Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Reaction Kinetics Question PDF
Enviado por
danielmahsaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Reaction Kinetics Question PDF
Enviado por
danielmahsaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name : ..
Year 12 AS Level Chemistry
80% 70% 60% 50% 40% Below
A B C D E U
Questions on Kinetics 2.3
43
1.
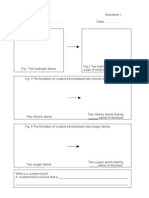
The diagram below shows the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve for a sample of gas at a fixed temperature. Ea is the activation energy for the decomposition of this gas.
Number of molecules with a given energy
Ea
Energy
(i)
On the diagram sketch the distribution curve for the sample of gas at a higher temperature.
(ii)
What is the effect of an increase in temperature on the rate of chemical reaction? Explain your answer with reference to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Effect ... Explanation .
(iii)
What is the effect of the addition of a catalyst on the rate of chemical reaction? Explain your answer with reference to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. Effect ... Explanation . (9) TOTAL 9 marks
2.
(a)
Below is a Maxwell-Boltzmann curve showing the distribution of molecular energies for a sample of gas at a temperature T
(i) (ii)
Label the axis on the diagram above. What does the area under the curve represent? .
(iii)
State why the curve starts at the origin. . (4)
(b)
(i)
State what is meant by the term activation energy. .
(ii)
The rate of a chemical reaction may be increased by an increase in reactant concentration, by an increase in temperature and by the addition of a catalyst.
State which, if any, of these changes involves a different activation energy. Explain your answer. Change(s) .. Explanation . (5) TOTAL 9 marks 3. (a) Give the meaning of the term catalyst. . (2) (b) Explain in general terms how a catalyst works. . (c) In an experiment, two moles of gas W reacted completely with solid Y to form one mole of gas Z as shown in the equation. 2W (g) + Y (s) Z (g).
The graph below shows how the concentration of Z varied with time at constant temperature
Concentration
Time
(i)
On the axis above sketch a curve to show how the concentration of W would change with time in the same experiment. Label this curve W.
(ii)
On the same axis above, sketch a curve to show how the concentration of Z would change with time if the reaction were to be repeated under the same conditions but in the presence of a catalyst. Label this curve Z.
(iii)
In terms of the behaviour of particles, explain why the rate of this reaction decreases with time. (2) TOTAL 10 marks
4.
(a)
An excess of calcium carbonate was added to some hydrochloric acid in a flask on a balance which was immediately set to zero. The mass reading on the balance was then recorded over a period of time. Other similar experiments were performed at the same temperature and the results were shown below.
0 5 Reading on balance 4
Time
The reaction of lumps of calcium carbonate with 100 cm3 of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid gave curve 4. Which one of the curves, Labelled 1-5 could have been produced using the following mixtures? Each curve may be used once only. (i) 100 cm3 of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid with finely powered calcium carbonate . (ii) 50 cm3 of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid with lumps of calcium carbonate. . (iii) 50 cm3 of 0.2 M hydrochloric acid with lumps of calcium carbonate? . (3)
(b)
A large excess of zinc was added to 100 cm3 of 0.2 M hydrochloric acid. After the reaction had ended, 240 cm3 of hydrogen has been formed. In three further experiments, extra substances were added to the original mixture as shown in the table below. Fill in the table to show the total volume of hydrogen formed in each experiment and the qualitative effect of these additions on the initial rate of reaction compared to the original experiment.
Substances added to an excess of zinc and 100 cm3 of 0.2 M hydrochloric acid 100cm3 water l0g zinc 50 cm3 0.2 M hydrochloric acid
Volume of hydrogen/cm3
Effect on initial rate of reaction
(6) TOTAL 9 marks 5. (a) Explain the term rate of reaction . (1) (b) Explain, in terms of the collision theory, why the rate of reaction decreases as time increases (3)
(c)
Explain why the rate of reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid is increases much more by changing the magnesium from powder than by doubling the concentration of the acid. (2) TOTAL 6 marks
Você também pode gostar
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1Documento27 páginasChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1ZekZanaAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No LogoDocumento96 páginasChemistry Perfect Score Module Form 4 2011 No Logohome8008100% (2)
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDocumento48 páginasChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic Configuration New 2025Documento2 páginasElectronic Configuration New 2025Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]Ainda não há avaliações
- Solaf Chemistry SPM 2014: Chapter 1 Form 5: Rate of ReactionDocumento18 páginasSolaf Chemistry SPM 2014: Chapter 1 Form 5: Rate of ReactionNik Diana Hartika Nik Husain100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Documento9 páginasRate of Reaction 2 QP (Tomek)Tomasz OstrowskiAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetics Worksheet AnswersDocumento7 páginasKinetics Worksheet AnswerslinaAinda não há avaliações
- Form 4 Chapter 8Documento60 páginasForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemical Kinetics MCQ - Questions - Paper 2Documento6 páginasChemical Kinetics MCQ - Questions - Paper 2sadaf yousafzaiAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 16 Answer Scheme Ver 2Documento19 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 16 Answer Scheme Ver 2Nicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Documento19 páginasSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticsDocumento12 páginasH2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticskitoniumAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Matter & The Atomic Structure ModulDocumento43 páginas1 Matter & The Atomic Structure Modulryder1man6433100% (1)
- Oxidation and ReductionDocumento21 páginasOxidation and ReductionKaroline UhlemannAinda não há avaliações
- Redox Electrochem H2 QuestionsDocumento7 páginasRedox Electrochem H2 QuestionskitoniumAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Module 1-3Documento5 páginasChem Module 1-3John CincoAinda não há avaliações
- FORM 4 ENERGY CHANGES IN CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROCESSES QUESTIONS Teacher - Co - .KeDocumento8 páginasFORM 4 ENERGY CHANGES IN CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROCESSES QUESTIONS Teacher - Co - .KeCitron Akhala100% (1)
- 49 Question Trial SPM ChemistryDocumento1 página49 Question Trial SPM ChemistrychongpeisiAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 4Documento9 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 4Nicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDocumento70 páginasKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisAinda não há avaliações
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Documento27 páginasStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15Documento26 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 15Nicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDocumento24 páginasChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundTiviya Tarini ManiamAinda não há avaliações
- Relative Atomic MassDocumento2 páginasRelative Atomic MassenyexAinda não há avaliações
- Rate Law Worksheet PDFDocumento3 páginasRate Law Worksheet PDFJunghoon Lee100% (1)
- Group 1 ElementsDocumento5 páginasGroup 1 ElementsLeong Kit WaiAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Average Atomic MassDocumento4 páginasCalculating Average Atomic MassBrenda SchroederAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 1 - Answer SchemeDocumento12 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 1 - Answer SchemeNicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- IT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Documento14 páginasIT Chem F5 SPM Model Paper (BL)Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarAinda não há avaliações
- Alkali Metals PPQDocumento6 páginasAlkali Metals PPQ张米Ainda não há avaliações
- A2 CHM Sol 05 Acid and Base WSDocumento28 páginasA2 CHM Sol 05 Acid and Base WSnsAinda não há avaliações
- CH 3 ReviewDocumento4 páginasCH 3 ReviewAref DahabrahAinda não há avaliações
- Pioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsDocumento31 páginasPioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsTimothy HandokoAinda não há avaliações
- JC H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocumento13 páginasJC H2 Chemistry Prelim Paperschong56Ainda não há avaliações
- A1 Bonding WS5Documento13 páginasA1 Bonding WS5Ashani0001Ainda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSDocumento29 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 15 MSNicholas Ow100% (1)
- EJSK SK025 Physical PropertiesDocumento30 páginasEJSK SK025 Physical PropertieschiaAinda não há avaliações
- A2 CHM 01 Energetics NotesDocumento16 páginasA2 CHM 01 Energetics NotesMuhammad Saif AmirAinda não há avaliações
- WS Household Electricity 2014 (Sol)Documento4 páginasWS Household Electricity 2014 (Sol)Lowry GuettaAinda não há avaliações
- Ib PPT 3 SL PDFDocumento24 páginasIb PPT 3 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra Practice: Name: - CL Ass: 2H2Documento11 páginasAlgebra Practice: Name: - CL Ass: 2H2Timothy HandokoAinda não há avaliações
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerDocumento36 páginasUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- Cie QDocumento17 páginasCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- Worksheet Chapter 5Documento9 páginasWorksheet Chapter 5Maktok Azi RahimAinda não há avaliações
- Unity Secondary School Physics Chapter 22: Electromagnetic Induction AnswersDocumento20 páginasUnity Secondary School Physics Chapter 22: Electromagnetic Induction AnswersFrancis Ho HoAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 20 Answer SchemeDocumento19 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 20 Answer SchemeNicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDocumento12 páginasH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoAinda não há avaliações
- Thermo Kin Ws CompleteDocumento20 páginasThermo Kin Ws CompleteMohommad YawariAinda não há avaliações
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 19Documento16 páginast2 Chem Revision Ex 19Nicholas OwAinda não há avaliações
- Rate of ReactionDocumento20 páginasRate of ReactionQueen BlehAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 9 - The Periodic Table - TutorialDocumento33 páginasTopic 9 - The Periodic Table - TutorialMOHAMED SHAMIR BIN TAJUDEENAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kDocumento22 páginasChemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kJamaludin Abu KassimAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Paper 3 SampleDocumento3 páginasChemistry Paper 3 Samplerihdus2100% (2)
- Rate of Reaction NotesDocumento27 páginasRate of Reaction NotesYong SiewkuanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter F5: Changing Matter: Topic NotesDocumento8 páginasChapter F5: Changing Matter: Topic NotesdavidteoAinda não há avaliações
- Linear LawDocumento4 páginasLinear LawJoann NgAinda não há avaliações
- Asrjc QPDocumento24 páginasAsrjc QPLorraine HoonAinda não há avaliações
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNo EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsAinda não há avaliações
- Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisNo EverandEnzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Quiz #2 Agents, Spontaneous Reactions, Oxidation #'S, and StrengthDocumento1 páginaQuiz #2 Agents, Spontaneous Reactions, Oxidation #'S, and Strengthdanielmahsa0% (1)
- OCR A2 Chemistry Student Teacher Technician Worksheets Activity 5Documento3 páginasOCR A2 Chemistry Student Teacher Technician Worksheets Activity 5danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Lattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsDocumento2 páginasLattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Trial Examination April 2017 Paper 1 MSDocumento1 páginaTrial Examination April 2017 Paper 1 MSdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Titration Questions Set 1Documento8 páginasTitration Questions Set 1danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- As Chem Question 7Documento3 páginasAs Chem Question 7danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- As Chem Atomic Structure Question 2Documento1 páginaAs Chem Atomic Structure Question 2danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Test 4Documento1 páginaTest 4danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- At Room Temperature, Both Sodium Metal and Sodium Chloride Are Crystalline Solids Which Contain IonsDocumento3 páginasAt Room Temperature, Both Sodium Metal and Sodium Chloride Are Crystalline Solids Which Contain IonsdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 2 Questions For Trial ExaminationDocumento8 páginasPaper 2 Questions For Trial ExaminationdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch7SumMARY AlkeneDocumento2 páginasCh7SumMARY AlkenedanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- As Chemistry CIE Question 1Documento3 páginasAs Chemistry CIE Question 1danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- SAQ Ans 1Documento2 páginasSAQ Ans 1danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch7Summary AlcoholDocumento6 páginasCh7Summary AlcoholdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Paper 5 Question Week 2Documento2 páginasPaper 5 Question Week 2danielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch7SumMARY ALAKNEDocumento2 páginasCh7SumMARY ALAKNEdanielmahsaAinda não há avaliações
- Dzung Quat RefineryDocumento67 páginasDzung Quat Refinerytungxuanbr100% (1)
- Distortions: M. Vedani Failure and Control of Metals - AY 2020/21Documento7 páginasDistortions: M. Vedani Failure and Control of Metals - AY 2020/21MarcoAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid Mechanics and HyderalicDocumento549 páginasFluid Mechanics and HyderalicMuhammad Aslam100% (2)
- Air On The Move (Coanda Effect)Documento35 páginasAir On The Move (Coanda Effect)ႏ်ဴမာန္ မိုးတားAinda não há avaliações
- 17Documento3 páginas17JosafatAinda não há avaliações
- Sterilization 2Documento8 páginasSterilization 2RhiaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Brouchure PDFDocumento16 páginasChem Brouchure PDFPirpasha UjedeAinda não há avaliações
- General Sizing Spreadsheet Equation SheetDocumento3 páginasGeneral Sizing Spreadsheet Equation SheetNellaiappa1975 DuraiAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used For Wastewater TreatmentDocumento11 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used For Wastewater TreatmentGirish GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Example Problems ConductionDocumento9 páginasExample Problems ConductionAJ100% (1)
- Geotechnical Engineering-IIDocumento1 páginaGeotechnical Engineering-IISubhadip GhosalAinda não há avaliações
- HW8 CLL121Documento1 páginaHW8 CLL121sanskar soniAinda não há avaliações
- Year 10 Loft Insulation CourseworkDocumento4 páginasYear 10 Loft Insulation CourseworkNosh AnbreenAinda não há avaliações
- Aqsoa 1210eDocumento4 páginasAqsoa 1210em.khurana093425Ainda não há avaliações
- 2 3Documento2 páginas2 3Nhimrod SanjoseAinda não há avaliações
- Dep 7Documento28 páginasDep 7BiswasAinda não há avaliações
- cOMMISSIONING 1 - WorksheetDocumento60 páginascOMMISSIONING 1 - WorksheetPramod Dhir100% (1)
- BJ Frac Manual v10 June 2005a4 5 PDF FreeDocumento265 páginasBJ Frac Manual v10 June 2005a4 5 PDF FreeFabianChainBenavidesAinda não há avaliações
- SNO-I-DS-003 - C2 Data Sheet For Control ValvesDocumento132 páginasSNO-I-DS-003 - C2 Data Sheet For Control Valvesono_czeAinda não há avaliações
- Esquema Hidraulico Rbb1-1127Documento2 páginasEsquema Hidraulico Rbb1-1127David Turpo100% (1)
- 07A - Chapter 7 - Sec 7.1-7.3, App F - BlackDocumento14 páginas07A - Chapter 7 - Sec 7.1-7.3, App F - BlackStevina LangrimariAinda não há avaliações
- Aeroshell Fluid 31Documento1 páginaAeroshell Fluid 31Mohammed BabatinAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid-Fueled Strut-Based Scramjet Combustor Design: A Computational Fluid Dynamics ApproachDocumento8 páginasLiquid-Fueled Strut-Based Scramjet Combustor Design: A Computational Fluid Dynamics ApproacharAinda não há avaliações
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger SpreadsheetDocumento2 páginasShell and Tube Heat Exchanger SpreadsheetHernan Cardenas Franco100% (1)
- RCU - RCUP AUZ SM Service ManualDocumento36 páginasRCU - RCUP AUZ SM Service ManualRexCrazyMind100% (3)
- WPDocumento5 páginasWPGabriel Rincón RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Psa Nitrogen GeneratorDocumento7 páginasPsa Nitrogen GeneratorFarjallahAinda não há avaliações
- Api682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsDocumento62 páginasApi682 Iso21049 John Crane General CommentsMixtli Garcia100% (4)
- An Evaluation of Ablation Mechanisms For The Apollo Heat Shield MaterialDocumento7 páginasAn Evaluation of Ablation Mechanisms For The Apollo Heat Shield MaterialKanishka LankatillakeAinda não há avaliações
- Plane Strain & Plane StressDocumento3 páginasPlane Strain & Plane Stressbadr amAinda não há avaliações