Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Microeconomics Concept
Enviado por
Muhammad Akmal HussainTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Microeconomics Concept
Enviado por
Muhammad Akmal HussainDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Elasticity
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Jon Mansfield Micro Lecture 2
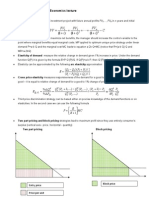
1. Elasticity - sensitivity, responsiveness Can Be Calculated for Any Variable in the Demand Function. Examples: Price, Income, Advertising, etc. Compare Percentage Changes to Avoid a Units Problem in Measurement
Definition:
e p = ( % Q) /( % P)
( Q / Q) / ( P / P)
( Q / P) ( P / Q)
Arc Elasticity Discrete Range e p = (( Q2 - Q1) / Q) / ((P2 - P1) / P) e p = [ (Q2 - Q1) / (Q1 + Q2) / 2] / [ (P2 - P1) / (P1 + P2) / 2]
Point Elasticity Point on the Demand Curve e p = (Q / P ) ( P / Q ) Linear demand curve (price form): P = a + bQ b = (P / Q ) and (1 / b) = (Q / P ) e p = (Q / P ) ( P / Q)
e p = [ (Q2 - Q1) / (Q1 + Q2)] / [ (P2 - P1) / (P1 + P2)]
e p = (1 / b) [P / (P - a) / b] = [P / (P - a)]
Values |ep| > 1 |ep| < 1 |ep| = 1 Elastic Inelastic Unit Elastic %Q>%P %Q<%P %Q=%P
You should be able to work through the derivation of both elasticity formulas.
Elasticity
2. Downward-sloping Linear Demand Curve Demand Function Total Revenue Function (TR) Average Revenue Function (AR) Marginal Revenue Function (MR) MR using calculus (MRc) P = 12 - Q (or Q = 12 - P) TR = (P)(Q) = (12 - Q)(Q) = 12Q - Q 2 AR = TR / Q = [(P)(Q)] / Q = P MR = (TR) / (Q) = (TR2 - TR1) / (Q2 - Q 1) MRc = TR / Q = 12 - 2Q
Calculate the elasticities using the formulas.
TR
MR
MRc
Arc elasticity e p = [ (Q2 - Q1) / (Q1 + Q2)] / [ (P2 - P1) / (P1 + P2)]
Point elasticity e p = [P / (P - a)]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 11 20 27 32 35 36 35 32 27 20 11 0
11 9 7 5 3 1 -1 -3 -5 -7 -9 -11
12 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 -12
-23
-11
As the price decreases from 12, what happens with both types of elasticities?
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Jon Mansfield
Elasticity
Based on the information and table above, graph the Demand and Marginal Revenue functions on one diagram and the Total Revenue function directly beneath.
P$ 12
P = 12 - Q MR = 12 - 2Q
Q 6 TR $ 40 TR = 12Q - Q 2 12
Q 6 12
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Jon Mansfield
Elasticity
3. Price Elasticity and Total Revenue: The Price Effect and Quantity Effect of a Price Change.
P1 P2
A area A B Demand area B
C D
Q1
Q2
4. What is the significance of vertical and horizontal demand curves?
D D ep = 0 ep =
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Jon Mansfield
Elasticity
5. How sensitive is the amount demanded to a change in price? This is primarily determined by: Elastic number of substitute goods importance in consumers budget product durability time period under consideration
6. Other Elasticities Income Elasticity of Demand e I = (% QX) / (% I) (= ( Q X / I) (I / QX)) e I > 0 Normal Good e I < 0 Inferior Good Cross Elasticity of Demand e C = (% QX) / (% PY) (= ( Q X / P Y) (P Y / QX)) e C > 0 Substitute Goods e C < 0 Complementary Goods
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Jon Mansfield
Você também pode gostar
- Slide 3. Demand Related and Consumer BehaviorDocumento44 páginasSlide 3. Demand Related and Consumer Behaviorminhln16.sicAinda não há avaliações
- Price Quantity Total Marginal Revenue Revenue 10 1 10 9 2 18 8 8 3 24 6 7 4 28 4 6 5 30 2 5 6 30 0 4 7 28 - 2 3 8 24 - 4 2 9 18 - 6 1 10 10 - 8Documento37 páginasPrice Quantity Total Marginal Revenue Revenue 10 1 10 9 2 18 8 8 3 24 6 7 4 28 4 6 5 30 2 5 6 30 0 4 7 28 - 2 3 8 24 - 4 2 9 18 - 6 1 10 10 - 8Rahul Chawla0% (1)
- Managerial Economics Ch4 1Documento18 páginasManagerial Economics Ch4 1Abhishek ModakAinda não há avaliações
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory B: Undergraduate Lecture NotesDocumento34 páginasIntermediate Microeconomic Theory B: Undergraduate Lecture Notesamrith vardhanAinda não há avaliações
- Managerial EconomicsDocumento18 páginasManagerial EconomicsMohamed MustefaAinda não há avaliações
- H & Q, CH 11, Welfare EconomicsDocumento68 páginasH & Q, CH 11, Welfare EconomicsNeethu KinaraAinda não há avaliações
- ElasticityDocumento34 páginasElasticityKamble AbhijitAinda não há avaliações
- Elasticity Practice Problems - FinalDocumento22 páginasElasticity Practice Problems - Finalpavani sabarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics: EIT ReviewDocumento33 páginasFluid Mechanics: EIT ReviewSharath ChandraAinda não há avaliações
- Economics Study Guide Chapter Summary Varian For Midterm 2Documento6 páginasEconomics Study Guide Chapter Summary Varian For Midterm 2Josh SatreAinda não há avaliações
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocumento38 páginasElasticity of Demand and SupplyYu LeonAinda não há avaliações
- M06 Handout - DifferentiationDocumento18 páginasM06 Handout - DifferentiationKatherine SauerAinda não há avaliações
- CH 03Documento25 páginasCH 03MoshAinda não há avaliações
- ECON1003 Tut02 2023s2Documento26 páginasECON1003 Tut02 2023s2guohaolan0804Ainda não há avaliações
- The Application of Derivatives To The Concepts of Marginal CostDocumento4 páginasThe Application of Derivatives To The Concepts of Marginal CostLuke ShawAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Outcome 2 - Ac 2 (Analytical Methods)Documento7 páginasLearning Outcome 2 - Ac 2 (Analytical Methods)Chan Siew ChongAinda não há avaliações
- Econ 11 Final Exam Solutions: 1 Problem 1Documento18 páginasEcon 11 Final Exam Solutions: 1 Problem 1Juan MadrigalAinda não há avaliações
- FormulasDocumento1 páginaFormulasHalilcan AtikAinda não há avaliações
- ME Chapter3Documento14 páginasME Chapter3HarlinniAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Demand AnalysisDocumento55 páginasQuantitative Demand AnalysisJessica Adharana KurniaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 4 - Decline Curve AnalysisDocumento41 páginasLecture 4 - Decline Curve Analysisgeber39Ainda não há avaliações
- Technical Note - Autoregressive ModelDocumento12 páginasTechnical Note - Autoregressive ModelNumXL ProAinda não há avaliações
- Reduction of A Symmetric Matrix To Tridiagonal Form - Givens and Householder ReductionsDocumento7 páginasReduction of A Symmetric Matrix To Tridiagonal Form - Givens and Householder ReductionsAntonio PeixotoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Demand AnalysisDocumento6 páginasChapter 3 Demand AnalysismyraAinda não há avaliações
- Demand ElasticityDocumento5 páginasDemand Elasticitykhawaralisher7105100% (3)
- Steel-Concrete Composite Column-IiDocumento25 páginasSteel-Concrete Composite Column-Iihemant_durgawaleAinda não há avaliações
- Forecasting (Prediction) Limits: Example Linear Deterministic Trend Estimated by Least-SquaresDocumento27 páginasForecasting (Prediction) Limits: Example Linear Deterministic Trend Estimated by Least-Squareszahid_rezaAinda não há avaliações
- 10e 06 Chap Student WorkbookDocumento23 páginas10e 06 Chap Student WorkbookMarielle Aria SantosAinda não há avaliações
- 4 DifferentiationDocumento28 páginas4 Differentiationanvu1018.nifoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Demand EstimationDocumento9 páginasChapter 4 Demand EstimationdelisyaaamilyAinda não há avaliações
- Math ConceptsDocumento17 páginasMath ConceptsAli Al SHareifAinda não há avaliações
- Handout 7: MonopolyDocumento8 páginasHandout 7: MonopolyRaulAinda não há avaliações
- Review Topics For The Midterm: AcroeconomicsDocumento17 páginasReview Topics For The Midterm: AcroeconomicsFeliks Dwi KristiantoAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Relationships and Economic ModelsDocumento4 páginasFunctional Relationships and Economic ModelsBellindah GAinda não há avaliações
- Review of Econ 203Documento73 páginasReview of Econ 203api-235832666Ainda não há avaliações
- Efficient Observation of Random PhenomenaDocumento34 páginasEfficient Observation of Random PhenomenaponjoveAinda não há avaliações
- ENCS 6161 - ch12Documento13 páginasENCS 6161 - ch12Dania AlashariAinda não há avaliações
- MIT Pricing Traffic 1Documento53 páginasMIT Pricing Traffic 1Muhamad AndiAinda não há avaliações
- Microeconomics Group Assignment ReportDocumento12 páginasMicroeconomics Group Assignment ReportMeselu TegenieAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 - ElasticityDocumento78 páginasChapter 5 - ElasticityDenise CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Definite IntegralDocumento3 páginasDefinite Integralbadarali2Ainda não há avaliações
- Quadratic Programming: Optimization of Chemical ProcessesDocumento12 páginasQuadratic Programming: Optimization of Chemical ProcessesDeepak SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- MTHS112 Week 6 2020 Efundi 1 Afr HersieningDocumento9 páginasMTHS112 Week 6 2020 Efundi 1 Afr HersieningChristiaan HenningsAinda não há avaliações
- ECON 3125 Chap3Documento10 páginasECON 3125 Chap3Noman Khosa100% (1)
- Group Assignment: II. WorkoutDocumento5 páginasGroup Assignment: II. Workoutyohannes lemiAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Table-Based Testing Decision Tables - WikipediaDocumento5 páginasDecision Table-Based Testing Decision Tables - WikipediaManjunath DupatiAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 - Topic 2 Demand and Supply Functions (Microeconomics)Documento14 páginasLesson 3 - Topic 2 Demand and Supply Functions (Microeconomics)Marianne Jade HonorarioAinda não há avaliações
- LP ModelingDocumento18 páginasLP ModelingKaran Veer SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Singapore Institute of Management: University of London Preliminary Exam 2015Documento5 páginasSingapore Institute of Management: University of London Preliminary Exam 2015viktor6Ainda não há avaliações
- Load ForecastingDocumento30 páginasLoad Forecastingyogi_maha50% (2)
- Microeconomics I - MidtermDocumento6 páginasMicroeconomics I - Midtermcrod123456Ainda não há avaliações
- X X . Explain ( (0)Documento2 páginasX X . Explain ( (0)Machaca Alvaro MamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Microeconomics Cue CardDocumento4 páginasMicroeconomics Cue CardAndrew Halpern100% (1)
- Similitude, Dimensional Analysis ModelingDocumento128 páginasSimilitude, Dimensional Analysis ModelingMostafa Ayman Mohammed NageebAinda não há avaliações
- The Educational Use of Calculator fx-570ESDocumento64 páginasThe Educational Use of Calculator fx-570ESlboon_1100% (2)
- Handout 6: Market Equilibrium With Perfect CompetitionDocumento8 páginasHandout 6: Market Equilibrium With Perfect CompetitionKuchayRiyazAinda não há avaliações
- Regression SPSSDocumento21 páginasRegression SPSSOana JagîteAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionNo EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Executive Summary Krwan e HayatDocumento4 páginasExecutive Summary Krwan e HayatMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- METRO Supply ChainDocumento28 páginasMETRO Supply ChainMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Uni FerozDocumento19 páginasUni FerozMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Google Vs FacebookDocumento19 páginasGoogle Vs FacebookMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Channel ManagementDocumento25 páginasChannel ManagementMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Final Newsletter Karwan e HayatDocumento4 páginasFinal Newsletter Karwan e HayatMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Workplace Bullies: Case Study 2Documento16 páginasWorkplace Bullies: Case Study 2Muhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- BulliesDocumento8 páginasBulliesMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Gallo WineryDocumento43 páginasGallo WineryMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson-2-4 Consumer Behavior in ServicesDocumento37 páginasLesson-2-4 Consumer Behavior in ServicesMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- RM Final ThesisDocumento12 páginasRM Final ThesisMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Strategic MarketingDocumento72 páginasStrategic MarketingMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Service Development and DesignDocumento15 páginasService Development and DesignMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Risk, Return & Opportunity Cost of CapitalDocumento19 páginasRisk, Return & Opportunity Cost of CapitalMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- TNS Apache MotorcycleDocumento2 páginasTNS Apache MotorcycleMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Risk, Return & Capital BudgetingDocumento18 páginasRisk, Return & Capital BudgetingMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- TNS Apache MotorcycleDocumento33 páginasTNS Apache MotorcycleDavid Everitt-Carlson100% (1)
- Management of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02Documento31 páginasManagement of Financial Institutions - BNK604 Power Point Slides Lecture 02aimanbatool24Ainda não há avaliações
- The Cost of CapitalDocumento28 páginasThe Cost of CapitalMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- The Cost of CapitalDocumento28 páginasThe Cost of CapitalMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Gallo WineryDocumento43 páginasGallo WineryMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- MarkovDocumento11 páginasMarkovMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Gallo WineryDocumento43 páginasGallo WineryMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 - CommunicationDocumento19 páginasChapter 10 - CommunicationMuhammad Akmal Hussain100% (1)
- Elasticity CorrectDocumento4 páginasElasticity CorrectMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Foundations of Strategic Marketing ManagementDocumento38 páginasFoundations of Strategic Marketing ManagementsyedanwaruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Zaira CVDocumento1 páginaZaira CVMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Risk, Return & Opportunity Cost of CapitalDocumento19 páginasRisk, Return & Opportunity Cost of CapitalMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Bottled Water Jan-Mar 2011with AnnexDocumento19 páginasBottled Water Jan-Mar 2011with AnnexMuhammad Akmal HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Relationship Management As A Macro Business ProcessDocumento17 páginasSupplier Relationship Management As A Macro Business ProcessABCAinda não há avaliações
- Bot LuckygamesDocumento16 páginasBot LuckygamesMokkaAinda não há avaliações
- Property DigestDocumento9 páginasProperty DigestJoy OrenaAinda não há avaliações
- Hr-Analytics (Case Study)Documento3 páginasHr-Analytics (Case Study)Jeeshan IdrisiAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Life Cycle AssessmentDocumento1 páginaEnvironmental Life Cycle Assessmentkayyappan1957Ainda não há avaliações
- Job Schedule Sheet: 'Lead Time Monitoring GraphDocumento48 páginasJob Schedule Sheet: 'Lead Time Monitoring GraphEndraAinda não há avaliações
- 34-Samss-718 (12-02-2015)Documento14 páginas34-Samss-718 (12-02-2015)Mubin100% (1)
- ISM JRF BrochureDocumento37 páginasISM JRF BrochureVikas Patel100% (1)
- 1st Division Mancom MinutesDocumento18 páginas1st Division Mancom MinutesseiAinda não há avaliações
- New Micra BrochureDocumento14 páginasNew Micra BrochureGlobalGroupOfDealersAinda não há avaliações
- Transport ADRDocumento3 páginasTransport ADRZbinca CristianAinda não há avaliações
- AWS Solution Architect SampleDocumento3 páginasAWS Solution Architect SamplepandiecAinda não há avaliações
- Synchronization Checklist PDFDocumento8 páginasSynchronization Checklist PDFAdhyartha KerafAinda não há avaliações
- BSM - Company ProfileDocumento15 páginasBSM - Company ProfileLarasanto Cipta AgungAinda não há avaliações
- How To Use The R Software: July 2019Documento28 páginasHow To Use The R Software: July 2019Paul GokoolAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Task 1: Written Questions 1. Identify and Describe Five Common Components of A Business PlanDocumento6 páginasAssessment Task 1: Written Questions 1. Identify and Describe Five Common Components of A Business PlanJoanne Navarro AlmeriaAinda não há avaliações
- Agriculture Water Usage Poster ProjectDocumento1 páginaAgriculture Water Usage Poster Projectapi-339004071Ainda não há avaliações
- Contracts Act, 2010Documento59 páginasContracts Act, 2010Sam KAinda não há avaliações
- ''Adhibeo'' in LatinDocumento5 páginas''Adhibeo'' in LatinThriw100% (1)
- Literature Review On Climate Change in NigeriaDocumento9 páginasLiterature Review On Climate Change in Nigeriac5rn3sbr100% (1)
- DLL Health 10 Q1-W7Documento8 páginasDLL Health 10 Q1-W7Robert ManiboAinda não há avaliações
- AAU Karate Handbook: "Sports For All, Forever"Documento58 páginasAAU Karate Handbook: "Sports For All, Forever"jeffrey_trzaskusAinda não há avaliações
- GX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsDocumento60 páginasGX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsMontevideo PortalAinda não há avaliações
- Community Support For IYCF As of 22 SeptDocumento57 páginasCommunity Support For IYCF As of 22 SeptMJ ArcillaAinda não há avaliações
- Abstract 2 TonesDocumento8 páginasAbstract 2 TonesFilip FilipovicAinda não há avaliações
- Forging 2Documento17 páginasForging 2Amin ShafanezhadAinda não há avaliações
- Pass4sure 400-101Documento16 páginasPass4sure 400-101Emmalee22Ainda não há avaliações
- Power GREPDocumento392 páginasPower GREPCeles NubesAinda não há avaliações
- Aquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingDocumento5 páginasAquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingMarhaendra UtamaAinda não há avaliações
- ZIOIEXCELDocumento4 páginasZIOIEXCELSunil GAinda não há avaliações