Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
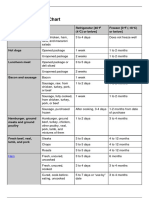
Cold Storage Chart: Product Refrigerator (40 °F) Freezer (0 °F) Eggs
Enviado por
glatchoumiTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cold Storage Chart: Product Refrigerator (40 °F) Freezer (0 °F) Eggs
Enviado por
glatchoumiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
http://www.sdbest.com/Food_Safety/cold_storage.
html
Cold Storage Chart
These short, but safe, time limits will help keep refrigerated food from spoiling or becoming dangerous to eat. Because freezing keeps food safe indefinitely, recommended storage times are for quality only.
Product Eggs
Fresh, in shell Raw yolks & whites Hard cooked Liquid pasteurized eggs, egg substitutes opened unopened Commercial Mayonnaise Refrigerate after opening Frozen Dinners & Entrees Keep frozen until ready to heat Deli & Vacuum-Packed Products Store-prepared (or homemade) egg, chicken, ham, tuna, & macaroni salads
Refrigerator (40 F)
3 to 5 weeks 2 to 4 days 1 week
Freezer (0 F)
Do not freeze 1 year Does not freeze well
3 days 10 days 2 months Keep frozen
Does not freeze well 1 year Do not freeze 3 to 4 months
3 to 5 days
Does not freeze well
Hot dogs & Luncheon Meats
Hot dogs opened package unopened package Luncheon meat opened package unopened package 3 to 5 days 2 weeks 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months 1 week 2 weeks 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months
Bacon & Sausage
Bacon Sausage, raw -- from chicken, turkey, pork, beef Smoked breakfast links, patties 7 days 1 to 2 days 7 days 1 month 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months
Hard sausage -- pepperoni, jerky sticks
2 to 3 weeks
1 to 2 months
Summer sausage -- labeled "Keep Refrigerated" opened unopened 3 weeks 3 months 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months
Ham, Corned Beef
Corned beef, in pouch with pickling juices 5 to 7 days Drained, 1 month
Ham, canned -- labeled "Keep Refrigerated" opened unopened Ham, fully cooked, vacuum sealed at plant, undated, unopened Ham, fully cooked, vacuum sealed at plant, dated, unopened Ham, fully cooked. whole half slices 7 days 3 to 5 days 3 to 4 days 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months 3 to 5 days 6 to 9 months 2 weeks "Use-By" date on package 1 to 2 months Do not freeze 1 to 2 months 1 to 2 months
Hamburger, Ground & Stew Meat
Hamburger & stew meat Ground turkey, veal, pork, lamb, & mixtures of them 1 to 2 days 1 to 2 days 3 to 4 months 3 to 4 months
Fresh Beef, Veal, Lamb, Pork
Steaks Chops Roasts Variety meats -- tongue, liver, heart, kidneys, chitterlings Pre-stuffed, uncooked pork chops, lamb chops, or chicken breasts stuffed with dressing Soups & Stews with Vegetables or meat added 3 to 5 days 3 to 5 days 3 to 5 days 1 to 2 days 1 day 6 to 12 months 4 to 6 months 4 to 12 months 3 to 4 months Does not freeze well
3 to 4 days
2 to 3 months
Cooked Meat Leftovers
Cooked meat & meat casseroles 3 to 4 days 2 to 3 months
Gravy & meat broth
1 to 2 days
2 to 3 months
Fresh Poultry
Chicken or turkey, whole Chicken or turkey, pieces Giblets 1 to 2 days 1 to 2 days 1 to 2 days 1 year 9 months 3 to 4 months
Cooked Poultry Leftovers
Fried chicken Cooked poultry casseroles Pieces, plain Pieces covered with broth, gravy Chicken nuggets, patties Pizza, cooked Stuffing, cooked 3 to 4 days 3 to 4 days 3 to 4 days 1 to 2 days 1 to 2 days 3 to 4 days 3 to 4 days 4 months 4 to 6 months 4 months 6 months 1 to 3 months 1 to 2 months 1 month
http://www.sdbest.com/Food_Safety/food_bacteria.html
So What Made Me Sick?
BACTERIA
Campylobacter
WHERE FOUND
Intestinal tracts of animals, raw milk, untreated water, and sewage.
SOURCE
Contaminated water, raw milk, and raw or undercooked meat, poultry, or shellfish.
SYMPTOMS
Fever, headache and muscle pain followed by diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea that appear 2 to 5 days after eating; may last 7 to 10 days. Toxin affects the nervous system. Symptoms usually appear 18 to 36 hours, but can sometimes appear as few as 4 hours or as many as 8 daysafter eating; double vision, droopy eyelids, trouble speaking and swallowing, and difficulty breathing. Fatal in 3 to 10 days if not treated. Diarrhea and gas pains mayappear 8 to 24 hours after eating; usually last about 1 day, but less severe symptoms may persist for 1 to 2 weeks.
Botulism
Widely distributed in soil, water, on plants, and intestinal tracts of animals. Grows only in little or no oxygen.
Bacteria produce a toxin that causes illness. Improperly canned foods, garlic in oil, vacuum-packed and tightly wrapped food.
Clostridium
Soil, dust, sewage, and intestinal tracts of animals. Grows only in little or no oxygen.
Food left for long periods in steam tables or at room temperature. Bacteria destroyed by cooking, but some toxinproducing spores may survive. Contaminated water, raw milk, raw or rare ground beef, unpasteurized apple juice or cider, uncooked fruits and vegetables; person-to-person. Ready-to-eat foods such as hot dogs, luncheon
E. coli
Intestinal tracts of some mammals, raw milk and unchlorinated water.
Diarrhea or bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea, and malaise; can begin 2 to 5 days after food is eaten, lasting about 8 days.
Listeria
Intestinal tracts of humans and animals,
Fever, chills, headache, backache, sometimes upset
milk, soil, leaf vegetables; meats, cold cuts, can grow slowly at fermented or dry refrigerator temperatures. sausage, and other delistyle meat and poultry, soft cheeses and unpasteurized milk.
stomach, abdominal pain and diarrhea; may take up to 3 weeks to become ill. More serious illness may develop in pregnant women, newborns, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. Stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, chills, fever, and headache usually appear 8 to 72 hours after eating; may last 1 to 2 days. Disease referred to as "shigellosis" or bacillary dysentery. Diarrhea containing blood and mucus, fever, abdominal cramps, chills, and vomiting; 12 to 50 hours from ingestion of bacteria; can last a few days to 2 weeks. Severe nausea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and diarrheaoccur 1 to 6 hours after eating; recovery within 2 to 3 days -- longer if severe dehydration occurs.
Salmonella (over 2300 types)
Intestinal tracts and feces of animals and sometimes in eggs.
Raw or undercooked eggs, poultry, and meat; raw milk and dairy products; seafood, and food handlers. Person-to-person by fecal-oral route; fecal contamination of food and water. Most outbreaks result from food, especially salads, prepared and handled by workers using poor personal hygiene. Person-to-person through food from improper food handling. Multiply rapidly at room temperature to produce a toxin that causes illness.
Shigella (over 30 types)
Human intestinal tract; rarely found in other animals.
Staphylococcus
On humans (skin, infected cuts, pimples, noses, and throats).
Você também pode gostar
- Homemade Healthy Dog Food Cookbook: The Comprehensive Guide to 100 Nutrious Meals and Treats to Keep your Dog HappyNo EverandHomemade Healthy Dog Food Cookbook: The Comprehensive Guide to 100 Nutrious Meals and Treats to Keep your Dog HappyAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento7 páginasUntitledNathaniel VenusAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Stocks and Soups: How to Make Healthy Soups and StocksNo EverandIntroduction to Stocks and Soups: How to Make Healthy Soups and StocksAinda não há avaliações
- Refrigerator Freezer Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasRefrigerator Freezer Storage ChartMarko BregovecAinda não há avaliações
- Paleo Freezer: Delicious, Fix & Freeze, Gluten-Free, Paleo Recipes for Busy People: Paleo Diet Solution SeriesNo EverandPaleo Freezer: Delicious, Fix & Freeze, Gluten-Free, Paleo Recipes for Busy People: Paleo Diet Solution SeriesAinda não há avaliações
- AcrosticDocumento4 páginasAcrosticBlue Shineyy MusicAinda não há avaliações
- Cat Food Cookbook: A Selection of Healthy Homemade Cat Food RecipesNo EverandCat Food Cookbook: A Selection of Healthy Homemade Cat Food RecipesAinda não há avaliações
- Basics For Handling Food Safely: April 2003 Information For ConsumersDocumento5 páginasBasics For Handling Food Safely: April 2003 Information For ConsumersPatricia HenriquesAinda não há avaliações
- Slow Cooker Cookbook for Beginners: Master the Art of Easy Set-and-Forget Meals with Cost-Effective Recipes Ready for Your Return [IV EDITION]No EverandSlow Cooker Cookbook for Beginners: Master the Art of Easy Set-and-Forget Meals with Cost-Effective Recipes Ready for Your Return [IV EDITION]Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (9)
- Storing Food at Safe TemperaturesDocumento16 páginasStoring Food at Safe TemperaturesIskandar FirdausAinda não há avaliações
- Dog Food Cookbook: A Selection of Healthy Homemade Dog Food RecipesNo EverandDog Food Cookbook: A Selection of Healthy Homemade Dog Food RecipesAinda não há avaliações
- Health: Food Storage For Safety and Quality No. 9.310Documento4 páginasHealth: Food Storage For Safety and Quality No. 9.310Dalibor PurhmajerAinda não há avaliações
- Autoimmune Cookbook: Delicious Autoimmune Protocol Paleo Diet Recipes For Naturally Healing Autoimmune Disease and DisordersNo EverandAutoimmune Cookbook: Delicious Autoimmune Protocol Paleo Diet Recipes For Naturally Healing Autoimmune Disease and DisordersAinda não há avaliações
- Cookery Las G10 Quarter-4 Week-56Documento5 páginasCookery Las G10 Quarter-4 Week-56Ahron BenedictAinda não há avaliações
- The All New Ball Book Of Canning And Preserving: Over 350 of the Best Canned, Jammed, Pickled, and Preserved RecipesNo EverandThe All New Ball Book Of Canning And Preserving: Over 350 of the Best Canned, Jammed, Pickled, and Preserved RecipesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (8)
- Family Nutrition ProgrameDocumento4 páginasFamily Nutrition ProgrameArunee KongpengAinda não há avaliações
- OOD Echnology: Bacteria - Linked With Micro-Organisms in Food ProductionDocumento9 páginasOOD Echnology: Bacteria - Linked With Micro-Organisms in Food ProductionlelascepanovicAinda não há avaliações
- Treating Food Poisoning: Contaminant Onset of Symptoms Foods Affected and Means of TransmissionDocumento2 páginasTreating Food Poisoning: Contaminant Onset of Symptoms Foods Affected and Means of TransmissionMonica Lauretta SembiringAinda não há avaliações
- Step Ahead April 2, 2012 EggsDocumento1 páginaStep Ahead April 2, 2012 EggsMedford Public Schools and City of Medford, MAAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartMau-mau Lantoria BalotAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartSerSales CamerounAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartRamirez DomyojiAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartSujith Kesavan Vadakke IllathAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartDz CapssoulaAinda não há avaliações
- COOKERY 10 - LO.4 Methos of Preserving MeatDocumento34 páginasCOOKERY 10 - LO.4 Methos of Preserving MeatDianne Joy Corpuz100% (2)
- Cold Food Storage Chart PDFDocumento3 páginasCold Food Storage Chart PDFrogerAinda não há avaliações
- COOKERY 10 LO 4 Methos of Preserving MeatDocumento34 páginasCOOKERY 10 LO 4 Methos of Preserving MeatNosh Jimenez ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- The Paleo Diet CookbookDocumento26 páginasThe Paleo Diet CookbookYahia Bob100% (2)
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento4 páginasCold Food Storage ChartKen HaddadAinda não há avaliações
- Intoxicaciones Alimentarias - ConsumidorDocumento2 páginasIntoxicaciones Alimentarias - ConsumidorMartha Patricia López PimentelAinda não há avaliações
- Meat Stock 2023Documento18 páginasMeat Stock 2023Margarida CarnotoAinda não há avaliações
- Nutritional TipsDocumento6 páginasNutritional TipsCarlos LuqueAinda não há avaliações
- Holiday or Party BuffetsDocumento2 páginasHoliday or Party BuffetsjulianaAinda não há avaliações
- Pimsat Colleges: COLLEGE OF International Hospitality MANAGEMENT Kitchen Essentials and Basic Food PreparationDocumento2 páginasPimsat Colleges: COLLEGE OF International Hospitality MANAGEMENT Kitchen Essentials and Basic Food PreparationIsmael HanAinda não há avaliações
- TLEFOP CompressedDocumento75 páginasTLEFOP CompressedTayapad, Irene C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Genter FoodstorageDocumento3 páginasGenter FoodstorageTrong MacAinda não há avaliações
- Food - Safety (1) A Good General Power PointDocumento64 páginasFood - Safety (1) A Good General Power PointOpik PetetAinda não há avaliações
- Food SafeDocumento3 páginasFood SafeDhila FayaAinda não há avaliações
- Store MeatDocumento20 páginasStore Meatabejarm7Ainda não há avaliações
- Common Food Poisoning BacteriaDocumento3 páginasCommon Food Poisoning BacteriaYani NyiikAinda não há avaliações
- Refrigeration and Freezing of FoodsDocumento3 páginasRefrigeration and Freezing of FoodsJohn Frederick Castillo100% (1)
- Bone BrothDocumento5 páginasBone BrothLeea WordAinda não há avaliações
- ScriptDocumento3 páginasScriptPrincess Fatima De JuanAinda não há avaliações
- Store Egg DishesDocumento12 páginasStore Egg DishesJoevic SuyodAinda não há avaliações
- PoultryDocumento10 páginasPoultryAnonymous LJ9JdSBKHAinda não há avaliações
- FS Cold Storage Chart PDFDocumento3 páginasFS Cold Storage Chart PDFHSE CCDC 32Ainda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento3 páginasCold Food Storage Chartadam emryAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento3 páginasCold Food Storage ChartJade Bianca StricklandAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Food Storage ChartDocumento3 páginasCold Food Storage ChartAndreea LarisaAinda não há avaliações
- Egg and Flesh Foods: by Surya BND 3 Semester 2 2 0 5 2 5 0 1 5Documento21 páginasEgg and Flesh Foods: by Surya BND 3 Semester 2 2 0 5 2 5 0 1 5surya bhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- Homemade Bone Broth - The Heal Your Gut CookbookDocumento4 páginasHomemade Bone Broth - The Heal Your Gut CookbookChelsea Green Publishing100% (1)
- Food PoisoningDocumento23 páginasFood PoisoningEsther NyawiraAinda não há avaliações
- Easy Lasagna Three VerdsionsDocumento2 páginasEasy Lasagna Three Verdsionsok rightAinda não há avaliações
- Food Safety During PregnancyDocumento12 páginasFood Safety During PregnancysatishAinda não há avaliações
- Store Egg Dishes Grade 10 July 30, 2019Documento11 páginasStore Egg Dishes Grade 10 July 30, 2019nelmaeAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 5Documento22 páginasLesson 5Nika KatanoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Shelf Life of EggsDocumento7 páginasWhat Is The Shelf Life of EggsBushra ChuadhryAinda não há avaliações
- Food-Storage-And-Shelf LifeDocumento13 páginasFood-Storage-And-Shelf LifeANDREAMIBAinda não há avaliações
- Meat and PoultryDocumento47 páginasMeat and Poultryprincess padojenog100% (1)
- A Feeding TipDocumento6 páginasA Feeding TipDimand StefanAinda não há avaliações
- Kids Health ProteinDocumento13 páginasKids Health ProteinglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Seasons Worksheet PDFDocumento2 páginasSeasons Worksheet PDFMaria Iurcea BondeaAinda não há avaliações
- Living Juices Vitamin ChartDocumento5 páginasLiving Juices Vitamin ChartarchanavedantamAinda não há avaliações
- Kids Fruit - Nutrient ChartDocumento9 páginasKids Fruit - Nutrient ChartglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Examples of TestquestionsDocumento1 páginaExamples of TestquestionsglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Kids Nuts and GrainsDocumento9 páginasKids Nuts and GrainsglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Kilberry MotionCyckel JC820Documento24 páginasKilberry MotionCyckel JC820glatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Aeg Electrolux Lav76810Documento40 páginasAeg Electrolux Lav76810glatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- English Course PDFDocumento49 páginasEnglish Course PDFglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- GEN GT-P5210 Galaxy Tab 3 English JB User Manual MFA F4Documento215 páginasGEN GT-P5210 Galaxy Tab 3 English JB User Manual MFA F4Siriveri Lakshmi KanthAinda não há avaliações
- Mayo ClinicDocumento48 páginasMayo ClinicAbdul RazzaqAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurveda For Home RemediesDocumento15 páginasAyurveda For Home Remedieskarthiraja_1981Ainda não há avaliações
- Table of Plants UsesDocumento4 páginasTable of Plants Usesapi-3750955100% (1)
- Tamil Herbs With Botanical NamesDocumento5 páginasTamil Herbs With Botanical Namesloganathan198588% (17)
- Your HTC Smart: User GuideDocumento131 páginasYour HTC Smart: User GuideMikey SlawsonAinda não há avaliações
- Webuser - 21 February 2013-Edition, Free EditionDocumento76 páginasWebuser - 21 February 2013-Edition, Free EditionglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- FAQ ModelDocumento3 páginasFAQ ModelglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- AbcDocumento1 páginaAbcglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Cuimrh 93001Documento39 páginasCuimrh 93001glatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurveda For Home RemediesDocumento15 páginasAyurveda For Home Remedieskarthiraja_1981Ainda não há avaliações
- 3G - UsageDocumento1 página3G - UsageglatchoumiAinda não há avaliações
- Content Details of Brahman SabhanDocumento5 páginasContent Details of Brahman SabhanIp SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Mcat Power Practice Learningexpress PDFDocumento244 páginasMcat Power Practice Learningexpress PDFMamoAinda não há avaliações
- MaslowDocumento1 páginaMaslowCik Sri SyarifahAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasMedical Nutrition Therapy A Case Study Approach 5th Edition Nelms Solutions Manualwinifredmilcah4oo1100% (15)
- Process of LactationDocumento5 páginasProcess of LactationKimberly Mondala (SHS)Ainda não há avaliações
- Assessment 5Documento2 páginasAssessment 5Niña Mae BelgaAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Adams Solutions ManualDocumento26 páginasPharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Adams Solutions ManualToniPerryptfo100% (36)
- EFIC European Pain Diploma Reading ListDocumento7 páginasEFIC European Pain Diploma Reading ListJoana MoreiraAinda não há avaliações
- Screening and Quantification of Anti-Quorum Sensing and Antibiofilm Activities of Phyllosphere Bacteria Against Biofilm Forming BacteriaDocumento5 páginasScreening and Quantification of Anti-Quorum Sensing and Antibiofilm Activities of Phyllosphere Bacteria Against Biofilm Forming BacteriaIthnan PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Reflexology-Key To Perfect HealthDocumento340 páginasHand Reflexology-Key To Perfect Healthpadoita01100% (1)
- Best (Discussion) Molecular Epidemiology Ofbabesiaspecies, Theileria Parva, Andanaplasmamarginaleinfecting Cattle in UgandaDocumento9 páginasBest (Discussion) Molecular Epidemiology Ofbabesiaspecies, Theileria Parva, Andanaplasmamarginaleinfecting Cattle in UgandaAamir muse osmanAinda não há avaliações
- Secondary - Report Card Comment CodesDocumento2 páginasSecondary - Report Card Comment CodesRICHARD SARDON LEONAinda não há avaliações
- OTC wv1Documento42 páginasOTC wv1Sheena GagarinAinda não há avaliações
- Post Operasi Sectio Sesarea Di Rsud Dr. Slamet Garut: Gambaran Tingkat Cemas, Mobilisasi, Dan Nyeri Pada IbuDocumento12 páginasPost Operasi Sectio Sesarea Di Rsud Dr. Slamet Garut: Gambaran Tingkat Cemas, Mobilisasi, Dan Nyeri Pada IbuDede NunuAinda não há avaliações
- Check List For Development of HospitalDocumento3 páginasCheck List For Development of HospitaltexaltergatckaAinda não há avaliações
- Diurnal Variation of Maximal Fat-Oxidation Rate in Trained Male AthletesDocumento8 páginasDiurnal Variation of Maximal Fat-Oxidation Rate in Trained Male AthletesPrecision Wellness Precision WellnessAinda não há avaliações
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 9 Mon Tieng Anh Thi Diem Phong GD DT Hoa An Cao Bang Co Dap AnDocumento16 páginasDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Lop 9 Mon Tieng Anh Thi Diem Phong GD DT Hoa An Cao Bang Co Dap AnViệt KhôiAinda não há avaliações
- Med Surg 1Documento14 páginasMed Surg 1Wendera T. S CooperAinda não há avaliações
- 1) Health and Safety Interaction Form TemplateDocumento1 página1) Health and Safety Interaction Form TemplateIgaDan100% (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of Steel Supports For Gratings at TR A...Documento9 páginasMethod Statement For Installation of Steel Supports For Gratings at TR A...Faraaz MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Argumentative EssayDocumento1 páginaArgumentative EssayJune PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Treatment Center PDFDocumento120 páginasTreatment Center PDFShellyAinda não há avaliações
- Leadership in Healthcare Essential Values and Skills Third Edition PDF Version PDFDocumento42 páginasLeadership in Healthcare Essential Values and Skills Third Edition PDF Version PDFmarilyn.llamas494100% (38)
- EAPP - q2 - Mod1 - Arguments in ManifestoesDocumento9 páginasEAPP - q2 - Mod1 - Arguments in ManifestoesAngelica Dyan MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.1 Planning and Simplified Project Execution PlanDocumento19 páginas3.1 Planning and Simplified Project Execution Planindra syifaiAinda não há avaliações
- Methods of Plant PropagationDocumento56 páginasMethods of Plant PropagationMaryhester De leonAinda não há avaliações
- DLL Catch Up Friday Week 4Documento16 páginasDLL Catch Up Friday Week 4Maryanne Labaso93% (27)
- Articles Efficacy of EMDR Therapy For Children With PTSD: A Review of The LiteratureDocumento19 páginasArticles Efficacy of EMDR Therapy For Children With PTSD: A Review of The LiteratureNerea F GAinda não há avaliações
- Project: My City Centre Masdar, Abu Dhabi, Uae: Method Statement For Installation of Fire Alarm SystemDocumento13 páginasProject: My City Centre Masdar, Abu Dhabi, Uae: Method Statement For Installation of Fire Alarm SystemUmair BaBerAinda não há avaliações
- Germiston +27833736090 Dr. Jabulile/cheap Abortion Pills 4 Sale in Germiston/johannesburg ClinicDocumento1 páginaGermiston +27833736090 Dr. Jabulile/cheap Abortion Pills 4 Sale in Germiston/johannesburg Clinicsseruwagi miyodiAinda não há avaliações
- Waiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterNo EverandWaiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (487)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNo EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookNo EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Magnolia Table, Volume 3: A Collection of Recipes for GatheringNo EverandMagnolia Table, Volume 3: A Collection of Recipes for GatheringNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldNo EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (5)
- The Blue Apron Cookbook: 165 Essential Recipes & Lessons for a Lifetime of Home CookingNo EverandThe Blue Apron Cookbook: 165 Essential Recipes & Lessons for a Lifetime of Home CookingAinda não há avaliações
- The Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoNo EverandThe Stark Naked 21-Day Metabolic Reset: Effortless Weight Loss, Rejuvenating Sleep, Limitless Energy, More MojoAinda não há avaliações
- Pati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingNo EverandPati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (9)
- Chicano Eats: Recipes from My Mexican-American KitchenNo EverandChicano Eats: Recipes from My Mexican-American KitchenAinda não há avaliações
- Authentic Mexican: Regional Cooking from the Heart of MexicoNo EverandAuthentic Mexican: Regional Cooking from the Heart of MexicoAinda não há avaliações
- Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideNo EverandSurprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Not That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsNo EverandNot That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsAinda não há avaliações
- Mostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyNo EverandMostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Eat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthNo EverandEat Complete: The 21 Nutrients That Fuel Brainpower, Boost Weight Loss, and Transform Your HealthNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Eating Clean: The 21-Day Plan to Detox, Fight Inflammation, and Reset Your BodyNo EverandEating Clean: The 21-Day Plan to Detox, Fight Inflammation, and Reset Your BodyNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Poilâne: The Secrets of the World-Famous Bread BakeryNo EverandPoilâne: The Secrets of the World-Famous Bread BakeryAinda não há avaliações
- Instant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayNo EverandInstant Pot Miracle 6 Ingredients Or Less: 100 No-Fuss Recipes for Easy Meals Every DayNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Just Feed Me: Simply Delicious Recipes from My Heart to Your PlateNo EverandJust Feed Me: Simply Delicious Recipes from My Heart to Your PlateNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Rice, Noodle, Fish: Deep Travels Through Japan's Food CultureNo EverandRice, Noodle, Fish: Deep Travels Through Japan's Food CultureNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (20)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingNo EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomNo EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleNo EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Saved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayNo EverandSaved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (10)








![Slow Cooker Cookbook for Beginners: Master the Art of Easy Set-and-Forget Meals with Cost-Effective Recipes Ready for Your Return [IV EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/617863506/149x198/155fd98e8e/1711213123?v=1)