Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Granite Slurry
Enviado por
Chandan BleeDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Granite Slurry
Enviado por
Chandan BleeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
SOIL STABILIZATION USING STONE-SLURRYWASTE RECOVERED FROM CUTTING STONE PROCESS IN ROCK QUARRIES
Journal Publisher ISSN Subject Issue Pages DOI Online Date The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management Widener University 1088-1697 Environment, solid waste and waste management Volume 37, Number 2 / May 2011 141-152 10.5276/JSWTM.2011.141 Monday, June 27, 2011
Add to marked items Add to shopping cart Add to saved items Recommend this article
PDF (474.7 KB) Authors Mousa F. Attom , Magdi El-Emam
1 1 1
Civil Engineering Department, American University of Sharjah
Abstract This paper investigated the effect of using cutting stones slurry waste (SSW) as a stabilizing material with clay soil. For this study, three types of clayey soils with different plasticity indices and different clay fractions were selected to be used. Physical properties of the clayey soils such as Atterberg's limits, maximum dry density, optimum water content, specific gravity, and clay fraction were evaluated in accordance with American Standard for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standard specification. The testing program includes measurement of cohesion, angle of internal friction and unconfined compressive strength of soil samples, remolded and compacted at different water content and different SSW content. For unconfined compression tests, two sets of soil samples were prepared to be identical in all physical properties except the type of fluid that is occupying the voids. The first set (i.e. unstabilized soil) was prepared by mixing a specific weight of pure water with pre-determined weight of clay solids and compact it to reach specific water content and dry density. However, in the second set (i.e. stabilized soil) a weight of clay solids similar to that used in the first set is mixed with an amount of SSW that has weight similar to the pure water used in the first set. Four different initial dry densities at each soil type with the same water content (unstabilized soil) or with the same SSW content (stabilized soil) have been used. For direct shear test, six specimens of each soil type (i.e. three for unstabilized soil and three for stabilized soil) are prepared at maximum dry density and optimum water content, or optimum SSW content. Results indicated that mixing the clay soil with cutting stone slurry waste increased maximum dry density and decreased optimum water content. Also, both unconfined and direct shear strength and stiffness were improved significantly due to the addition of stone slurry waste to the clay soil. Finally, it was found that the cutting stone slurry waste has more effect on soil with high plasticity. Keywords Shear strength, soil stabilization, clay, stiffness, slurry waste
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
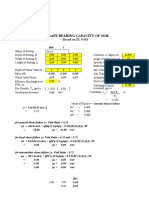
- Calculation of Safe Bearing Capacity of Soil: - Based On IS: 6403Documento31 páginasCalculation of Safe Bearing Capacity of Soil: - Based On IS: 6403sourabh_gupta_54100% (1)
- Floating Concrete StructuresDocumento27 páginasFloating Concrete StructuresSharath JagadeeshanAinda não há avaliações
- Pile Foundations PhotosDocumento26 páginasPile Foundations PhotosChandan Blee100% (1)
- The Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Homeopathy, Vaccination and Autism Website Dr. Tinus SmitsDocumento58 páginasThe Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Post-Vaccination Syndrome - Homeopathy, Vaccination and Autism Website Dr. Tinus SmitsChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Lec 1 Properties and Handling of Particulate SolidsDocumento95 páginasLec 1 Properties and Handling of Particulate SolidsAli HasSsanAinda não há avaliações
- Masonry NotesDocumento34 páginasMasonry NotesNisar Khan80% (5)
- BakemonogatariDocumento62 páginasBakemonogatarimarcipanmacsekAinda não há avaliações
- Thomas Kamps Model Jet EnginesDocumento109 páginasThomas Kamps Model Jet EnginesMustafa Umut Sarac100% (2)
- HeaterDocumento4 páginasHeaterManoloEskobarAinda não há avaliações
- 723 SF6 Measurument GuideDocumento75 páginas723 SF6 Measurument Guidefajar9nugraha-2100% (1)
- CHM170L Exp2 DensityDocumento6 páginasCHM170L Exp2 DensityKaiser SaltoAinda não há avaliações
- Kiln EquationsDocumento189 páginasKiln EquationsAnonymous NxpnI6jC100% (2)
- CompactionDocumento6 páginasCompactionChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Compensation TechniquesDocumento48 páginasCompensation TechniquesChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Cohesion and Consistency of Clay SoilsDocumento2 páginasCohesion and Consistency of Clay SoilsChandan Blee100% (1)
- Srichand MestruDocumento1 páginaSrichand MestruChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Self Boring PressuremeterDocumento8 páginasSelf Boring PressuremeterChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Paper CommunicatedDocumento1 páginaPaper CommunicatedChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- GIT MethodsDocumento17 páginasGIT MethodsChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Energy EfficiencyDocumento9 páginasMeasuring Energy EfficiencyChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Energy EfficiencyDocumento9 páginasMeasuring Energy EfficiencyChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- GIT ConceptsDocumento27 páginasGIT ConceptsChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Granite SlurryDocumento1 páginaGranite SlurryChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Durability of Cement Stabilised Earth WallsDocumento16 páginasDurability of Cement Stabilised Earth WallsChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Granite SlurryDocumento1 páginaGranite SlurryChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Ground ImprovementDocumento11 páginasGround ImprovementFauziaKusumawardhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Abstract On GITDocumento3 páginasAbstract On GITChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Isobar ChapterDocumento37 páginasIsobar ChapterNaveen BP100% (1)
- Aditya Hridayam-Meaning in EnglishDocumento9 páginasAditya Hridayam-Meaning in EnglishChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Ground ImprovementDocumento11 páginasGround ImprovementFauziaKusumawardhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Ground ImprovementDocumento11 páginasGround ImprovementFauziaKusumawardhaniAinda não há avaliações
- Unit II-Dewatering and Drainage - GT-II Study Material-Nagaraj.H.BDocumento27 páginasUnit II-Dewatering and Drainage - GT-II Study Material-Nagaraj.H.BChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Text Books On GITDocumento6 páginasText Books On GITChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- Srichand MestruDocumento1 páginaSrichand MestruChandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- 03 - Compaction Theory SlidesDocumento14 páginas03 - Compaction Theory SlidesSamuel Laura HuancaAinda não há avaliações
- Glossary 1Documento7 páginasGlossary 1Chandan BleeAinda não há avaliações
- 9 Science Imp ch1 2 PDFDocumento5 páginas9 Science Imp ch1 2 PDFParamita KaranAinda não há avaliações
- Conversion FactorsDocumento10 páginasConversion FactorsTheServitor TheServitorAinda não há avaliações
- Training at Gurjar Ki Thadi Under Pass, JaipurDocumento37 páginasTraining at Gurjar Ki Thadi Under Pass, JaipurDevendra SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Mass Transfer-1Documento38 páginasMass Transfer-1shahzadali0786Ainda não há avaliações
- As 1289.6.1.2-1998 Methods of Testing Soils For Engineering Purposes Soil Strength and Consolidation TestsDocumento2 páginasAs 1289.6.1.2-1998 Methods of Testing Soils For Engineering Purposes Soil Strength and Consolidation TestsSAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- Mass, Volume & Density: 8 Grade PhysicsDocumento19 páginasMass, Volume & Density: 8 Grade PhysicsHaniAinda não há avaliações
- Summary SectionDocumento71 páginasSummary SectionAhmed Khalil JaberAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment - 3: Highway Engineering-II 2011 E.CDocumento4 páginasAssignment - 3: Highway Engineering-II 2011 E.CABexample GgideyAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Documento16 páginasCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Nghi Ngo DongAinda não há avaliações
- Quality Control Specification Clause 900Documento33 páginasQuality Control Specification Clause 900MAULIK RAVALAinda não há avaliações
- CE 335 Practice ExamDocumento4 páginasCE 335 Practice ExamMatt CebulaAinda não há avaliações
- HCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP1 MergedDocumento13 páginasHCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP1 MergedGleanna NiedoAinda não há avaliações
- C1603.29733 - Solidos AguaDocumento4 páginasC1603.29733 - Solidos AguaEliasTalaAllcaAinda não há avaliações
- Gecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsDocumento25 páginasGecolea, ME143-2 Sample QuestionsJazztine Andrei GecoleaAinda não há avaliações
- Origin and Classification of SoilDocumento16 páginasOrigin and Classification of SoilMysti Metin MesinaAinda não há avaliações
- Lagrangian Particle TrackingDocumento35 páginasLagrangian Particle TrackingLiviuAinda não há avaliações
- Die Casting Process Optimization Using Taguchi Methods: G.P. SyrcosDocumento7 páginasDie Casting Process Optimization Using Taguchi Methods: G.P. SyrcosfaisalAinda não há avaliações
- Materials 13 04965Documento14 páginasMaterials 13 04965paulo passeiosAinda não há avaliações
- PHE - 4 Section For Ice Cream MixDocumento9 páginasPHE - 4 Section For Ice Cream MixMuhammad JunaidAinda não há avaliações
- Silos Design - Flow of PowderDocumento18 páginasSilos Design - Flow of Powdercésar vásquez osorioAinda não há avaliações
- HART User Manual V2.5-Neutral - VF7000 SeriesDocumento17 páginasHART User Manual V2.5-Neutral - VF7000 SeriesanaAinda não há avaliações
- خرسانة عملي الفصل الاول والثانيDocumento58 páginasخرسانة عملي الفصل الاول والثانيAhmed AlyasAinda não há avaliações