Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Audio-Video Systems: Principle of Colour TV Receiver Trainer
Enviado por
Atit PatelDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Audio-Video Systems: Principle of Colour TV Receiver Trainer
Enviado por
Atit PatelDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Audio-Video Systems
Experiment No. 01 DATE:
Subject:
Title:
Principle of Colour TV Receiver Trainer
Rev. No.
1.00
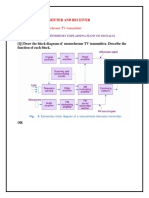
AIM: - To study the, block diagram and working principle of colour TV receiver trainer REQUIRMENTS: - Colour T.V. receiver THEORY: The main function of a colour T.V. receiver are as under 1. To select the signals of the channel and to amplify these and convert them in to IF signals. 2. To amplify the video and sound IF signals, to demodulate the video IF signals to obtain the composite video signal to mix the two - IF signals to obtain the inter carrier sound IF signal and to preamplify these. 3. To separate the combined luminance Y and chroma signals from the video IF signals and to amplify these. 4. To separate the luminance (Y) and chroma i.e. U&V(R-Y and B-Y) signals from the combined video signal. 5. To generate sub-carrier signal with phase locking the sub-carrier burst. 6. To decode the chroma signal to obtain the modulated U & V signals and to demodulate them with the help of regenerated reference carrier. 7. To combine the Y, U V signals (Matrix) to obtain the colour i.e. R G & B signals. 8. To amplify them and to give them to the respective cathodes of the colour picture which. Reproduces these as colour picture with the help of -horizontal and vertical sweep. 9. To produce horizontal and vertical sweeps Synchronized with the respective sync signals and to &e them to the. Respective deflection, coil for producing the sweep. 10. To separate the sound -IF signal, to amplify, limit and demodulate them, and to give them to the loudspeaker at sufficient amplitude. 11. To provide power at suitable D.C. voltages for operating various stages, providing supply to the loud speaker at sufficient amplitude. 12. To provide infrared remote control operations.
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.1
These functions are performed by various stages of the T.V. Receiver, which are explained as under. The Block, diagram showing different sections is shown in fig. 1 1) TUNER: The signal received at the antenna are given to the tuner through the balun. The tuner, which consists of two stages -RF amplifier and converter, partly selects the signal of the desired channel, amplifies it and converts it into I.F. signals. The R.F. amplifier amplifies the signals with the addition of a little noise as possible and gives them to the mixer. The gain of this stage is controlled by A.G.C. The Converter consists of two stages: 1. Local Oscillator. 2. Mixer. The converter changes the frequency of the incoming signals in to the I.F. The local oscillator produces oscillations at a frequency which is higher than the picture carrier frequency by 38.9 MHz, (Which is the Video I.F.).The mixer mixes the incoming signals and the oscillations. This results in the production of the video I.F. (38.9 MHz) and sound I.F. (33.4 MHz ). 2) SOUND IF SECTION (S.I.F):The intercarrier SIF (5.5MHz is given to the sound section - based -on IC CA 1190, which contains sub.- sections SIF detection and sound output amplifier. The SIF signal, which is frequency modulated is amplified and detected. The detected audio is amplified by output amplifier to drive the loud taken. 3)CHROMA SECTION/COLOUR DECODER SECTION (CD):The section consists of two sub-section: (A) Video buffer amplifier. (B) Chroma section. (A)Video buffer amplifier. The CVD signal obtained from VIF section is given to video buffer amplifier which amplifies this signal which consists of luminance signal-Y, Chroma signals R-Y and B-Y, horizontal sync signal , vertical sync signal and the colour sub-carrier burst (colour sync) signal . This stage consists of one transistor. The amplified CVD signal by video buffer section is given to the (i) Chroma section IC TDA 3561A-,and (ii) Sync separator in IC TDA 1940 F( Horizontal section). (B) Chroma section: Chroma section is the most important in a colour TV Receiver. It extracts- the -colour -signals from the modulated and oded chroma signal and gives them to the R,G,B video lifier output stages.
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.2
The main function of thechroma section are 1) Amplification of chroma signals (with colour IdIler) 2) Separating the quadrature modulated chroma signals -in to their constituents i.e. modulated U & V components. 3) Demodulating the modulated U 8-& V signals with the help of a regenerated sub-carrier 4) Regenerating the sub-carrier to enable demodulation of the U & V modulated signals which are transmitted with suppressed carrier/an giving the sub carrier in correct phase to the U & V demodulators. 5) Obtaining the colour signals i.e. R-Y,B-Y, and G-Y, signals from the U&,V signals. 6) Obtaining the colour signals i.e. R,G, and B signals from the colour difference signals and the luminance signals (y). These function aretperformed by a number of tages/ sub-sections in the chroma section as explained below. 4.Chroma Amplifier Thus sub-section includes a band pass ter to ass the chroma signals and a two amplifiers. It amplifies the chroma signals which consists of the adrature modulated U & V signals. The gain of second roma amplifier is controlled by the colour control so the output of colour killer section is given to the 2nd oma amplifier to reduce its gain to zero during onochrome (B/W) reception. The sub-carrier oscillator which is -crystal controlled for high stability produces oscillations at the desired frequency (4.43361875 MHz ).As even a crystal -controlled oscillator cannot ensure the desired degree of accuracy and correct phase of the sub-carrier, phase discriminator circuits is used to compare the frequency of the oscillator with the sub-carrier burst ( transmitted on the back-porch of the H. sync signal ) and to synchronize the phase and frequency of the oscillation with that of this burst. 5.Phase Shift As the quadrature modulation is used for transmitting the chroma signals, the sub-carrier used for modulating the U signal has a 90 degree phase shift, for demodulating the U signals the phase of the sub-carrier given to the U demodulator should also have a 90 degree phase shift . The phase shift stage shifts the phase of the sub-carrier given to the U demodulator by 90 degree. 6.Bistable multivibrator and PAL switch As in PAL system the phase of the V signals is reversed on alternate lines. To demodulate these the phase of the sub-carrier given to the V demodulator should also be reversed on alternate lines. The PAL switch is used to bistable multivibrator along with reverse the phase of the sub-carrier oscillations given to the V demodulator on alternate lines. The Bistable multivibrator which has two positions is operated by the Indent signal obtained from the burst signals. This in turn operates the PAL: switch. The PAL switch gives the sub-carrier to the V demodulator as it is in one position and reverses its phase in the other position.
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.3
7.Colour Killer Colour killer is used to block the chroma amplifier on black and white transmission. This is controlled by the colour -burst signal and on black and white transmission, when the colour burst is absent, it biases the, chroma amplifier to cut-off. Thus it prevents any spurious s signals getting, through the chroma section which can cause coloured snow on the picture tube- screen. 8. Burst Gate: 8 to 10 cycles of the sub-carrier are transmitted on the back porch of the line sync ( h. sync ) signals. These signals are used for synchronizing the regenerated sub-carrier as well as also for obtaining the identifying (indet) signal for the phase reversed V lines. To separate these signals a part of the CVD signal is given to the burst gate. The burst gate which is controlled by the line (horizontal )sync pulses allows the signals to pass only during the burst period. Thus it separates the burst signal. 9.Matrix:Matrix sub-section consists of amplifier stages along with voltage combining and dividing networks. This section obtains back the primary colour signals ( i.e. R,G,B signals ) from the chroma (i.e. U & V ) signals and the luminance signals (Y) given to it. (The Y signal is obtained from CVD signal, The output of H. oscillator section is given to the horizontal driver stage in the EHT section.
The muting circuit is also provided in this section. The mute output signal is given to sound section for putting sound off under no signal condition. 10.VERTICAL OSCILLATOR AND OUTPUT:This section is based on the IC TDA 1675A. It consists of vertical oscillator and output section. The V.osc. produces oscillations at the vertical sweep rate. This is further amplified by vertical output section to drive the vertical deflection coils. The phase and freq. of the V. oscillator is synchronized by the V. Sync. signal, receiving from sync separator. It also provides vertical retrace blanking output signal. 11. OUTPUT VIDEO AMPLIFIERS SECTION: This section consists of three identical stages, one each for the colours R,G,andB. Each of these stages utilizes a transistor in, R-C coupled circuit. These amplifies colour signals at suitable level for driving the colour picture tube. their outputs are given to the respective cathodes of the colour picture tube.
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.4
12. PICTURE TUBE SECTION The colour picture tube stage consists of the picture tube along with its accessories i.e. the deflection coil assembly and colour purity and centering magnets placed on Picture tube neck. The colour picture tube displays the R,G, and B signals given to its cathodes in the form of the colour picture with the help of the sweeps given to the deflection coil assembly. The colour picture tube is precision-in-line (PIL) type Full Flat Square Tube (FFST). 13. HORIZONTAL DRIVEIEL AN D EHT SECTION: (A) Horizontal driver The output voltage obtained from the oscillator is not sufficient to drive the horizontal output stage. A driver is therefore . used between the oscillator and output stage.. This stage is based on a transistor BF383 in transformer coupled circuit. (B) Horizontal output stage (EHT) : The EHT stage drives current of saw-tooth waveform through the horizontal deflection coil with the help of the driver stage. The following voltages are also obtained from the EHT stage. 1) DC voltage of about 25 KV for giving to the final anode of the picture tube (EHT). 2) Dc voltage of about 5KV for giving to the focusing anode ofthe picture tube (Vfc). 3) DC voltage of about 150V volts for giving to the accelerating anode (screen) (vacc). 4) DC voltage of about 150V volts for giving to the collectors of the R.G.B. output transistor. 5) DC voltage of 12V, 25V for_ -operating the various stages. 6) AC voltage of about 6.3 volts for giving to the heater of the picture tube. The transistor BU208D is used in the EHT stage. An auto-transformer known as EHT transformer having several windings is used with this transistor to obtain the different D.C. voltages as also to match the output impedance of the transistor with that of the horizontal deflection coil. 14. SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLY SECTION (SMPS) The SMPS provides +1 15V DC and +20V DC supply. As the performance of color TV receivers depends largely on the supply voltage.- The supply voltage has been stabilized to maintain it very close to the nominal voltage. 33V DC voltage is also generated from 115V to provide it to Tuner-section. BD508A is used as a switching transistor. SMPS has high efficiency than the linear Regulated. power supply. Hence it is used in colour TV receiver. 15. REMOTE RECEIVER SECTION This section is based on three ICs. It provides different operational keys to operate the remote colour T.V. viz. Tuning control ( +/- ), Volume control(+/-), Channel selection control (+/-), Store and function control. The main command IC decodes the decoded infrared signals received from the remote transmitter section and provides necessary control value of Brightness, Contrast, colour, volume, tuning voltage in selected program position
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.5
CONCLUSION: -
ATMIYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, RAJKOT
1.6
Você também pode gostar
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNo Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesNo EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- TelevisionDocumento211 páginasTelevisionazimut.azimut9327100% (1)
- Catv Block DiagramDocumento7 páginasCatv Block DiagramJenny Babe Lindugan-Lopez0% (1)
- Basic Television, Bernard GrobDocumento15 páginasBasic Television, Bernard GrobaledieAinda não há avaliações
- 31 High-Scoring Formulas To Answer The IELTS Speaking QuestionsDocumento368 páginas31 High-Scoring Formulas To Answer The IELTS Speaking QuestionsAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Ieee PapersDocumento8 páginasIeee PapersAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- DSP Lecture 02Documento121 páginasDSP Lecture 02sitaram_1100% (1)
- TV C 2 KeyDocumento6 páginasTV C 2 KeyVanitha DAinda não há avaliações
- TV PDFDocumento10 páginasTV PDFNarayan Krishan Vyas100% (1)
- Topic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterDocumento10 páginasTopic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterNarayan Krishan VyasAinda não há avaliações
- Topic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterDocumento10 páginasTopic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterNarayan Krishan Vyas100% (1)
- Topic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterDocumento10 páginasTopic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterNarayan Krishan VyasAinda não há avaliações
- PAL Encoder: Y 0.3R + 0.59G + 0.11B U 0.477 (R-Y) V 0.895 (B-Y)Documento3 páginasPAL Encoder: Y 0.3R + 0.59G + 0.11B U 0.477 (R-Y) V 0.895 (B-Y)Sanket Patil100% (1)
- Color TV ReceiverDocumento16 páginasColor TV Receiveraniruddhaphatak930% (1)
- Study of Pattern Generator and Its UseDocumento55 páginasStudy of Pattern Generator and Its UseesesesAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Television: TV StandardsDocumento5 páginasModern Television: TV StandardsNurul Syafiqah Jaafar SidekAinda não há avaliações
- TV TrainingDocumento33 páginasTV TrainingTesfaye Mengistie ZewdeAinda não há avaliações
- Television Practical Manual Pass RMPDocumento22 páginasTelevision Practical Manual Pass RMPrahul2480Ainda não há avaliações
- VSBDocumento12 páginasVSBNinh TranAinda não há avaliações
- LM2889, LM1889, LM1886: AN-402 LM2889 RF ModulatorDocumento14 páginasLM2889, LM1889, LM1886: AN-402 LM2889 RF ModulatorSaiful Edwend Bin DaswirAinda não há avaliações
- Television and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFDocumento77 páginasTelevision and Video Engineering Lab Manual PDFtariq76100% (2)
- Progress Report AM ReceiverDocumento6 páginasProgress Report AM ReceiverKtine TaoataoAinda não há avaliações
- Audio Video System LabmanualDocumento54 páginasAudio Video System LabmanualBhavin GajjarAinda não há avaliações
- General Electric 802 TV Radio Receiver and PhonografDocumento21 páginasGeneral Electric 802 TV Radio Receiver and PhonografRicardo CachorrãoAinda não há avaliações
- Monochrome TV TransmissionDocumento2 páginasMonochrome TV TransmissionSam DyAinda não há avaliações
- Am Transmitter: Department of Electronics Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Saint Louis UniversityDocumento19 páginasAm Transmitter: Department of Electronics Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Saint Louis UniversitySubaru_101100% (1)
- Study of Pattern Generator and Its UseDocumento4 páginasStudy of Pattern Generator and Its UseKhakhariaHétálAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics - Working Principle Television (TV)Documento9 páginasElectronics - Working Principle Television (TV)Suman DasAinda não há avaliações
- Theory:: Experiment 1 ObjectiveDocumento13 páginasTheory:: Experiment 1 ObjectivesakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 2Documento11 páginasExp 2Mai Đức CườngAinda não há avaliações
- 09 Com104Documento8 páginas09 Com104CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Com123n TXDocumento7 páginas12 Com123n TXCauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- Slides On Low Power TV TransmitterDocumento16 páginasSlides On Low Power TV TransmitterSiva Rama Krishna KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- 10 KW TV TransmitterDocumento58 páginas10 KW TV TransmitterKirti Khandelwal80% (5)
- Frequency Division Multiplexing: ObjectivesDocumento8 páginasFrequency Division Multiplexing: ObjectivesAbdelrahman RagabAinda não há avaliações
- TV Broadcasting (ECE 421)Documento17 páginasTV Broadcasting (ECE 421)Jay-r De GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- At 2400Documento36 páginasAt 2400Gheorghiu CostinAinda não há avaliações
- Am Balanced ModulatorDocumento9 páginasAm Balanced ModulatorjucxxxAinda não há avaliações
- Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Optical LinkDocumento11 páginasFrequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Optical LinkPriyansh RupaniAinda não há avaliações
- How To Tune Your TVDocumento5 páginasHow To Tune Your TVGnnaprakasan ArulAinda não há avaliações
- 20 Com208Documento16 páginas20 Com208CauVong JustinAinda não há avaliações
- TV DictionaryDocumento10 páginasTV DictionaryGaniza LongAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4Documento9 páginasExperiment 4mohammed_524176180Ainda não há avaliações
- Study of Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Voice LinkDocumento5 páginasStudy of Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Using Voice LinkRakkuyil SarathAinda não há avaliações
- Ec8103-Digital Video Signal CodingDocumento9 páginasEc8103-Digital Video Signal CodingMegha SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Radio Station Training ReportDocumento37 páginasRadio Station Training Reportapi-26629623100% (1)
- Television and Video Engineering EC345Documento20 páginasTelevision and Video Engineering EC345Sreejith KunjachanAinda não há avaliações
- Chassis M28!01!2135MH-MA1 Manual de ServicioDocumento81 páginasChassis M28!01!2135MH-MA1 Manual de ServicioGiovanny Gregorio Gonzalez SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Analog CommunicationDocumento48 páginasAnalog CommunicationBrzata Ptica100% (1)
- Simulation of DVB CH For Antena Diversity RXDocumento6 páginasSimulation of DVB CH For Antena Diversity RXStarLink1Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 7Documento17 páginasModule 7jimmyboyjr50% (2)
- Exp2 Electronic TunerDocumento4 páginasExp2 Electronic TunerRaj HakaniAinda não há avaliações
- AND8261/D Introduction To Analog VideoDocumento5 páginasAND8261/D Introduction To Analog VideoAmarnath M DamodaranAinda não há avaliações
- Am ModulationDocumento9 páginasAm ModulationBrzata PticaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4 PDFDocumento9 páginasExperiment 4 PDFljjbAinda não há avaliações
- 11AK37 Chassis: General InformationDocumento65 páginas11AK37 Chassis: General InformationBenjamin MaxwellAinda não há avaliações
- Analog Communication - Transmitters & Receiver by Arijit Manna (Midnapore City College, Post Graduate 1 Sem)Documento7 páginasAnalog Communication - Transmitters & Receiver by Arijit Manna (Midnapore City College, Post Graduate 1 Sem)arijit mannaAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Nec TransmitterDocumento31 páginasStudy of Nec TransmitterSri HarshaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Instrument Assessment 2Documento10 páginasElectronic Instrument Assessment 2Ashish JhaAinda não há avaliações
- Air FileDocumento12 páginasAir FileManish NaharAinda não há avaliações
- Mod - 6 Counter ADocumento2 páginasMod - 6 Counter AAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Aim: Design 8 Bit Siso, Sipo, Piso, Pipo Shift Register .: (A) Serial in Serial Out (Siso) : VHDL ProgramDocumento6 páginasAim: Design 8 Bit Siso, Sipo, Piso, Pipo Shift Register .: (A) Serial in Serial Out (Siso) : VHDL ProgramAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Aim: Design Mod 8 Down CounterDocumento3 páginasAim: Design Mod 8 Down CounterAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Changes Need To Do: "Count: Buffer Integer 0 To 15 And: "If Clear 1 or Count 5) ThenDocumento4 páginasChanges Need To Do: "Count: Buffer Integer 0 To 15 And: "If Clear 1 or Count 5) ThenAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: Institute of Technology & Science, RajkotDocumento1 páginaAudio-Video Systems: Institute of Technology & Science, RajkotAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Analog LinkDocumento5 páginasAnalog LinkAtit Patel75% (4)
- Audio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of Sound SectionDocumento2 páginasAudio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of Sound SectionAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Avs Question BankDocumento1 páginaAvs Question BankAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- High Definition TV: Audio-Video SystemsDocumento4 páginasHigh Definition TV: Audio-Video SystemsAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Digital TV: Audio-Video SystemsDocumento2 páginasDigital TV: Audio-Video SystemsAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Colour Pattern Generator ST2670: A I O T & S, RDocumento2 páginasColour Pattern Generator ST2670: A I O T & S, RAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of AV SectionDocumento2 páginasAudio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of AV SectionAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: SubjectDocumento3 páginasAudio-Video Systems: SubjectAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Avs - Exp-6Documento4 páginasAvs - Exp-6Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: Vif Section Through Test PointDocumento2 páginasAudio-Video Systems: Vif Section Through Test PointAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of RF - SectionDocumento3 páginasAudio-Video Systems: Circuit Description of RF - SectionAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Vlsi Lab Manual7Documento8 páginasVlsi Lab Manual7Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing Practical 4Documento4 páginasDigital Signal Processing Practical 4Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Audio-Video Systems: AIM: - To Study About Tuner SectionDocumento5 páginasAudio-Video Systems: AIM: - To Study About Tuner SectionAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4: Introduction To UNIX Operating System and Basics of File Management and Interposes CommunicationDocumento7 páginasExperiment 4: Introduction To UNIX Operating System and Basics of File Management and Interposes CommunicationAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing Practical 3Documento5 páginasDigital Signal Processing Practical 3Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Vlsi Lab Manual4Documento3 páginasVlsi Lab Manual4Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing Practical 5Documento3 páginasDigital Signal Processing Practical 5Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Ieee PapersDocumento19 páginasIeee PapersAtit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Signal Processing Practical 1Documento4 páginasDigital Signal Processing Practical 1Atit PatelAinda não há avaliações
- 7915Documento24 páginas7915Balkrushna KankotiyaAinda não há avaliações
- A264518S0Documento2 páginasA264518S0юрий ермошенкоAinda não há avaliações
- T2600Documento2 páginasT2600kylegazeAinda não há avaliações
- Component RequiredDocumento41 páginasComponent RequiredThe JokerguyAinda não há avaliações
- I Unit Os OverviewDocumento14 páginasI Unit Os OverviewChandramouli KolavasiAinda não há avaliações
- Low Power CMOS VLSI Circuit Design (LPVD) : Dr. Veena S ChakravarthiDocumento43 páginasLow Power CMOS VLSI Circuit Design (LPVD) : Dr. Veena S ChakravarthiVeena SridharAinda não há avaliações
- Yuan 2016Documento11 páginasYuan 2016Ahmed ShafeekAinda não há avaliações
- E40Documento3 páginasE40Nanda Kumar100% (1)
- Data Sheet 6ES7131-6BF01-0BA0: General InformationDocumento3 páginasData Sheet 6ES7131-6BF01-0BA0: General Informationamir sfaihiAinda não há avaliações
- Havis Econ 2000Documento2 páginasHavis Econ 2000voltus88Ainda não há avaliações
- DS6130 User ManualDocumento30 páginasDS6130 User ManualmnemonicdensAinda não há avaliações
- Cat and Dog RepellentDocumento2 páginasCat and Dog RepellentJojo LeaonAinda não há avaliações
- An 164 Vinculum II USB Slave Writing A Function DriverDocumento22 páginasAn 164 Vinculum II USB Slave Writing A Function DriverBruno CamposAinda não há avaliações
- Aspire 5540 - 5560 - 5590Documento112 páginasAspire 5540 - 5560 - 5590Anusorn KoedsriAinda não há avaliações
- MCQs of EC Electrical N ElectronicsDocumento22 páginasMCQs of EC Electrical N ElectronicsSatish Bojjawar100% (2)
- 19b LCD Display 1602Documento4 páginas19b LCD Display 1602Nguyen Thai Bao (K15 HL)Ainda não há avaliações
- Real World FPGA Design With VerilogDocumento75 páginasReal World FPGA Design With Verilogsandeepscribd123Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9 Analysis and Design of Digital Filter: Z L Z X Z Y Z HDocumento42 páginasChapter 9 Analysis and Design of Digital Filter: Z L Z X Z Y Z HRajasekhar AtlaAinda não há avaliações
- FactoryTalk View SE LabDocumento2 páginasFactoryTalk View SE LabRodrigoBurgosAinda não há avaliações
- TD62083AFNG, TD62084AFNG: 8ch Darlington Sink DriverDocumento11 páginasTD62083AFNG, TD62084AFNG: 8ch Darlington Sink DriverManuel Jesus Vera DuranAinda não há avaliações
- 2N3055 (NPN), MJ2955 (PNP) Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsDocumento3 páginas2N3055 (NPN), MJ2955 (PNP) Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsMichaelAngeloDelaCruzAinda não há avaliações
- Cad 1133 Powersupply FinalreportDocumento47 páginasCad 1133 Powersupply Finalreportapi-300000636Ainda não há avaliações
- Precommissioning Test ReportDocumento5 páginasPrecommissioning Test ReportMathur DineshAinda não há avaliações
- Specification IC DK124 PDFDocumento7 páginasSpecification IC DK124 PDFordamAinda não há avaliações
- Single-Door Access Controller (Card/Password) User InstructionDocumento1 páginaSingle-Door Access Controller (Card/Password) User InstructionRicardo Ribeiro MouraAinda não há avaliações
- Schneider-Electronic Pressure SensorsDocumento80 páginasSchneider-Electronic Pressure SensorsGirish OniyilAinda não há avaliações
- Pi SQF CCL Traf 435Documento5 páginasPi SQF CCL Traf 435maheshAinda não há avaliações
- The Application of Cvavr, Avrstudio, Proteus in Mcu TeachingDocumento2 páginasThe Application of Cvavr, Avrstudio, Proteus in Mcu Teachinghusam haiderAinda não há avaliações
- MAKE A Mind Control Hypnosis Dream Machine CheapDocumento12 páginasMAKE A Mind Control Hypnosis Dream Machine CheapjohnrighAinda não há avaliações