Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Student Manual 2 For Forensic Medicine & Medicolegal 2012-2013 - 2
Enviado por
Muhammad Ikhlas YasinTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Student Manual 2 For Forensic Medicine & Medicolegal 2012-2013 - 2
Enviado por
Muhammad Ikhlas YasinDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CLINICAL SKILL HANDOUT FORENSIC MEDICINE AND MEDICOLEGAL
Clinical Skill Lab Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin University Makassar 2012
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
TABLE OF CONTENT
Cover Table of Content ............................................................................................. Preface ........................................................................................................... Medicolegal in Patient Care (theoritical background) ..................................... Learning Objective ......................................................................................... Learning Stretegies ........................................................................................ Reference ....................................................................................................... Preparation .................................................................................................... Evaluation ....................................................................................................... 1 2 3 5 6 6 7 8
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
PREFACE
This Clinical Skill Handout is for medical student in Forensic Medicine and Medicolegal. The major objective of this manual is that the student can master some major skills needed in patient care management that in line with Good Medical Practice,
We would like to appreciate to all contributors who have helped in compiling this Clinical Skill Manual .
Makassar, 1 October 2010 Coordinator of Clinical Skill Lab Forensic Medicine and Medicolegal
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
MEDICOLEGAL IN PATIENT CARE
Medical Indications are the facts, opinions, and interpretations about the patient's physical and/or psychological condition that provide a reasonable basis for diagnostic and therapeutic activities aiming to realize the overall goals of medicine: prevention, cure, and care of illness and injury.
Every discussion of an medicolegal problem in clinical medicine should begin with a statement of medical indications. Therefore, medical indications are those facts about the patient's physiological or psychological condition that indicate which forms of diagnostic, therapeutic, or educational interventions are appropriate. Medical Indications describe the day-to-day work of clinical care for patients diagnosing their condition and providing helpful treatments. The medicolegal principles that should govern these activities are the 4 moral principles of physician, that is respect patients autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence and justice. The most ancient moral maxim of medicine, stated in the Hippocratic oath, is "I will use treatment to benefit the sick according to my ability and judgment but never with a view to injury and wrongdoing." Another Hippocratic imperative to physicians states, "be of benefit and do no harm" . Therefore, in medicolegal, beneficence primarily means do the best for the sake of patient, the duty to try to bring about those improvements in physical or psychological health that medicine can achieve. These objective effects of diagnostic and therapeutic actions as well as rehabilitation. Nonmaleficence means going about these activities in ways that prevent further injury or reduce its risk. In this skill training session, the attitude of doctor in patient management will be learnt. This will incorporate some major topics: 1. Four basic moral principle of physician 2. Taking Good Medical Record 3. Establishing a proper Informed Consent 4. Exercising respect for Patient Confidentiality
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
In addition, doctors are professional whose main objective is caring for patients health; there are ten professional responsibilities that should be noted: 1. Commitment to professional competence. 2. Commitment to honesty with patients, emphasizing both informed consent, and prompt reporting and analysis of medical error. 3. Commitment to patient confidentiality. 4. Commitment to maintaining appropriate relations with patients such as the avoidance of patient exploitation for sexual advantage, financial gain, or other private purpose. 5. Commitment to improving quality of care. 6. Commitment to improving access to care. 7. Commitment to just distribution of finite resources. 8. Commitment to scientific knowledge. 9. Commitment to maintain trust by managing conflicts of interest. 10. Commitment to professional responsibilities emphasizing the individual and collective obligations to participate in processes to improve patient care
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
General Objective After conducting the skill training, students are expected to be able to conduct taking proper medical record, informed consent and exercise to respect patients confidentiality. Above all, the four basic moral principle of physician should always be the basis in our patient care management. Spesific Objective After finishing the skills training in this manual, students are expected to be able to apply : 1. Four basic moral principle of physician 2. Good Medical Record 3. Proper Informed Consent 4. Patient Confidentiality
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
LEARNING STRATEGIES Instruments and Tools : Manual book of CSL for Medicolegal Standart measurement / Ruler Patient status, ballpoint Audio-visual / Camera Spygmomanometer Stetoscope Patient Scenario
Learning Method : 1. Observation on the play 2. Discusssion 3. Active participation (simulation) 4. Evaluation using check list
References Beauchamp TL, Childress JF. Chapter. In: Beauchamp TL, Childress JF, eds. Principles of Biomedical Ethics. 6th ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2009:140186; 197239. Brennan T, Blank L, Cohen J, et al. Medical professionalism in the new millennium: a physician charter. Ann Int Med 2002; 136:243246.
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
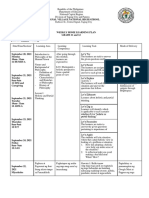
PREPARATION Prepare the room used for role play The setting used was a GP ( General Practicioner) office with three patients already seated inside the room waiting for the doctor Brief the patient about their scenario Instruct the other student to observe the play and to take note if necessary Instruction for the patient Play accordingly to the scenario provided for each patient When the doctor is conducting history taking and the scenario does not contained the solution, the patient is allowed to improvised Instruction for the doctor Play as a doctor taking the patient history as already been teached in previous major (system) Instruct the doctor to enter the room prepared and thus begin the play
Forensic Medicine-Medicolegal
Evaluation No 1 Activity Greet the patient, introduce self to the patient
Ask two of the other patient to wait outside the examination room (patient confidentiality; nonmaleficence; justice)
Take consent from the patient after informed the patient the purpose of the history taking and examination afterward (informed consent; autonomy)
Start the history taking properly (beneficence) and fill the medical record provided accordingly (medical record)
Chek the patient vital status (informed consent; autonomy; beneficence)
Made the working diagnosis based on the history taking result and vital status (beneficence; nonmaleficence) TOTAL 0 1 2 : not performed : performed but not perfect / complete : perfectly performed
Você também pode gostar
- Bank Windu Kentjana International TBKDocumento3 páginasBank Windu Kentjana International TBKMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Case Report of Hernia Inguinalis Lateralis ReponibleDocumento23 páginasCase Report of Hernia Inguinalis Lateralis ReponibleMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Hiv/Aids: Dr. M. Ikhlas YakinDocumento9 páginasHiv/Aids: Dr. M. Ikhlas YakinMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
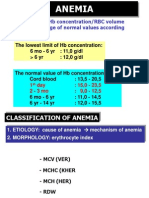
- Reduction of HB concentration/RBC Volume Below The Range of Normal Values According To Age & SexDocumento7 páginasReduction of HB concentration/RBC Volume Below The Range of Normal Values According To Age & SexMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- ATLSDocumento5 páginasATLSAnonymous QguKQDpNAinda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Neuroblastoma PDocumento14 páginasNeuroblastoma PMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Acute Nephritic Syndrome (Ans) : Clinical FeaturesDocumento8 páginasAcute Nephritic Syndrome (Ans) : Clinical FeaturesMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- ForensikDocumento8 páginasForensikMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Leonardo Da VincidsagaDocumento39 páginasLeonardo Da VincidsagaMuhammad Ikhlas YasinAinda não há avaliações
- Oxford Handbook of Clinical Specialties: Seventh EditionDocumento9 páginasOxford Handbook of Clinical Specialties: Seventh EditionMuhammad Ikhlas Yasin0% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Work Teams and GroupsDocumento6 páginasWork Teams and GroupsFides AvendanAinda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Marketing PlanDocumento41 páginasMarketing PlanMark AbainzaAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Quarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityDocumento2 páginasQuarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityIRIS JEAN BRIAGASAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Windows SCADA Disturbance Capture: User's GuideDocumento23 páginasWindows SCADA Disturbance Capture: User's GuideANDREA LILIANA BAUTISTA ACEVEDOAinda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- RubricsDocumento1 páginaRubricsBeaMaeAntoniAinda não há avaliações
- Predictive Tools For AccuracyDocumento19 páginasPredictive Tools For AccuracyVinod Kumar Choudhry93% (15)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Chapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresDocumento40 páginasChapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresTeltel BillenaAinda não há avaliações
- Kormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Documento29 páginasKormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Anonymous rDHWR8eBAinda não há avaliações
- Design Thinking PDFDocumento7 páginasDesign Thinking PDFFernan SantosoAinda não há avaliações
- ACCA Advanced Corporate Reporting 2005Documento763 páginasACCA Advanced Corporate Reporting 2005Platonic100% (2)
- Reflection On Harrison Bergeron Society. 21ST CenturyDocumento3 páginasReflection On Harrison Bergeron Society. 21ST CenturyKim Alleah Delas LlagasAinda não há avaliações
- Romanian Oil IndustryDocumento7 páginasRomanian Oil IndustryEnot SoulaviereAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges For Omnichannel StoreDocumento5 páginasChallenges For Omnichannel StoreAnjali SrivastvaAinda não há avaliações
- 1stQ Week5Documento3 páginas1stQ Week5Jesse QuingaAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Top 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFDocumento16 páginasTop 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFmohammed arsalan khan pathan100% (1)
- A Guide To Relativity BooksDocumento17 páginasA Guide To Relativity Bookscharles luisAinda não há avaliações
- Indg 264.3 w02Documento15 páginasIndg 264.3 w02FrauAinda não há avaliações
- Functions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan ADocumento29 páginasFunctions & Role of Community Mental Health Nursing: Srinivasan AsrinivasanaAinda não há avaliações
- Daud Kamal and Taufiq Rafaqat PoemsDocumento9 páginasDaud Kamal and Taufiq Rafaqat PoemsFatima Ismaeel33% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Trudy Scott Amino-AcidsDocumento35 páginasTrudy Scott Amino-AcidsPreeti100% (5)
- The Systems' Institute of Hindu ASTROLOGY, GURGAON (INDIA) (Registered)Documento8 páginasThe Systems' Institute of Hindu ASTROLOGY, GURGAON (INDIA) (Registered)SiddharthSharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Annexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsDocumento1 páginaAnnexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsMannepalli RamakrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- IBM System X UPS Guide v1.4.0Documento71 páginasIBM System X UPS Guide v1.4.0Phil JonesAinda não há avaliações
- Percy Bysshe ShelleyDocumento20 páginasPercy Bysshe Shelleynishat_haider_2100% (1)
- Bfhi Poster A2Documento1 páginaBfhi Poster A2api-423864945Ainda não há avaliações
- MINIMENTAL, Puntos de Corte ColombianosDocumento5 páginasMINIMENTAL, Puntos de Corte ColombianosCatalina GutiérrezAinda não há avaliações
- Enunciado de La Pregunta: Finalizado Se Puntúa 1.00 Sobre 1.00Documento9 páginasEnunciado de La Pregunta: Finalizado Se Puntúa 1.00 Sobre 1.00Samuel MojicaAinda não há avaliações
- Unified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsDocumento7 páginasUnified Power Quality Conditioner (Upqc) With Pi and Hysteresis Controller For Power Quality Improvement in Distribution SystemsKANNAN MANIAinda não há avaliações
- Best-First SearchDocumento2 páginasBest-First Searchgabby209Ainda não há avaliações
- Approved Chemical ListDocumento2 páginasApproved Chemical ListSyed Mansur Alyahya100% (1)