Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
sm1 62
Enviado por
tommypurdueDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
sm1 62
Enviado por
tommypurdueDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PROBLEM 1.
62
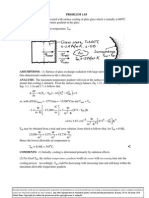
KNOWN: Duct wall of prescribed thickness and thermal conductivity experiences prescribed heat flux q o at outer surface and convection at inner surface with known heat transfer coefficient. FIND: (a) Heat flux at outer surface required to maintain inner surface of duct at Ti = 85C, (b) Temperature of outer surface, To , (c) Effect of h on To and q o. SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) Steady-state conditions, (2) One-dimensional conduction in wall, (3) Constant properties, (4) Backside of heater perfectly insulated, (5) Negligible radiation.
ANALYSIS: (a) By performing an energy balance on the wall, recognize that q o = q cond . From an energy balance on the top surface, it follows that q cond = q conv = q o . Hence, using the convection rate equation,
2 2 q o = q conv = h ( Ti T ) = 100 W / m K ( 85 30 ) C = 5500W /m . (b) Considering the duct wall and applying Fouriers Law,
<
q o =k
T T T =k o i L X
q L 5500 W/m 2 0.010 m D = ( 85 + 2.8 ) C = 87.8D C . To = Ti + o = 85D C + k 20 W/m K (c) For Ti = 85C, the desired results may be obtained by simultaneously solving the energy balance equations To Ti T Ti and q k o = h ( Ti T ) o =k L L Using the IHT First Law Model for a Nonisothermal Plane Wall, the following results are obtained.
12000
Surface temperature, To(C)
<
91 90 89 88 87 86 85
10000
Heat flux, q''o(W/m^2)
8000 6000 4000 2000 0 0 40 80 120 160 200 Convection coefficient, h(W/m^2.K)
40
80
120
160
200
Convection coefficient, h(W/m^2.K)
Since q conv increases linearly with increasing h, the applied heat flux q o and q cond must also increase. An increase in q cond , which, with fixed k, Ti and L, necessitates an increase in To .
COMMENTS: The temperature difference across the wall is small, amounting to a maximum value of ( To Ti ) = 5.5C for h = 200 W/m2K. If the wall were thinner (L < 10 mm) or made from a material
with higher conductivity (k > 20 W/mK), this difference would be reduced.
Excerpts from this work may be reproduced by instructors for distribution on a not-for-profit basis for testing or instructional purposes only to students enrolled in courses for which the textbook has been adopted. Any other reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Fourier Number: 2 ReferencesDocumento2 páginasFourier Number: 2 Referencesrogerio_felix_38100% (1)
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDocumento5 páginasShell and Tube Heat Exchanger DesignDominic CareoAinda não há avaliações
- 4A'S Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Documento7 páginas4A'S Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Dina ReclaAinda não há avaliações
- Design Practices-ReboilerDocumento7 páginasDesign Practices-Reboileragarwalashwin32100% (1)
- Heat Geek Mastery Workbook Home Print OffDocumento101 páginasHeat Geek Mastery Workbook Home Print OffJason HaywardAinda não há avaliações
- Data Sheet - Gas-Gas Heat ExchangerDocumento1 páginaData Sheet - Gas-Gas Heat ExchangerPrabhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Climatic Zones of IndiaDocumento3 páginasClimatic Zones of Indiaa_j_sanyalAinda não há avaliações
- BS en 1264-1-2021Documento34 páginasBS en 1264-1-20217620383tlAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.73 (B) K NOWN: Configuration of A Flat Plate Solar Collector. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes With and Without A Cover Plate. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.73 (B) K NOWN: Configuration of A Flat Plate Solar Collector. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes With and Without A Cover Plate. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.73 (C) K NOWN: Configuration of A Solar Collector Used To Heat Air For Agricultural Applications. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.73 (C) K NOWN: Configuration of A Solar Collector Used To Heat Air For Agricultural Applications. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.73 (A) K NOWN: Room Air Is Separated From Ambient Air by One or Two Glass Panes. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.73 (A) K NOWN: Room Air Is Separated From Ambient Air by One or Two Glass Panes. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.73 (D) K NOWN: Features of An Evacuated Tube Solar Collector. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes For One of The Tubes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.73 (D) K NOWN: Features of An Evacuated Tube Solar Collector. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes For One of The Tubes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- 4 4 G J S J: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976Documento1 página4 4 G J S J: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976tommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (A) K NOWN: Solar Radiation Is Incident On An Asphalt Paving. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.72 (A) K NOWN: Solar Radiation Is Incident On An Asphalt Paving. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (D) K NOWN: Tungsten Filament Is Heated To 2900 K in An Air-Filled Glass Bulb. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.72 (D) K NOWN: Tungsten Filament Is Heated To 2900 K in An Air-Filled Glass Bulb. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (E) K NOWN: Geometry of A Composite Insulation Consisting of A Honeycomb Core. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.72 (E) K NOWN: Geometry of A Composite Insulation Consisting of A Honeycomb Core. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- sm1 71Documento2 páginassm1 71tommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (G) K NOWN: Fireplace Cavity Is Separated From Room Air by Two Glass Plates, Open at Both Ends. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematicDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.72 (G) K NOWN: Fireplace Cavity Is Separated From Room Air by Two Glass Plates, Open at Both Ends. F IND: Relevant Heat Transfer Processes. SchematictommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (B) KNOWN: Physical Mechanism For Microwave Heating. FIND: Comparison of (A) Cooking in A Microwave Oven With A Conventional Radiant orDocumento1 páginaPROBLEM 1.72 (B) KNOWN: Physical Mechanism For Microwave Heating. FIND: Comparison of (A) Cooking in A Microwave Oven With A Conventional Radiant ortommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- PROBLEM 1.72 (C) : To Fuel Cell To Fuel CellDocumento2 páginasPROBLEM 1.72 (C) : To Fuel Cell To Fuel CelltommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- sm1 70Documento1 páginasm1 70awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 67Documento1 páginasm1 67awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 68Documento1 páginasm1 68awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 66Documento1 páginasm1 66awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 56Documento1 páginasm1 56awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 69Documento2 páginassm1 69tommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- sm1 61Documento1 páginasm1 61awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 65Documento1 páginasm1 65tommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- sm1 64Documento2 páginassm1 64awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 57Documento2 páginassm1 57awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 55Documento2 páginassm1 55awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 63Documento1 páginasm1 63awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 59Documento2 páginassm1 59awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 58Documento2 páginassm1 58awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 60Documento2 páginassm1 60awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 54Documento1 páginasm1 54awoods12835Ainda não há avaliações
- sm1 53Documento1 páginasm1 53tommypurdueAinda não há avaliações
- Measuring Temperature at the North PoleDocumento4 páginasMeasuring Temperature at the North PoleJoanne Cheah100% (1)
- Experimental Study of Convective Heat Transfer by Using Aluminum Pin-Fin With Metal Matrix CompositesDocumento5 páginasExperimental Study of Convective Heat Transfer by Using Aluminum Pin-Fin With Metal Matrix CompositesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Engine Heat TransferDocumento37 páginas10 Engine Heat TransferArsalan AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Heating and Air Conditioning1 PDFDocumento38 páginasHeating and Air Conditioning1 PDFmercil88Ainda não há avaliações
- CH 02 - Intro To HVAC SystemsDocumento38 páginasCH 02 - Intro To HVAC SystemsKamaruz DanialAinda não há avaliações
- HCHEM Notes Specific Heat Capacity 3 2Documento21 páginasHCHEM Notes Specific Heat Capacity 3 2leimendozaschoolAinda não há avaliações
- Black Body Radiation StudyDocumento7 páginasBlack Body Radiation StudyxGamma AIAinda não há avaliações
- Central Lennox Inverter BrochureDocumento4 páginasCentral Lennox Inverter BrochurecleansafeptyAinda não há avaliações
- Specific Heat CapacityDocumento2 páginasSpecific Heat CapacitysagesethAinda não há avaliações
- 132 KV Maithan Smelter FeederDocumento4 páginas132 KV Maithan Smelter Feederbiren dasAinda não há avaliações
- Mazda 121 CoolingDocumento14 páginasMazda 121 CoolingLuix AriaxAinda não há avaliações
- Aplikasi HE Baru 8095 PDFDocumento5 páginasAplikasi HE Baru 8095 PDFAndre KusadyAinda não há avaliações
- BOILING AND CONDENSATION: KEY CONCEPTSDocumento19 páginasBOILING AND CONDENSATION: KEY CONCEPTSnivasssvAinda não há avaliações
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocumento34 páginasConduction Convection RadiationlintangnurAinda não há avaliações
- Modelling and Simulation of Absorption Solar Air Conditioning SystemDocumento20 páginasModelling and Simulation of Absorption Solar Air Conditioning SystemShadi KarkabaAinda não há avaliações
- HVAC Investigation: Window Air ConditionersDocumento5 páginasHVAC Investigation: Window Air ConditionersJadenAinda não há avaliações
- HVAC Equipment Inventory Project DataDocumento10 páginasHVAC Equipment Inventory Project DataGERARDO CAMPOSAinda não há avaliações
- INGM 427 Slides - 5 Cooling TowersDocumento17 páginasINGM 427 Slides - 5 Cooling TowersCornelius RheedersAinda não há avaliações
- As 2243.4-1998 Safety in Laboratories Ionizing RadiationsDocumento9 páginasAs 2243.4-1998 Safety in Laboratories Ionizing RadiationsSAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- Q DT /DX:) ) Rsub (X) ( (W) Over ( (M) (2) )Documento8 páginasQ DT /DX:) ) Rsub (X) ( (W) Over ( (M) (2) )Aiza AlbuferaAinda não há avaliações
- HMT Minor1Documento1 páginaHMT Minor1ISHU SHUKRALIAAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Transfer of Fluids Inside PipesDocumento25 páginasHeat Transfer of Fluids Inside Pipesbronxtoles4ever100% (1)