Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Syllabi MTech EE PDF
Enviado por
Saurabh KumarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Syllabi MTech EE PDF
Enviado por
Saurabh KumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Banaras Hindu University
Syllabus
For
M.Tech. in Electrical/Systems Engineering (Effective from session 2006-07)
Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Technology Banaras Hindu University
M.TECH. IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Specialization: Electrical Machines and Drives Semester-I Theory 1. EE-5101 Subjects Digital Techniques and Instrumentation Contacts hours/Week 3 4x3 Credits 3 4x3
2, 3, 4 & 5 ELECTIVES (any four from the followings) EE-5111 EE-5112 EE-5121 EE-5122 EE-5134 EE-5153 EE-5155 Practical: 6. EE-5371 Electromagnetic Fields Applied to Electrical Machines Special Electrical Machines Power Electronics Converters I Power Electronics Converters II Advanced Protection of Power Apparatus and Systems Operations Research Digital Signal Processing Laboratory
3 18
2 17
Total of Semester I Semester-II Theory: 1, 2, 3 & 4 ELECTIVES (any four from the followings)
4x3
4x3
EE-5211 Dynamics of Electrical Machines EE-5221 Power Semi Conductor Controlled Drives EE-5222 Microcomputer Applications in Power Electronics and Drives EE-5225 Artificial Intelligence EE-5233 Power Systems Transients EE-5254 Condition Monitoring and Energy Conservation EE-5255 Energy Systems Management 5 IT OPEN ELECTIVE (from other Departments/Schools) 3 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5471 7. EE-5472 8. EE-5473 CAD and Analysis of Electrical Machines Seminar Dissertation Preparation 3 2 3 23
2 1 2 20
TOTAL of Semester II Semester III EE-6371 Part of dissertation work completed
SEMESTER IV 1-EE-6471 Dissertation Open Defense 2-EE-6472 Dissertation Evaluation Total of Semester IV Credits 5 15
TOTAL OF M.TECH.
57
M.TECH. IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Specialization: Power Electronics Semester I Theory 1. EE-5101 Subjects Digital Techniques and Instrumentation Contact hours/Week 3 4x3 3 4x3 Credits
2, 3, 4 & 5 ELECTIVES (any four from the followings) EE-5121 EE-5122 EE-5123 EE-5142 EE-5155 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5376 Power Electronic Converters-I Power Electronics Converters-II Power Semi-Conductor Digital Control Systems Digital Signal Processing Laboratory Total of Semester I SEMESTER II THEORY: 1, 2, 3 & 4 ELECTIVES (any four from the followings)
3 18
2 17
4x3
4x3
EE-5221 Power Semi-Conductor Controlled Drives EE-5222 Microcomputer Applications in Power Electronics and Drives EE-5223 Converter Application EE-5224 Design of Power Electronics Converters EE-5225 Artificial Intelligence EE-5254 Condition Monitoring and Energy Conservation EE-5255 Energy Systems Management 5. IT OPEN ELCTIVE (from other Departments/Schools) 3 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5476 7. EE-5472 8.. EE-5474 Simulation of Power Electronics Converters Seminar Dissertation Preparation TOTAL of Semester II SEMESTER III EE-6376 SEMESTER- IV 1. EE-6476 2. EE-6477 Dissertation Open Defense Dissertation Evaluation Part of dissertation work completed 3 2 3 23
2 1 2 20
5 10 15
Total of Semester IV Credits
TOTAL OF M. TECH.
57
M.TECH. IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Specialization: Power Systems Semester I Theory 1. EE-5101 Subjects Digital Techniques and Instrumentation Contact hours/Week 3 4x3 3 4x3 Credits
2, 3, 4 & 5 ELECTIVES (any FOUR from the followings) EE-5131 EE-5132 EE-5133 EE-5134 EE-5142 EE-5153 EE-5155 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5381
Power Systems Analysis EHV Transmission Dynamics of Power Apparatus and systems Advanced Protection of Power Apparatus and Systems Digital Control Systems Operations Research Digital Signal Processing Laboratory 3 18 2 17
Total of Semester I SEMESTER II THEORY: 1, 2, 3 & 4 ELECTIVES (any Four from the followings) EE-5225 Artificial Intelligence EE-5231 Power Systems Operation and Control EE-5232 High Voltage and Insulation Engineering EE-5233 Power System Transients EE-5234 Special Topics in Power systems EE-5251 Systems Reliability EE-5254 Condition Monitoring and Energy Conversation EE-5255 Energy Systems Management 5. IT OPEN ELCTIVE (From other Departments/Schools) PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5481 7 EE-5482 8. EE-5483 Power Systems Simulation Laboratory Seminar Dissertation Preparation
4x3
4x3
3 2 3 23
2 1 2 2 5
TOTAL of Semester II SEMESTER III EE-6381 SEMESTER- IV 1. EE-6481 2. EE-6482 Dissertation Open defense Dissertation Evaluation Total of Semester IV Part of dissertation work completed
5 10 15
TOTAL OF M.TECH.
57
M.TECH IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Specialization: Control Systems Semester-I
Theory Subject Contact hours/week 1. EE-5101 Digital Techniques and Instrumentation 3 4X3 3 4x3 Credits
2,3,4 &5 Electives (any four from the followings) EE-5133 EE-5141 EE-5142 EE-5143 EE-5144 EE-5153 EE-5155 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5386 SEMESTER-II THEORY: 1, 2, 3 & 4 Electives (any Four from the followings) EE-5221 EE-5222 EE-5225 EE-5231 EE-5241 EE-5242 EE-5252 EE-5255 5 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5486 7. EE-5487 8. EE-5488 CAD and Analysis of Electric Machines Seminar Dissertation Preparation TOTAL of Semester II SEMESTER III EE-6386 Parts of dissertation work completed SEMESTER-IV Dissertation Open Defense Dissertation Evaluation Total of Semester IV TOTAL OF M.TECH. Power Semiconductor Controlled Devices Microcomputer Application in Power Electronics and Drives Artificial Intelligence Power Systems Operation and Control Optimal Adaptive Control Systems Special Topics in Control System Information Systems Energy Systems Management IT OPEN ELECTIVE (from other Departments/Schools) Dynamics of Power Apparatus and Systems Nonlinear Control Systems Digital Control Systems Control System Design Stochastic Processes and System Identification Operations Research Digital Signal Processing Laboratory Total of Semester I
3 18
2 17
4X3
4X3
3 2 3 23
2 1 2 20
5 5 10 15 57
1.EE-6486 2.EE-6487
M.TECH IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Specialization: Systems Engineering Semester-I Theory Subject Contact hours/week 3 4X3 Credits 3 4X3
1. EE-5101 Digital Techniques and Instrumentation 2,3,4 &5 Electives (any four subjects from the followings) EE-5151 Systems Theory EE-5152 Modeling and Simulation EE-5153 Operations Research EE-5154 Computer and Distributed Processing EE-5155 Digital Signal Processing PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5391 Laboratory Total of Semester I SEMESTER-II THEORY: 1,2, & 3 Electives (Any four subjects offered by the department) EE-5225 EE-5251 EE-5252 EE-5253 EE-5255 EE-5256 EE-5257 5 PRACTICALS: 6. EE-5491 7. EE-5492 8. EE-5493 Systems Simulation Laboratory Seminar Dissertation Preparation TOTAL of Semester II SEMESTER III Parts of dissertation work completed SEMESTER-IV 1.EE-6486 2.EE-6487 Dissertation Open Defense Dissertation Evaluation Total of Semester IV TOTAL OF M.TECH. Artificial Intelligence Systems Reliability Information Systems Software Engineering Energy Systems Management Transportation Systems Computer Networks IT OPEN ELECTIVE (from other Departments/Schools)
3 18
2 17
4X3
4X3
3 2 3 23
2 1 2 20
EE-6391
5 10 15
57
EE-5111: ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS APPLIED TO ELECTRICAL MACHINES: Review of Maxwells equations, applications, Magnetic scalar and vector potential. Boundary conditions. Concept of current sheet and flux sheet. Comparison between field theory and circuit theory, Field-mapping technique applied to electromagnetic devices, analytical, graphical and experimental. Method of images. Computer aided mapping of flux distribution-fields in irregular boundary problems, finite difference, finite element and Monte Carlo technique, Introduction to FEM package. Eddy current and field distribution in conducting and ferromagnetic media moving in quasi-stationary magnetic fields. Formulation of emf and torque equations for electrical machines. Inductance calculations, force calculations, Lorentz force, Maxwells second stress tensor, energy and loss Calculations. Field distribution patterns in electromagnetic devices. EE-5112: SPECIAL ELECTRICAL MACHINES Constructional aspects, design and analysis of reluctance motors, shaded pole motors, hysteresis motors, printed circuit motors, axial field motors, servo motors, tachogenerators, stepper motors, special forms of cross-field machines, permanent magnet synchronous motors, spherical motors, written pole motors, brushless motors. Eddy current devices, electromagnetic clutches, couplings and brakes. Linear devices and actuators. Linear electric motors, Classification, application, constructional aspects, design and analysis. Goodness factor. Transverse edge effect, entry-end and exit-end effect, short primary effect, short secondary effect in linear induction motors. LIMS: Force, energy and power, motors for low, medium and high-speed applications. Electromagnetic levitation and guidance schemes-attraction, repulsion, partial attraction type. EE-5121: POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTER-I AC to DC converters: Review of uncontrolled and controlled converters: Configuration of phase controlled converters, analysis under R, RL and back emf loads, effects of source inductance, influence of firing angle delay on reactive power control, reactive power control methods, four quadrant operation using dual converters with and without circulating current power factor improvement methods, harmonics and their suppression, transformer connection, reduction of ripple in load voltage and current, firing circuits. AC-to-AC converters: Phase control: Configuratioin, analysis with R, RL and back emf loads, symmetrical and unsymmetrical firing control, power factor improvement, harmonics, transformer tap changer, firing circuit. Integral cycle control: Analysis, harmonics, power factor improvement, and applications. Phase controlled Cyclo-converters: Principle of operation, configration, circulating and non-circulating current modes of operation, effect of source inductance, load commutation, control circuits, harmonics. EE-5122: POWER ELECTROINIC CONVERTER-II DC-to-DC Converters: Choppers: Classification, configuration, series and parallel capacitor turn-off circuit configuration and analysis, effect of source inductance, two and four quadrant choppers, thyristor commutation circuit, voltage, current and load commutation. Switch Mode Regulators, Introduction, buck, boost, buck-boost converters-configuration and analysis, Cuk converter, full bridge DC DC converter-bipolar and univocal, voltage switching analysis, control circuits, PWM and current mode control, synchronous rectifiers. Resonant DC-to-DC converter: Classification, basic resonant circuit concepts, zero voltage, zero current switching. DC to AC Converters: Basic Inverters: Principle of operation, circuit configuration, classification, commutation, performance parameters, voltage source inverter, single phase and three phase analysis, voltage and frequency control, load commutation, Current source Inverter, modes of operation, load commutated and forced commutated, harmonics, control circuits. Switch Mode Inverters: Basic concepts, single and three phase circuits, effect of blanking time in PWM inverters, control and switching schemes, harmonics. Resonant Inverter: Basic concepts, series and parallel resonant inverters, resonant DC link inverters with zero voltage and zero current switching, high- frequency-link inverter.
EE-5123: POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES Device structure and theory of operation, characteristics, rating and specifications, thermal considerations, protection, gate/base drive circuits, and other application aspects of power semiconductor devices: diode, thyristor, GTO, BJT, MOSFET, IGBT and other recent devices. EE-5101: DIGITAL TECHNIQUES AND INSTRUMENTATIOIN Basic concepts and classification of transducers. Performance characteristics of instrumentation systems, analog and digital transducers, instrumentation amplifiers, filtering, data acquisition system and conversion, signal processing and transmission, grounding, EMI/EMC interference effects and shielding. Microcontroller and PC based data acquisition systems, input-output devices and displays. Telemetry. EE-5131: POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS Component modeling, Y-bus and Z-bus formation, sparsity techniques-L-U decomposition and optimal ordering. Load flow: Newton-Raphson, fast decoupled, second order methods, hybrid method, multiple load flow solutions, 3-phase unbalanced load flow, harmonic load flow, continuation load flow. Fault studies- short circuit and open conductors, simultaneous fault. State estimation: Estimation techniques, bad data detection and identification. Load forecasting: Short, medium and long-term forecasting, statistical and AI based methods. Generation and transmission planning. EE-5132: EHV TRANSMISSION Operation aspects of EHV transmission systems, design features of transmission lines, towers and associated switchyards, conceptualization of VAR requirements in EHV AC Configurations. Transmission capacity enhancement through controllable elements, basic concept, planning strategies. Series and shunt compensation: Optimal location studies, sub-synchronous resonance in compensated networks. Reactive Power Control: Reactive power flow in electric power transmission systems, thyristor controlled reactor (TCR) analysis, operating characteristics of a TCR-FC type compensator, Thyristor Switched Capacitor (TSC): Analysis, operating characteristics of TCR-TSC type compensator, control of static compensators, Concepts of Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) devices and control. HVDC Transmission Systems: Introduction and planning for HVDC transmission. Analysis of HVDC converters: Pulse, choice of converter configurations, analysis of GRAETZ circuit, converter bridge characteristics, twelve pulse converter operation, harmonics and filters, analysis and design. Control of HVDC systems: Introduction to basic control concepts, control characteristics, current control at inverter, current margin control principle, effect of DC line resistance on static characteristics, modification of Inverter characteristics, Voltage dependent current order limit (VDCOL), tap changer control, power reversal in DC link, Basic Converter control system. Individual Phase Control (IPC): Constant Extinction Angle (CEA) control with IPC, CEA control with EPC, Starter and shut down of HVDC link, effect of AC systems, strength on operational feature of AC /DC systems, multiterminal HVDC systems, DC circuit breaker operating principle. EE-5133: DYNAMICS OF POWER APPARATUS AND SYSTEMS State space models, Synchronous machine and excitation systems, Hydro and steam turbines and governors. Load modeling large induction and synchronous motors. Cyclic loads (rolling mill drives, nuclear reactor and others). FACTS devices. ULTC. Small signal stability: Effect of excitation systems analysis of interconnected systems, power system stabilizers. Large signal stability: Introduction to transient energy function method, stability of large-scale system, reduction decomposition, coherence, and identification. Stability Improvement: excitation and other method of control. Voltage stability: Phenomenon of voltage collapse, global experiences. Methods of analysis. Multiple load flow. Eigen value, singular values decomposition, energy integral, continuation load flow, dynamic analysis, methods of improvement.
EE-5134: ADVANCED PROTECTION OF POWER APPARATUS AND SYSTEM Philosophy of protection, review of protection schemes for power apparatus and systems. Protection of Transmission Lines: Review of distance protection, carrier current protection, directional and phase comparison relaying. Carrier transfer tripping carrier aided distance protection carrier acceleration and carrier blocking schemes: Optical fiber channels, Protection of series compensated lines. Protection of Machines and Bus Zone: Protection of generators, motors, transformers and bus-zone. Numerical Protection: Protective relaying algorithms, over current protection, distance protection of transmission lines, protection of generators, motors and transformers. Intelligent Protection: ANN and Fuzzy logic based schemes for power apparatus and systems. Traveling Wave Relays: Distance and differential relays. Adaptive Relaying: Concepts, selection of algorithms, relay setting, adaptive protection systems. Dynamic Relay Testing Bench. Introduction to Integrated Protection Systems. Recent developments in switchgear. EE-5141: NONLINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS: Approximate analysis: Phase plane and limit cycle, Describing functions and jump resonance, Dual input describing function (DIDF). Singular perturbation method and applications, computational techniques. Stability: definitions, positive definite functions, Lyapunovs direct method, generation of Lyapunov functions. Popovs result and frequency domain criterion, extension to Popov result and circle criterion. Kalman-Yakubovich lemma. Normed spaces and operators, contraction mapping theorem and its application. Input-output stability using small gain theorem. EE-5142: DIGITAL CONTROL SYSTEMS Sampling Process, Z-transform analysis, modified Z-transforms stability criteria. State variable analysis. Analysis and stability of non-linear digital control systems. Characteristic features of computer control systems, controller designs. Implementation of digital controller: Quantization and time delay effects, real time requirements, and finite arithmetic effects. Case studies using digital signal processors. EE-5143: CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN Frequency domain design, gain adjustment using M-circle and inverse Nyquist plot. Compensator design: inverse Nyquist diagrams and Rosen Brock design, algorithmic approach, root locus design. Introduction to multivariable systems, Model representation, decoupling. Controllability, Observability and canonical forms. State variable feedback: pole-zero assignment, Ackermanns formula. Introduction to observer design. Performance criterion and parameter optimization. EE-5144: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES AND SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Probability axioms, random variables, expectations, distribution function and density function, stationary and ergodic processes, auto correlation and cross correlation functions. Power density spectrum. Linear system response to stochastic inputs, Gauss-Markov processes and stochastic differential equations. Processing noisy data and properties of estimators, moments, ML-MAP, LS-estimation, indirect estimation and LMS estimation. State estimation and Kalman filter, recursive algorithms. Model structure and identifying impulse response from cross correlation function, white noise signal, persists excitation. Transfer function from impulse response curve, choice of identification criteria. Black box models.
EE-5151: SYSTEMS THEORY Concept of systems and its classifications. Mathematical Models. Time response analysis of continuous and discrete systems. System modeling using transfer function, rules of interconnections, signal flow graphs. System with multiple inputs and outputs. Graph Theory: Linear graph of different components, systems graph matrices, graph theoretic approach of system modeling and static equations. State Variable-modeling techniques: State equations from differential equations, and transfer functions and viceversa. Similarity transformations and canonical forms of MIMO systems STATE Variable models of interconnected systems. Time response analysis of continuous and discrete time systems. Stability, Sensitivity, Controllability and Observability analysis of continuous and discrete time systems. Large Scale Systems: Graph theoretic representation, basic structures, analysis, optimization and control. Reduced order modeling using time and frequency domain techniques. EE-5152: MODELLING AND SIMULATION SYSTEM: Concept, environment, stochastic activities, continuous and discrete time systems, systems modeling and types of system model. Subsystems, corporate models and their segments. Type of system studies, analysis, design and postulation. Continuous system simulation: system models differential equations, analog methods, CSMP Feedback and interactive simulation, Real time simulation. System Dynamics: Exponential Growth and decay models. Logistic curves, system dynamic diagram, multi-segment models, time delays, feedback in socio-economic system world models. Probability concepts in simulation. Queuing system: Arrival patterns, exponential, carling and hyper exponential distribution service time, queuing disciplines, measures of queues, mathematical solutions. Discrete system simulation: Discrete events, representation of time, generation of arrival patterns, simulation, programming tasks, gathering statistics, counters and summary statistics. Measuring utilization and occupancy. Recording distributions and transit times. Introduction to simulation Languages. EE-5153: OPERATIONS RESEARCH Mathematical formulation. Linear programming and applications. Dynamic Programming, shortest route problem. Integer programming. Branch and bound techniques. Introduction to non-linear programming Deterministic and probabilistic inventory models. Decision theory, game theory, PERT, queuing theory, and Markov chains. EE-5154: COMPUTERS AND DISTRIBUTED PROCESSING Computer system overview, Instruction set RISC and CISC. Operating System: Objectives and function. Memory Management: Hierarchical arrangement. Paging and segmentation. Process description and control: Concurrency, uniprocess scheduling. I/O and file management. Networking and distributed processing: Communication architecture. Message passing. EE-5155: DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Discrete Time Signals and Systems: Generation (sampling, aliasing and impostors), algebraic manipulation, Properties, signal spectrum, power and energy, difference equation, convolution. Z-Transform: z-Transform and its inverse, system function, pole zero maps, bilinear s to z transformation, chirp transformation. Discrete Orthogonal Transforms: Discrete Fourier transform, sine transform, cosine transform, Walsh Hadamard transformation.
Frequency Analysis and Discrete Fourier Transform: Frequency analysis of discrete time windows, windowing, and FFT algorithms. Discrete Time System Realizations: Finite Impulse Response and Infinite Impulse Response systems, parallel and cascade forms. Digital Filters and Design: Finite Impulse Response and Infinite Impulse Response systems, parallel and cascade forms. Digital Filters and Design: Finite Impulse Response and Infinite Impulse Response filters, design techniques. Applications and Hardware for DSP. EE-5201: SPECIAL OPERARTIONAL AND DESIGN FEATURES OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES Physical phenomena of induction machines: Unbalanced operation under various fault conditions, effect of space and time harmonics. Unbalanced magnetic pull. Single phase induction motor: Analysis using cross-field and double revolving field. Design of starting winding for capacitor split phase motors. Principle of summarization in the design of armature winding for production of aiding torque. Large rotating machines: Turbo alternator rotor construction, operational aspects, waterwheel driven vertical shaft machines, vibration considerations. Short circuit forces and switching transients in transformers. Effects of physical dimensions on losses and power output. Heating and cooling of electrical machines: Rating and duty cycle, ventilation, hydrogen cooing, direct cooling, cooling of totally enclosed machines. EE-5211: DYNAMICS OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES Dynamic conditions: concepts and constraints. Modeling and performance simulation methods. DC machines dynamics: Ideal machines, dynamic equations, transfer function, block diagram state equations, linear analysis of DC motors and generators, effects of saturation: analysis and performance under disturbances. Induction machines: Transients and dynamics, basic electromechanical equations, non-linearised and linearised analyses, space phasor model. Synchronous machine transients, Coupled circuit viewpoint. Approximate physical picture. Equivalent circuits under transient conditions and its applications. Synchronous motor operation under fixed load, variable load and variable excitation. Equal area criterion for the study of transient stability. Sudden short circuit test. EE-5221: POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR CONTROLLED DRIVES Review of Electric Drive Systems: Concept, Classification, requirements, selection and rating, equivalent system of motor-load combination general form of dynamical equations of motion, quadrennial diagram, steady state and dynamic operation, criteria for steady state stability. DC Drives: Phase controlled and chopper controlled drives-performance parameters, analysis and performance characteristics of series and separately excited motors. Application area and considerations. Electric braking closed loop control. AC Drives: Operation, analysis and performance characteristics of induction and synchronous motors fed from VSI and CSI, slip-controlled induction motor drives, self-controlled synchronous motor drives. Closed loop control. Other forms of Drives, Brushless DC and AC motor drives, switched reluctance motor drives, stepper motor drives, vector controlled induction motor drives. EE-5222: MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN POWER ELECTRONICS AND DRIVES Microcomputers: Architecture, Operating System, assembly language programming. Interfacing and data acquisition. Control and performance analysis: Gating control, closed loop control, monitoring and fault detection. Microcomputer applications-case studies.
EE-5223: CONVERTER APPLICATIONS: Application considerations in the use of power semiconductor converters in HVDC, Static VAR compensation, active filters, welding and heating control, UPS, SMPS, aircraft power supplies. Converter interfaces for nonconventional energy sources. EE-5224: DESIGN OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS: Introduction to design concepts selection criteria for power switching devices and their rating. Design of numbers and magnetic circuit. Thermal design: temperature rise, heat sink and thermal protection, control circuit design for semiconductor switches. Design considerations for rectifiers, inverters, SMPS, UPS and resonant converters-case studies. EE-5225: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Introduction, problem solving methods, knowledge representation, natural language processing, AI languages Expert Systems: Components, production rules, inference mechanism, knowledge engineering, Expert system shells and Tools kits. Artificial neural Networks: Biological concepts, neuron model, and transfer function, networks architectures, learning methods. ANN design procedure. Fuzzy Logic: Fuzzy set theory, fuzzy logic systems, Membership functions, fuzzy inference, and uncertainty in information, fuzziness in expert system and neural networks. Genetic Algorithms Case studies. EE-5231: POWER SYSTEM OPERATIONS AND CONTROL Automatic generation control, modeling of boiler turbine and generator, load frequency control schemes, steady state and dynamic analysis in frequency domain for single and multi area systems. Economic Dispatch: Problem formulation, loss coefficients, unit commitment, hydrothermal scheduling, dynamic programming optimal active and reactive power flow, linear and non-linear solution methods. Reactive power control and management: HVAC Network, AC/DC interconnected network, and optimal reactive power flow local and regional level. Security and contingency analysis SCADA, real time control Deregulated mode of operation. EE-5232: HIGH VOLTAGE AND INSULATION ENGINEERING, Failure mechanism of solid, liquid, gases and composite dielectrics, Treeing and tracking phenomena. Generation of HVDC, HVAC and impulse voltages. Design considerations. Testing of High Voltage equipments: Transformers, Cables, bushings, insulators, lightning, and arrestor circuit breakers. Insulation coordination: coordination: classical and statistical methods, insulation design for practical cases. Partial Discharges: mechanisms, equivalent circuits, measurements in practical systems such as transformers, cables and capacitors. Aging theory: Ageing and mechanism of ageing under electrical, thermal and combined stresses. Accelerated aging tests. Aging data analysis. Pollution: causes, effects, mathematical modeling, and performance evaluation of insulators, bushing and surge diverters. Measurement and Instrumentation: measurement of AC, DC and impulse voltages, classical methods, sources of EMI, grounding and shielding, application of fiber optics methods, optical sources and detectors. Modern gas insulation methods, SF6 and gas mixtures, vacuum application of barriers. GIS. GITL. EE-5233: POWER SYSTEM TRANSIENTS Switching transient: On single isolated and multi-conductor systems with ground effects, abnormal cases. Traveling wave solution. Graphical techniques. Transient Network Analyzer (T.N.A.) Transient Simulation: Electromagnetic Transient Programme (EMTP), finite difference methods, frequency dependence of parameters.
Transient in HVDC, transformers. Ferrorsonance, true saturation characteristics of magnetic materials. Lightning surges: Effects on transmission lines, insulation coordination. Protection against lightning: Lighting arresters, their ratings and location. Overhead ground wires. Grounding techniques. Statistical computation of transients in transformers, cable, and overhead lines. Fast transient over voltages in GIS. EE-5234: SPECIAL TOPICS IN POWER SYSTEMS (Any two as offered by the department) (a) Flexible AC Transmission Systems Technology
Dynamics of power system under changing operational conditions. Study of power network with conventional damping controllers. Concept of FACTS. Comparable study of the transmission network with FACTS devices and other alternate strategy. Modeling and study of FACTS devices: Thyristor Controlled Series capacitor (TCSC), Static Condenser (STATCON), Static Var Compensators (SVC), Thyristor Controlled Phase Angle Regulator (TCPAR), Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC), Voltage Source Converter, Controlled Shunt Reactor, HVDC, Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC). Coordinated control of FACTS devices in an integrated power network. Present trend in the selection of FACTS devices and their location in power network, economic evaluation of FACTS devices for comparative benefits, Industrial/Utility experiences of FACTS devices installations. (b) Distribution Systems General distribution: Domestic, industrial and specific applications. Distribution planning. Sub-station: Design, equipments, protection. Voltage control: Loss minimization, reconfiguration, and capacitor placement. Economics of distribution and tariffs. Private power plant. Introduction to distribution automation. (c) Deregulated operations. General Philosophy: Energy market deregulation, international principle of transmission access, pricing, deregulatory auction, Power Supply options: Coordinated re-dispatch/counter trading, transmission capacity option, market splitting. Criterion of Participation: GTL cost criteria, generator to access grid, transport to/from the borders, load to access grid. Transmission and Distribution Planning: Market development, interconnected trading and settlement, system support services, market development achievements, universal solution to right trading systems. Tariff Structure: New wheeling tariffs, power charge, system service, losses and other Para-fiscal charges. International Scenario: Deregulation in Europe, Japan, Australia, USA, Legislative and infrastructural aspects, regulatory changes and alternative models.
EE-5241: OPTIMAL CONTROL SYSTEMS Optimal Control System: Minimum time, minimum-fuel, minimum-energy problem. Calculus of Variations: Optimal control using Pontryagins maximum principle, Hamilton-Jaccobi equation. Dynamic programming and its applications. Optimal regulator problem, solution of Riccatti equation. Frequency domain design of optimal controllers and its robustness properties. EE-5241: ADAPTIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS Adaptive control problem and definitions. Learning in adaptive systems. On-line identification and recursive methods of parameter estimation. Basic MRAC and STR schemes. Stability problem and matching condition.
Lyapunov design of MRAC systems. Minimum variance and pole placement-STR algorithm. Robustness of adaptive controllers. EE-5242: SPECIAL TOPICS IN CONTROL SYSTEMS (Any two as offered by the department) (a) Robotic Control Introduction: Types of industrial manipulators, Components of robot systems, arm manipulator geometry, different degree of freedom. Kinematics and dynamics, relations between links and joints. Arm solution. Jacobian, dynamic model of arm manipulators. Path planning. Path control: Collision free path planning. Cartesian control, force control. Force control and stability. Neural network models. Learning, decision making and adaptive learning of manipulator. (b) Supervisory control of discrete Events Dynamic Systems (DES) Formation of discrete event systems models. Supervision of discrete event system: Modular supervision of DES, hierarchical supervision of DES. Supervisory control with partial observations. State based control of DES. Supervision of vector DES, supervisory control of timed discrete event system. (c) Intelligent Instrumentation and Control: Application of decision theory, fault detection theory and signal detection theory for validation of measured quantity. Self-diagnosis of instrumentation systems. Information retrieval. Adaptive sensing. Robust control, Fault detection. Fuzzy controllers. Neural network controllers. Gain scheduling and multiple model switching control. (d) Model Reduction Techniques Importance of reduced order models. Pades approximation, Rouths method, continued fraction and other methods. Mixed method and sub-optimal control using reduced order models. Order reduction using modal analysis. Aggregated modeling of large scale systems.
EE-5251: SYSTEMS RELIAABILITY Probability Laws: Independent, discrete, Markovian and other processes. Reliability Concepts: Failure data analysis, reliability functions, hazard models. Combinational Reliability: Series, parallel and r out of n configuration. Tie-set cut-set logic diagrams. Construction of different reliability models and evaluation. Fault Tree analysis. Reliability improvement: Component improvement, redundancy, and reliability-cost trade-off. Static and dynamic redundancy. Triple modular Redundancy (TMR). Maintainability, repair and availability, Reliability and availability functions. k out of m systems. Markov Models. Network reliability. Digital Systems: Testability, fault tolerance and performability. Coding for error detection and correction. EE-5252: INFORMATION SYSTEMS Types of information, Management structure, management and information requirement, qualities of information.
Example of Information Systems: Various functions in an organization, varieties of information system. Information processing an overview. Overview of Information System Analysis: Overview of design of an information system. System design life cycle. Role and tasks of a system analyst. Attributes of a system analyst, Tools used by system analysts. Information Gathering: Strategy, sources, methods of obtaining information. Systems Requirements Specification: Data dictionary, system analysis, modularizing, requirements specifications. Feasibility Analysis: Project goals, examining alternative solutions, evaluation of solution, payback period. Feasibility report. Data Flow Diagram: Describing a system with DFDs, conventions in developing DFDs, leveling of DFDs, logical and physical DFDs. Process Specifications: process specification methods, structured English. Decision Tables: Decision table terminology and developments, types of decision tables, checking the correctness of decision tables and use of Karnaugh maps to detect errors. Eliminating redundant specifications. Logical Database Design: E-R models, cardinality and participation, relation, normalization and normal forms. Data Input Methods: Data inputs, coding techniques, detection of errors in codes, validating data inputs, interactive. Data Input. Database Management Systems (DBMS). File based system, Database and DBMS, Objectives and overview of DBMS, Database administration, Database design. Object Oriented System Modeling: Objects and their properties, implementation of classes, identifying objects in an application. Modeling Systems with objects. Unified Modeling Language. Designing Outputs: Objectives of output design, output devices, output reports and screening, use of business graphics. Control Audit and Security of Information System: Control and audit of information system. Testing of information system security. Electronic Commerce: Advantage and disadvantages of e-commerce system architecture, Electronic Data Interchange, security in e-commerce electronic payment systems. EE-5253: SOFTWARE ENGIINEERING Software: Evolution and ageing of software. Classical life cycle model. Metrics: product and quality metrics. Collection, computation and evaluation of metrics. Project Management: Estimation of resources. Model and automated tools for estimation. Project Planning: Risk analysis. Project scheduling. Re-engineering. Requirement Analysis: Structure analysis. Object oriented analysis and data modeling. Alternative analysis techniques Jackson system development. Automated techniques. Design and implementation: fundamentals. Modular, architectural procedural design. Data flow oriented design. Object user interface design. Real time design. Oriented design. Design documentation. Programming languages and coding. Integrity and Reliability: Quality metrics. Measures of reliability and availability. Testing: Strategies and techniques. Maintainability. Configuration management and version control. Automation: Computer Aided software Engineering (CASE) tools. EE-5254: CONDITION MONITORING AND ENERGY CONSERVATION Condition Monitoring: Case for monitoring. Types of failures in service. Elements of monitoring schemes. Electrical, chimerical vibration and temperature monitoring techniques. Application of condition monitoring. Case studies. Identification of failures or faults. Electromechanical fault protection. Computer aided instrumentation and testing: Parameter identification, sensors and transducers for condition monitoring, data acquisition and processing, spectral analysis. Power Quality monitoring and its effect on electrical equipment. Energy conservation schemes: Design issues. Optimal utilization of materials. Reduction in core losses. Stator winding, air gap slot opening. Flux density, number of stator/rotor slots. Other constructional aspects. Energy efficient motors: Electric power saving and estimation of life cycle cost. Efficiency determination, International standards, experimental methods, segregated losses. Equivalent circuit calculation. Power factor improvement. Factors affecting efficiency.
EE-5255 ENERGY SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT Energy systems management perspective: Deterministic and stochastic systems representation, systems acceptability index and its significance. Concept of energy management: Classical and systems approach. Energy availability studies: Technology, selection evaluation patterns of energy consumption, supply and demand projections. Analysis and simulation: Energy models, energy efficiency, and energy economics and risk evaluation. Selection criteria for alternative solutions. Energy management strategy and policy formulation: Elements, symbiotic relation between information energy models and decision-making. Energy audit and instrumentation. Energy saving using power electronic circuits and drives case studies: lighting system, air conditioning, refrigeration, chemical, steel industries, and flow control. Power factor correction. EE-5256: TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS Field of transportation engineering and its components: Transportation technology, transportation systems, transportation network, and economic and environmental role in transportation planning. Vehicle Flow: Time space diagram, flow and control of vehicles, capacity and level of service. Continuous-Flow System: General characteristics, belt conveyers, pipeline. Transport Costs: Cost estimation, network and cost models, current costs in terms of time facility. Trip Generation Traffic zone, inventory of existing transportation facility. Methods of predicting multiple linear regressions, category analysis. Trip Distribution: Trip distribution by growth factor, uniform factor, average factor, gravity model, electro static field and opportunities models. Maximum Entropy Models: Measures, principles and its use in transportation systems. Semantics and ranking. EE-5257: COMPUTER NETWORKS Data communication: Transmission media, encoding, multiplexing. Local Area Networks: Technology and systems. Wireless LAN Bridges. Wide Area Networks: Circuit switching and pocket switching. Communication Architecture and Process: Internetworking, transport protocols, network security. Distributed applications. Elements of intranet, extranet and Internet. SESSIONAL ITEMS: EE-5471: CAD AND ANALYSIS OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES Recent advancements in conducting, magnetic and insulating materials. Problem in the design of large electrical machines, Cooling, noise and vibration problems. Integrated approach to design of AC and DC armature windings, Harmonic analysis and their control. Review of design processes, design methodology, design strategy, pre-requisite for design. Selection of design variables, Mathematical modeling for design analysis. Flow Chart and programming for design and analysis. Design optimization, Strategy and variable selection. Objective function, constraints equation. Techniques. Use of CAD, optimization and electromagnetic field software packages for design and analysis of electrical machines. EE-5476: SIMULATION OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS Dynamic modeling of power semiconductor devices. Use of CAD packages. Simulation and performance evaluation of converter circuits. Study of converter controlled systems using simulation packages.
Você também pode gostar
- Aim & ObjectivesDocumento6 páginasAim & ObjectivesSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Brushless DC Motors in Environmental ConservationDocumento6 páginasRole of Brushless DC Motors in Environmental ConservationSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Gesture Automation of Electrical AppliancesDocumento3 páginasHand Gesture Automation of Electrical AppliancesSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Distribution MC Lab SEM III 2012Documento37 páginasDistribution MC Lab SEM III 2012Saurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- World Eyes Student PresentationDocumento12 páginasWorld Eyes Student PresentationSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Distribution MC Lab SEM III 2012Documento37 páginasDistribution MC Lab SEM III 2012Saurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Resonant Converter ProjectDocumento14 páginasResonant Converter ProjectSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cycloconverter Circuits and Waveforms ExplainedDocumento10 páginasCycloconverter Circuits and Waveforms ExplainedSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Laboratory Manual - IIDocumento65 páginasMachine Laboratory Manual - IISaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Torque Calculation of Hysteresis Motor Using Fem With - 2Documento26 páginasTorque Calculation of Hysteresis Motor Using Fem With - 2Saurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 16 (1) - MR K Sivaram - CII - Godrej GBCDocumento7 páginas16 (1) - MR K Sivaram - CII - Godrej GBCraosp66Ainda não há avaliações
- Closed Loop Speed Control of DC Separately Excited MotorDocumento1 páginaClosed Loop Speed Control of DC Separately Excited MotorSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Core-Less MotorDocumento21 páginasCore-Less MotorSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
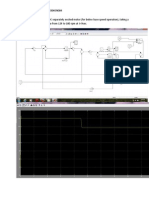
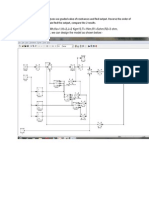
- Taking V 220v, La 10 MH, Ke 1, KT 2, J 2 KGM 2, TL 1Nm, R1 5ohm, R2 3 Ohm, R3 20hm, Ra 4ohm, B 0.4, We Can Design The Model As Shown BelowDocumento5 páginasTaking V 220v, La 10 MH, Ke 1, KT 2, J 2 KGM 2, TL 1Nm, R1 5ohm, R2 3 Ohm, R3 20hm, Ra 4ohm, B 0.4, We Can Design The Model As Shown BelowSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Linear Motors PDFDocumento19 páginasLinear Motors PDFPiyush GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- AC Linear Induction MotorDocumento16 páginasAC Linear Induction MotorSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Extra High Voltage AcDocumento535 páginasExtra High Voltage AcRachid HamianiAinda não há avaliações
- Matlab AssignmentDocumento2 páginasMatlab AssignmentSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- James Prescott JouleDocumento1 páginaJames Prescott JouleSaurabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Ebs CohostDocumento91 páginasEbs CohostAndres FelipeAinda não há avaliações
- SRS Immigration PDFDocumento8 páginasSRS Immigration PDFAnzal AshrafAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Maintenance & Reliability Module SpecificationDocumento5 páginasPlant Maintenance & Reliability Module SpecificationHopeson Kang'omaAinda não há avaliações
- FMP Project Management v3.1Documento201 páginasFMP Project Management v3.1Repseed Consult100% (1)
- DYSSOLDocumento7 páginasDYSSOLJeffrey TatendaAinda não há avaliações
- SRS LML SoftwareDocumento8 páginasSRS LML SoftwareAkul Shivam0% (1)
- Proses Keperawatan KeluargaDocumento20 páginasProses Keperawatan KeluargamichaelAinda não há avaliações
- MBSE Primer - 2nd EditionDocumento122 páginasMBSE Primer - 2nd EditionzavabossAinda não há avaliações
- Life Cycle Evaluation and Condition Assessment of StructuresDocumento52 páginasLife Cycle Evaluation and Condition Assessment of StructuresRithesh PkAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus EEE4018 Advanced Control TheoryDocumento2 páginasSyllabus EEE4018 Advanced Control TheoryKshitiz SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2 Human FactorsDocumento131 páginasLecture 2 Human Factorsdonald gandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Risk assessment and managementDocumento15 páginasRisk assessment and managementKishor Kolhe50% (2)
- International Standard Classification of Occupations GuideDocumento238 páginasInternational Standard Classification of Occupations Guidev0idlessAinda não há avaliações
- The Impact of Organizational Learning On Work PerformanceDocumento6 páginasThe Impact of Organizational Learning On Work PerformanceShahbaz khanAinda não há avaliações
- Complexity and Management Book PDFDocumento29 páginasComplexity and Management Book PDFGustavo YépezAinda não há avaliações
- Systemic Risk - A Practitioner's Guide To Measurement, Management and Analysis (2017)Documento344 páginasSystemic Risk - A Practitioner's Guide To Measurement, Management and Analysis (2017)Achraf Ben DhifallahAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 8 Responsibility AccountingDocumento51 páginasChap 8 Responsibility AccountingXel Joe BahianAinda não há avaliações
- Interview Transcript - David DanksDocumento11 páginasInterview Transcript - David DanksJoon JangAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Learning: Key Understandings inDocumento37 páginasMathematics Learning: Key Understandings inMkhululiAinda não há avaliações
- Humane AssessmentDocumento19 páginasHumane AssessmentTudor GirbaAinda não há avaliações
- Antigua and BarbudaDocumento68 páginasAntigua and BarbudaRodrigoLermesAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ManagementDocumento16 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Management9827430198100% (5)
- Model Design Process AnaplanDocumento6 páginasModel Design Process AnaplanDavid SavarinAinda não há avaliações
- New Ideas in Psychology: Raymond M. BergnerDocumento7 páginasNew Ideas in Psychology: Raymond M. BergnerAnggiDyahPratiwiAinda não há avaliações
- Design For Human and Planetary Health PDFDocumento10 páginasDesign For Human and Planetary Health PDFIsabella MunizAinda não há avaliações
- The Nature of The Laws of NatureDocumento10 páginasThe Nature of The Laws of NatureMatías AmayaAinda não há avaliações
- Reliance 380PG Pharmaceutical Grade Washer Technical DataDocumento7 páginasReliance 380PG Pharmaceutical Grade Washer Technical DataNirbhayAinda não há avaliações
- Outline Capstone BsitDocumento2 páginasOutline Capstone BsitJet S. SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC) - An Effective Tool For Better ManagementDocumento10 páginasActivity-Based Costing (ABC) - An Effective Tool For Better ManagementFachrul NawawiAinda não há avaliações
- H-Holger Rogner ICTP June2017 Energy System Modelling PDFDocumento38 páginasH-Holger Rogner ICTP June2017 Energy System Modelling PDFWonde BogAinda não há avaliações