Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Electrical Engineering Formulas
Enviado por
ssk_2k7Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Electrical Engineering Formulas
Enviado por
ssk_2k7Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
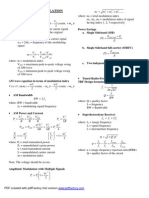
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING FORMULAS
BASIC ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT FORMULAS
CIRCUIT ELEMENT RESISTANCE INDUCTANCE IMPEDANCE VOLT-AMP EQUATIONS RMS values for sinusoidal signals Vrms=IrmsR Vrms=Irms2fL Vrms=Irms/(2fC) absolute complex instantaneous value form values R 2fL R jL 1/jC v=iR v=Ldi/dt i=Cdv/dt ENERGY (dissipated on R or stored in L, C) E=Irms2Rt E=Li2/2 E=Cv2/2
CAPACITANCE 1/(2fC)
Notes: R- electrical resistance in ohms, L- inductance in henrys, C- capacitance in farads, f - frequency in hertz, t- time in seconds, 3.14159; =2f - angular frequency; j - imaginary unit ( j2=-1 )
BASIC ELECTRICAL THEOREMS AND CIRCUIT ANALYSIS LAWS LAW DEFINITION RELATIONSHIP Lorentz force law, Faraday's law and Drude model Conservation of electric charge Conservation of energy =Z, where and - voltage and Ohm's Law modified current phasors, Z - complex for AC circuits with impedance sinusoidal signals (for resistive circuits: u=Ri ) Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) The sum of electric currents which flow into any junction in an electric circuit is equal to the sum of currents which flow out The sum of the electrical voltages around a closed circuit must be zero
EQUATIONS FOR SERIES AND PARALLEL CONNECTIONS
CIRCUIT ELEMENT SERIES CONNECTION Rseries= R1+R2+... PARALLEL CONNECTION Rparallel= 1/ (1/R1+1/R2+...)
RESISTANCE
INDUCTANCE
Lseries= L1+L2+...
Lparallel= 1/(1/L1+1/L2+...)
CAPACITANCE
Cseries= 1/ (1/C1+1/C2+...)
Cparallel= C1+C2+...
RLC IMPEDANCE FORMULAS
CIRCUIT CONNECTION COMPLEX FORM Z=R+jL+1/jC Series ABSOLUTE VALUE
Z= 1/(1/R+1/jL+jC) Parallel
MAGNETIC FIELD UNITS AND EQUATIONS
SYMBOL CGS UNIT CGS EQUATION CONVERSION FACTOR
QUANTITY
SI UNIT
SI EQUATION
Magnetic induction Magnetic field strength Magnetic flux
B H
tesla (T) ampere/ meter (A/m) weber (Wb)
B=o(H+M)
Gauss (G)
B = H+4M H = 0.4NI/lc (lc - magnetic path, cm)
1T= 104 G 1 A/m = 4 10-3 Oe 1 Wb = 108 M
H = NI/lc Oersted ( lc - magnetic (Oe) path, m) = BAc (Ac - area, m2 ) M=m/V (m- total magnetic moment, V- volume, m3 ) o= 410-7
Maxwell = BAc (M) (Ac - area, cm2 ) M=m/V (m- total magnetic moment, V- volume, cm3 ) L= =0.4N2Ac/lc 10-8 (N- turns, Ac-area, cm2, lc - magnetic path, cm) V= -10-8 Nd/dt (N- turns)
Magnetization
ampere/ meter (A/m)
emu/cm
1 A/m = 10-3 emu / cm3
Magnetic permeability of vacuum
newton/ ampere2
410-7
Inductance
henry
L=oN2Ac/lc (N- turns, Ac- area, m2, lc - magnetic path, m) V= -Nd/dt (N- turns)
henry
Emf (voltage)
volt
volt
MAXWELL'S EQUATIONS IN FREE SPACE (IN SI UNITS)
LAW DIFFERENTIAL FORM INTEGRAL FORM
Gauss' law for electricity Gauss' law for magnetism Faraday's law of induction Ampere's law
NOTES: E - electric field, - charge density, 0 8.8510-12 - electric permittivity of free space, 3.14159, k - Boltzmann's constant, q - charge, B - magnetic induction, - magnetic flux, J - current density, i - electric current, c 299 792 458 m/s - the speed of light, 0 = 410-7 - magnetic permeability of free space, - del operator (if V is a vector function, then . V - divergence of V, V - the curl of V).
For more reference info see EE Information Online 2009 Lazar Rozenblat SMPS Power Supply Guide ( http://www.smps.us/ ) - tutorials, electronics reference, formulas, schematics.
L.Rozenblat on Google+
Você também pode gostar
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Ainda não há avaliações
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocumento4 páginasElectrical Engineering Formulassanjay975Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3No EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Nota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocumento0 páginaElectrical Engineering FormulasPULKITJOSHI100% (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocumento4 páginasElectrical Engineering FormulasVinod MuruganAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesNo EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocumento4 páginasElectrical Engineering FormulasMehdi Aydın DuramazAinda não há avaliações
- Bütün Fizik FormülleriDocumento13 páginasBütün Fizik Formüllerimhasan13Ainda não há avaliações
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksNo EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering FormulasDocumento4 páginasElectrical Engineering Formulasarthur guil-anAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionNo EverandLinear Network Theory: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Vector Form of Coulomb'S Law Basic: The Resultant Force Is and The Direction Is Given by and The Direction Is Given byDocumento8 páginasVector Form of Coulomb'S Law Basic: The Resultant Force Is and The Direction Is Given by and The Direction Is Given byVijay TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- 1.3.3 Electricity and magnetism Name Symbol SI unit Notes Q ρ ρ = Q/V σ Σ = Q/A C V, φ V = dW/dQ U, U = V E E = Ψ Ψ = ∫D⋅ dA C C = Q/U ε ε ε ε εDocumento2 páginas1.3.3 Electricity and magnetism Name Symbol SI unit Notes Q ρ ρ = Q/V σ Σ = Q/A C V, φ V = dW/dQ U, U = V E E = Ψ Ψ = ∫D⋅ dA C C = Q/U ε ε ε ε εcvz240159Ainda não há avaliações
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current by AlienDocumento13 páginasElectromagnetic Induction and Alternating Current by AlienSanatan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocumento3 páginasFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranAinda não há avaliações
- MCAT Physics Equation ListDocumento4 páginasMCAT Physics Equation ListChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Eder - Ferreira - Task 3Documento8 páginasEder - Ferreira - Task 3daniel FerreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Formula SheetDocumento3 páginasFormula SheetMax MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Mobile - BasicsDocumento54 páginasChapter 3 - Mobile - Basicsn2hj2nAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasDocumento1 páginaMidterm1 2afgkmnbv FormulasManny LemosAinda não há avaliações
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFDocumento24 páginasCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFHector Ledesma IIIAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Physics: U NKTDocumento6 páginasThermal Physics: U NKTzzyingAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Alternating CurrentsDocumento23 páginas2 Alternating CurrentsKunalWadhawanAinda não há avaliações
- Formulae Using Symbols Notation: - 1 - 1 B P V eDocumento5 páginasFormulae Using Symbols Notation: - 1 - 1 B P V eJohn Laurence Gonzaga AlcantaraAinda não há avaliações
- Equations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsDocumento3 páginasEquations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsLeseat NocaAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Book Formulas Communication TeliDocumento3 páginasHand Book Formulas Communication TeliJet'sAinda não há avaliações
- Oliver ElectronicsDocumento35 páginasOliver Electronicsprem_singh_nepal100% (1)
- Antenna BasicsDocumento37 páginasAntenna BasicsRishabh Sharma100% (2)
- High-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissDocumento18 páginasHigh-Field Laser Physics: ETH Zürich Spring Semester 2010 H. R. ReissjasmonAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 01Documento8 páginasLecture 01Obed Salu PasambaAinda não há avaliações
- Atomic Physics by AlienDocumento10 páginasAtomic Physics by AlienSanatan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Alternating Current NotesDocumento5 páginasAlternating Current Noteskamali.v777Ainda não há avaliações
- Fiber Optics 2Documento36 páginasFiber Optics 2ekramul98131Ainda não há avaliações
- The Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Documento36 páginasThe Output of Ac Generator Is:: E E Sinwt (E Nbaw) E - (D/DT) (Ø)Lasya notesAinda não há avaliações
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocumento4 páginasMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéAinda não há avaliações
- 'Physics Laws 2nd Term 2017' PDFDocumento7 páginas'Physics Laws 2nd Term 2017' PDFBasant HanyAinda não há avaliações
- Phys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesDocumento2 páginasPhys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesNadya B.Ainda não há avaliações
- Guide13 PDFDocumento40 páginasGuide13 PDFAgus MursidiAinda não há avaliações
- Formulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Documento9 páginasFormulas Optica Ondulatoria (By Carrascal)Iñaki0% (1)
- Task 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkDocumento16 páginasTask 3 - Electromagnetic Waves in Guided Media Individual WorkHaiberAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1, Sept. 8, 2005: 6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications Prof. Markus Zahn Page 1 of 7Documento7 páginasLecture 1, Sept. 8, 2005: 6.013 Electromagnetics and Applications Prof. Markus Zahn Page 1 of 7esesesAinda não há avaliações
- BookkkkDocumento207 páginasBookkkkNadin NirvanaAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude Modulation-Voltage DistributionDocumento10 páginasAmplitude Modulation-Voltage DistributionThejaswar Teja0% (1)
- Analog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationDocumento17 páginasAnalog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationIbra NazlaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergyDocumento19 páginasPhysics: List of Formulae: Vertical Circular Motion Tension Velocity Total EnergySucharita KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2Documento26 páginasLecture 2Ahmed Diaa AlwakilAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical and Eletronic PrinciplesDocumento206 páginasElectrical and Eletronic PrinciplesvelisbarAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles Magnetic Circuits-2p PDFDocumento28 páginasBasic Principles Magnetic Circuits-2p PDFgecicihesappAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial-1 Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) Design: by Rashad.M.Ramzan Rashad@isy - Liu.se ObjectiveDocumento18 páginasTutorial-1 Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) Design: by Rashad.M.Ramzan Rashad@isy - Liu.se ObjectiveRakesh Rt100% (1)
- Chap 3. Light-Matter Interaction: - Electromagnetic Wave (SR 5.2) (Outline)Documento12 páginasChap 3. Light-Matter Interaction: - Electromagnetic Wave (SR 5.2) (Outline)Azhar MahmoodAinda não há avaliações
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocumento24 páginasCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Transmission Line Zero Seq ReactanceDocumento39 páginasTransmission Line Zero Seq ReactanceShyamkant VasekarAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Magnetoresistance SidDocumento7 páginasStudy of Magnetoresistance SidBhargav TangiralaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocumento13 páginasPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- PCB Material Selection For RF Microwave and Millimeter Wave Designs 1Documento61 páginasPCB Material Selection For RF Microwave and Millimeter Wave Designs 1Umair IllahiAinda não há avaliações
- Rectangular Cavity: A Metal Enclosed Box of Volume V A B D TE - ModeDocumento8 páginasRectangular Cavity: A Metal Enclosed Box of Volume V A B D TE - ModePalash SwarnakarAinda não há avaliações
- EMI and ACDocumento14 páginasEMI and ACbharathAinda não há avaliações
- Current ElectricityDocumento6 páginasCurrent ElectricityKannanSubramanianAinda não há avaliações