disabled for Line Concentrator. Not applicable. Not applicable. Defines the role of the NMS Port of MIU. Set to Master for Line concentrators. Defines the speed of the NMS Port in bits-per-second (bps). Defines the wiring (interface) protocol used Terminates the RS485 protocol line when enabled.
* Not used by Line concentrator.
- 43 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8.1.5
Other Properties
To change the Line concentrator Port configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected Line Concentrator to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button. 4. The Line Concentrators NE Properties window will appear. The default is the Other Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The Other properties window contains the parameters defining the Time and Flash ROM settings of the target Line Concentrator. The definition of the Other parameters is shown in Table 7.5.
Table 7.5 Other Properties
Parameter Definition Auto Set Time Set Time Interval If enabled, the PMC automatically sets it time to match that of the PNMS or the CPMC. The time interval before the PMC periodically synchronizes its time to the PNMS or CPMC. If enabled, the PMC automatically writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM. The time interval before the PMC writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM.
Set Time
Flash ROM
Auto Write Back Write Back Interval
- 44 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.8.1.6 Editing Line Concentrators PNMS Properties
To change the Line Concentrator PNMS configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC Normal] button. 4. The Line Concentrators NE Properties window will appear. The default is the PNMS Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The PNMS properties window contains the parameters defining the PNMS connection type, IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and other network parameters of the Line concentrator. As connection LAN or RS232/RS422 is selected, the corresponding parameters in the ensuing box are applied. The definition of the PNMS port parameters is shown in Table 7.6.
- 45 -
ROI-S03671
Table 7.6 PNMS Properties
Parameter PNMS Connection Definition Defines the type of connection that the PMC in the Line concentrator has the PNMS. There are three (3) possible PNMS connections allowed by the PMC namely: RS-232C: PNMS connects to the PMC using RS232C/19.2kbps Asynchronous interface. RS-422: PNMS connects to the PMC using RS422/19.2kbps/V.11 Asynchronous Interface LAN: PMC connects directly to an Ethernet network using 10BaseT/10Mbps interface. LAN* IP Address Net Mask Default Gateway Defines the IP address that will be assigned to the LANPNMS port of the PMC. Defines the subnet mask used by the LAN port of the PMC. Defines the IP address where of the machine where the traps from the PMC will be forwarded. In cases where the PNMS PC/WS is in the same network (LAN) as the PMC, this will be normally the IP address of the PNMS PC/WS. In case of WAN or networks wherein the PNMS is located in another network, this will be the IP address of the nearest router. RS232C/RS422 Connection Type Specifies whether the RS232C/RS422 connection is Direct or through Router. Direct - connection means the PNMS PC connects to the CPMC using its local COM ports. Router means that the CPMC is connected to the PNMS through a router. In this case the IP address must be in the same subnet as the routers serial port. IP Address Net Mask Defines the IP address that will be assigned to the PNMS port of the PMC. Defines the subnet mask used by the PNMS port of the PMC.
*Option only available if the PMC used in the Line Concentrator supports LAN connection
- 46 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9
MIU (Hop) Properties
This is a type of MIU that equips with microwave radio and can be used as CPMC, SCPMC or RPMC. To modify MIU (Hop) properties: 1. Right click on the selected MIU (Hop) to bring up the context menu
2. Click on Properties to open the Properties window of the selected MIU (Hop).
3. The Properties window of the MIU contains the parameters shown and defined in Table 7.1 below: 4. Click on [OK] button after completing the MIU properties setup.
- 47 -
ROI-S03671
Table 8.1: MIU (Hop) Properties
Parameter System Equipment Definition Specifies the type of equipment monitored by the MIU. They are 2000S or 2300S or 2500S or 2600S or 3000S or 3500S or Other equipment, which can Pasolink NE without PM card or other vendors equipment. The redundancy of the selected equipment. (1+0, 1+ 1, or N+1 system.) The total number of PMCs needed to monitor the selected equipment. When the selected equipment is 2000S or 2500S or 2600S, the termination type is specified in this parameter. The equipment type specified above can either be Repeater or Terminal type. The repeater type specifies the mode of repeating the signal at the 2600S radio. The 2600S can function as either a Dropins or Through repeater. This is only available for 2600S radio that has the repeater function enabled. (See also Type.) This parameter specifies the bit rate of the 2500S radio (32MB, 8x2MB or 4x2MB). When Other Equipment is selected the bit rate selection is (34MB, 17MB, or 8MB). This parameter is not available for other equipment types. This data is used for the Block Error Counter (BEC) of the Performance Monitor function. Specifies when the FASYNC alarm is active for the selected equipment. (Low Active or High Active) This data is used in UAS measurement of the Performance Monitor. The primary name that will be associated with the target MIUs symbol in the workspace. This name will be the displayed on the NetCfgTool workspace and will NOT be associated to the configuration files. To set the NE name for the configuration files, please go to section 2.6.9.1.1 Editing the MIU NE Properties General Tab, Table 8.2) and set the PMCs individually if more than one PMC is installed in the target MIU. Name Position Line Direction PMC Button [CMPC/SCPCM/RPMC Normal/Additional/etc] The position where the name of the target MIU will be displayed. Defines which side the NMS line will be added to the MIU. This button contains the NE properties of the MIU. This contains the network, HDLC, port and other parameters connected to the NMS setting of the MIU. It also describes the PMC type (CPMC, SCPMC, or RPMC) and the PMC Usage (Normal, Additional PC, Regular CH, or Protection CH). (See Appendix A: MIU Setting)
Redundancy Total PMC Type
Repeater Type
Bit Rate ID
FASYNC Alarm Active
Symbol
Name
MIU
- 48 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9.1
PMC Button - CMPC/SCPMC/RPMC Normal/Additional PMC
To set the NE properties of the MIU: 1. Right-click on the target MIU NE. 2. Select Properties from the context menu. 3. Click on [CPMC (or SCPMC or RPMC) Normal] button on the ensuing window.
4. The NE properties of the MIU will be displayed. Click on [OK] button to apply the save and close the window. [Cancel] button will close the window without saving the changes.
- 49 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9.1.1
Editing the MIU properties General Tab
To change the MIU General configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC (or SCPMC or RPMC) Normal] button. 4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the General Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. In this window, the NE Name, Area Name, Note, Equipment Type, Performance Monitoring, A/D Convert Type and PMC Type can be changed. The definitions of these parameters are listed in Table 7.2.
- 50 -
ROI-S03671
Table 8.2 General MIU Properties
Parameter System NE Name Area Name Note PMC Usage Definition The name that will be associated to the target NE. This name will be applied in the configuration files. The area where the NE is located (optional). Additional description of the NE (optional). In case that the selected MIU contains more than one PMC. The following PMC usage will apply: 1. ) For 1+0/1+1/Line Concentrator/Other Equipment system: a.)1st PMC is used as Normal. b.) and the other PMC's are used as Additional PMC. 2.) For N+1 system: a) 1st PMC is used as Protection CH. B.) and the other PMC's are used as Regular CH or Additional PMC. The type of equipment monitored by the target MIU. The number of MIU channels used for performance monitoring functions. The MIU can accommodate up to 2 CH for performance monitoring purposes. The number of Analog-to-Digital conversions used in the MIU. The MIU is capable of processing a maximum of two (2) A/D conversions. The role of the PMC in the target MIU NE in the HDLC chain.
Equipment Type Performance Monitor Input A/D Convert Type
PMC Type
2.8.9.1.2
Editing the MIU Network Properties
(See 2.8.6.2 Editing the Network Parameters.)
- 51 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9.1.3
Editing the MIU HDLC Properties
To change the MIU HDLC configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC (or SCPMC or RPMC) Normal] button. 4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the HDLC Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The HDLC properties window contains the parameters concerning the HDLC settings of the target MIU. Note that the HDLC default values are the optimum (recommended) settings. The definition of the HDLC parameters is shown in Table 7.3.
- 52 -
ROI-S03671
Table 8.3 MIU HDLC Properties
Parameters HDLC Timer Master Timeout Definition The time in seconds wherein the PMC will assume that it has lost communication link with the master PMC. The time in seconds where in the PMC will check for the polling signal from the master PMC. The time in seconds wherein the master PMC will assume that the link with its slave PMC is lost. If enabled, the PMC will automatically change its role from slave to master PMC, once it has lost its link with the master PMC in the upper network. It will also automatically change back to slave once the link with the master is restored. This is normally set to "Enable". The elapsed time in seconds that the slave PM card waits for the polling message from the CPMC before it changes itself to assume the role of the CPMC. If High BER DPU Inhibit is set to Enable, Hi BER alarm is inhibited. This means that it will not be activated even if the DPU port receives degraded data.
Master Interval Slave Timeout Role Change Auto Role Change
Role Change Timeout
HDLC Relay
High BER DPU Inhibit
2.8.9.1.4
Editing the MIU Port Properties
To change the MIU Port configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC (or SCPMC or RPMC) Normal] button.
- 53 -
ROI-S03671
4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the Port Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The Port properties window contains the parameters defining the port settings of the target MIU. The definition of the Port parameters is shown in Table 7.4.
Table 8.4 Port Properties
Parameters DPU Port Action Mode Baud Rate Mode Definition Defines the role of the DPU Port of MIU. Defines the speed of the DPU Port in bits-per-second (bps). Defines the protocol used in the DPU port. RS422/RS232 and G.703 can be used in the MIUs DPU port. Defines the role of the NMS Port of MIU. Defines the speed of the NMS Port in bits-per-second (bps). Defines the wiring (interface) protocol used Terminates the RS485 protocol line when enabled
NMS Port
Action Mode Baud Rate Mode Terminal Control
- 54 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9.1.5
Editing the MIU Other Properties
To change the MIU Port configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CMPC/RPMC Normal] button. 4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the Other Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The Other properties window contains the parameters defining the Time and Flash ROM settings of the target MIU. The definition of the Other parameters is shown in Table 7.5.
Table 8.5 Other Properties
Parameter Set Time Auto Set Time Set Time Interval Flash ROM Auto Write Back Write Back Interval Definition If enabled, the PMC automatically sets it time to match that of the PNMS or the CPMC. The time interval before the PMC periodically synchronizes its time to the PNMS or CMPMC. If enabled, the PMC automatically writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM. The time interval before the PMC writes the Log data and PM data to the Flash ROM.
- 55 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.9.1.6
Editing the MIU PNMS Properties
To change the Line Concentrator PNMS configuration Parameters: 1. Right click on the selected MIU to bring up the context menu. 2. Click on Properties to open the MIU Properties window. 3. Click on [CPMC (or SCPMC or RPMC) Normal] button. 4. The MIUs NE Properties window will appear. The default is the PNMS Tab window, which shows the current configuration.
5. The PNMS properties window contains the parameters defining the PNMS connection type, IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and other network parameters of the Line concentrator. As connection LAN or RS232/RS422 is selected, the corresponding parameters in the ensuing box are applied. The definition of the PNMS port parameters is shown in Table 7.6.
- 56 -
ROI-S03671
Table 8.6 PNMS Properties
Parameter PNMS Connection Definition Defines the type of connection that the PMC in the Line concentrator has with the PNMS. There are three (3) possible PNMS connections allowed by the PMC namely: RS-232C: PNMS connects to the PMC using RS232C/19.2kbps Asynchronous interface. RS-422: PNMS connects to the PMC using RS422/19.2kbps/V.11 Asynchronous Interface LAN: PMC connects directly to an Ethernet network using 10BaseT/10Mbps interface. LAN* IP Address Net Mask Default Gateway Defines the IP address that will be assigned to the LAN-PNMS port of the PMC. Defines the subnet mask used by the LAN port of the PMC. Defines the IP address where of the machine where the traps from the PMC will be forwarded. In cases where the PNMS PC/WS is in the same network (LAN) as the PMC, this will be normally the IP address of the PNMS PC/WS. In case of WAN or networks wherein the PNMS is located in another network, this will be the IP address of the nearest router. RS232C/RS422 Connection Type Specifies whether the RS232C/RS422 connection is Direct or through Router. Direct - connection means the PNMS PC connects to the CPMC using its local COM ports. Router means that the CPMC is connected to the PNMS through a router. In this case the IP address must be in the same subnet as the routers serial port. IP Address Net Mask Defines the IP address that will be assigned to the PNMS port of the PMC. Defines the subnet mask used by the PNMS port of the PMC.
*Option only available if the PMC used in the MIU supports LAN connection.
- 57 -
ROI-S03671
2.8.10 Setting line (cable) Properties.
To modify line properties: 1. Right click on the line to bring up the context menu.
2. Click on Line Properties on the context menu.
3. The Line Properties window will appear. In this window, the Connect Mode of the two Pasolinks connected with back-to-back connection can be changed. RS-485 or RS-232C can be used. Connect Port specifies the Pasolink+ port where line (back-to-back) is to be connected this is only available for Pasolink + NEs. Pasolink+ can have back-to-back connections on NE1, NE2 or LAN ports.
- 58 -
ROI-S03671
2.9
Creating Configuration
Create Configuration function allows flexibility in designing network configuration. This function can automatically make configuration for PM Cards and PNMS. IP Addresses and PM Type are automatically assigned to the PM Cards in the workspace. Configuration is done, by considering the size and the number of NE's available in the network. To create configurations: 1. Verify that the workspace is already finished and that all the Pasolinks and back-toback (B-B) lines to be contained in this network have been inserted. Also verify that the CPMC Properties and PPP connection have been properly set. (See sections 2.7 Setting PPP connection and 2.8 CPMC Properties.) 2. Click on Tools | Create Configuration in the main menu.
3. The create configuration window wizard will be displayed. Click on [Next] button to continue.
- 59 -
ROI-S03671
4. Check the Automatically set PMC type box if necessary on the ensuing window. By ticking this box, NetConfig Tool will automatically set PMC type and allocate NE's according to the maximum number of NE's that can be contained in a sub-network. Click on [Next] button to continue.
5. A message box, stating the status of the configuration will appear. If there are no errors encountered in the creation of the network configuration, this message will just prompt the user that process was "Completed successfully". Click on [Next] button to continue.
- 60 -
ROI-S03671
6. Click on [Finish] button to complete the operation. The [Changed NEs List] button provides information of the NEs that have been modified when the configuration was created. This is a useful feature when modifying an existing network configuration. Note: Please refer to 2.10 for the explanation of Changed NEs List button.
7. Slide over the pointer on the NEs displayed in the workspace to verify if all the NEs have been assigned with appropriate IP address and names.
- 61 -
ROI-S03671
2.10 Changed NE List
This function provides a quick view of the NEs whose contents have been changed since last update of the network. It indicates those NEs whose configuration information that need to be downloaded into PM cards because of the changes. To make sure that the accurate Change NE List is displayed, complete the operation of Export Configuration File to PM Card of the active workspace and downloading the configuration files to the PM cards before starting a new round of Create Configuration function. This window can be invoked at the end of Create Configurations operation (See 2.9 Creating Configuration) or click on File -> Changed NEs List in the main menu.
Save button can be used to save the listing to an Excel csv file.
- 62 -
ROI-S03671
2.11 Viewing the Subnet Information
NetCfgTool allows you to view the subnet information of the currently active or selected network. The subnet information contains the Network Address (and subnet mask) and IP addresses of the NEs in the selected network. To view the subnet information: 1. Click on Tools | Subnet Information in the main menu.
2. The Subnet Information contains the following information about the selected network: Network Address column: The network address is divided in to two parts this division represented by the / sign. The IP address on the left of the / is the network address of the NE and the one on the right is the subnet mask. Network Element Name: the associated name of the network element. IP Address: The IP address assigned to the NE. For SCPMCs with two IP addresses, this is normally the Primary IP address on the NE.
- 63 -
ROI-S03671
2.12 Exporting Network Configuration files.
2.12.1 Exporting Network Configuration files for PNMS
This function exports the data file for the PNMS, which allows the network designer to easily modify the network. The NetConfig Tool creates a network connection file, which can be later copied to the PNMS directory to facilitate the addition of new Pasolink NEs in the NMS network. To export network configuration file for PMNS: 1. Click on File | Export | File for PNMS on the main menu.
2. Specify the directory or folder where the NetCfg2Pnms.dat file will be saved. Note: you can save the file in another file name just make sure that the file type is NetCfgToolFiles(*.dat).
3. Click on OK button to continue the process. 4. Verify that the file saved in the specified folder.
- 64 -
ROI-S03671
2.12.2 Exporting Network Configuration Files for PM Card
This function allows the user to create PM card configuration files automatically. NetConfig Tool, creates the configuration for the given network and exports all configuration files (system.cfg and network.cfg) for each of the specified sites PMC's in the workspace.) This ultimately, saves time and minimizes error in the network design process. To export network configuration file for PM Card: 1. Click on File | Export | Configuration Files for PM Card on the main menu.
2. Specify the directory of folder where the PM Card network configuration file will be exported. The file type of the exported file should be config (*.cfg). The file will be stored in /../PM-Card/Network-x folder.
3. Click on [OK] button to continue the process. 4. Verify that the file saved in the specified folder.
- 65 -
ROI-S03671
2.13 Saving Current Workspace.
This function allows the network designer to save the current workspace in an *.nct file format that can be opened using the NetConfig Tool for future modifications in the network. It is recommended that the user save the existing workspace for an easier addition, and/or modification of the existing NMS network. To save the current workspace: 1. Click on File -> Save from the main menu of the main window.
2. Specify the Folder and File Name where the current workspace will be saved. 3. Click on [Save] button. 4. Verify that the workspace was saved in the selected folder.
- 66 -
ROI-S03671
2.14 Printing Current Network
This function allows the network designer to print the designed network. First please define an area of network for print. To define the Print Area: 1. Click on File -> Print Area from the main menu of the main window.
2. The default print area that covers the entire window is displayed with surrounding dotted line as shown below.
- 67 -
ROI-S03671
3. To define a new print area, press left button of the mouse and draw a box to cover the desired area as shown below.
4. Click on File -> Print from the main menu of the main window to start printing.
- 68 -
ROI-S03671
2.15 About Network Configuration Tool
To verify the version of the NetConfig Tool being used: 1. Click on Help | About NetCfgTool from the main menu of the main window.
2. Click on OK button to close the about box.
- 69 -
ROI-S03671
Multiple CPMC Workspace
PNMS in normal operations manages more than one CPMC cluster. This section describes the procedure in creating multiple-CPMC configuration for the PNMS. By default, the NetConfig Tool opens one workspace during startup. Each workspace represents one network and each network in turn represents one CPMC cluster or group. The default workspace is displayed as Network 1 in the NetConfig Tool window. To add another CPMC cluster or group 1. Click on Network -> New. This will open a new workspace in the NetConfig Tool.
2. Add the new NEs the new workspace as necessary.
- 70 -
ROI-S03671
3. You have to separately Create Configuration for each workspace/network. Select the network that you want to create configuration and then click on Tools Create Configuration. 4. The number of workspace depends on the network-sizing rule defined in the PNMS Engineering Manual.
- 71 -
ROI-S03671
Appendix A: MIU Settings
The NE Properties of the individual PMC you have to click on the PMC button on the MIU block of the MIU Properties. This appendix will explain the naming convention used in the PMC button show below. (1) (2)
The name of the PMC button is comprised of two distinct parts: (1) PMC type, (2) PMC Usage. The PMC type can either be RPMC, CPMC or SCPMC depending on the role of the PMC in the HLDC polling. The PMC Usage depends on the order of the PMC in the MIU and the redundancy. The table below illustrates the PMC usage convention used in the MIU. Total PMC Total PMC = 1 (Line concentrator/other equipment with no redundancy). Redundant System 1+0/1+1 PMC Type/PMC Usage RPMC Normal CPMC Normal SCPMC Normal N+1 RPMC Protection CH CPMC Protection CH SCPMC Protection CH Line Concentrator/ Other Equipment RPMC Normal CPMC Normal SCPMC Normal Total PMC >= 2 1+0/1+1 N+1 RPMC Additional PMC RPMC Regular CH
For N+1 configuration, the default value of the PMC Usage is Regular CH. When adding new PMCs the user must change the PMC usage of the additional PMCs individually in the MIU properties window. When changing the PMC Usage a warning message will appear. (i.e When adding a new PMC on the existing system the new PMC will be labeled as Additional PMC.) Line Concentrator RPMC Additional PMC
The additional PMCs are sequential. When deleting a PMC, the NetCfgTool will delete the last PMC added first. This means you cannot add an additional PMC without deleting the PMCs below it first.
- 72 -
ROI-S03671
Appendix B: Subnets
Table 10: Pasolink and Pasolink+ radio IP available sub-network Subnet Mask 255.255.254.0 (Default) 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.128 255.255.255.192 Number of available IP address /subnet 512 (2 class-C subnets) 256 (1 class-C subnet) 128 (2 subnets) 64 (4 subnets) Range (0~511) (0~255) (0~127) (128~255) (0~63) (64~127) (128~191) (192~255) (0~31) (32~63) (64~95) (96~127) (128~159) (160~191) (192~223) (224~255) (0~15) (16~31) (32~47) (48~63) (64~79) (80~95) (96~111) (112~127) (128~143) (144~159) (160~175) (176~191) (192~207) (208~223) (224~239) (240~255) (0~7) (8~15) (16~23) (24~31) (32~39) (40~47) (48~55) (56~63) (64~71) (72~79) (80~87) (88~95) (96~103) (104~111) Network Address xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.64 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.192 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.32 xxx.xxx.xxx.64 xxx.xxx.xxx.96 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.160 xxx.xxx.xxx.192 xxx.xxx.xxx.224 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.16 xxx.xxx.xxx.32 xxx.xxx.xxx.48 xxx.xxx.xxx.64 xxx.xxx.xxx.80 xxx.xxx.xxx.96 xxx.xxx.xxx.112 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.144 xxx.xxx.xxx.160 xxx.xxx.xxx.176 xxx.xxx.xxx.192 xxx.xxx.xxx.208 xxx.xxx.xxx.224 xxx.xxx.xxx.240 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.8 xxx.xxx.xxx.16 xxx.xxx.xxx.24 xxx.xxx.xxx.32 xxx.xxx.xxx.40 xxx.xxx.xxx.48 xxx.xxx.xxx.56 xxx.xxx.xxx.64 xxx.xxx.xxx.72 xxx.xxx.xxx.80 xxx.xxx.xxx.88 xxx.xxx.xxx.96 xxx.xxx.xxx.104
255.255.255.224
32 (8 subnets)
255.255.255.240
16 (16 subnets)
255.255.255.248
8 (32 subnets)
- 73 -
ROI-S03671
Subnet Mask
Number of available IP address /subnet
Range (112~119) (120~127) (128~135) (136~143) (144~151) (152~159) (160~167) (168~175) (176~183) (184~191) (192~199) (200~207) (208~215) (216~223) (224~231) (232~239) (240~247) (248~255) (0~3) (4~7) (8~11) (12~15) (16~19) (20~23) (24~27) (28~31) (32~35) (36~39) (40~43) (44~47) (48~51) (52~55) (56~59) (60~63) (64~67) (68~71) (72~75) (76~79) (80~83) (84~87) (88~91) (92~95) (96~99) (100~103) (104~107) (108~111) (112~115) (116~119) (120~123) (124~127) (128~131) (132~135)
Network Address xxx.xxx.xxx.112 xxx.xxx.xxx.120 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.136 xxx.xxx.xxx.144 xxx.xxx.xxx.152 xxx.xxx.xxx.160 xxx.xxx.xxx.168 xxx.xxx.xxx.176 xxx.xxx.xxx.184 xxx.xxx.xxx.192 xxx.xxx.xxx.200 xxx.xxx.xxx.208 xxx.xxx.xxx.216 xxx.xxx.xxx.224 xxx.xxx.xxx.232 xxx.xxx.xxx.240 xxx.xxx.xxx.248 xxx.xxx.xxx.0 xxx.xxx.xxx.4 xxx.xxx.xxx.8 xxx.xxx.xxx.12 xxx.xxx.xxx.16 xxx.xxx.xxx.20 xxx.xxx.xxx.24 xxx.xxx.xxx.28 xxx.xxx.xxx.32 xxx.xxx.xxx.36 xxx.xxx.xxx.40 xxx.xxx.xxx.44 xxx.xxx.xxx.48 xxx.xxx.xxx.60 xxx.xxx.xxx.56 xxx.xxx.xxx.56 xxx.xxx.xxx.64 xxx.xxx.xxx.68 xxx.xxx.xxx.72 xxx.xxx.xxx.76 xxx.xxx.xxx.80 xxx.xxx.xxx.84 xxx.xxx.xxx.88 xxx.xxx.xxx.92 xxx.xxx.xxx.96 xxx.xxx.xxx.100 xxx.xxx.xxx.104 xxx.xxx.xxx.108 xxx.xxx.xxx.112 xxx.xxx.xxx.116 xxx.xxx.xxx.120 xxx.xxx.xxx.124 xxx.xxx.xxx.128 xxx.xxx.xxx.132
255.255.255.252
4 (64 subnets)
- 74 -
ROI-S03671
Subnet Mask
Number of available IP address /subnet
Range (136~139) (140~143) (144~147) (148~151) (152~155) (156~159) (160~163) (164~167) (168~171) (172~175) (176~179) (180~183) (184~187) (188~191) (192~195) (196~199) (200~203) (204~207) (208~211) (212~215) (216~219) (220~223) (224~227) (228~231) (232~235) (236~239) (240~243) (244~247) (248~251) (252~255)
Network Address xxx.xxx.xxx.136 xxx.xxx.xxx.140 xxx.xxx.xxx.144 xxx.xxx.xxx.148 xxx.xxx.xxx.152 xxx.xxx.xxx.156 xxx.xxx.xxx.160 xxx.xxx.xxx.164 xxx.xxx.xxx.168 xxx.xxx.xxx.172 xxx.xxx.xxx.176 xxx.xxx.xxx.180 xxx.xxx.xxx.184 xxx.xxx.xxx.188 xxx.xxx.xxx.192 xxx.xxx.xxx.196 xxx.xxx.xxx.200 xxx.xxx.xxx.204 xxx.xxx.xxx.208 xxx.xxx.xxx.212 xxx.xxx.xxx.216 xxx.xxx.xxx.220 xxx.xxx.xxx.224 xxx.xxx.xxx.228 xxx.xxx.xxx.232 xxx.xxx.xxx.236 xxx.xxx.xxx.240 xxx.xxx.xxx.244 xxx.xxx.xxx.240 xxx.xxx.xxx.252
- 75 -
Você também pode gostar
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1No EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Ainda não há avaliações
- NetConfigTool ManualDocumento68 páginasNetConfigTool ManuallevanchuvtAinda não há avaliações
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkAinda não há avaliações
- Netconfig Tool Oper ManualDocumento68 páginasNetconfig Tool Oper ManualMiguel Angel Cara Rios100% (1)
- Net CFG ToolDocumento78 páginasNet CFG ToolGadi Huaman Flores100% (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102No EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Small InternetworksDocumento26 páginasSmall InternetworksSrinivasReddyAinda não há avaliações
- RSLogix Gateway ConfigDocumento9 páginasRSLogix Gateway ConfigLuis TecaAinda não há avaliações
- Intercell Dual-Carrier TDD Enterprise Small Cell Configuration GuideDocumento54 páginasIntercell Dual-Carrier TDD Enterprise Small Cell Configuration GuideCarlos GuevaraAinda não há avaliações
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationAinda não há avaliações
- 11 5 1Documento56 páginas11 5 1Mario Alejandro Godoy PatiñoAinda não há avaliações
- Open-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsNo EverandOpen-Source Robotics and Process Control Cookbook: Designing and Building Robust, Dependable Real-time SystemsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- Networks Lab ManualDocumento53 páginasNetworks Lab ManualM'atto DipnotAinda não há avaliações
- The Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceNo EverandThe Effects of Traffic Structure on Application and Network PerformanceAinda não há avaliações
- Using OpNetDocumento5 páginasUsing OpNetMalebogo BabutsiAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Simulation With QualnetDocumento16 páginasWireless Simulation With Qualnetkdilip05Ainda não há avaliações
- HP COMPAQ D330UT-Network & InternetDocumento20 páginasHP COMPAQ D330UT-Network & Internetgebo_manAinda não há avaliações
- LAN 2 .VNBDocumento21 páginasLAN 2 .VNBLê NghĩaAinda não há avaliações
- Itnsa Pra WSMB2023Documento10 páginasItnsa Pra WSMB2023hazwanAinda não há avaliações
- Local Area Network (Lan) TrainerDocumento36 páginasLocal Area Network (Lan) TrainerCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 04-OptiX RTN 900 Data Configuration (Hybrid Domain)Documento66 páginas04-OptiX RTN 900 Data Configuration (Hybrid Domain)Paulo DembiAinda não há avaliações
- En ENetwork IPTM v4040Documento38 páginasEn ENetwork IPTM v4040abdelhf1Ainda não há avaliações
- CCNA Exploration 4.0.4.0 Instructor Packet Tracer Lab ManualDocumento38 páginasCCNA Exploration 4.0.4.0 Instructor Packet Tracer Lab ManualshaytoonballaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Manual For DCCNDocumento13 páginasLab Manual For DCCNYehualashet BelaynehAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 1151Documento20 páginasLab 1151Kiri RaveendrarasaAinda não há avaliações
- Dash Q8 400 - System Panel GuideDocumento6 páginasDash Q8 400 - System Panel GuideAndrés MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- iM-Connect: Protocol Conversion Software User GuideDocumento61 páginasiM-Connect: Protocol Conversion Software User GuideGeovanni CandoAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless Sync Howto: Using Jpilot To Sync Your Palmos Device To Your Desktop Across A Wireless (802.11B) NetworkDocumento9 páginasWireless Sync Howto: Using Jpilot To Sync Your Palmos Device To Your Desktop Across A Wireless (802.11B) Networka.gAinda não há avaliações
- CiscoDocumento35 páginasCiscoFlorin Zamfir100% (1)
- Network Configuration Toolj: Operation Manual (Java Version)Documento78 páginasNetwork Configuration Toolj: Operation Manual (Java Version)Micheal TamerAinda não há avaliações
- 1.1 Configuring The NetworkDocumento14 páginas1.1 Configuring The NetworkSam eagle goodAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 2Documento49 páginasLab 2studentAinda não há avaliações
- PNMS Engineering Manual (Pasolink)Documento67 páginasPNMS Engineering Manual (Pasolink)صديقكالوفيAinda não há avaliações
- Nexenta ISCSI Multipath ConfigurationDocumento72 páginasNexenta ISCSI Multipath ConfigurationangelitobluAinda não há avaliações
- DC Rec RemainingDocumento25 páginasDC Rec Remainingbilnot9Ainda não há avaliações
- Installation Guide - Tecnomen NGM 5.1.3 - IG - 6000700 - 11Documento110 páginasInstallation Guide - Tecnomen NGM 5.1.3 - IG - 6000700 - 11fahad01Ainda não há avaliações
- MT880 User ManualDocumento74 páginasMT880 User ManualsergioperrAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Assignment 2018-2019Documento15 páginasLab Assignment 2018-2019tuyambaze jean claudeAinda não há avaliações
- Net CFG ToolDocumento209 páginasNet CFG ToolFaisal HidayatAinda não há avaliações
- NetConigTool Operation ManualDocumento168 páginasNetConigTool Operation ManualLAPPTNYAinda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento28 páginasReport 1zeeshan sohailAinda não há avaliações
- Opnet Labs: Due by Nov 17 2003 Before Class Start and Please Provide Cover Page With Your Names On It. Thanks!Documento17 páginasOpnet Labs: Due by Nov 17 2003 Before Class Start and Please Provide Cover Page With Your Names On It. Thanks!Mehdi MorsaliAinda não há avaliações
- Deluge ManualDocumento12 páginasDeluge ManualLaur Best0% (1)
- Beowulf SetupDocumento46 páginasBeowulf SetupBiswa DuttaAinda não há avaliações
- ACT350 POWERCELL - PROFINET - PLC - EngineeringNote - EN - 202004Documento38 páginasACT350 POWERCELL - PROFINET - PLC - EngineeringNote - EN - 202004Vhsr Perfil UnoAinda não há avaliações
- 3600-4171 01 TN EiprslogixDocumento16 páginas3600-4171 01 TN EiprslogixElias VelezAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 2 HandoutDocumento7 páginasLab 2 Handouthassaan tanveerAinda não há avaliações
- LeTrungNghia - 20070864Documento23 páginasLeTrungNghia - 20070864Lê NghĩaAinda não há avaliações
- Linux HPC Cluster Setup GuideDocumento28 páginasLinux HPC Cluster Setup GuideEdmund OchiengAinda não há avaliações
- Banner Safety Controler XS 26 deDocumento9 páginasBanner Safety Controler XS 26 desgksevenAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Switch Config v2 0Documento24 páginasCisco Switch Config v2 0chituoi100% (1)
- Welcome: To The Constructing A Secure SD-WAN Architecture LabDocumento44 páginasWelcome: To The Constructing A Secure SD-WAN Architecture LabSypher100% (2)
- Ccna I Exploration Lab 2 - Intro To Packet Tracer Lab Required Materials - Data File Lsg01-Ptskills1.PkaDocumento4 páginasCcna I Exploration Lab 2 - Intro To Packet Tracer Lab Required Materials - Data File Lsg01-Ptskills1.PkaElizabeth NewmanAinda não há avaliações
- WISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualDocumento39 páginasWISP-68: 802.11bg High-Power Outdoor AP/CPE User ManualLynn DavisAinda não há avaliações
- Protonode Fpc-N34 and Protonode Fpc-N35 Start-Up Guide For Interfacing Weil-Mclain ProductsDocumento61 páginasProtonode Fpc-N34 and Protonode Fpc-N35 Start-Up Guide For Interfacing Weil-Mclain ProductsRaphael PalaciosAinda não há avaliações
- NETLAB Network Fundamentals Pod PDFDocumento52 páginasNETLAB Network Fundamentals Pod PDFDavid PovedaAinda não há avaliações
- S7-1200 OPC SIMATIC-NET eDocumento25 páginasS7-1200 OPC SIMATIC-NET eMurat KulustepeAinda não há avaliações
- A05 Attachment Invalid PMDocumento1 páginaA05 Attachment Invalid PMKhaled El-RayesAinda não há avaliações
- MW Transmission NECDocumento34 páginasMW Transmission NECzaabullaAinda não há avaliações
- AndrewDocumento1 páginaAndrewKhaled El-RayesAinda não há avaliações
- Hybrid Converter For NEC Microwave Network Management SystemDocumento2 páginasHybrid Converter For NEC Microwave Network Management SystemKhaled El-RayesAinda não há avaliações
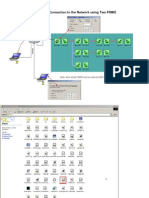
- Connection To The Network Using Two PNMS: Strait CableDocumento2 páginasConnection To The Network Using Two PNMS: Strait CableKhaled El-RayesAinda não há avaliações
- Prj5 - Optional Phase 3Documento4 páginasPrj5 - Optional Phase 3adminAinda não há avaliações
- Google Professional DeveloperDocumento76 páginasGoogle Professional DeveloperzhangstevenAinda não há avaliações
- DX DiagDocumento47 páginasDX DiagStefan IsakowAinda não há avaliações
- DAHUA IP Camera Recovery v1.0Documento3 páginasDAHUA IP Camera Recovery v1.0Pablo JoaquinAinda não há avaliações
- NetstatinfoDocumento8 páginasNetstatinfonfazalAinda não há avaliações
- Codigo Errores Probador de PlacasDocumento16 páginasCodigo Errores Probador de PlacasPaul Perez SantosAinda não há avaliações
- EPMP Release Notes v3.5Documento23 páginasEPMP Release Notes v3.5klanderAinda não há avaliações
- Meraki Campus Deployment GuideDocumento10 páginasMeraki Campus Deployment GuideMarcAinda não há avaliações
- Users Manual 3552381Documento55 páginasUsers Manual 3552381Tobias KornmayerAinda não há avaliações
- Security of W2K Server in DMZ - Baiju ShahDocumento90 páginasSecurity of W2K Server in DMZ - Baiju Shahraer errrtAinda não há avaliações
- OCI User Guide PDFDocumento1.724 páginasOCI User Guide PDFangieAinda não há avaliações
- D1T1 - T. Yunusov K. Nesterov - Bootkit Via SMSDocumento84 páginasD1T1 - T. Yunusov K. Nesterov - Bootkit Via SMSAndrea Escalante LLanoAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Windows Server 2019 (16-Core) Datacenter Reseller Option Kit English Sw-Psn1011483586czen (398443)Documento4 páginasMicrosoft Windows Server 2019 (16-Core) Datacenter Reseller Option Kit English Sw-Psn1011483586czen (398443)PrabakaranAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems (Eceg-5702) : Lecture 6: Ccs Pic C Compiler RtosDocumento21 páginasEmbedded Systems (Eceg-5702) : Lecture 6: Ccs Pic C Compiler RtossmithAinda não há avaliações
- How To Replace The Motherboard or Service Processor in A Logical Domain (LDom) Environment (Doc ID 1019720.1)Documento9 páginasHow To Replace The Motherboard or Service Processor in A Logical Domain (LDom) Environment (Doc ID 1019720.1)Hieu TranAinda não há avaliações
- README 8.1 5in1 x32 Aug2015Documento2 páginasREADME 8.1 5in1 x32 Aug2015Abdul HafidhAinda não há avaliações
- Infinix Note 12 USB Driver For Windows (Official Mobile Driver)Documento4 páginasInfinix Note 12 USB Driver For Windows (Official Mobile Driver)Kurdo KurdAinda não há avaliações
- DHCP Sniffer TutorialDocumento6 páginasDHCP Sniffer TutorialRob KentAinda não há avaliações
- CCNA 2 FinalDocumento38 páginasCCNA 2 FinalTuấnAinda não há avaliações
- ISSCC2023 Digital ProcessorsDocumento282 páginasISSCC2023 Digital Processorshello worldAinda não há avaliações
- Management Plane ProtectionDocumento104 páginasManagement Plane ProtectionIvan MachuzaAinda não há avaliações
- Nexlog Push Upgrade InstructionsDocumento2 páginasNexlog Push Upgrade InstructionsahmedAinda não há avaliações
- June 2012 Ugc Net Computer Science - SolvedDocumento20 páginasJune 2012 Ugc Net Computer Science - Solvedvani_ppcAinda não há avaliações
- Vmware Vsphere Networking: Nutanix Best PracticesDocumento37 páginasVmware Vsphere Networking: Nutanix Best PracticesDavid Hernan Lira CarabantesAinda não há avaliações
- D-Lab 1 MPU Kit V2.00Documento13 páginasD-Lab 1 MPU Kit V2.00Luiz MoraisAinda não há avaliações
- Acer Travelmate 5730/5630 - Service ManualDocumento176 páginasAcer Travelmate 5730/5630 - Service ManualHiranAmarasingheAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 3 CCNDocumento4 páginasLab 3 CCNAreeba NoorAinda não há avaliações
- B-EP Ifm 2ndDocumento773 páginasB-EP Ifm 2ndBes GesAinda não há avaliações
- CC Lab ManualDocumento17 páginasCC Lab ManualNilesh KulalAinda não há avaliações
- Webinar - Introduction To MatterDocumento48 páginasWebinar - Introduction To MatterKhoa NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNo EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxNo EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (67)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringNo EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (40)
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityNo EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamAinda não há avaliações
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionNo EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900No EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Ainda não há avaliações
- Azure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectNo EverandAzure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectAinda não há avaliações
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNo EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsAinda não há avaliações
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNo EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationAinda não há avaliações
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNNo EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Terraform for Developers: Essentials of Infrastructure Automation and ProvisioningNo EverandTerraform for Developers: Essentials of Infrastructure Automation and ProvisioningAinda não há avaliações
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNo EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignAinda não há avaliações
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamNo EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideNo EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideAinda não há avaliações