Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
2b Electrolytes
Enviado por
Erica Alviyanti BastiandDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
2b Electrolytes
Enviado por
Erica Alviyanti BastiandDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Electrolytes & Nonelectrolytes
Electrolytes are substances that produce ions in solution. Substances can be categorized as strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes or nonelectrolytes. Strong Electrolytes Strong electrolytes are substances that only exist as ions in solution. Ionic compounds are typically strong electrolytes. Strong acids, strong bases and salts are strong electrolytes. When solid NaCl is placed in water, it completely dissociates to form Na+ and Cl- ions. Weak Electrolytes A weak electrolyte only partially dissociates in solution and produces relatively few ions. Polar covalent compounds are typically weak electrolytes. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes.
H2O CH3COOH(l) CH3COO- (aq) + H+(aq) H2O NaCl(s) Na+ (aq) + Cl-(aq)
Nonelectrolytes A nonelectrolyte does not dissociate at all in solution and therefore does not produce any ions. Nonelectrolytes are typically polar covalent substances that do dissolve in water as molecules instead of ions. Sugar (C12H22O11) is a good example of a nonelectrolyte.
H2O
C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) Examples of Electrolytes
Strong electrolyte Sea water Hydrochloric acid Sulphuric acid Aqueous copper sulphate Molten lead bromide Aqueous sodium chloride Nitric acid Aqueous potassium hydroxide Weak electrolyte Tap water Carbonic acid Acetic acid Ammonium hydroxide Citric acid Oxalic acid Non-electrolyte Chemically pure water Alcohol Kerosene Aqueous sugar solution Carbon disulphide
How to Distinguish Electrolytes from Nonelectrolytes
Electrolytes are substances that conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Nonelectrolytes are substances that dont conduct electricity when in these states. When an ionic compound such as sodium chloride is put into water, the water molecules attract both the cations and anions in the crystal and pull them into the solution (see the crystal shown in the figure). The cations and anions get distributed throughout the solution.
The crystal structure of sodium chloride.
You can detect the presence of these ions by using an instrument called a conductivity tester. A conductivity tester tests whether water solutions of various substances conduct electricity. Its composed of a light bulb with two electrodes attached. The light bulb is plugged into a wall outlet, but it doesnt light until some type of conductor (substance capable of transmitting electricity) between the electrodes completes the circuit. (A finger will complete the circuit, so this experiment should be done carefully.) When you place the electrodes in pure water, nothing happens, because theres no conductor between the electrodes. Pure water is a nonconductor. But if you put the electrodes in the NaCl solution, the light bulb lights, because the ions conduct the electricity (carry the electrons) from one electrode to the other. You dont even need the water. If you were to melt pure NaCl (it requires a lot of heat!) and then place the electrodes in it, youd find that the molten table salt also conducts electricity. In the molten state, the NaCl ions are free to move and carry electrons, just as they are in the saltwater solution. Scientists can get some good clues as to the type of bonding in a compound by discovering whether a substance is an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte. Ionically bonded substances act as electrolytes. But covalently bonded compounds, in which no ions are present, are commonly nonelectrolytes. Table sugar, or sucrose, is a good example of a nonelectrolyte. You can dissolve sugar in water.
QUESTION:
List two electrolytes and two non-electrolytes. What characteristics give them the distinction of being electrolytes or non-electrolytes.
Você também pode gostar
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNo EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Water Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorNo EverandWater Level Indicator Circuit Using Bipolar Junction TransistorNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (7)
- Class 10 Chemistry Electrolysis PDF 2020-21Documento26 páginasClass 10 Chemistry Electrolysis PDF 2020-21HpAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Physical Science Sample LessonsDocumento51 páginas8 Physical Science Sample LessonsPatrick FadriquelaAinda não há avaliações
- Organic ChemistryDocumento864 páginasOrganic Chemistryforumchemitry100% (1)
- Electrolysis PDFDocumento37 páginasElectrolysis PDFHarini SridharanAinda não há avaliações
- Study Material - Chemical - Effect - of - Electric Current - classVIIIDocumento15 páginasStudy Material - Chemical - Effect - of - Electric Current - classVIIIRajarshiAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis PDFDocumento14 páginasElectrolysis PDFBaryaAinda não há avaliações
- Amine Oxides PDFDocumento21 páginasAmine Oxides PDFvahid100% (1)
- Chemistry Exam Review PackageDocumento30 páginasChemistry Exam Review PackageSagar ArenjaAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrochemistryDocumento43 páginasElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickAinda não há avaliações
- Ws 2 StoichiometryDocumento2 páginasWs 2 StoichiometryAlbertKoretzky100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced ChemistryDocumento137 páginasAdvanced ChemistryMaheshAinda não há avaliações
- Sulfide Saturation in Mafic Magmas: Is External Sulfur Required For Magmatic Ni-Cu - (PGE) Ore Genesis?Documento14 páginasSulfide Saturation in Mafic Magmas: Is External Sulfur Required For Magmatic Ni-Cu - (PGE) Ore Genesis?Berthing HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrolysisDocumento25 páginasElectrolysisMuhammad UmerAinda não há avaliações
- ACS ExampracticeDocumento18 páginasACS ExampracticeNiyanthesh Reddy100% (1)
- 2b Electrolytes PDFDocumento3 páginas2b Electrolytes PDFauliaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolyte and NonDocumento7 páginasElectrolyte and NonSuwahono, M.PdAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry and ElectrolysisDocumento42 páginasElectrochemistry and ElectrolysisAnthonya KnightAinda não há avaliações
- EXPERIMENT 4 chm520Documento1 páginaEXPERIMENT 4 chm520aradilla_93Ainda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis 2022-23Documento18 páginasElectrolysis 2022-23Yasha RizviAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis SlidesDocumento43 páginasElectrolysis SlidesAyesha HoorainAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry: Electrolyte Vs Non-Electrolyte Conductor Vs Electrolyte Electrolysis Electrolytic CellDocumento26 páginasElectrochemistry: Electrolyte Vs Non-Electrolyte Conductor Vs Electrolyte Electrolysis Electrolytic CellIzzati Zakirah Mohd GhazaliAinda não há avaliações
- ChhemiistryyyDocumento2 páginasChhemiistryyyTryxiaa Ö Althea JennAinda não há avaliações
- AcidsDocumento12 páginasAcidspradyummmna9856Ainda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis 1 TEDocumento5 páginasElectrolysis 1 TETom TommmaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter I - ElectrolysisDocumento41 páginasChapter I - ElectrolysisRodella ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
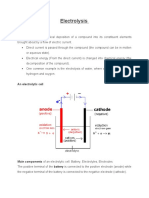
- Electrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsDocumento3 páginasElectrolysis: Electrolysis Is The Chemical Deposition of A Compound Into Its Constituent ElementsEngrDebashisMallickAinda não há avaliações
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 Revision NotesJackson David JebakumarAinda não há avaliações
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 08Documento11 páginasClass IX Chemistry Chapter 08Sam FisherAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis ReviewDocumento13 páginasElectrolysis ReviewAliyah HamiltonAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocumento5 páginasExperiment 5 Dissimilarity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsNurasyilah YakubAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE 10 Chemistry ElectrolysisDocumento4 páginasICSE 10 Chemistry ElectrolysisShreyas.HAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 ElechtrochemistryDocumento23 páginasChapter 6 ElechtrochemistryDannarajen ChandranAinda não há avaliações
- C2 Topic 2 NotesDocumento4 páginasC2 Topic 2 NotesfractoremAinda não há avaliações
- Simulation: Electrochemical CellDocumento17 páginasSimulation: Electrochemical CellyatiEMOAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Solutions POWERPOINT 3Documento81 páginasUnit 3 Solutions POWERPOINT 3Jenny YoonAinda não há avaliações
- Overview : Process of ElectrolysisDocumento5 páginasOverview : Process of Electrolysisn73686861Ainda não há avaliações
- Determining The Dissociation Products of ElectrolytesDocumento3 páginasDetermining The Dissociation Products of Electrolytesnicole olivaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Experiment Chapter 8: Sma Pradita DirgantaraDocumento5 páginasChemistry Experiment Chapter 8: Sma Pradita DirgantaraDoni Wahyu PrabowoAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisDocumento9 páginasElectrochemistry Chemistry - 5070 Electrochemistry in ThisTopikHamdanAinda não há avaliações
- 5 - ConductivityDocumento5 páginas5 - ConductivitydhanielieneAinda não há avaliações
- CHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTEDocumento5 páginasCHEMICAL EFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT ,,,,,,,, Topic - ELECTROLYTESanjaya SahooAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabDocumento1 páginaProperties of Ionic and Covalent Compounds LabKevonSingh1Ainda não há avaliações
- Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationDocumento3 páginasIonic vs. Covalent Bonding Lab InvestigationIngridAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 1-5 Revision ChemDocumento5 páginasTopic 1-5 Revision Chemchloe daviesAinda não há avaliações
- March 10Documento22 páginasMarch 10api-3759646Ainda não há avaliações
- Does Salt Water Make Electricity?: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - BataanDocumento5 páginasDoes Salt Water Make Electricity?: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - BataanLouie SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrochemistryDocumento152 páginasElectrochemistrypapaioasAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Chapter 9.ABakshDocumento16 páginasChemistry Chapter 9.ABakshNaomi JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessDocumento2 páginasChap 11: Electrolysis: ProcessAbdur RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Notes - Chapter 7Documento21 páginasNotes - Chapter 7Chemistry Experts Tutors of ScienceAinda não há avaliações
- Ionic EquilibriumDocumento93 páginasIonic EquilibriumhappyAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Lab Report No. 02Documento3 páginasPhysical Lab Report No. 02atif javed atif javedAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis NotesDocumento19 páginasElectrolysis NotesXGC Ahssn YtAinda não há avaliações
- ElectrolysisDocumento3 páginasElectrolysisPrashiAinda não há avaliações
- Science Curriculum by Aaron KellerDocumento7 páginasScience Curriculum by Aaron KellerResta THawAinda não há avaliações
- Electrolysis 2015Documento13 páginasElectrolysis 2015martinmbondjo062Ainda não há avaliações
- Meaning of ElectrolyteDocumento12 páginasMeaning of ElectrolyteSuzilfarinda SamikAinda não há avaliações
- Olevel NotesDocumento110 páginasOlevel Notestatendachimbandi1Ainda não há avaliações
- ElectrochemistryDocumento8 páginasElectrochemistryTeandraAinda não há avaliações
- The Battery is-WPS OfficeDocumento2 páginasThe Battery is-WPS OfficeKrisha Mae InguaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes: Chapter 4 SolutionsDocumento10 páginas2 Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes: Chapter 4 SolutionsMohamed AlQallafAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsDocumento11 páginasChapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous SolutionsMilinPatelAinda não há avaliações
- The Romance of War Inventions: A Description of Warships, Guns, Tanks, Rifles, Bombs, and Other Instruments and Munitions of Warfare, How They Were Invented & How They Are EmployedNo EverandThe Romance of War Inventions: A Description of Warships, Guns, Tanks, Rifles, Bombs, and Other Instruments and Munitions of Warfare, How They Were Invented & How They Are EmployedAinda não há avaliações
- Nuclear ReactionsDocumento3 páginasNuclear ReactionsErica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- Enz04 InhibitionDocumento2 páginasEnz04 InhibitionErica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- KFT 131 Kinetic TheoryDocumento28 páginasKFT 131 Kinetic TheoryErica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- Nps ECDocumento6 páginasNps ECdont_cry06Ainda não há avaliações
- PP KF Non ElektroliteDocumento13 páginasPP KF Non ElektroliteErica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- Rutgers Alroche Ochem Ch14Documento13 páginasRutgers Alroche Ochem Ch14someone2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Spring 2002 Org II Exam #2 CH 18-19 (100 Points)Documento14 páginasSpring 2002 Org II Exam #2 CH 18-19 (100 Points)Erica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- Formal Informal LangDocumento4 páginasFormal Informal Langviolet174Ainda não há avaliações
- SP 00 Org 2 e 2Documento16 páginasSP 00 Org 2 e 2Erica Alviyanti BastiandAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanisms of Moisture Transport Within SolidsDocumento7 páginasMechanisms of Moisture Transport Within SolidsDeeDeeJAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Thermal Physics1Documento18 páginas2 Thermal Physics1Hakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya100% (1)
- 2.1 Assessed Homework Energetics 57: Year 12 AS Level ChemistryDocumento8 páginas2.1 Assessed Homework Energetics 57: Year 12 AS Level ChemistryfdjjAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 1152 Test 1 With Answers KeyDocumento7 páginasCHEM 1152 Test 1 With Answers KeyiirmiicaAinda não há avaliações
- SBP Trial SPM 2011 Chemistry Kertas 1,2,3 With Answer For K1, K2 and K3Documento18 páginasSBP Trial SPM 2011 Chemistry Kertas 1,2,3 With Answer For K1, K2 and K3Adroit MemberAinda não há avaliações
- Open Blank Landscape PDFDocumento9 páginasOpen Blank Landscape PDFchloeAinda não há avaliações
- Princeton Barron 9Documento13 páginasPrinceton Barron 9bioforlyfeAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concepts: 1.1 Bond Dissociation EnergyDocumento31 páginasBasic Concepts: 1.1 Bond Dissociation Energyrashid100% (1)
- Notes of CH 2 Acids, Bases and Salts - Class 10th Science Study RankersDocumento5 páginasNotes of CH 2 Acids, Bases and Salts - Class 10th Science Study Rankerssamy100% (1)
- HandwarmerDocumento17 páginasHandwarmerapi-238747348Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab Report FinalDocumento13 páginasLab Report Finalidyllic20Ainda não há avaliações
- Drainage Basin: Geomorphological ProcessDocumento125 páginasDrainage Basin: Geomorphological ProcessRudra AbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Body Fluids-1Documento14 páginasIntroduction To Body Fluids-1Lazuardi FadhullahAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 12-Food Shelf Life Evaluation-2-English-1Documento54 páginasTopic 12-Food Shelf Life Evaluation-2-English-1Nur Ghaffar100% (2)
- Application of ESD and PR+Wong Sandler Mixing Rule Equations of State To Study Methane Hydrate Formation in The Presence of Different InhibitorsDocumento15 páginasApplication of ESD and PR+Wong Sandler Mixing Rule Equations of State To Study Methane Hydrate Formation in The Presence of Different InhibitorscansuAinda não há avaliações
- Module 4Documento24 páginasModule 4Vo Truong GiangAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Abundance of The Stable Isotopes of C, O and HDocumento36 páginasNatural Abundance of The Stable Isotopes of C, O and Hkishan kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Water Chemistry PDFDocumento11 páginasWater Chemistry PDFLeandro MichelsenAinda não há avaliações
- R 0.1889 Kpa M T PDocumento10 páginasR 0.1889 Kpa M T PAriel Carlos De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical ProcessDocumento43 páginasChemical ProcesstavolenAinda não há avaliações
- Spec Heat QsDocumento9 páginasSpec Heat QsjosephbainAinda não há avaliações
- Table A - 1: 910 ThermodynamicsDocumento36 páginasTable A - 1: 910 ThermodynamicsLivia MauriAinda não há avaliações
- Elctrolysis XDocumento6 páginasElctrolysis XManash SinghaAinda não há avaliações