Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
TopicVI Busines Intelligent Systems PDF
Enviado por
Rohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
TopicVI Busines Intelligent Systems PDF
Enviado por
Rohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
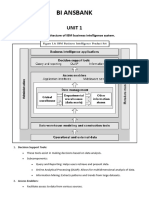
INS 601 MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Topic VI Business Intelligent Systems
Decision Support systems
Business Intelligence Systems Level of management Decision making Information Quality Dimensions Management Information systems DSS
DSS Types DSS Components DSS Analyses
A.I in Business
Neural Networks Fuzzy Logic Virtual Reality Expert System
Business Intelligence Systems
Applications & Technologies that focus on: Gathering Storing Analysing Providing Access to data
From many different sources to help users make better business decisions. eg MIS, DSS, Artificial Intelligence based systems
Decisions in the E-Business
Decision Characteristics
Unstructured Excutive Level
In rm fo
Information Characteristic Ad-Hoc, Unscheduled, Wide Scope
cis i
Semistructured
on
io at
De
Management Level
Structured
Operational Level
Pre-specified, Detailed, Narrow Scope
Decisions in the E-Business
Strategic Management: Board of Directors, CEOs etc
They develop overall organisational goals, strategies, policies as part of strategic planning process.
Tactical Management: General Manager, Divisional Director
They develop short & medium range plans. They allocate resources and monitor performance of their subunits.
Operational Management: Operational Managers, Supervisors etc
They direct the use of resources and performance of tasks according to procedures and within budgets & schedules.
Attributes of Decision Making
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
Information, Decisions & Management
Three Dimensions of Information Quality
Time
Content
Form
Information Quality Dimensions
Time Dimension : Timeliness Frequency Currency Time Period Content Dimension : Accuracy Relevance Completeness Performance
Information Quality Dimensions
Form Dimension :
Clarity Detail Order Presentation Media
10
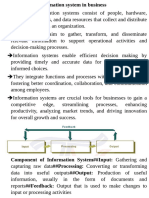
Management Information Systems [MIS]
MIS primarily provide information on the firms performance to help managers in monitoring & controlling the business. They typically produce fixed, regularly scheduled reports based on the data extracted and summarized from the organisations underlying TPS.
11
Management Information System Reports
Scheduled Scheduled Reports Reports Exception Exception Reports Reports
Major Management Information Systems Reports
Demand Demand Reports Reports Push Push Reports Reports
12
MIS Reports:
Periodic Scheduled Reports:
This traditional form of providing information to managers uses a prespecified format designed to provide managers with information on a regular basis. eg: Daily or weekly Sales Analysis Reports, Monthly Financial Statements.
Exception Reports:
These reports are produced only when exception occurs. In some cases, reports are produced periodically, but contain information only about these exceptional conditions. eg: Credit Managers can be provided with a report that contains only information on customers who exceed their credit limits.
13
MIS Reports:
Demand Report:
Information is available only when a manager demands it. eg : Query Languages & Report Generators enable managers at PC workstations to get immediate responses or obtain customised reports as a result of their requests for the information they need.
Push Report:
Information is PUSHED to a managers networked workstation. eg: Many companies are using web casting software to selectively broadcast reports and other information to the networked PCs of managers and specialists over their corporate Intranets.
14
MIS Examples:Organisation
MIS Application
California Pizza Kitchen
Inventory Express applications remember each restaurants ordering patterns and compares the amount of ingredients used per menu item to predefined portion measurements established by management. The system identifies restaurants with out-of-line portions and notifies their management so that corrective action can be taken.
15
Decision Support Systems
DSS are computer based Information Systems that provide interactive information support to managers & business professionals during the decision making process.
DSS systems are :1. Analytical Models. 2. Specialized databases. 3. An Interactive computer based modeling process to support the making of semi structured & unstructured business decisions.
16
Components of a DSS
17
MODEL Driven DSS
Model Driven DSS were primarily stand alone systems isolated from major organisational Information systems that used some type of model to perform What-if analysis or Sensitivity analysis. Such systems were often developed by end user divisions or groups not under central Information system control. Their analysis capabilities were based on a strong theory or model combined with a good user interface that made the model easy to use.
Model Driven DSS
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
18
19
What If ? Analysis
This analysis involves observing how changes to selected variables, or relationships among variables result into changes in the values of other variables. Eg If the Advertising Budget is cut by 10% - What would be the affect on Sales? This type of analysis would be repeated until the manager is satisfied with what results are revealed about affects of various possible decisions.
20
Sensitivity Analysis
This analysis observes how repeated changes to a single variable affect other variables? Sensitivity analysis is a special case of What if? analysis where typically the value of only one variable is changed repeatedly and the resulting changes on other variables are observed. e.g. Lets cut advertising budget repeatedly by $100 so we can see its impact on sales?
21
Goal Seeking Analysis
(How Can? Analysis)
This involves making repeated changes to select variables until a chosen variable reaches a target value. This reverses the direction of the analysis done in What if & Sensitivity analysis. eg. Lets try increasing the advertising budget until Sales reach $ 1 Million.
22
Optimisation Analysis
This involves finding an optimum value for selected variables ( given certain constraints) Optimisation Analysis is more complex extension of Goal seeking analysis. Instead of setting a specific target value for one or more target variables, giving certain constraints. eg. Whats the best amount of adverting to have given our budget and choices of media?
23
Online Analytical Processing
OLAP enables managers and analysts to interactively examine & manipulate large amounts of detailed & consolidated data from many perspectives. OLAP involves analyzing complex relationships among 1000s or even millions of data items stored in multi-dimensional databases to discover patterns, trends & exception conditions.
24
Online Analytical Processing
Data is retrieved from corporate databases and staged in an OLAP multi-dimensional database
Client PC
OLAP OLAP Server Server
Corporate Databases
Web-enabled OLAP Software
Multidimensional database
Operational DB Data Marts Data Warehouse
OLAP analytical operations:-
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
25
26
OLAP analytical operations:
Consolidation: Consolidation involves the aggregation of data. This can involve simple roll-ups or complex groupings.
eg SALES Data can be rolled up to DISTRICT level from OFFICE level.
Drill Down: OLAP can go in the reverse direction and automatically display detail data that comprise consolidated data. This process is called Drill Down.
eg SALES figures of Individual products.
27
OLAP analytical operations:
Slicing & Dicing: Slicing & Dicing refers to the ability to look at the database from different viewpoints. eg
One Slice: of Sales database would be all sales of product type within all regions. Another Slice: of Sales database might show all sales channel within each product type.
Slicing & Dicing is often performed along a time axis in order to analyse trends & find time based patterns in the data.
28
Components of a DSS DSS Database
DSS Database is a collection of current or
historical data from a number of applications. It may be a small database residing on a PC, combined with external data or a huge data warehouse. The data in DSS database are copies of Production databases so that using the DSS does not interfere with critical operational systems.
29
Components of a DSS DSS Software System
It contains software tools that are used for data analysis. It contains : OLAP tools Data mining Tools
30
Components of a DSS DSS User Interface
The DSS user interface permits easy interaction between users of the system and the DSS software Tools. A Graphical, Easy-to-use, flexible user interface supports a dialogue between the user & the DSS. DSS requires a high level of user participation to make sure that the system provides the information needed by the managers.
31
Group Decision Support Systems
DSS focus primarily on Individual Decision Making. But much of the work is accomplished in Groups within groups, hence a special category of DSS has been developed to support group decision making GDSS.
32
GDSS
A GDSS is an interactive computer based system to facilitate the solution of unstructured problems by a set of decision makers working together as a group. GDSS make meetings more productive by providing tools to facilitate planning, generating, organizing and evaluating ideas, establishing priorities & documenting meeting proceeding for others in organisations.
GDSS Components
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
33
34
GDSS Components
Hardware: It includes : Electronic Hardware:
Electronic Display Boards Audio Visuals Computers Networking Equipments
Conference Facilities:
ROOM CHAIRS TABLES
Laid out in a manner that supports Group Collaboration
35
GDSS Components
Software Tools:Although groupware tools for collaborative work can be used to support Group Decision Making, there are specific GDSS tools for supporting Group Meetings. These tools were originally developed for meetings in which all participants are in the same room, but they can be used for networked meetings in which participants are in different locations.
36
GDSS Software TOOLS
Electronic Questionnaires Electronic Brain Storming Tools Idea Organizers Questionnaire tools Tools for voting or setting priorities Stakeholder Identification & Analysis Tools Policy Formation Tools Group Dictionaries
37
Collaboration Laboratories
In a collaboration laboratory, individuals work on their own desktop PCs or workstations. Their Input is integrated on a file server and is viewable on a common screen to all participants. In most systems the integrated Input is also viewable on the individual participant's screen
38
Electronic Meeting System
In an EMS :Each attendee has a workstation. The workstations are networked and connected to the facilitators console, which acts as Control panel for the meeting. Attendees have full control over their own desktop systems can work on PC tools or on the screen associated with current meeting agenda & tools. During the meeting, all input to the integrated screens is saved on the file server & the participants work is kept confidential. On completion of meeting, the full record of the meeting is available to anyone in need for access
39
Overview of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of Science &
Technology based on disciplines such as
Computer Science Biology Linguistics Mathematics Engineering
The Goal of (AI) is to develop computers that can
Think Hear See Walk Talk Feel Like Humans
40
Overview of AI
A Major thrust in is to develop computer functions
normally associated with Human Intelligence:
Reasoning Learning Problem Solving
Turing Test (Alan Turing 1950)
According to this test, a computer could demonstrate intelligence if a human interviewer conversing with an unseen human or an unseen computer could not tell which is which.
41
AI Application Areas in Business
Neural Neural Networks Networks
Fuzzy Fuzzy Logic Logic Systems Systems Virtual Virtual Reality Reality
AI AIApplication Application Areas Areasin in Business Business
Expert Expert Systems Systems
42
Neural Networks
Neural Networks are computing systems modeled
after the brains mesh-like network of interconnected processing elements called as neurons. Like the brain, the interconnected processors in a neural network operate in parallel and interconnect dynamically with each other, enabling the network to learn from data it processes.
43
Neural Networks
44
Neural Networks
A neural network can be trained to learn which
credit characteristics can lead to :
Good Loan Bad Loan
In the above example the developers of the
neural network can provide it with data from many examples of credit applications and loan results to process the knowledge in Neurons
45
Fuzzy Logic Systems
Fuzzy Logic systems represents a small but gradually growing application of AI in business. Fuzzy Logic resembles Human reasoning as it allows approximate values and inferences and incomplete or ambiguous data instead of relying on crisp data such as Yes/No choices.
Fuzzy Logic Systems
Fuzzy Logic systems consist of:-
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
46
47
Fuzzy Logic Systems Credit Analysis Application
Fuzzy Logic Rules If INCOME is INCREASING Then RISK is somewhat DECREASING If CASH RESERVES are LOW Then RISK is very INCREASED
Fuzzy Logic SQL Query
SELECT companies FROM database WHERE Revenues are very HIGH AND (Income/Total Employee) Ratio is Reasonable.
48
Fuzzy Logic Systems
Notice that Fuzzy Logic uses terminology such as Very High, Increasing, Somewhat Decreasing. This enables Fuzzy Systems to process incomplete data and quickly provide approximate but acceptable solutions to problems that are difficult for other methods to solve.
49
Virtual Reality
VR is a computer simulated reality, and is a fast
growing area of AI that had its origins in efforts to build more natural, multi sensory human computer interfaces. VR relies on multi sensory I/O devices such as
Tracking Headset with Video Goggles & Stereo phones. Data glove with fiber optic sensors that track your body movements. A Walker that monitors the movement of your feet.
50
Virtual Reality
51
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality - Applications
INS 601
23rd May 2011 Akre
Vishwesh
52
53
Expert Systems
A Knowledge Based Information System (KBIS) adds a knowledge base to the major components found in other types of CBIS. An Expert System (ES) is a KBIS that uses its knowledge about a specific complex application area to act as an expert consultant to end users. Expert Systems provide answers to questions in a very specific problem area by making human like inferences about knowledge contained in a specialized knowledge base.
54
Components of Expert Systems
The Expert System
Expert Advice
User User Interface Interface Programs Programs
Inference Inference Engine Engine Program Program
Knowledge Base
User
Workstation
Expert System Development
Knowledge Engineering
Knowledge Knowledge Acquisition Acquisition Program Program Workstation
Expert and/or Knowledge Engineer
55
Expert Systems - Components
Knowledge Base
1. Facts about a specific area 2. Heuristics (rules of thumb) that expresses the reasoning
procedures of an Expert on the subject.
Software Resources
1. Inference Engine 2. Software User Interface 3. Knowledge acquisition programs
56
Expert System Applications
Decision DecisionManagement Management Diagnostic/Troubleshooting Diagnostic/Troubleshooting Maintenance/Scheduling Maintenance/Scheduling Design/Configuration Design/Configuration
Major Application Categories of Expert Systems
Selection/Classification Selection/Classification Process ProcessMonitoring/Control Monitoring/Control
57
Expert Systems can be used to accomplish many business tasks:
Decision Management. This includes systems
that appraise situations or consider alternatives and make recommendations based on criteria supplied during the discovery process. Examples include loan portfolio analysis, employee evaluation, insurance underwriting, demographic forecasts.
58
Expert Systems can be used to accomplish many business tasks: Diagnostic/Troubleshooting. This is the use of
systems that infer underlying causes from reported symptoms and history. Examples include equipment calibration, help desk operations, software debugging, medical diagnosis. Maintenance/Scheduling. This includes systems that prioritize and schedule limited or time-critical resources. Examples include maintenance scheduling, production scheduling, education scheduling, project management.
59
Expert Systems can be used to accomplish many business tasks: Design/Configuration. This is the use of systems that help configure equipment components, given existing constraints that must be taken into account. Examples include computer option installation, manufacturability studies, communications networks, optimum assembly plan. Selection/Classification. These are systems that help users choose products or processes from among large or complex sets of alternatives. Examples include material selection, delinquent account identification, information classification, suspect identification.
60
Expert Systems can be used to accomplish many business tasks: Process Monitoring/Control. This includes systems that monitor and control procedures or processes. Examples include machine control (including robotics), inventory control, production monitoring, chemical testing. Expert systems provide a business with faster, consistent expertise. They also help preserve organizational knowledge. However, they are not without limitations. ES are not suitable for every problem situation. They excel only in solving specific types of problems in a limited domain of knowledge. They fail to solve problems requiring a broad knowledge base. Expert Systems are also difficult and costly to develop and maintain.
Você também pode gostar
- Vq40de Service ManualDocumento257 páginasVq40de Service Manualjaumegus100% (4)
- MISDocumento9 páginasMISSaurabh JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Music Production EngineeringDocumento1 páginaMusic Production EngineeringSteffano RebolledoAinda não há avaliações
- MIS - Past Years Papers With SolutionDocumento60 páginasMIS - Past Years Papers With SolutionArvindYadavAinda não há avaliações
- Bill of Quantities 16FI0009Documento1 páginaBill of Quantities 16FI0009AJothamChristianAinda não há avaliações
- The Future of FinanceDocumento30 páginasThe Future of FinanceRenuka SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Case ColorscopeDocumento7 páginasCase ColorscopeRatin MathurAinda não há avaliações
- Present Tenses ExercisesDocumento4 páginasPresent Tenses Exercisesmonkeynotes100% (1)
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Partnership Digest Obillos Vs CIRDocumento2 páginasPartnership Digest Obillos Vs CIRJeff Cadiogan Obar100% (9)
- Knight's Microsoft Business Intelligence 24-Hour Trainer: Leveraging Microsoft SQL Server Integration, Analysis, and Reporting Services with Excel and SharePointNo EverandKnight's Microsoft Business Intelligence 24-Hour Trainer: Leveraging Microsoft SQL Server Integration, Analysis, and Reporting Services with Excel and SharePointNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (1)
- 03 Business Process IS (TPS, MIS, DSS, ESS)Documento62 páginas03 Business Process IS (TPS, MIS, DSS, ESS)Shivangi AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-Decision Support System (DSS) (Domain-3)No EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-Decision Support System (DSS) (Domain-3)Ainda não há avaliações
- MB0047 Semester II, Set 2 SMU Assignments (Winter Drive 2011-Exams May 2012)Documento17 páginasMB0047 Semester II, Set 2 SMU Assignments (Winter Drive 2011-Exams May 2012)sahuja_25Ainda não há avaliações
- MB0047 - Management Information Systems Semester - II Assignment Set - IDocumento11 páginasMB0047 - Management Information Systems Semester - II Assignment Set - ISantosh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Q1. What Is MIS? Define The Characteristics of MIS? What Are The Basic Functions of MIS? Give Some Disadvantage of MIS? AnswerDocumento19 páginasQ1. What Is MIS? Define The Characteristics of MIS? What Are The Basic Functions of MIS? Give Some Disadvantage of MIS? AnswerSameer RukeAinda não há avaliações
- Information Systems For Managerial Decision SupportDocumento10 páginasInformation Systems For Managerial Decision SupportAshok YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESSDocumento49 páginasChapter 2 - GLOBAL E-BUSINESSToukyer AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Name: Haseeb Mujeeb. Roll No: 033. Class: Bba. Samester: 5 (TH) - Subject: MIS. (CH.10) Submitted To: Sir - Aneeb LashariDocumento7 páginasName: Haseeb Mujeeb. Roll No: 033. Class: Bba. Samester: 5 (TH) - Subject: MIS. (CH.10) Submitted To: Sir - Aneeb LashariHaseeb MujeebAinda não há avaliações
- Data Flow Diagrams Processes: Name: Amit Pathak ROLL NO: 1302016570Documento6 páginasData Flow Diagrams Processes: Name: Amit Pathak ROLL NO: 1302016570pkm7929Ainda não há avaliações
- 3.mis Chapter Three Computer Based IsDocumento36 páginas3.mis Chapter Three Computer Based IsEndash HaileAinda não há avaliações
- MB 0047Documento23 páginasMB 0047Rayan ZenAinda não há avaliações
- August 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0076 - Management Information Systems - 4 CreditsDocumento11 páginasAugust 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0076 - Management Information Systems - 4 CreditsChandan Singh KanyalAinda não há avaliações
- Name Imran Desai Roll No. 511010274 Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0047 - Set 1Documento39 páginasName Imran Desai Roll No. 511010274 Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0047 - Set 1imrandesaiAinda não há avaliações
- MB0047spring Drive 2012 SolvedDocumento45 páginasMB0047spring Drive 2012 Solvedtarun_h2Ainda não há avaliações
- MisDocumento41 páginasMisinnocentevilshahidAinda não há avaliações
- Streamline Business OperationsDocumento7 páginasStreamline Business OperationsBao TranAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityDocumento4 páginasAdvantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityShivansh tomarAinda não há avaliações
- Bi Unit ! CH 2Documento26 páginasBi Unit ! CH 2skyverma0709Ainda não há avaliações
- Business Analytics and Decision MakingDocumento47 páginasBusiness Analytics and Decision Makingyhh5swqrnjAinda não há avaliações
- Management Information System: Un It - 3Documento49 páginasManagement Information System: Un It - 3Bhuvana GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- Management Information System: Un It - 3Documento44 páginasManagement Information System: Un It - 3Bhuvana GanesanAinda não há avaliações
- MIS "Types of DSS"Documento12 páginasMIS "Types of DSS"maba2610100% (1)
- Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Management Information Systems Assignment MB0047 - Set 1Documento25 páginasCourse Mba - 2 Semester Subject Management Information Systems Assignment MB0047 - Set 1barthwalnishaAinda não há avaliações
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester II (Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Documento17 páginasMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester II (Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Shiv KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2Documento24 páginasChapter 2Rojesh BasnetAinda não há avaliações
- Q1. What Is MIS? Define The Characteristics of MIS? What Are The Basic Functions of MIS? Give Some Disadvantage of MIS?Documento16 páginasQ1. What Is MIS? Define The Characteristics of MIS? What Are The Basic Functions of MIS? Give Some Disadvantage of MIS?Sushanth PerambraAinda não há avaliações
- ITunit 2Documento12 páginasITunit 2ShreestiAinda não há avaliações
- MIS AssignmentDocumento23 páginasMIS AssignmentSharmila PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- CBIS (Computer Based Information System) : DataDocumento7 páginasCBIS (Computer Based Information System) : Dataخالد ناهض نايف نجمAinda não há avaliações
- BI AnsBankDocumento37 páginasBI AnsBankwacay74365Ainda não há avaliações
- 10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSDocumento6 páginas10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSJobaiyerAinda não há avaliações
- MBA Anna University-Management Information System 2 MarksDocumento24 páginasMBA Anna University-Management Information System 2 Markspadma_abivarshini92% (12)
- Computerized Information SystemDocumento25 páginasComputerized Information SystemLaxmiPantAinda não há avaliações
- Part A - Questions & Answers: Input Processing OutputDocumento15 páginasPart A - Questions & Answers: Input Processing OutputParthiban SAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Support SystemDocumento11 páginasDecision Support SystemSUBASHINIAinda não há avaliações
- Structure of MIS: Decision Support SystemDocumento19 páginasStructure of MIS: Decision Support SystemAnkur RajputAinda não há avaliações
- Course MBA - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0047 - Set 1: Production and Operations ManagementDocumento11 páginasCourse MBA - 2 Semester Subject Assignment MB0047 - Set 1: Production and Operations ManagementalokbirlaAinda não há avaliações
- CS 507 - Lect-10 - GraphicsDocumento13 páginasCS 507 - Lect-10 - GraphicsAsghar AliAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1-Decision Support SystemsDocumento10 páginasUnit 1-Decision Support SystemsDisha Verma KalraAinda não há avaliações
- ISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Documento48 páginasISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Abhishek PatilAinda não há avaliações
- Managment Information SystemDocumento64 páginasManagment Information SystemTech ProffesorAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9 - ClassDocumento24 páginasChapter 9 - Classnyra auliaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2: Information Systems in The EnterpriseDocumento37 páginasChapter 2: Information Systems in The Enterpriseak9922Ainda não há avaliações
- Management Information System: Bba LLB by The - Lawgical - WorldDocumento15 páginasManagement Information System: Bba LLB by The - Lawgical - WorldK venkataiahAinda não há avaliações
- Information Technologies: Concepts and ManagementDocumento41 páginasInformation Technologies: Concepts and ManagementParth PatadiaAinda não há avaliações
- INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 1Documento43 páginasINFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 1Thirumal Azhagan100% (1)
- MIS AssignmentDocumento7 páginasMIS AssignmentFreya LytchAinda não há avaliações
- Amity Business School: MBA, Semester - 3 Management of Software Projects Teena BaggaDocumento55 páginasAmity Business School: MBA, Semester - 3 Management of Software Projects Teena BaggaAvi KoolAinda não há avaliações
- For Sybca - Heta Desai: Student Notes On Information SystemDocumento56 páginasFor Sybca - Heta Desai: Student Notes On Information SystemHeta DesaiAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Support Systems and Executive Support SystemsDocumento33 páginasDecision Support Systems and Executive Support SystemsSakshi JindalAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Support SystemDocumento3 páginasDecision Support SystemDeeplakhan BhanguAinda não há avaliações
- Business Intelligence - Chapter 5 - TBITDocumento4 páginasBusiness Intelligence - Chapter 5 - TBITNAVNEET VANIYAAinda não há avaliações
- Decision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Documento8 páginasDecision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Suvarna LangadeAinda não há avaliações
- Foundations of Information SystemsDocumento14 páginasFoundations of Information SystemsPooja KapriAinda não há avaliações
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4Ainda não há avaliações
- Cadburys Chocolate Mass ComDocumento70 páginasCadburys Chocolate Mass Commansithgr8100% (2)
- Business Policy & StrategyDocumento25 páginasBusiness Policy & StrategyRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- Accenture Personal Lines Consumer SurveyDocumento16 páginasAccenture Personal Lines Consumer SurveyRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- UAE Insurance 2012 Survey - EYDocumento36 páginasUAE Insurance 2012 Survey - EYRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- Manipal SM L1Documento44 páginasManipal SM L1Rohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- Manipal P&BM L4Documento30 páginasManipal P&BM L4Rohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Portfolio - Apple Sec 2Documento52 páginasBrand Portfolio - Apple Sec 2Arif ZamanAinda não há avaliações
- Mis 601: Management Information SystemsDocumento33 páginasMis 601: Management Information SystemsRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- Mis 601: Management Information SystemsDocumento33 páginasMis 601: Management Information SystemsRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- INS 601 - Telecommunications Networks - 23-11-09Documento56 páginasINS 601 - Telecommunications Networks - 23-11-09Rohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- MIS 601: Information Systems Management: Security and Ethical ChallengesDocumento36 páginasMIS 601: Information Systems Management: Security and Ethical ChallengesRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- TopicVII Information Systems DevelopmentDocumento45 páginasTopicVII Information Systems DevelopmentRohan Sivaramakrishnan IyerAinda não há avaliações
- LU 5.1 ElectrochemistryDocumento32 páginasLU 5.1 ElectrochemistryNurAkila Mohd YasirAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFDocumento268 páginas2015 NSPC Proposed Changes Book PDFMichelle Pinohermoso JabatAinda não há avaliações
- Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocumento30 páginasEquilibrium of A Rigid BodyChristine Torrepenida RasimoAinda não há avaliações
- Flipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Documento37 páginasFlipkart Labels 06 Jul 2022 09 52Dharmesh ManiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Ships Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyDocumento2 páginasShips Near A Rocky Coast With Awaiting Landing PartyFouaAj1 FouaAj1Ainda não há avaliações
- Ultimate Trading Guide - Flash FUT 2023Documento33 páginasUltimate Trading Guide - Flash FUT 2023marciwnw IAinda não há avaliações
- Law of AttractionDocumento2 páginasLaw of AttractionKate SummersAinda não há avaliações
- Standard BMW PDFDocumento19 páginasStandard BMW PDFIna IoanaAinda não há avaliações
- Extraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDocumento7 páginasExtraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDaniel BartoloAinda não há avaliações
- Prediction of CBR From Index Properties of Cohesive Soils: Magdi ZumrawiDocumento1 páginaPrediction of CBR From Index Properties of Cohesive Soils: Magdi Zumrawidruwid6Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento3 páginasNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelAinda não há avaliações
- ABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBDocumento2 páginasABBindustrialdrives Modules en RevBMaitry ShahAinda não há avaliações
- EPMS System Guide For Subcontractor - V1 2Documento13 páginasEPMS System Guide For Subcontractor - V1 2AdouaneNassim100% (2)
- Less Homework More TroubleDocumento7 páginasLess Homework More Troubleg697a0mw100% (1)
- PCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?Documento14 páginasPCM Cables: What Is PCM Cable? Why PCM Cables? Application?sidd_mgrAinda não há avaliações
- 1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXDocumento7 páginas1KHW001492de Tuning of ETL600 TX RF Filter E5TXSalvador FayssalAinda não há avaliações
- Wordbank 15 Coffee1Documento2 páginasWordbank 15 Coffee1akbal13Ainda não há avaliações
- Capgemini - 2012-06-13 - 2012 Analyst Day - 3 - Michelin - A Better Way ForwardDocumento12 páginasCapgemini - 2012-06-13 - 2012 Analyst Day - 3 - Michelin - A Better Way ForwardAvanish VermaAinda não há avaliações
- FIREBASE Edited PresentationDocumento12 páginasFIREBASE Edited PresentationNiraj MirgalAinda não há avaliações
- Institutions and StrategyDocumento28 páginasInstitutions and StrategyFatin Fatin Atiqah100% (1)
- Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleDocumento2 páginasRevenue Memorandum Circular No. 55-2016: For ExampleFedsAinda não há avaliações
- Visi RuleDocumento6 páginasVisi RuleBruce HerreraAinda não há avaliações
- Creating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelDocumento5 páginasCreating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelNazwa MustikaAinda não há avaliações