Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Anatomy of The Skeletal System
Enviado por
Pauline JoyceTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy of The Skeletal System
Enviado por
Pauline JoyceDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Anatomy of the Skeletal System
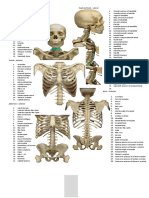
Bone Scapula
Clavicle Humerus
Radius Ulna
Carpals(8) Pelvic (2 hip bones)
Femur
Tibia
Fibula Tarsals (7)
Description Depression that articulates with humerus Long, posterior process for muscle attachment Articulates with clavicle Articulates with scapula Articulates with manubrium of sternum Round process that articulates with scapula Round process for the deltoid muscle Posterior, oval depression for the olecranon process of the ulna Round process superior to radius Concave surface that articulates with ulna Articulates with the ulna Fits into olecranon fossa of humerus Half-moon depression that articulates with the trochlea of ulna Proximal Row Distal Row Flared, upper portion Upper edge of ilium Posterior continuation of iliac rest Lower, posterior portion Anterior, medial portion Joint between the 2 pubic bones Deep depression that articulates with femur Round process that articulates with hip bone Constricted portion distal to head Large lateral process for muscle attachment Medial process for muscle attachment Rounded processes that articulate with tibia Articulates with the femur Round process for the patellar ligament Vertical ridge Distal process; medial ankle bone Articulates with tibia Distal process; lateral ankle bone Heel Bone Articulates with calcaneus and tibia
1. Axial skull, vertebrae, rib cage Skull o Eight cranial bones form through the braincase which also protects the eyes and ears; 14 facial bones make up the face; immovable joints between these bones are called sutures. o Paranasal sinuses are air cavities in the maxillae, frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones; they lighten the skull and provide resonance for voice o Three auditory bones in each middle ear cavity transmit vibrations for the hearing process. Vertabral Column o Individual column are called vertebrae: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic; 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 4 to 5 coccygeal. Supports trunk and head, encloses and protects the spinal cord in the vertebral canal. Discs of fibrous cartilage absorb shock between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae, also permit slight movement. Four natural curves center head over body for walking upright Rib cage o Sternum and 12 pair of ribs; protects thoracic and upper abdominal organs from mechanical injury and is expanded to contribute to inhalation. Sternum consists of manubrium, body and xiphoid process. 2. Appendicular bone of the arms and legs and the shoulder and pelvic girdles Shoulder and arm o Scapula shoulder muscles are attached; glenoid fossa articulates with humerus o Clavicle braces the scapula o Humerus upper arm; articulates with the scapula and the ulna o Radium and ulna forearm articulate with one another and with carpals o Carpals eight wrists; metacarpals five hand; phalanges 14 - fingers Hip and leg o Pelvic bone two hip bones; ilium ischium, pubis, acetabulum articulates with femur o Femur thigh; articulates with pelvic bone and tibia o Patella kneecap; in tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle o Tibia and fibula lower leg; tibia bears weight; fibula does not bear weight, but does anchor muscles and stabilizes ankle. o Tarsals seven ankle; calcaneus is heel bone o Metatarsals five foot; phalanges 14 toes
Physiology of the Skeletal system Disease Osteoarthritis Description Natural consequence of getting older. In joints that have borne weight for many years, the articular cartilage is gradually worn away. The large, weight-bearing joints are most often subjected to this form of arthritis. Signs and symptoms Pain, stiffness and swelling of the joints. Deformed joints Redu ced range of motion Muscle weakness Treatment Acetomenophen Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs Narcotics Therapy Surgical -cortisone shots -joint replacement -realigning bones -lubriction injections -physical and occupational therapy -nutrition and diet therapy -pain relievers
Rheumatoid arthritis
Scoliosis
Kyphosis Pagets disease
Autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system mistakenly directs its destructive capability against part of the body. Exactly what triggers this abnormal response by the immune is not known with certainty, but certain bacterial and viral infections have been suggested as possibilities. Abnormal lateral curvature, which may be congenital, the result of having one leg longer than the other, or the result of chronic poor posture during childhood while the vertebrae are still growing. Usually the thoracic vertebrae are affected, which displaces the rib cage to one side. In severe cases, the abdominal organs may be compressed, and the expansion of the rib cage during inhalation may be impaired An exaggerated thoracic curve; sometimes referred to as hunchback known as a bone remodeling disorder. Bone may seem like a very inactive tissue, but bone is constantly
-Swelling, stiffness of thejoints -redness and warmth in the joints -pain in the joints
-abnormal curve of the spine
-surgery -wearing a brace to correct the growth of the spine
-curved spine
-plaster casts and braces if it is mild kyphosis
-Osteoporosis drugs (bisphosphonates) -surgery
Pain Enlarged bones Broken bones
Osteoporosis
Herniated disc (Slipped disc)
undergoing 'turnover' or replacement. New bone is formed, and old bone is absorbed. This process is known as bone remodeling. In most people this remodeling process occurs without problems. However, the process can go awry and create abnormalities of the bone. In Paget's disease, the bone remodeling process is disregulated. Characterized by excessive loss of calcium from bones without sufficient replacement. Contributing environmental factors include smoking, insufficient dietary intake of calcium, inactivity, and lack of the sex hormones. Factors such as bed rest or inability to get even minimal exercise will make calcium loos even more rapid. Occurs when then nucleus pulposus breaks through the anulus and enters the vertebral canal. This condition can lead to compression of the roots of the sciatic nerve (sciatica). Most frequently occurs in the lumbar region.
Damaged cartilage in joints
-back pain -loss of height and stooped posture -curved upper back -broken bones(fracture) -compression fractures in the spine
-medication -Actonel -Binosto
-Boniva -Fosamax
-back pain -sciatica -leg pain
-keeping active -physiotherapy -osteopathy and chiropractic -medication -analgesics -corticosteriods -muscle relaxants -codeine -non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs -take in foods or vitamins containing vitamin D -exposure to sunlight -surgery -injections of
Rickets
disease characterized by abnormal bone formation and skeletal deformities
-soft bones -deforemed bones
Osteomyletis
inflammation of bone or bone marrow, usually caused by infection by such microorganisms as
-fever -acute pain and swelling above the site of the
antibiotics such as nafcillin
Staphylococcus aureus, various streptococci, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and a host of others, as well as several fungi
Inflammation -The inflammation
begins in the marrow cavity and causes softening and erosion of the long bones, often with the formation of puscontaining abscesses, and soon spreads over the entire bone, with consequent death of the hard portions of the bone.
-local pain -tenderness -swelling with some degree of deformity -anitseptics and antibiotics if there is infection -strectching or traction if broken bones are adjacent to each to each other -if bones cannot be aligned then it will operated with nails, nuts, wires or metal plates
Fracture
-break or crack in a bone
or in ossified cartilage.
Você também pode gostar
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento88 páginasThe Skeletal SystemjpotiAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocumento46 páginasReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal SystemDocumento5 páginasSkeletal SystemWynne Michael David GogoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 The Skeletal SystemDocumento22 páginasChapter 5 The Skeletal SystemJUSTINE MAE MANTILLAAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal SystemDocumento19 páginasSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhAinda não há avaliações
- 30.1 Organization of The Human BodyDocumento30 páginas30.1 Organization of The Human Bodymoniaguayo98Ainda não há avaliações
- Muscular System Web QuestDocumento5 páginasMuscular System Web Questaidibwahab0% (1)
- The Skeletal System: Classification and Structure of BonesDocumento6 páginasThe Skeletal System: Classification and Structure of BonesAllie Rei JuntelaAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal System 1Documento30 páginasSkeletal System 1api-298936084100% (1)
- ANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1Documento4 páginasANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1jbradeeAinda não há avaliações
- Body CavitiesDocumento10 páginasBody CavitiesGoutam ChandraAinda não há avaliações
- Reproductive SystemDocumento42 páginasReproductive SystemAileen Grace Delima100% (1)
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento27 páginasThe Musculoskeletal SystemEduardoAlejoZamoraJr.Ainda não há avaliações
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuDocumento48 páginasHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuScar Shadow100% (1)
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocumento4 páginasPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoAinda não há avaliações
- A&P1 Final Exam Study GuideDocumento7 páginasA&P1 Final Exam Study GuideRhett ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- The Skeletal System: Functions and AnatomyDocumento28 páginasThe Skeletal System: Functions and AnatomyDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Session 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal PlanDocumento69 páginasSession 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal Planataraxialli100% (1)
- Overview of Anatomical PositionsDocumento8 páginasOverview of Anatomical Positionsmarcus colgrove0% (1)
- Introduction of AnatomyDocumento18 páginasIntroduction of Anatomyjames nginyangiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure & Function Unit 1: Cell: The Unit of LifeDocumento41 páginasChapter 3: Cell Structure & Function Unit 1: Cell: The Unit of LifeMark Harwell Rifo100% (1)
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Documento10 páginasSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041Ainda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System Anatomy in 40 CharactersDocumento19 páginasRespiratory System Anatomy in 40 CharactersKBDAinda não há avaliações
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento62 páginasMusculoskeletal SystemAnjanette Lopez PorlucasAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento43 páginasAnatomy of Urinary SystemIrfan Ali JunejoAinda não há avaliações
- AnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemDocumento7 páginasAnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemLM KishimotoAinda não há avaliações
- The ABC's in Pediatric Assessment and Care: Cymbeline Joan L. Pooten, RN NUM - Pediatric ICUDocumento39 páginasThe ABC's in Pediatric Assessment and Care: Cymbeline Joan L. Pooten, RN NUM - Pediatric ICUggrrk7Ainda não há avaliações
- Bone Formation & GrowthDocumento3 páginasBone Formation & GrowtherinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Anatomy SCDocumento92 páginas1 Anatomy SCAmber Ian Bouie Divina-DayaoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 4 Blood VesselsDocumento14 páginasLesson 4 Blood VesselsCarolyn D MayugaAinda não há avaliações
- D.muscular System PDFDocumento8 páginasD.muscular System PDFJohn Lawrence YbanezAinda não há avaliações
- Skeletal SystemDocumento103 páginasSkeletal SystemiamarrhinneAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Digestive SystemDocumento6 páginasAnatomy Digestive Systempearl042008Ainda não há avaliações
- The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocumento12 páginasThe Lymphatic System and Body DefensesGuenevere DamasinAinda não há avaliações
- Muscular System Quiz Study GuideDocumento10 páginasMuscular System Quiz Study Guidejbradee100% (2)
- BSN Anatomy and Physiology - The Muscular SystemDocumento27 páginasBSN Anatomy and Physiology - The Muscular SystemMary Grace MapulaAinda não há avaliações
- HeartDocumento6 páginasHeartAhmed OmaarAinda não há avaliações
- Bone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFDocumento35 páginasBone Formation - Ossification 2 PDFalan100% (1)
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Documento13 páginasLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizAinda não há avaliações
- Circle of WillisDocumento3 páginasCircle of WillisRisah Mae SarinoAinda não há avaliações
- NCD Prevention & Control StrategiesDocumento80 páginasNCD Prevention & Control Strategiesbiniam yohannesAinda não há avaliações
- The Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDocumento130 páginasThe Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesTricia Mae CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDocumento24 páginasThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodAinda não há avaliações
- Organization of The BodyDocumento32 páginasOrganization of The BodyCharlotte ChanAinda não há avaliações
- Histology of BoneDocumento20 páginasHistology of Boneyudha anantha khaerul putraAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer - MTMS 2020Documento4 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer - MTMS 2020Myrielle Trisha SAYREAinda não há avaliações
- Muscular SystemDocumento24 páginasMuscular SystemMD100% (1)
- Introduction To General AnatomyDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To General AnatomyPia Abila100% (1)
- Human Nervous-SystemDocumento32 páginasHuman Nervous-SystemhwzeeeAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy LectureDocumento20 páginasAnatomy Lectureshiba ngujo100% (1)
- Skeletal Muscle ContractionDocumento68 páginasSkeletal Muscle ContractionDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Anatomical Positions and Terminology GuideDocumento127 páginasAnatomical Positions and Terminology GuideMaria JozilynAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomyDocumento28 páginasAn Introduction To The Human Body: - AnatomydishkuAinda não há avaliações
- Human Excretory System Removes WasteDocumento15 páginasHuman Excretory System Removes WasteJames AysonAinda não há avaliações
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocumento59 páginasAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocumento8 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAdor AbuanAinda não há avaliações
- System of The Human BodyDocumento31 páginasSystem of The Human BodyMari Thomas100% (1)
- Fetal DevelopmentDocumento15 páginasFetal DevelopmentOmar HammadAinda não há avaliações
- Support Systems in AnimalsDocumento17 páginasSupport Systems in AnimalsYong LingAinda não há avaliações
- Silent WorshipDocumento4 páginasSilent WorshipPauline JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- How a PC's Components Work TogetherDocumento2 páginasHow a PC's Components Work TogetherPauline JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- Begin AgainDocumento5 páginasBegin AgainPauline JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- An Elderly CarpenterDocumento8 páginasAn Elderly CarpenterPauline JoyceAinda não há avaliações
- Chest and Lungs - Supplementary Handout - Laboratory SessionDocumento7 páginasChest and Lungs - Supplementary Handout - Laboratory SessionPaul AculladorAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Atlas of Human Anatomy Vol IIDocumento253 páginasHand Atlas of Human Anatomy Vol IIizogggAinda não há avaliações
- SHEPPARD, Joseph. Drawing The Living Figure (1984)Documento147 páginasSHEPPARD, Joseph. Drawing The Living Figure (1984)arqevp100% (2)
- Anatomy MCQsDocumento26 páginasAnatomy MCQsMuhammadsiddique khanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Skeletal SystemDocumento4 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of the Skeletal SystemDANIEL LANCE NEVADOAinda não há avaliações
- (Mantak Chia) Chi Nei Tsang II PDFDocumento66 páginas(Mantak Chia) Chi Nei Tsang II PDFaxelmiko100% (1)
- Boney LandmarksDocumento39 páginasBoney LandmarksStefanie Kiss-PlucasAinda não há avaliações
- The Healing Art of Tenchi Seiki Te-AteDocumento29 páginasThe Healing Art of Tenchi Seiki Te-AteJames Deacon100% (7)
- Edan SE-2003 & SE-2012 Holter User ManualDocumento43 páginasEdan SE-2003 & SE-2012 Holter User Manualfpanci100% (2)
- Anatomy Introduction and TerminologyDocumento576 páginasAnatomy Introduction and TerminologyHABTEMARIAM ERTBANAinda não há avaliações
- Head and Neck - Anterior Head and Neck - LateralDocumento17 páginasHead and Neck - Anterior Head and Neck - LateralYma FeelAinda não há avaliações
- VISTA Plus ECG Holter Recorders User Manual EnglishDocumento65 páginasVISTA Plus ECG Holter Recorders User Manual Englishzemanelfandurgas50% (2)
- The Calm Mind - Various Techniques Incl TAT PDFDocumento56 páginasThe Calm Mind - Various Techniques Incl TAT PDFYuldash100% (1)
- Get Anatomy On Occupational StandardDocumento39 páginasGet Anatomy On Occupational StandardmisawAinda não há avaliações
- Iscan and Loth 1985 AgeDocumento11 páginasIscan and Loth 1985 AgejoseantoniogonzalezpAinda não há avaliações
- BooksDocumento388 páginasBooksMayank GoyalAinda não há avaliações
- Skeleton of The Cat: Prepared by John Mark Matulac BIO102 LabDocumento27 páginasSkeleton of The Cat: Prepared by John Mark Matulac BIO102 LabJoachimAinda não há avaliações
- Ln-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocumento2 páginasLn-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemAnnie GraceAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy Chapters 6&7Documento17 páginasAnatomy Chapters 6&7Tamara IdalyAinda não há avaliações
- Sas 3 AnaphyDocumento7 páginasSas 3 AnaphyClarrinne Geralence Galo RomoAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Anatomy of Respiratory System: External Respiration. The Exchange of Gases Between The Blood in The Capillaries ofDocumento35 páginasUnit 3 Anatomy of Respiratory System: External Respiration. The Exchange of Gases Between The Blood in The Capillaries ofAnne RonquilloAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing Thorax and LungsDocumento46 páginasAssessing Thorax and LungsmyfilesAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative Animal AnatomyDocumento324 páginasComparative Animal AnatomyMohammed Anuz80% (5)
- Heart Sounds, EKG Lead Placement & Memory TricksDocumento1 páginaHeart Sounds, EKG Lead Placement & Memory TricksJe KirsteneAinda não há avaliações
- Biology All Chapters F4Documento83 páginasBiology All Chapters F4Mohamed Abuukar AbdukadirAinda não há avaliações
- Bill Starr - Bench Press vs. Incline PressDocumento6 páginasBill Starr - Bench Press vs. Incline PressTomSusAinda não há avaliações
- OsteologiDocumento37 páginasOsteologiNasrul NasehatiAinda não há avaliações
- How To Examine A Patient - A Pocket Guide To Students of Medicine (3rd Ed) (Gnv64)Documento464 páginasHow To Examine A Patient - A Pocket Guide To Students of Medicine (3rd Ed) (Gnv64)Bogdan Lina100% (3)
- Clavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyDocumento24 páginasClavicle, Sternum & Applied AnatomyBishal Chauhan100% (1)
- PE CH 7 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento11 páginasPE CH 7 Anatomy and PhysiologyAditri GhoseAinda não há avaliações