Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Give Various Systems Where The Avionics Used in Aircrafts
Enviado por
Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Give Various Systems Where The Avionics Used in Aircrafts
Enviado por
Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Survivability(military) Availability Susceptibility vulnerability Life cycle cost(military) or cost of ownership(civil) Technical risk Weight & power
7. Give various systems where the avionics used in aircrafts. Aircraft intercoms Wide Area Augmentation System Terrain awareness and warning system Ground proximity warning system Aircraft collision avoidance systems Display systems Traffic Collision Avoidance System
8. Explain the steps involved in design of avionics system. The three stages are: i. Conceptual design - What will it do? ii. Preliminary design - How much will it weigh? iii. Detailed design - How many parts will it have?
9. What are digital computers? A device that processes numerical information; more generally / any device that manipulates symbolic information according to specified computational procedures is called as digital computers. The term digital computeror simply, computerembraces calculators, computer workstations, control computers (controllers) for applications such as domestic appliances and industrial processes. 10. What is a volatile memory and give examples? Volatile memory, also known as volatile storage, is computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored information, unlike non-volatile memory which does not require a maintained power supply. It has been less popularly known as temporary memory. Most forms of modern random access memory (RAM) are volatile storage 11. What is aliasing? In computing, aliasing describes a situation in which a data location in memory can be accessed through different symbolic names in the program. Thus, modifying the data through one name implicitly modifies the values associated to all aliased names, which may not be expected by the programmer. As a result, aliasing makes it particularly difficult to understand, analyze and optimize
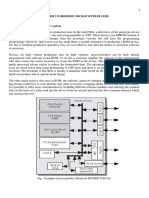
programs. Aliasing analyses intend to make and compute useful information for understanding aliasing in programs. 12. Differentiate between volatile and non volatile memories. Volatile memory: The data is lost on reboot, you will lost all of your data when your electricity go out.. This is the ram memory. Random-access-memory. Non-volatile memory: The data is saved to a hard drive or flash drive, or it could be a hard coded chip. This is rom memory. Read-only-memory. All data that stored in this type of memory will retain when you shutdown your computer. 13. What is microprocessor? A complex microcircuit (integrated circuit) or set of such chips that carries out the functions of the processor of an information technology system; that is, it contains a control unit (and clock), an arithmetic and logic unit, and the necessary registers and links to main store and to peripherals. 14. Explain the registers of microprocessor? In computer architecture, a processor register (or general purpose register) is a small amount of storage available on the CPU whose contents can be accessed more quickly than storage available elsewhere. Typically, this specialized storage is not considered part of the normal memory range for the machine. Processor registers are at the top of the memory hierarchy, and provide the fastest way for a CPU to access data.
Você também pode gostar
- IVth (7th Sem) Year Question bank-B.E AeronauticalDocumento362 páginasIVth (7th Sem) Year Question bank-B.E AeronauticalRaamaChandiran100% (1)
- Avionics 2marks For All UnitsDocumento15 páginasAvionics 2marks For All UnitsJ.Gowri ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- RTS Module 2 Part A NotesDocumento11 páginasRTS Module 2 Part A NotesVignesh H VAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems Components Part II: LessonDocumento14 páginasEmbedded Systems Components Part II: LessonSayan Kumar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Enhanced Discovering Computers 2017 Essentials 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento33 páginasEnhanced Discovering Computers 2017 Essentials 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFanselmthangxu5eo0100% (12)
- Unit 1 NewDocumento59 páginasUnit 1 NewHari PrasathAinda não há avaliações
- Iv Year - A & B: Embedded SystemsDocumento20 páginasIv Year - A & B: Embedded SystemsNithindev GuttikondaAinda não há avaliações
- Architecture Summary - 053057Documento7 páginasArchitecture Summary - 053057Muntaka AbdulkadirAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 (Module 6) 1. Describe The Hardware Referred To by The Terms, System Unit and ChassisDocumento21 páginasChapter 2 (Module 6) 1. Describe The Hardware Referred To by The Terms, System Unit and ChassisniklynAinda não há avaliações
- Enhanced Discovering Computers 2017 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento33 páginasEnhanced Discovering Computers 2017 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFanselmthangxu5eo0100% (11)
- Unit 1 EsDocumento29 páginasUnit 1 EsSree MathyAinda não há avaliações
- COE381 Microprocessors Marking Scheame: Q1 (A) - Write Explanatory Note On General-Purpose ComputersDocumento6 páginasCOE381 Microprocessors Marking Scheame: Q1 (A) - Write Explanatory Note On General-Purpose ComputersEric Leo AsiamahAinda não há avaliações
- Comfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsDocumento199 páginasComfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsRhdheh BdhehenAinda não há avaliações
- EMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDEDocumento191 páginasEMBEDDED SYSTEM DESIGN GUIDEanon_468121753Ainda não há avaliações
- Microcontroller Wikipedia Article SummaryDocumento8 páginasMicrocontroller Wikipedia Article Summarychella_duraiAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento23 páginasAssignment 1TAMMINEDI GANESH PRASAD 222010311030Ainda não há avaliações
- EMBEDDED SYSTEM ASSIGNMENT ON PROCESSORS AND COMMUNICATIONDocumento30 páginasEMBEDDED SYSTEM ASSIGNMENT ON PROCESSORS AND COMMUNICATIONajas777BAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Embedded MicrocontrollersDocumento5 páginasChapter 2 Embedded MicrocontrollersyishakAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Organization & Assembly LanguageFDocumento208 páginasComputer Organization & Assembly LanguageFRoberto Jr VelascoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Computer Systems: StructureDocumento13 páginasUnit 2 Computer Systems: StructureCamilo AmarcyAinda não há avaliações
- AssignmentDocumento6 páginasAssignmentapi-257167729Ainda não há avaliações
- OS - Unit 1Documento67 páginasOS - Unit 1Pawan NaniAinda não há avaliações
- A Best Intro 2 Computers PDFDocumento82 páginasA Best Intro 2 Computers PDFRedemptionAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded Systems 2marksDocumento28 páginasEmbedded Systems 2marksSushanth RajkumarAinda não há avaliações
- Esd 1Documento40 páginasEsd 1154Soyal LonareAinda não há avaliações
- CSC303 2023 - 2024 Lecture-1-IntroductionDocumento53 páginasCSC303 2023 - 2024 Lecture-1-IntroductionYuh FabsAinda não há avaliações
- Microprocessor Architecture Q&A 2018 - It Exams-Quick UnderstandingDocumento17 páginasMicroprocessor Architecture Q&A 2018 - It Exams-Quick UnderstandingAkhs SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is An Embedded System?: Laser PrinterDocumento9 páginasWhat Is An Embedded System?: Laser PrinterKajalAinda não há avaliações
- Embedded System PresentationDocumento17 páginasEmbedded System Presentationniravsoni001Ainda não há avaliações
- Main Articles: Central Processing Unit and MicroprocessorDocumento5 páginasMain Articles: Central Processing Unit and MicroprocessorSanctaTiffanyAinda não há avaliações
- CoDocumento80 páginasCogdayanand4uAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Ubiquitous System, Explain How Ubiquitous System Can Be Created?Documento8 páginasWhat Is Ubiquitous System, Explain How Ubiquitous System Can Be Created?Rozan FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Gip UNIT IDocumento39 páginasGip UNIT IjesudosssAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 8 - Information and Communication TechnologyDocumento42 páginasUnit 8 - Information and Communication TechnologyAbhishek Dali100% (1)
- Week 2 Internal Components of A Computer Fundamental Characteristics of A ProcessorDocumento4 páginasWeek 2 Internal Components of A Computer Fundamental Characteristics of A ProcessorSunil NagumallaAinda não há avaliações
- It 2354 QBDocumento28 páginasIt 2354 QBlogu87Ainda não há avaliações
- What Are Embedded Systems?Documento27 páginasWhat Are Embedded Systems?nicar190Ainda não há avaliações
- CO&A 18EC35 Module-1 Notes Dileep Kumar K SDocumento32 páginasCO&A 18EC35 Module-1 Notes Dileep Kumar K SThanushree RMAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT I-Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocumento28 páginasUNIT I-Introduction To Embedded SystemsKALAIVANIAinda não há avaliações
- Slide 1 (Introduction)Documento33 páginasSlide 1 (Introduction)Amit VishwakarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Prepared by Dasun Nilanjana ForDocumento24 páginasPrepared by Dasun Nilanjana ForKeshila JayasooriyaAinda não há avaliações
- Parisutham Institute of Technology & Science, Thanjavur - Embedded System Memory ManagementDocumento6 páginasParisutham Institute of Technology & Science, Thanjavur - Embedded System Memory ManagementgallantprakashAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento10 páginasChapter 3Xyza Faye RegaladoAinda não há avaliações
- Voice Controlled Wheel ChairDocumento48 páginasVoice Controlled Wheel ChairAjith manjuAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 2Documento20 páginasMod 2PraneethAinda não há avaliações
- UpdatedDocumento65 páginasUpdatedcsemaths11Ainda não há avaliações
- 2... Vijay-Advanced Security Systems in Jewellery Shops and Banks PDFDocumento97 páginas2... Vijay-Advanced Security Systems in Jewellery Shops and Banks PDFShanker PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Radian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessDocumento20 páginasRadian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessjosekinAinda não há avaliações
- COMPUTER CollegeDocumento26 páginasCOMPUTER CollegeHyper RiderAinda não há avaliações
- COA Module 1 BEC306CDocumento24 páginasCOA Module 1 BEC306Csachinksr007Ainda não há avaliações
- Hardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsDocumento33 páginasHardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsUchenna OgunkaAinda não há avaliações
- Operating SystemDocumento15 páginasOperating SystemBonventure KipkiruiAinda não há avaliações
- Computer FundementalsDocumento5 páginasComputer FundementalsHARIKIRAN PRAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocumento21 páginasComputer Organization and ArchitectureJoan VincentAinda não há avaliações
- Computer SciencesDocumento29 páginasComputer SciencesX x A7md x XAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocumento53 páginasUnit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerAKSHANSH MATHUR100% (1)
- 123 - EE8691, EE6602 Embedded Systems - NotesDocumento78 páginas123 - EE8691, EE6602 Embedded Systems - NotesNavin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Fundamentals Lesson: Basics of Computer SystemsDocumento257 páginasComputer Fundamentals Lesson: Basics of Computer SystemsRajendra RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- Boult AudioAASDADocumento2 páginasBoult AudioAASDAShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- AokaisjiDocumento1 páginaAokaisjiShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- New Text DocumentDocumento1 páginaNew Text DocumentShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Install High Efficiency Burners for 19,146 Therms/yr SavingsDocumento2 páginasInstall High Efficiency Burners for 19,146 Therms/yr SavingsShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- 24318Documento3 páginas24318Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Comments On Draft of Design EquationDocumento1 páginaComments On Draft of Design EquationShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Team Eco: Draft of Computer CodeDocumento1 páginaTeam Eco: Draft of Computer CodeShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- AdasygdyaDocumento1 páginaAdasygdyaShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Distances With An Ultrasonic Sensor Using ArduinoDocumento1 páginaMeasuring Distances With An Ultrasonic Sensor Using ArduinoShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Comments On Draft of Design EquationDocumento1 páginaComments On Draft of Design EquationShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Pick and Place: ME 560 Section #2Documento2 páginasPick and Place: ME 560 Section #2Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- ME 540: Advanced Mechanical VibrationsDocumento8 páginasME 540: Advanced Mechanical VibrationsShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- JNTU HYD B.Tech First Year SyllabusDocumento28 páginasJNTU HYD B.Tech First Year SyllabusrachamaduguAinda não há avaliações
- EconDocumento2 páginasEconShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Team Eco: Draft of Computer CodeDocumento1 páginaTeam Eco: Draft of Computer CodeShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- 1396275189-1. Robotics - Ijrrd - Kinematic Modelling and Analysis of - Vivek Deshpande - OpaidDocumento9 páginas1396275189-1. Robotics - Ijrrd - Kinematic Modelling and Analysis of - Vivek Deshpande - OpaidShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- A Complete Analytical Solution To The Inverse Kinematics of The Pioneer 2 Robotic ArmDocumento7 páginasA Complete Analytical Solution To The Inverse Kinematics of The Pioneer 2 Robotic ArmWm HanifAinda não há avaliações
- Uu 8Documento19 páginasUu 8Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Good Health Declaration Application For Extension Travel Policy PDFDocumento1 páginaGood Health Declaration Application For Extension Travel Policy PDFRohan RepaleAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Degrees of FreedomDocumento44 páginasMultiple Degrees of FreedomShafiq Ahmed Shahbaz100% (1)
- ME 573 Numerical Methods Assignment 1Documento1 páginaME 573 Numerical Methods Assignment 1Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- 0001 - CE541 Formula SheetDocumento12 páginas0001 - CE541 Formula SheetShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- My 2Documento1 páginaMy 2Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Pqe Vibration 09 Solution 1Documento15 páginasPqe Vibration 09 Solution 1Shafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Paper-Capillary Gas Chromatographic Determination of Isoniazid and Hydrazine in Pharmaceutical Preparations and BloodDocumento21 páginasPaper-Capillary Gas Chromatographic Determination of Isoniazid and Hydrazine in Pharmaceutical Preparations and BloodShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Multiple Degrees of FreedomDocumento44 páginasMultiple Degrees of FreedomShafiq Ahmed Shahbaz100% (1)
- 03 Lagranges EquationsDocumento7 páginas03 Lagranges EquationsOmar LSAinda não há avaliações
- HW3 HintsDocumento2 páginasHW3 HintsShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- HW3 HintsDocumento2 páginasHW3 HintsShafiq Ahmed ShahbazAinda não há avaliações
- Bugreport 2026 QP1A.190711.020 2021 07 30 10 39 33 Dumpstate - Log 18855Documento34 páginasBugreport 2026 QP1A.190711.020 2021 07 30 10 39 33 Dumpstate - Log 18855Elitaa PutriiAinda não há avaliações
- 308272005-Turbocompresores - TT2000 - ПереводDocumento23 páginas308272005-Turbocompresores - TT2000 - Переводrealgood1Ainda não há avaliações
- Turn An Old Cell Phone Into A SmartwatchDocumento33 páginasTurn An Old Cell Phone Into A SmartwatchBobbyAinda não há avaliações
- BioStation InstallationGuide V1 11 EnglishDocumento28 páginasBioStation InstallationGuide V1 11 EnglishCM BerAinda não há avaliações
- Biomedical Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento450 páginasBiomedical Digital Signal ProcessingEpitácio FariasAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Implementation of Static RAM Cell: Circuit Diagram of SRAMDocumento4 páginasDesign and Implementation of Static RAM Cell: Circuit Diagram of SRAMkomaladitya challaAinda não há avaliações
- ITE 6220 LessonsDocumento6 páginasITE 6220 LessonsRochie RoasaAinda não há avaliações
- KNX 100G - Setup Guide: E G H C D FDocumento4 páginasKNX 100G - Setup Guide: E G H C D FSkrapAinda não há avaliações
- AVTech Manual English CPD576W AVC776 V1.0Documento26 páginasAVTech Manual English CPD576W AVC776 V1.0han2solo8Ainda não há avaliações
- Siliconchip Softwave ListDocumento246 páginasSiliconchip Softwave ListLong Nguyen KimAinda não há avaliações
- Samsung Confidential: Chip Set: CpuDocumento60 páginasSamsung Confidential: Chip Set: CpuEdgardo CrespoAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Hardware TrainerDocumento10 páginasComputer Hardware TrainerBusiness BusinessAinda não há avaliações
- Prosys II Software: Iris InstrumentsDocumento2 páginasProsys II Software: Iris InstrumentsjupiterAinda não há avaliações
- Beamng DxdiagDocumento31 páginasBeamng DxdiagBogdan LunguAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Computers: A Guide to Hardware and Software ComponentsDocumento27 páginasIntroduction to Computers: A Guide to Hardware and Software ComponentsSaad MemonAinda não há avaliações
- E-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureDocumento29 páginasE-Commerce Client Server ArchitectureshankargowriAinda não há avaliações
- Spi Eeprom PDFDocumento44 páginasSpi Eeprom PDFEma HarmaAinda não há avaliações
- Access Wireless Networks with Your Mobile USB StickDocumento2 páginasAccess Wireless Networks with Your Mobile USB StickAnonymous aVA40W4Ainda não há avaliações
- Doodle Bot Instruction ManualDocumento12 páginasDoodle Bot Instruction ManualPepe DoserAinda não há avaliações
- Lastexception 63822451712Documento6 páginasLastexception 63822451712Sol PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of A Programmer Debugger in Software DevelopmentDocumento13 páginasImportance of A Programmer Debugger in Software DevelopmentjackAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On Super ComputerDocumento14 páginasPresentation On Super ComputerFaysal Islam50% (4)
- PIC-EK User ManualDocumento91 páginasPIC-EK User Manualdjdkd,fAinda não há avaliações
- licM08V Eng PDFDocumento2 páginaslicM08V Eng PDFFeeze WdsAinda não há avaliações
- Relocating Code and Data Using The KDS GCC Linker File For KinetisDocumento18 páginasRelocating Code and Data Using The KDS GCC Linker File For KinetisAnonymous 1Wb6JCkAinda não há avaliações
- 1991 16 Bit V-Series Microprocessor Data BookDocumento1.107 páginas1991 16 Bit V-Series Microprocessor Data BookJean GrégoireAinda não há avaliações
- DualCam Update Procedure - V3Documento2 páginasDualCam Update Procedure - V3Benjamim LangaAinda não há avaliações
- Amlogic USB Burning Tool V2 Guide V0.4Documento11 páginasAmlogic USB Burning Tool V2 Guide V0.4Miller CostaAinda não há avaliações
- Why MastercamDocumento30 páginasWhy MastercamMarius CucuietAinda não há avaliações
- FL1100Documento67 páginasFL1100test oeosAinda não há avaliações