Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Enviado por
Andrea TeranDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Enviado por
Andrea TeranDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
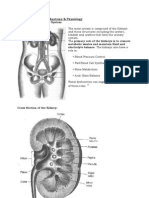
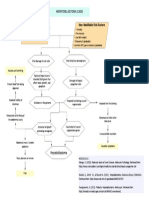
Hemolytic uremic syndrome An acute renal disease characterized by a triad of manifestations: ARF, hemolytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia Etiology
Hus caused by enteric infection of E.coli O157:H7 serotype is the most prevalent pathogen in the US and Europe. The disease usually follows an acute gastrointestinial or upper respiratory tract infection. Patho The primary site of injury appears to be the endothelial lining of the small glomerular arterioles, but other organs and tissues may be involved (e.g. liver, brain, heart, pancreatic islet cells, and muscles). The endothelium becomes swollen and occluded with the deposition of platelets and fibrin clots (intravascular coagulation). Red blood cells are damaged as they move through the partially occluded blood vessels. The spleen removes these fragmented red blood cells, causing acute hemolytic anemia. Fibrolytic action on the precipitated causes the fibrin split products to appear in the serum and urine. The characteristic thrombocytopenia is produced by the placenta aggregation within damaged blood vessels or the damage and removal of platelets. Clinical Manifestation This disease occurs after a prodromal period during which there is an episode of diarrhea and vomiting. Less often preceding illness is an upper respiratory tract infection or, ocassionally, varicella, measles or UTI. The hemolytic process persists for several days to 2 weeks. During this time the child is anorexia, irritable, and lethargic. There is marked and rapid onset of pallor accompanied by hemorrhagic manifestations such as bruising, purpura, or rectal bleeding. Severely affected pts. are anuric and often hypertensive. Seizures and stupors suggest CNS involvement, and there may be signs of acute heart failure. Mild cases demonstrate anemia, thrombocytopenia, and azotemia; urinary output may be reduced or increased. Diagnostic The triad of anemia, thrombocytopenia, and renal failure is sufficient for diagnosis. Proteinuria, hematuria, urinary casts evidence of renal involvement; BUN and serum creatinine levels are elevated. A low hemoglobin and hematocrit and a high reticulocyte count confirm the hemolytic nature of the anemia Therapeutic Management Providers direct treatment toward control of the complications and hematologic manifestations of renal failure.Those used in managing renal failure: Fluid replacement, tx of HTN, and correction of acidosis and electrolyte disorders. The most consistently effective tx is early hemodialysis for any pt who has been anuric for 24 hours or who demonstrate oliguria with uremia or HTN and seizures.
Diet: Low-salt diet to decrease risk of hypertension, Diet high in iron and folic acid content to help recover from anemia, High-energy diet to help patient regain lost weight
Você também pode gostar
- Hereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandHereditary Spherocytosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- TURPDocumento39 páginasTURPanon_727764033100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Brain Hypoxia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo EverandA Simple Guide to Brain Hypoxia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Crescentic IgA NephropathyDocumento64 páginasCrescentic IgA NephropathyRajiv MedankiAinda não há avaliações
- Swollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo EverandSwollen Kidney, (Hydronephrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAinda não há avaliações
- Esrd Ppt. - Alex (Final)Documento109 páginasEsrd Ppt. - Alex (Final)Shoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 Management of Hyperkalemia in CKD PatientsDocumento49 páginas1 Management of Hyperkalemia in CKD PatientsTelli KoromaAinda não há avaliações
- Elevated Arterial Pressure Is Called HypertensionDocumento27 páginasElevated Arterial Pressure Is Called Hypertensionsaurabhv89Ainda não há avaliações
- Hyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Documento23 páginasHyponatremia in Children 03.19.2010Emily EresumaAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDocumento22 páginasAn Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDz PutraAinda não há avaliações
- MNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryDocumento38 páginasMNT in Diseases of Kidney and UrinaryJosephine A. Bertulfo100% (1)
- A Brief Look at Renal AnatomyDocumento15 páginasA Brief Look at Renal AnatomyKristina De Peralta Willy100% (1)
- Glomerulonephritis 10Documento5 páginasGlomerulonephritis 10Eden Jay Calija AgoyAinda não há avaliações
- Urolithiasis: ObjectivesDocumento11 páginasUrolithiasis: ObjectivesOkki Masitah Syahfitri NasutionAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanDocumento30 páginasAcute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanHandre Putra100% (1)
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDocumento7 páginasManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaAinda não há avaliações
- SepsisDocumento33 páginasSepsisv_vijayakanth7656Ainda não há avaliações
- Pyelonephritis: Dr. Shraddha Koirala Department of Pathology NMCTHDocumento26 páginasPyelonephritis: Dr. Shraddha Koirala Department of Pathology NMCTHUrusha MagarAinda não há avaliações
- Renal PathologyDocumento28 páginasRenal PathologyApril Deveras JudillaAinda não há avaliações
- Hypertension Case StudyDocumento2 páginasHypertension Case Studyapi-344630051Ainda não há avaliações
- Hyponatremia: Michael TobinDocumento24 páginasHyponatremia: Michael Tobinmtob3516Ainda não há avaliações
- Hyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismDocumento12 páginasHyporeninemic HypoaldosteronismCésar Augusto Sánchez SolisAinda não há avaliações
- Sickle Cell Disease: Everything You Ever Wanted To KnowDocumento23 páginasSickle Cell Disease: Everything You Ever Wanted To KnowAnastasiafynn100% (1)
- Etiology of Hypertension PDFDocumento2 páginasEtiology of Hypertension PDFRuthAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Glomerulonep Hritis: By: Edelrose D. Lapitan BSN Iii-CDocumento29 páginasAcute Glomerulonep Hritis: By: Edelrose D. Lapitan BSN Iii-CEdelrose Lapitan100% (1)
- Etiology of HypertensionDocumento7 páginasEtiology of HypertensionAdelia Maharani DAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study For Chronic Renal FailureDocumento6 páginasCase Study For Chronic Renal FailureGabbii CincoAinda não há avaliações
- HypertensionDocumento9 páginasHypertensionEdmr SlzarAinda não há avaliações
- Pahtophysiology of EsrdDocumento5 páginasPahtophysiology of EsrdCarl JardelezaAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Documento182 páginasCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot MotAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento6 páginasAcute Renal Failurearif kurnia timurAinda não há avaliações
- Case 1 - Sickle Cell Disease - PPSXDocumento44 páginasCase 1 - Sickle Cell Disease - PPSXNICHOLAS KAUMBA100% (1)
- Arterial Hypertension Eng PDFDocumento29 páginasArterial Hypertension Eng PDFagustinaw1981Ainda não há avaliações
- Heart Failure: Zelalem T., MD Yr III Resident, PediatricsDocumento65 páginasHeart Failure: Zelalem T., MD Yr III Resident, PediatricsChalie MequanentAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Documento28 páginasCardiogenic Shock: Sparsh Goel 77Sparsh GoelAinda não há avaliações
- PancreatitisDocumento59 páginasPancreatitisAarif RanaAinda não há avaliações
- PresentationDocumento11 páginasPresentationShravan TuragaAinda não há avaliações
- Kidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsDocumento56 páginasKidney: Biochemical Tests For Assessing Renal FunctionsPaulina Paskeviciute100% (1)
- Chapter 34 Insulin & Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocumento24 páginasChapter 34 Insulin & Oral Antidiabetic DrugsIlham RamadhanAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento14 páginasNephrotic SyndromeAnna Michael AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Atlas of Diseases of The KidneyDocumento1.095 páginasAtlas of Diseases of The KidneyYanka IlarionovaAinda não há avaliações
- PericarditisDocumento3 páginasPericarditisKhalid Mahmud Arifin0% (1)
- Acute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocumento69 páginasAcute Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisJirran CabatinganAinda não há avaliações
- HypertensionDocumento4 páginasHypertensionKhaira CharmagneAinda não há avaliações
- Renal Pathology-Mreh 32104: Disorders of KidneyDocumento3 páginasRenal Pathology-Mreh 32104: Disorders of KidneyArvinth Guna SegaranAinda não há avaliações
- Anemia in CKD Patient On HeamodialysisDocumento32 páginasAnemia in CKD Patient On HeamodialysisEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- SIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt WastingDocumento20 páginasSIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt Wastingmaged_najehAinda não há avaliações
- Acid-Base Homeostasis: Dr. Abeer KhurshidDocumento42 páginasAcid-Base Homeostasis: Dr. Abeer Khurshidسلة فواكة100% (2)
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Cushing's Disease-1Documento34 páginasAdrenal Insufficiency and Cushing's Disease-1Mwanja MosesAinda não há avaliações
- Portal HypertensionDocumento4 páginasPortal HypertensiondrstalamAinda não há avaliações
- HyperglycemiaDocumento1 páginaHyperglycemiaanon_262360776Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology of ShockDocumento56 páginasPathophysiology of ShockDr. Haricharan AAinda não há avaliações
- CKDDocumento35 páginasCKDgailAinda não há avaliações
- Sickle Cell Disease: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento13 páginasSickle Cell Disease: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAditya Rangga Fandiarta100% (1)
- Ped Nephro 3rd Ed SchaeferDocumento10 páginasPed Nephro 3rd Ed SchaeferAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoAinda não há avaliações
- Hemolytic Uremic SyndromeDocumento2 páginasHemolytic Uremic SyndromeAndrea TeranAinda não há avaliações
- The Spleen: Schwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EdDocumento54 páginasThe Spleen: Schwartz's Principles of Surgery 11th EdaddelinsAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Liver FailureDocumento4 páginasChronic Liver FailureJasmine Faith SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (Agn)Documento42 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis (Agn)Rowshon AraAinda não há avaliações
- ENDOCRINE HYPERTENSION. A Number of Hormonal Secretions May Produce Secondary HyDocumento5 páginasENDOCRINE HYPERTENSION. A Number of Hormonal Secretions May Produce Secondary HyIsak ShatikaAinda não há avaliações
- Hemolytic Uremic SyndromeDocumento2 páginasHemolytic Uremic SyndromeAndrea TeranAinda não há avaliações
- Medsurg Notes F/EDocumento19 páginasMedsurg Notes F/EAndrea TeranAinda não há avaliações
- DO NowDocumento1 páginaDO NowAndrea TeranAinda não há avaliações
- AsthmaDocumento2 páginasAsthmaAndrea TeranAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Hepatoblastoma CaseDocumento1 páginaNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Hepatoblastoma CaseALYSSA AGATHA FELIZARDOAinda não há avaliações
- Reviews: Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors For Gene TherapyDocumento18 páginasReviews: Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors For Gene TherapyCarlos Meza HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy - Signs, Differential DiagnosisDocumento39 páginasDiagnosis of Pregnancy - Signs, Differential DiagnosisKripa SusanAinda não há avaliações
- DRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Documento10 páginasDRUG STUDY Setera Case 8Ceria Dorena Fe SeteraAinda não há avaliações
- Spex Practice Test1Documento29 páginasSpex Practice Test1nowAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Nov 27, 2022Documento3 páginasAdobe Scan Nov 27, 2022Wilson PintoAinda não há avaliações
- Medicine 018 Final PDFDocumento22 páginasMedicine 018 Final PDFdrkefyalewtayeAinda não há avaliações
- Cqi Indicators As Per Nabh 5Th Edition: S. No. Standard Ref. Deptt. KPI Formula FrequencyDocumento3 páginasCqi Indicators As Per Nabh 5Th Edition: S. No. Standard Ref. Deptt. KPI Formula FrequencyNatasha Bhasin91% (11)
- Special Needs in The General Education ClassroomDocumento15 páginasSpecial Needs in The General Education Classroomapi-267526572Ainda não há avaliações
- Ebook Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy PDF Full Chapter PDFDocumento64 páginasEbook Comprehensive Dermatologic Drug Therapy PDF Full Chapter PDFvictor.vega375100% (28)
- Daftar PustakaDocumento2 páginasDaftar PustakatiarAinda não há avaliações
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Concepts of Care in Evidence Based Practice Townsend 7th Edition Test BankDocumento24 páginasPsychiatric Mental Health Nursing Concepts of Care in Evidence Based Practice Townsend 7th Edition Test BankAnitaCareyfemy100% (35)
- African Swine Fever: Pesti Porcine Africaine, Peste Porcina Africana, Maladie de MontgomeryDocumento52 páginasAfrican Swine Fever: Pesti Porcine Africaine, Peste Porcina Africana, Maladie de MontgomeryDecereen Pineda Rodrigueza100% (1)
- Hand Hygiene in Dental Health-Care SettingsDocumento55 páginasHand Hygiene in Dental Health-Care SettingsManu DewanAinda não há avaliações
- FULL-TEXT - NCLEX-RN Practice Quiz Test Bank 3 - NurseslabsDocumento91 páginasFULL-TEXT - NCLEX-RN Practice Quiz Test Bank 3 - NurseslabsRonaldo Matos Perez100% (1)
- Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd. ProfileDocumento3 páginasCadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Profilemail_garaiAinda não há avaliações
- Epilepsy & Behavior: Ethan B. Russo, MDDocumento6 páginasEpilepsy & Behavior: Ethan B. Russo, MDJose Carlos Solis SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Prevalence of Abnormal Pap Smear During Pregnancy in A Teaching Hospital in South IndiaDocumento4 páginasPrevalence of Abnormal Pap Smear During Pregnancy in A Teaching Hospital in South IndiapebripulunganAinda não há avaliações
- Pain Management in ChildrenDocumento19 páginasPain Management in ChildrenNeo SamontinaAinda não há avaliações
- Hepatic Dysfunction in Dengue Fever - A ProspectiveDocumento20 páginasHepatic Dysfunction in Dengue Fever - A ProspectiveSanjay RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Prostate Cancer Between Prognosis and Adequate/proper TherapyDocumento8 páginasProstate Cancer Between Prognosis and Adequate/proper TherapyGabriel NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Derma BriefDocumento7 páginasDerma BriefjeharatAinda não há avaliações
- 0812 Gelofusine PDFDocumento2 páginas0812 Gelofusine PDFMsglow WulanAinda não há avaliações
- Summary Hivaids SetDocumento747 páginasSummary Hivaids Setv8qwxqb2shAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Use CaseDocumento3 páginasHospital Use Caseprashant gauravAinda não há avaliações
- RXPG Series-Preventive and Social Medicine BUSTER (2004) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Documento156 páginasRXPG Series-Preventive and Social Medicine BUSTER (2004) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Premangshu Ghoshal75% (4)
- DocxDocumento20 páginasDocxHarrington_773951393100% (1)
- Health and Wellness FULL RevisedDocumento30 páginasHealth and Wellness FULL RevisedNatalie PimbiAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Mental HealthDocumento2 páginasImportance of Mental HealthCp CsAinda não há avaliações
- SV300 Ventilator Product BrochureDocumento6 páginasSV300 Ventilator Product BrochureabnerkalilAinda não há avaliações
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNo EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNo EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (28)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNo EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (404)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNo EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (81)
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissNo EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (82)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsAinda não há avaliações
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Ainda não há avaliações
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNo EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipNo EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1135)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.No EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (110)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNo EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (328)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)