Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Gbe CH1
Enviado por
Jigisha MugdalDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Gbe CH1
Enviado por
Jigisha MugdalDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT
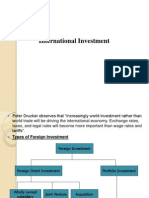
Peter Drucker observes that Increasingly world investment rather than world trade will be driving the international economy. Exchange rates, taxes, and legal rules will become more important than wage rates and tariffs. Types of Foreign Investment
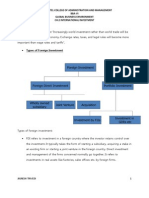
Types of foreign investment: FDI refers to investment in a foreign country where the investor retains control over the investment. It typically takes the form of starting a subsidiary, acquiring a stake in an existing firm or starting a joint venture in the foreign country. Direct investment and management of the firms concerned normally go together. It refers to investments in real assets like factories, sales offices etc. by foreign firms.
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT Portfolio investment refers to where the investor uses his capital in order to get a return on it, but has not much control over the use of the capital. It refers to cross border transactions in bonds and equities GDRs / ADRs and FCCBs are instruments issued by Indian companies in foreign markets for mobilizing foreign capital by facilitating portfolio investment by foreigners in Indian securities A depository receipt is a negotiable certificate denominated in US dollars in case of ADRs, that represents a non US companys publicly traded local currency (Indian Rupee) shares. DRs are created when the local currency shares of an Indian company are delivered to the depositorys custodian bank, against which the Depository Bank issues DRs in US dollars. FDIs are governed by long term considerations as the investments cannot be easily liquidated while portfolio investments can be easily liquidated and are influenced by short term gains. There are three motives of FDI ie resources seeking, market seeking and efficiency seeking ie. (low cost of production due to cheap labor). SIGNIFICANCE OF FOREIGN INVESTMENT Foreign capital facilitates essential imports required for carrying out development programmes, like capital goods, know-how, raw materials and other inputs and even consumer goods which might not be indigenously available. When export earnings are insufficient to finance vital imports, foreign capital could reduce the foreign exchange gap.
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT Foreign investment may also increase the countrys exports and reduce the import requirements if such investments take place in export oriented and import competing industries. As long as foreign investment raises productivity, it would benefit domestic labor in the form of increased real wages, consumers in case if foreign investment is cost reducing in a particular industry, the consumers might gain through lower product prices; government if the increase in production and foreign trade increases the fiscal revenue of the government. Foreign investment brings about four Es efficiency, equity, experience and expertise. Helps increase the investment level and thereby the income and employment in the host country. It facilitates transfer of technology to the recipient country, It may kindle a managerial revolution in the recipient country through professional management and employment of highly sophisticated management techniques. Foreign capital may enable the country to increase its exports and reduce import requirements. Foreign investment might stimulate domestic enterprises to perform better and increase competition and break domestic monopolies. For developing countries, FDI has the following advantages: FDI shifts the burden of risk of an investment from domestic to foreign investors. Repayments are linked to profitability of the underlying investment, whereas under debt financing the borrowed funds must be serviced regardless of project costs.
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT FDI is the only capital inflow strongly associated with higher GDP growth
Criticism against Foreign Capital Foreign capital tends to flow to the high profit areas rather than to the priority sectors. Technology imported might not be adapted to the needs of the customers. MNCs could undermine economic autonomy and control and their activities might not be in favor of national interests. Foreign investment could have unfavorable effect on the Balance of Payments of a country if the outflow is higher due to payment of royalty etc. Foreign investors at times engage in unfair practices and unethical trade practices. Foreign investment could result in minimizing / eliminating competition and facilitate creation of monopolistic structure. FACTORS AFFECTING INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT Resources: Availability and therefore exploitation of resources in the host country. Markets: FDI largely flows to the countries which have large markets with comparatively good infrastructure and political stability. Efficiency: Low cost of production, derived from cheap labor is the driving force of many FDIs in developing countries.
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT Rate of interest: Difference in the rate of interest acts as stimuli to attracting foreign investment. Capital has a tendency to move from a country with a low rate of interest to a country where interest rate is higher. Profitability: Private foreign capital is largely influenced by the profit motive. It is attracted to countries where the return on investment is higher. Economic conditions: Economic conditions particularly market potential and infrastructural facilities influence foreign investment. Government Policies and Political Factors: Policies encouraging FIIS and FDIs and a stable Government largely encourages the movement of foreign capital into the country
FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN INDIA
Direct foreign investment in India was adversely affected by the following factors: Public sector was assigned a dominant position in the important industries and thus the scope of private investment, both domestic and foreign was limited. When public sector enterprises needed foreign technology or investment, there was a preference for the foreign government sources. Government policy towards foreign capital was selective. Foreign investment was normally permitted in high technology industries in priority areas and in export oriented industries. Foreign equity participation was normally subject to a ceiling or 40%. Payment of dividends abroad, etc. as well as inward remittances were subject to stringent laws
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT Corporate taxation was high and tax laws and procedures were complex. These factors either limited the scope of or discouraged foreign investment in India. Government Policy: Pre 1991, India was following a very restrictive policy towards foreign capital and technology. Foreign collaboration was permitted only in fields of high priority and in areas where the import of foreign technology was necessary. The government had issued list of industries where: Foreign investment may be permitted Only foreign technical collaboration (but no foreign investment) may be permitted. No foreign collaboration (financial or technical) was considered necessary. The government policy on foreign equity participation was thus selective. Technical collaborations were to be considered on the basis of annual royalty payments which were linked with the value of total production. The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1973 served as a tool for implementing the national policy on foreign private investment in India. The FERA empowered the RBI to regulate or exercise direct control over the activities of foreign companies and foreign nationals in India. . According to FERA, non residents, foreign students resident in India and foreign companies required the permission of RBI to accept appointment as agents or technical management advisors in India. The trading, commercial and industrial activities in India of persons resident abroad, foreign citizens in India and foreign companies were regulated by FERA. They had to obtain permission from RBI for carrying on in India any activity of a trading, commercial or industrial nature.
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
SARDAR PATEL COLLEGE OF ADMINISTRATION AND MANAGEMENT BBA-VI GLOBAL BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT CH:2 INTERNATIONAL INVESTMENT
JIGNESH TRIVEDI
Você também pode gostar
- International InvestmentDocumento16 páginasInternational Investmentmisty_nairAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento13 páginasForeign Direct InvestmentGaurav GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report On FDI in RetailDocumento52 páginasProject Report On FDI in Retailprasenjitbiswas4515Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Foreign Direct Investment: An Overview: Outward FDIDocumento7 páginasTypes of Foreign Direct Investment: An Overview: Outward FDIRitu MakkarAinda não há avaliações
- INTRO, types, and more. SODocumento11 páginasINTRO, types, and more. SOpanchaljanak0021Ainda não há avaliações
- Bep 5Documento12 páginasBep 5Kajal singhAinda não há avaliações
- Fiiiii Impactt Over IniaDocumento22 páginasFiiiii Impactt Over IniakanishkAinda não há avaliações
- Project Report Master of Management Studies-MMS Degree in Partial Requirement During 3 Semester, 2010-11Documento14 páginasProject Report Master of Management Studies-MMS Degree in Partial Requirement During 3 Semester, 2010-11mandy_t06Ainda não há avaliações
- Or An Investor Located Outside Its BordersDocumento6 páginasOr An Investor Located Outside Its BordersIrshita TarafdarAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento8 páginasForeign Direct InvestmentpratikpawarAinda não há avaliações
- Fdi in IndiaDocumento21 páginasFdi in Indiabestowedart8905Ainda não há avaliações
- FDI Guide Explains Types, Factors, Advantages & LimitationsDocumento25 páginasFDI Guide Explains Types, Factors, Advantages & LimitationsSantosh Gunwant PandareAinda não há avaliações
- DR A K UpadhyayDocumento32 páginasDR A K UpadhyayMinhaz Iqbal HazarikaAinda não há avaliações
- SM Project .FinalDocumento40 páginasSM Project .Finalaniketbhosale_012Ainda não há avaliações
- Fdi and FiiDocumento19 páginasFdi and FiiManju TripathiAinda não há avaliações
- FDI Research ReportDocumento83 páginasFDI Research ReportAshish YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Buisnes EnvioDocumento18 páginasBuisnes EnvioAparna A D NairAinda não há avaliações
- FDI in India Case Study WalmartDocumento32 páginasFDI in India Case Study WalmartSaad KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Presented ToDocumento38 páginasPresented ToAnoop Raj SrivastvaAinda não há avaliações
- FDO ProjectDocumento75 páginasFDO ProjectHarish.PAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of Fdi in India - Annai MathammalDocumento7 páginasImpact of Fdi in India - Annai MathammalSubakarthi KarthiAinda não há avaliações
- FDI in India Case Study WalmartDocumento32 páginasFDI in India Case Study WalmartDhawal Khandelwal33% (3)
- Full Report On Reasons For FDIDocumento19 páginasFull Report On Reasons For FDIKrishnapalsinh Indrajitsinh VirparaAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 4 BeDocumento25 páginasMod 4 BePratha JainAinda não há avaliações
- IEBDocumento25 páginasIEBAnkit Kumar SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Economics ProjectDocumento7 páginasEconomics ProjectelizaroyAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct InvestmentsDocumento25 páginasForeign Direct InvestmentsRohit DhillonAinda não há avaliações
- SM Assignment 1Documento25 páginasSM Assignment 1Utkarsh AryanAinda não há avaliações
- Significance: Study of Fdi in IndiaDocumento73 páginasSignificance: Study of Fdi in Indiatarun41100% (1)
- FDI Project ReportDocumento31 páginasFDI Project ReportJasmandeep brarAinda não há avaliações
- Globalization and FDI in India: An AnalysisDocumento34 páginasGlobalization and FDI in India: An AnalysisAnonymous qFWInco8cAinda não há avaliações
- Fdi in IndiaDocumento63 páginasFdi in IndiaPratik Prakash100% (7)
- Trend Analysis of FDI in IndiaDocumento66 páginasTrend Analysis of FDI in IndiaRajat Goyal100% (4)
- Ibf Group 4Documento19 páginasIbf Group 4QUADRI YUSUFAinda não há avaliações
- Research Publication SeemaDocumento7 páginasResearch Publication SeemaAmit MirjiAinda não há avaliações
- FDI in Developing EconomiesThis concise title "FDI in Developing EconomiesDocumento19 páginasFDI in Developing EconomiesThis concise title "FDI in Developing EconomiesFaisal MohdAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct Investment and Its Growth in IndiaDocumento75 páginasForeign Direct Investment and Its Growth in IndiaRohit SoniAinda não há avaliações
- FDI in India Types, Advantages & TrendsDocumento6 páginasFDI in India Types, Advantages & TrendsVinay NairAinda não há avaliações
- K.E.S. Shroff College of Arts & CommerceDocumento19 páginasK.E.S. Shroff College of Arts & CommerceNirali AntaniAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project On Fdi in IndiaDocumento66 páginasFinal Project On Fdi in Indiasantosh_boyeAinda não há avaliações
- FDI ReportDocumento22 páginasFDI Reportbeenish87Ainda não há avaliações
- A Study On Foreign Direct Investment Specialization (Repaired)Documento65 páginasA Study On Foreign Direct Investment Specialization (Repaired)yatinAinda não há avaliações
- Fdi Eco Project (Quillbot)Documento4 páginasFdi Eco Project (Quillbot)ANANDA PADMANABAN SURESHAinda não há avaliações
- Investment Law F.D.Documento26 páginasInvestment Law F.D.Abhishek K. SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Mithra Mini Project 2019Documento10 páginasMithra Mini Project 2019abhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Greenfield FDI for Sustainable Development in IndiaDocumento14 páginasGreenfield FDI for Sustainable Development in IndiakinjAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project On FDI and FIIDocumento39 páginasFinal Project On FDI and FIIReetika BhatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Foreign Direct Investment (FDIDocumento67 páginasUnderstanding Foreign Direct Investment (FDIShivam singhAinda não há avaliações
- Impact of FDI On Indian Economy: Term Paper On Financial SystemDocumento19 páginasImpact of FDI On Indian Economy: Term Paper On Financial SystempintuAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento11 páginasForeign Direct Investmentdivyesh_variaAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign CapitalDocumento30 páginasForeign CapitalKaushal SekhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Project 1Documento71 páginasProject 1vipulAinda não há avaliações
- Foreign Direct InvestmentDocumento5 páginasForeign Direct InvestmentRiddhee GosarAinda não há avaliações
- Ahmad Husnain FDI IBDocumento5 páginasAhmad Husnain FDI IBChaudhary Ahmad HusnainAinda não há avaliações
- Corporate Governance SystemDocumento16 páginasCorporate Governance SystemRajib RoyAinda não há avaliações
- FDI INVESTMENT GUIDEDocumento32 páginasFDI INVESTMENT GUIDEVikas GaurAinda não há avaliações
- Fdi in IndiaDocumento81 páginasFdi in IndiasuryakantshrotriyaAinda não há avaliações
- ADB International Investment Agreement Tool Kit: A Comparative AnalysisNo EverandADB International Investment Agreement Tool Kit: A Comparative AnalysisAinda não há avaliações
- Exit PolicyDocumento2 páginasExit PolicyJigisha Mugdal100% (1)
- ReportDocumento19 páginasReportJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- DIPOSITEDocumento3 páginasDIPOSITEJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- VJDocumento12 páginasVJJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- FDI Types and SignificanceDocumento7 páginasFDI Types and SignificanceJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Exit PolicyDocumento2 páginasExit PolicyJigisha Mugdal100% (1)
- ReportDocumento19 páginasReportJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- JIGIDocumento14 páginasJIGIJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Ob 2Documento12 páginasOb 2jackooo123Ainda não há avaliações
- VJDocumento12 páginasVJJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Management accounting provides vital data for planning and controlDocumento2 páginasManagement accounting provides vital data for planning and controlJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- FDI Types and SignificanceDocumento7 páginasFDI Types and SignificanceJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento52 páginasReport 1Jigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- There Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTDocumento2 páginasThere Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Management accounting provides vital data for planning and controlDocumento2 páginasManagement accounting provides vital data for planning and controlJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento52 páginasReport 1Jigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento52 páginasReport 1Jigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- There Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTDocumento2 páginasThere Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- The "New" Population PolicyDocumento13 páginasThe "New" Population PolicyJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- Report 1Documento52 páginasReport 1Jigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- There Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTDocumento2 páginasThere Is No Need For Other Adjectives.: This Is Just ELEGANTJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- ReportDocumento19 páginasReportJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- The "New" Population PolicyDocumento13 páginasThe "New" Population PolicyJigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações
- BIO4Documento1 páginaBIO4Jigisha MugdalAinda não há avaliações