Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Second Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2
Enviado por
yabaeveDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Second Sempre Finals PHC EXAM K2
Enviado por
yabaeveDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PERPETUAL HELP PARAMEDICAL SCHOOL
Happy Homes Subdivision Tagas, Tabaco City Ched Recognition No. H 0029 series 1994 e mail: phpcollege@yahoo.com
PRIMARY HEALTH CARE 2
FINAL EXAMINATION By: EDUARD E. GANDUL JR, RM, RN, EMT-B, MAN (c) Name: _________________________________ Year and Course: __________________ Date: ____________
INSTRUCTIONS: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. 1. This refers to group of people who share common characteristics, or developmental stage, common exposure to environmental factors thus has common health problems: A. Family B. Groups C. Sentinel D. Aggregate 2. In EPI immunization, the immunity is called: A. active acquired B. passive acquired C. active artificial D. natural passive D. recurrent convulsions D. pandemic
3. Which of the following are contraindicated for submitting the child for immunization? A. scar in the extremities B. recurrent convulsions C. fever 4. Diseases that occurs occasionally is referred to as: A. endemic B. sporadic C. epidemic
5. Living bodies that harbor, sustain and maintain the growth and multiplication of infectious agent: A. reservoir B. vehicle means to transport C. fomites inanimate objects of materials D. antibodies 6. Which type of infection control does an externally ill hospitalized patient with AIDS require? A. Respiratory isolation B. Blood and body fluids C. Contact isolation D. reverse isolation
7. A person who harbors the microorganism but does not manifest the signs and symptoms of the disease is called: A. Contact B. Infected C. Suspect D. Carrier 8. Which of the following term refers to the degree of pathogenicity of a microbe, or in other words the relative ability of a microbe to cause disease? A. Susceptibility B. Virulence C. Infection D. None of the above 9. Direct sputum smear microscopy (DSSM) is the primary diagnostic tool in tuberculosis case finding. Which of the following conditions does a DSSM is contraindicated? A. Fever B. Cough C. Hemoptysis D. Tonsillitis 10. The most hazardous period for development of clinical disease is how many months after infection with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis? A. 4-5 months B. 2-3 months C. 6-12 months D. 12-18 months 11. Treatment regimen for Category I TB patient on the continuation phase includes which Anti-TB drugs? A. Isoniazid and Rifampicin B. Pyrazinamide and Ethambutol C. Etambutol and Streptomycin D. Pyrazinamide, Etambutol, Isoniazid and Rifampicin 12. A client with TB who is taking anti-TB drugs who calls the nurse because of urine discoloration. According to the client his urine turned reddish-orange. The nurse told the client that the reddish-orange discoloration of urine is the side effect of which anti-TB drug? A. Isoniazid B. Rifampicin C. Pyrazinamide D. Ethambutol 13. Prevention of TB includes the following measures: A. BCG vaccination newborns B. Public education about TB and its mode of transmission, methods of control and early diagnosis. C. Availability and accessibility of medical, laboratory and x-ray facilities for examination. D. All of these The time interval between the first exposure to the appearance of the first signs and symptoms is called: A. Prodromal period B. Incubation period C. Stage of illness D. Convalescence
14.
15. To prevent whooping cough, which of the following vaccines should be given to infants? A. BCG B. DPT C. OPV D. IPV 16. When a disease can be easily transmitted from one person to another, such infection is: A.communicable B.Infectious C. CONTAGIOUS D.Virulent
17. It is an illness due to a specific agent transmitted by an agent from a reservoir to a susceptible host through different modes of transmission: A. Contagious disease B.Communicable disease C. Infectious disease D.Iatrogenic disease
18. A clinically manifest disease of a man or animal resulting from an infection: A. Contagious disease B. Communicable disease C. Infectious disease D. Iatrogenic disease 19. An organism that is capable of invading and multiplying in the body of the host: A. Causative agent B. Reservoir C. Bacteria D. Carrier 20. The infecting ability of a microorganism depends on its degree of: A. Pathogenecity B. Communicability C. Teratogenecity D. Epidemiology
21. Another Term for Hepatitis B. A. Hepatitis A B. Homologous Serum Hepatitis C. Epidemic Hepatitis 22. Most common type of Hepatitis A. Hepatitis A B. Hepatitis B 23. Type of hepatitis that is oral-fecal Infection. A. Hepatitis A B. Hepatitis B 24. Measles is also known as, except. A. Three-day measles B. Rubeola 25. The pathognomonic signs of Measles is? A. Forscheimer spot B. Kopliks Spot
D.Post-Transfusion Hepa
C. Hepatitis C
D. Hepatitis D
C. Hepatitis C
D. Hepatitis D
C. 10 day fever
D. Morbili
D. Stimson Sign
D. Postherpetic Neuraglia
26. The Appearance of rashes of measles is characterized by all of the following except. A. Begins at the hairline and behind the ear C. Appears at the trunk first (unifocal) B. Desquamation occurs after rashes D. Cephalocaudal Appearance of Rashes is observed. 27. Measles Vaccine is given with the following consideration except. A. Introduced once at Nine Months C. 0.5 cc is introduced at deltoid, ID B. AMV can be given as early as 6 months D. Report experience of fever and mild rashes for 3-4 days 28. The STI disease that is the most concern in the Philippines A. Syphilis B. Gonorrhea
C. Chlamydia
D. Trichomonas
29. The Leading Mode of Transmission of HIV and STI in the Philippines. A. Sharing needles for injection of drug use C. Vertical Transmission B. Sexual Contact D. Blood transmission 30. What is the most Preventive means of STI A. Used of Condom B. Contact Tracing 31. The Pathognomonic Sign of gonorrhea is, Except A. Nocturnal Ani B. Gleet
C. Drug Compliance
D. Routine Screening of Sexual Workers
C. Dyspareunia
D. Chancre
32. Neisseria Gonorrhea can be transmitted or has the ability to be transferred from infective male going to partner through. A. Adhesion of the microorganism to the sperm during expulsion B. Enterotoxin Production that is transmitted by the Sperm C. Penile Contact to the Mucosa of the vagina Transmit the Microorganism D. Oral and anal Sex even without withdrawals 33. The process of rendering immune is? A. Immunity B. Antibody C. Immunization D. Passive 34. Tetanus Toxoid provide what kind of Immunity? A. Active Artificial B. Passive Artificial 35. Tetanus Immunoglobulin is what type of immunity? A. Active Artificial B. Passive Artificial
D. Active Natural
D. Active Passive
D. Active Natural
D. Active Passive
36. BCG Vaccination is given during at birth provides what type of immunity?
A. Active Artificial B. Passive Artificial D. Active Natural D. Active Passive 37. the process of rendering the area free all types of microorganism is? A. Infertility B. Sterile Technique C. Medical Mission D. Hand Washing 38. The single and most effective Way of Preventing Transmission of Microorganism from one person to another is? A. Infertility B. Sterile Technique C. Medical Mission D. Hand Washing 39. the following are the characteristics of conybacterium diptheraie, except. A. Aerobic, non motile B. Gram positive C. Arrange like Chinese Character D. Drum stick in Appearance 40. Patient with Diptheria must have how many negative results should be taken to confirm absence of infection? A. Three B. Two C. One D. None, Clinical Manifestation is enough to confirm absence 41. If the client is experiencing Diptheria, Which of the following is a must at the clients bedside? A. Pair of scissors B. Mechanical Ventilator C. Tracheostomy set D. Bottle 42. Preventive Measures against Diptheria is through vaccination. Which of the following considerations are not intended for diphtheria vaccine? A. 3 doses, given first 6 weeks C. Booster dose every 2 years especially for travelers B. Injected at deltoid region D. DPT antigen is a whole cell vaccine 43. What is the causative agent of tuberculosis? A. Mycobactrum Tubercolosis B. Mycobacterium Diptherae C. Mycobacterium Tubercolosis D. SECRET 44. Tubercolosis causing agent can be transmitted by any of the following means except? A. Coughing,Sneezing, singing C. Feco-Oral Route B. Direct invasion through mucosa or break in the skin D. Unpasteurized milk or dairy Products 45. which of the following TB category according to DOH, has new smear negative PTB with Minimal Parenchymal lesion on Chest X-ray A. Categoy I B. Category II C. Category III D. Category IV 46. the standard diagnostic procedure for tuberculosis is? A. Direct Sputum Smear B. Chest X-ray C. Mantous Test D. Purified protein derivatives 47. Which of the following drug for TB is in capsule form? A. Rifampicin B. Ethambutol C. Pyrazynamide D. Isoniazid 48. Allergic Reaction is frequently observed with A. Rifampicin B. Ethambutol C. Pyrazynamide D. Isoniazid 49. Which drug is also used for chemoprophylaxis for TB A. Rifampicin B. Ethambutol C. Pyrazynamide D. Isoniazid 50. BCG immunization came from what type of mycobacterium strain? A. Mycobacterium Tubercolosis C. Mycobacterium Africanum B. Mycobacterium Bovis D. Mycobacterium Caninum
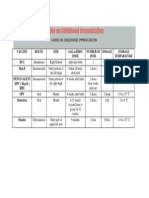
Vaccine
1. BCG a. Infant b. School Entrants 2. OPV 3. Hepatitis B 4. DPT
Dose
# of Dos e
8. 1
Minimum Age at 1st Dose
14. Birth 15. School entrants
Site of Administration
25. Deltoid region of the
Route of Administrati on
Intradermal
1.0.05 ml 2.0.1 ml
right arm left arm
27. Mouth
26. Deltoid region of the Oral Intramuscular 30. Deep IM
2 drops 0.5 ml
9. 3 10. 3 11. 3
16. 6 weeks 17. A birth 18. 6 weeks
28. Upper outer portion
of the thigh 29. Deltoid region of the thigh
0.5 ml
5. Measles 12. 1 19. 9 months Deltoid region of the arm Subcutaneous
0.5 ml
6. Tetanus Toxoid
0.5 ml
13. 5
20.TT1 as early as possible during pregnancy. 21. TT 2- 1 month later 22. TT3 at least 6 mos. later 23. TT4 at least 1 year late 24. TT5 at least
1 year later
Você também pode gostar
- Primary Health Care Exam MikaDocumento14 páginasPrimary Health Care Exam Mikaairon jake100% (2)
- Innoculations The True Weapons of Mass DestructionDocumento3 páginasInnoculations The True Weapons of Mass DestructionRedza100% (3)
- Question Bank EpidemiologyDocumento32 páginasQuestion Bank EpidemiologyRamesh Beniwal88% (8)
- Vaccination Myths - A. G. PhillipsDocumento11 páginasVaccination Myths - A. G. PhillipsBrendan D. MurphyAinda não há avaliações
- Environmental Science SyllabusDocumento4 páginasEnvironmental Science Syllabusyabaeve100% (5)
- PHC Feb 3Documento6 páginasPHC Feb 3SteveAinda não há avaliações
- GermTheory eDocumento8 páginasGermTheory eDanindra Adi Pratama100% (1)
- MCN Post Test IIDocumento14 páginasMCN Post Test IIquidditch07Ainda não há avaliações
- Local Media6484230877636161591Documento22 páginasLocal Media6484230877636161591AZ BaldovidonaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam PHCDocumento7 páginasFinal Exam PHCPrince Rener Velasco PeraAinda não há avaliações
- Elc093 November 2021 Final Test - Question PaperDocumento13 páginasElc093 November 2021 Final Test - Question PaperNik Ahmad Amirul AimanAinda não há avaliações
- Determinants of HealthDocumento29 páginasDeterminants of HealthMayom MabuongAinda não há avaliações
- Communicable Disease NursingDocumento5 páginasCommunicable Disease NursingNeil Jupiter100% (1)
- Preventive Veterinary MedicineDocumento48 páginasPreventive Veterinary MedicineBorja Bueno Garcia100% (3)
- Goat Production Handbook WEBDocumento100 páginasGoat Production Handbook WEBAakritee100% (1)
- Club Election ScriptDocumento2 páginasClub Election ScriptyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Preboard OBDocumento11 páginasPreboard OBMarie Cecille Soliven Varilla100% (1)
- CHN Final ExamDocumento12 páginasCHN Final ExamChristine UdhayAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric Nursing ExamDocumento21 páginasPediatric Nursing ExamChristianmel JavierAinda não há avaliações
- CD - Question PoolDocumento13 páginasCD - Question PoolGeff Ramos100% (1)
- Pgd-Test DrillDocumento11 páginasPgd-Test Drillkristel ludangcoAinda não há avaliações
- Funda 1Documento7 páginasFunda 1Ajurs UrsabiaAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric Homework 2Documento16 páginasPediatric Homework 2turner_marsha0% (1)
- CHN Practice Exam 3Documento7 páginasCHN Practice Exam 3Jaja BookAinda não há avaliações
- OB Midwifery Set 1 PDFDocumento9 páginasOB Midwifery Set 1 PDFSquidward Tentacles100% (1)
- Imci ExamDocumento2 páginasImci ExamJohn Michael ClimacoAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics Nursing QuestionsDocumento13 páginasObstetrics Nursing Questionsicy43150% (2)
- WWW - Prc.gov - PH: Page 1 of 3Documento12 páginasWWW - Prc.gov - PH: Page 1 of 3PRC BaguioAinda não há avaliações
- PGD Midterm ExamDocumento6 páginasPGD Midterm ExamMhianne SarmientoAinda não há avaliações
- 100 Items OB Questions byDocumento17 páginas100 Items OB Questions byPetrovich Tamag100% (1)
- FHCDocumento8 páginasFHCAmiel Francisco ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Dianne Gay Leaño 23 Years Old FSUU Batch 2017 November 2017 PNLE (85.20)Documento213 páginasDianne Gay Leaño 23 Years Old FSUU Batch 2017 November 2017 PNLE (85.20)Matt AndreyAinda não há avaliações
- Professional Regulatory Board of Midwifery: Not For SaleDocumento20 páginasProfessional Regulatory Board of Midwifery: Not For SalePRC BaguioAinda não há avaliações
- Handout COPARDocumento10 páginasHandout COPARkrissyAinda não há avaliações
- Community Evaluation Exam 2022Documento11 páginasCommunity Evaluation Exam 2022Ryan-Jay Abolencia100% (1)
- Delivery Room Rating SheetDocumento2 páginasDelivery Room Rating Sheetyabaeve100% (2)
- Imci Test Quest SamplerDocumento6 páginasImci Test Quest Samplerjenalyn_ingaran_sanluisAinda não há avaliações
- Icf PBRC Nov 2017Documento5 páginasIcf PBRC Nov 2017Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMAinda não há avaliações
- CHN Uv PosttestDocumento6 páginasCHN Uv PosttestMeeKo VideñaAinda não há avaliações
- ICFDocumento8 páginasICFSean CamingueAinda não há avaliações
- II-3hc With AnswersDocumento3 páginasII-3hc With Answersfairwoods100% (2)
- Test Sample For ICFDocumento6 páginasTest Sample For ICFNeptali CardinalAinda não há avaliações
- Pediatric NursinggDocumento13 páginasPediatric NursinggShalina RizalAinda não há avaliações
- MCN Post Test IDocumento15 páginasMCN Post Test Iquidditch07Ainda não há avaliações
- Prelims in CHNDocumento6 páginasPrelims in CHNcharmaineAinda não há avaliações
- Study Questions 1Documento8 páginasStudy Questions 1CGAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamental of Health Care 2017-2015 - HarlyDocumento17 páginasFundamental of Health Care 2017-2015 - HarlyDENNIS N. MUÑOZAinda não há avaliações
- NP1 CHN 2018 PDFDocumento86 páginasNP1 CHN 2018 PDFJOHN CARLO APATANAinda não há avaliações
- Community Health Service Management ExamDocumento8 páginasCommunity Health Service Management ExamCharlie Cotoner Falguera100% (1)
- Mid 103 FinalsDocumento3 páginasMid 103 FinalsMhianne Sarmiento100% (1)
- 10 Herbal PlantsDocumento12 páginas10 Herbal PlantsyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- NP1 Family Nursing 3Documento2 páginasNP1 Family Nursing 3Jonas Marvin AnaqueAinda não há avaliações
- OBDocumento4 páginasOBCharlie Cotoner FalgueraAinda não há avaliações
- NP2Documento12 páginasNP2mhamaenphapa27100% (2)
- Exam RationalizationDocumento73 páginasExam RationalizationPrince Jhessie L. AbellaAinda não há avaliações
- Communicable Disease NursingDocumento28 páginasCommunicable Disease NursingCyrin Once100% (2)
- Primary Health Care Exam MikaDocumento14 páginasPrimary Health Care Exam Mikaairon jakeAinda não há avaliações
- PRC - ICF - Compilations 2009-2016Documento18 páginasPRC - ICF - Compilations 2009-2016Jonas Marvin AnaqueAinda não há avaliações
- Midterm IntegDocumento5 páginasMidterm IntegHenrick VaquilarAinda não há avaliações
- Community Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisDocumento7 páginasCommunity Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisHannah BuquironAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Health CareDocumento133 páginasPrimary Health CareSteveAinda não há avaliações
- OB Answer KeyDocumento23 páginasOB Answer Keyicy431Ainda não há avaliações
- Professional GrowthDocumento10 páginasProfessional GrowthKhadija AmaraniAinda não há avaliações
- Communicable Disease NursingDocumento41 páginasCommunicable Disease NursingBJ DUQUESA100% (2)
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read The Following Questions and Choose The Best Answer by Shading TheDocumento14 páginasMULTIPLE CHOICE. Read The Following Questions and Choose The Best Answer by Shading ThePrince Mark BadilloAinda não há avaliações
- Earthquake and Fire DrillDocumento51 páginasEarthquake and Fire Drillyabaeve100% (1)
- Ob Set A and B QuesDocumento17 páginasOb Set A and B QuesBok Delos SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Knowledge Post-Test With Answer KeyDocumento8 páginasIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Knowledge Post-Test With Answer KeyCarissa De Luzuriaga-BalariaAinda não há avaliações
- CDDocumento8 páginasCDec-bs0% (1)
- PHC-1 Mid Term Exam-Final Questions With Answers-2023Documento4 páginasPHC-1 Mid Term Exam-Final Questions With Answers-2023Galakpai KolubahAinda não há avaliações
- XXXXXDocumento14 páginasXXXXXJonas Marvin AnaqueAinda não há avaliações
- Comprehensive Exam of Community Health Nursing I. MCQDocumento15 páginasComprehensive Exam of Community Health Nursing I. MCQA.A M.A.RAinda não há avaliações
- MCARE1 Drill Set 3Documento12 páginasMCARE1 Drill Set 3Lisette UmadhayAinda não há avaliações
- 50 ItemsDocumento6 páginas50 ItemsPaul EspinosaAinda não há avaliações
- HttpsDocumento4 páginasHttpsyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- The Four Priorities For ActionDocumento2 páginasThe Four Priorities For ActionyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Map Indicating All Provinces Including Metro Manila, The National Capital Region (NCR) of The PhilippinesDocumento1 páginaPhilippine Map Indicating All Provinces Including Metro Manila, The National Capital Region (NCR) of The PhilippinesyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- IDRN 1300 Spear v5 20120110Documento6 páginasIDRN 1300 Spear v5 20120110yabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Your Scenarios Here Are Examples of The Three Types of Fluid Volume DeficitDocumento2 páginasYour Scenarios Here Are Examples of The Three Types of Fluid Volume DeficityabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction HandoutsDocumento4 páginasDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction HandoutsyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- China Is A Socialist Country. The Government Owns and Controls Almost All Natural ResourcesDocumento6 páginasChina Is A Socialist Country. The Government Owns and Controls Almost All Natural ResourcesyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- General ScienceDocumento147 páginasGeneral ScienceyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Finals 1bDocumento1 páginaBiology Finals 1byabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Guide On Childhood Immunization 2014Documento1 páginaGuide On Childhood Immunization 2014yabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Geological Science Final Examination: 1. Stages of Thunder Storm 10-12 (Plate Boundaries)Documento1 páginaGeological Science Final Examination: 1. Stages of Thunder Storm 10-12 (Plate Boundaries)yabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- From Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsDocumento6 páginasFrom Continental Drift To Plate TectonicsyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Eve Application LetterDocumento1 páginaEve Application LetteryabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Integumentary SystemDocumento4 páginasIntegumentary SystemyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Step To Follow Intrapartal CareDocumento3 páginasStep To Follow Intrapartal CareyabaeveAinda não há avaliações
- Pharm - Biotechnology - Question BankDocumento8 páginasPharm - Biotechnology - Question BankujjwalAinda não há avaliações
- Sementis IM June 2011Documento21 páginasSementis IM June 2011zozareliAinda não há avaliações
- SS2 3RD Term Animal Husbandry E-NotesDocumento18 páginasSS2 3RD Term Animal Husbandry E-Noteskanajoseph2009Ainda não há avaliações
- PEP Past QuestionsDocumento12 páginasPEP Past QuestionsCynthia ObiAinda não há avaliações
- Recalls 1 CompilationDocumento180 páginasRecalls 1 CompilationReka LambinoAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Translation Textbook2020Documento27 páginasIntroduction To Translation Textbook2020Taef AljohaniAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar PustakaDocumento4 páginasDaftar PustakaCholida RachmatiaAinda não há avaliações
- Vaccination: DR Hodan Ahmed, MBBS, Mmed, Depr of Pediatrics, Amoud Medical School, AuDocumento13 páginasVaccination: DR Hodan Ahmed, MBBS, Mmed, Depr of Pediatrics, Amoud Medical School, Auabdisalaan hassanAinda não há avaliações
- Disease and Immunity MicroorganismsDocumento8 páginasDisease and Immunity MicroorganismsAmna SaleemAinda não há avaliações
- ImmunizationDocumento16 páginasImmunizationShafie ElmiAinda não há avaliações
- Community Medicine BCQs (Immunization)Documento7 páginasCommunity Medicine BCQs (Immunization)Sajid Ali100% (1)
- VaccineDocumento2 páginasVaccinedarshan baskarAinda não há avaliações
- New Generation Vaccines Seminar19Documento4 páginasNew Generation Vaccines Seminar19Nerma0% (1)
- Covid VaccinesDocumento2 páginasCovid VaccinesChloe MaeAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 Assessment BookletDocumento45 páginasTopic 2 Assessment BookletLinAinda não há avaliações
- Dental Caries VaccineDocumento30 páginasDental Caries Vaccinepublic health health svsidsAinda não há avaliações
- Form One Exams PDFDocumento67 páginasForm One Exams PDFEZEKIEL JUMAAinda não há avaliações
- First Language English: 4 Mark Questions: 5 Questions: (2 Prose + 2 Poem + 1 Comprehension Passage)Documento44 páginasFirst Language English: 4 Mark Questions: 5 Questions: (2 Prose + 2 Poem + 1 Comprehension Passage)karanAinda não há avaliações
- Foundation of Nursing Practice Exam For Infection Asepsis Basic Concept of Stress and IllnessDocumento34 páginasFoundation of Nursing Practice Exam For Infection Asepsis Basic Concept of Stress and IllnessAdrian MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- The Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuideDocumento52 páginasThe Immune System Defense Against Disease Study GuidemaddoxAinda não há avaliações
- The Immune System British English StudentDocumento6 páginasThe Immune System British English StudentIzabela WiśniewskaAinda não há avaliações