Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Acc
Enviado por
Jill EneroTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Acc
Enviado por
Jill EneroDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
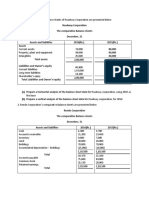
Chapter 5 p.246 1.) B. an expense that is incurred during an accounting period 2.) D.
a contra account on the balance sheet 3.) B. salaries that have been neither earned by employees nor paid 4.) D. contra asset, credit 5.) B. debit Depreciation Expense; credit Accumulated Depreciation 6.) D. 10,000 Annual Depreciation = (Cost salvage value) / useful life =(100000 10000) / 9 = 10,000 7.) D. owners capital 8.) C. 140,000 Net book Value = Cost of equipment Accumulated Depreciation = 200,000 60,000 = 140,000 9.) C. salaries expense being understated 10.) 11.) A. debit Prepaid Insurance, P600; credit Insurance Expense, P6oo B. debit Salaries Expense, P120,000; credit Salaries Payable, P120,000 200000 / 5 = 40000 x 3 = 120000 12.) C. a balance sheet account and an income statement account
13.) 14.) p.249
A. assets to be overstated. B. total expenses to be understated
1. A. Expiration of usefulness of equipment during the accounting period 2. B. Cost of employee salaries 3. D. Salaries Expense 4. B. Service rendered on credit 5. C. to produce liabilities 6. B. an expense 7. D. increase the assets for the company 8. A. the cost of the asset is allocated to an expense account 9. A. a revenue account will increase 10. C. during the slack season 11. A. The use of equipment 12. B. to make comparison meaningful 13. B. the cash basis of accounting 14. C. Recording advertising revenues at the time the cash payment is receive 15. A. Recording utilities expense when the monthly bill Is received 16. B. The purchase of a company vehicle 17. B. Recording depreciation 18. D. Land
19. B. the original cost minus accumulated depreciation 20. B. Interest Revenues and Unearned Revenues 21. D. Debit Store Supplies Expense, P2,200 and credit Store Supplies P2,200 Supplies Balance Supplies on hand 2,800 600 = 2,200 22. C. liabilities would be overstated 23. C. overstatement of owners equity 24. A. Debit Salaries Expense P3,000 and credit Salaries Payable P3,000 5,000 / 5 = 1000 x 3 = 3000 25. A. overstatement of profit for the period 26. D. both test that the ledger is still in balance after the accounts have been adjusted 27.) b. Depreciation Expense-Equipment 28.) C. all these errors will cause unequal trial balance totals Page 254 1.) c. after it has been earned, but not before. 2.) d. all of the above 3.) b. adjusting entries 4.) b. accrual and deferrals 5.) a. asset 6.) c. depreciation
7.) c. owners equity will be overstated 8.) a. a liability 9.) d. an unearned revenue 10.) a. a prepaid expense 11.) c. an accrued revenue 12.) c. an accrued revenue 13.) b. increase assets 14.) d. increase liabilities 15.) c. expense and liability 16.) a. asset and income 17.) d. Money has not been paid or received but the service has already been performed or rendered. 18.) Solution: (P16, 000 + P29, 000) P21, 000 b. P24, 000. 19.) d. debits salaries expense and credits salaries payable. 20.) a. debit unearned revenues and credit revenues for P19,000. 21.) a. balance sheet 22.) d. at least one real and one nominal account. 23.) d. recording the payment of salaries to employees 24.) d. reflecting unrecorded expenses incurred during the accounting period
Page 248 1.) b. a change in an account balance that is neither an accrual or a deferral. 2.) b. The recording of depreciation on equipment. 3.)Solution: (P2, 750 + P1, 500) P875 c. P3, 375. 4.) Solution: P5, 600 / 2 d. P2, 800. 5.) b. P375, 000. 6.) b. seller when a service is rendered before receipt of cash. 7.) c. when an expense is incurred before cash is paid. 8.) b. seller when a customer pays for a service before the service is rendered. 9.) d. cash is paid before an expense has been incurred. 10.) d. a deferred expense. 11.) d. an accrued expense. 12.) c. liabilities on the balance sheet. 13.) c. assets on the balance sheet. 14.) a. revenues on the income statement. 15.) d. liabilities on the balance sheet Page 261
1.) d. an investment in the business by the owner 2.) a. cash withdrawal by the owner 3.) b. owners equity 4.) b. going concern assumption 5.) a. supplies 6.) b. cash withdrawal by the owner 7.) d. Land 8.) a. a commission collected in advance 9.) c. interest earned but not yet received 10.) d. cash 11.) b. asset and a credit to a liability 12.) d. liability and a credit to a revenue 13.) d. Unearned Revenues and credit Service Revenues 14.) c. Interest Expense and a credit to Notes Payable 15.) b. understatement of owners equity 16.) b. overstatement of total liabilities 17.) c. debit to Supplies Expense 18.) b. credit to Prepaid Insurance for P3, 000 19.) a. credit to Accumulated Depreciation Office Equipment 20.) c. debit to Rent Expense for P10, 000 21.) d. credit to Service Revenues for P12, 500 22.) c. debit to Supplies Expense for P8, 000 23.) b. credit to Accumulated Depreciation Buildings for P50, 000 24.) b. credit to Prepaid Insurance for P5, 000
25.) d. debit to Interest Expense for P1, 000 26.) a. debit to Unearned Service Revenues for P27, 000 27.) a. P18, 700 Solution: P18 000 + P3 500 = P21 500 P21 500 P2 800 = P18 700 28.) d. P43, 500 Solution: P42 000 + P7 500 = P49 000 P49 500 P6000 = P43 000 29.) d. P5, 400 Solution: P11 400 + P3 000 = P14 400 P14 400 P9000 = P5 400 Page 267 1.) d. Unearned Revenue for entire proceeds 2.) c. Prepaid Insurance: P34, 900; Insurance Expense: P10,100 3.) b. P36,000 4.) 5.) b. P450, 000 6.) c. P350, 000 7.) a. P470, 000 8.) d. P448, 000 9.) c. P1, 440, 000
Você também pode gostar
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Kite Black RoseDocumento1 páginaKite Black RoseJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Touhou Kurenai Ma Sato Gatsu Tokei Runa Daiaru: ZUN, Yohka Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Allegro Vivace ( 138)Documento4 páginasTouhou Kurenai Ma Sato Gatsu Tokei Runa Daiaru: ZUN, Yohka Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Allegro Vivace ( 138)Jill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Ghost in The Shell - Stand Alone Complex - I Do: Y Oko Kanno Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Largo ( 66)Documento6 páginasGhost in The Shell - Stand Alone Complex - I Do: Y Oko Kanno Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Largo ( 66)Jill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Hitomi Wo To JiteDocumento2 páginasHitomi Wo To JiteJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Gentle WindDocumento2 páginasGentle WindJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- To You My DearestDocumento1 páginaTo You My DearestJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Hikaru No Go - SincerelyDocumento3 páginasHikaru No Go - SincerelyJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Haruhi No OmoiDocumento2 páginasHaruhi No OmoiJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Strike The Blood - Signal PDFDocumento3 páginasStrike The Blood - Signal PDFJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Wildarms PDFDocumento2 páginasWildarms PDFJamesG_112Ainda não há avaliações
- Hitomi Wo To JiteDocumento2 páginasHitomi Wo To JiteJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Gentle WindDocumento2 páginasGentle WindJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - The Tailor Shop On EnbizakaDocumento6 páginasVocaloid - The Tailor Shop On EnbizakaKratos de GuzmanAinda não há avaliações
- To You, My Dearest: Chikayo Fukuda Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Largo ( 46)Documento1 páginaTo You, My Dearest: Chikayo Fukuda Transcribed by Jill-J Enn Vie Largo ( 46)Jill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Love Is WarDocumento5 páginasVocaloid - Love Is WarJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- JBF PianoDocumento4 páginasJBF PianowillpawnAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Paradise of Light and ShadowDocumento3 páginasVocaloid - Paradise of Light and ShadowJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Servant of Evil Sheet MusicDocumento2 páginasServant of Evil Sheet MusicRavenSorchess100% (1)
- Vocaloid - Rolling Girl (Marasy8 Ver.)Documento6 páginasVocaloid - Rolling Girl (Marasy8 Ver.)Jill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Madness of Duke VenomaniaDocumento9 páginasVocaloid - Madness of Duke VenomaniaJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Dark Woods CircusDocumento5 páginasVocaloid - Dark Woods CircusJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid Judgement of Corruption PDFDocumento9 páginasVocaloid Judgement of Corruption PDFJasmine TanAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Double LariatDocumento1 páginaVocaloid - Double LariatJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - CanarellaDocumento1 páginaVocaloid - CanarellaJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vampire Knight - Still DollDocumento2 páginasVampire Knight - Still DollRodrigo Ivan Henriquez AbalosAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid - Daughter of EvilDocumento2 páginasVocaloid - Daughter of EvilJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vampire Knight Guilty - Main ThemeDocumento7 páginasVampire Knight Guilty - Main ThemeJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Vocaloid Broken Human MachineDocumento7 páginasVocaloid Broken Human MachineexceledeAinda não há avaliações
- Silent Night: The Full Pitcher Music ResourcesDocumento1 páginaSilent Night: The Full Pitcher Music ResourcesJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Sil Night BB MelDocumento1 páginaSil Night BB MelJill EneroAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- On Residential Status and Scope of Total IncomeDocumento72 páginasOn Residential Status and Scope of Total Incomeaim_naina100% (3)
- Unit 5: Company LawDocumento4 páginasUnit 5: Company LawDiệp Quỳnh TrầnAinda não há avaliações
- 20200407-MC-015-2020 - GSIS Loan - MoratoriumDocumento3 páginas20200407-MC-015-2020 - GSIS Loan - MoratoriumPamAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Map - 1 To 4Documento4 páginasConcept Map - 1 To 4Roby Gerard Corpuz100% (1)
- QuestionsDocumento2 páginasQuestionsSneha Giji SajiAinda não há avaliações
- Jayan V Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited: 2009 Indlaw KER 587Documento2 páginasJayan V Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited: 2009 Indlaw KER 587Harsha AmmineniAinda não há avaliações
- PEP Final Presentation by Saud, Ali & UsmanDocumento22 páginasPEP Final Presentation by Saud, Ali & UsmanHassan AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Student Loans-: A Guide To Terms and Conditions 2020 To 2021Documento17 páginasStudent Loans-: A Guide To Terms and Conditions 2020 To 2021XXXXXXXXAinda não há avaliações
- Retail Investors Participation in Indian PDFDocumento7 páginasRetail Investors Participation in Indian PDFPavan PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Far 103 - Accounting For Receivable Financing, Loans Receivables and ImpairmentDocumento3 páginasFar 103 - Accounting For Receivable Financing, Loans Receivables and ImpairmentKeanna Denise Gonzales100% (1)
- Dividend DecisionsDocumento26 páginasDividend DecisionsRemonAinda não há avaliações
- Adjusting EntriesDocumento5 páginasAdjusting EntriesDyenAinda não há avaliações
- JKR Design and Build ConditionDocumento14 páginasJKR Design and Build Conditionjerrycl67% (3)
- Soal OFC III Akt DSR - Cash, Receivable, InventoryDocumento44 páginasSoal OFC III Akt DSR - Cash, Receivable, InventorygempitapAinda não há avaliações
- Banking WorksheetDocumento2 páginasBanking WorksheetvimalparkAinda não há avaliações
- The Punjab Land Administration ManualDocumento523 páginasThe Punjab Land Administration ManualMuhammad Ibrahim100% (1)
- Final Project PDFDocumento50 páginasFinal Project PDFsiddique bushraAinda não há avaliações
- Financial AccountingDocumento217 páginasFinancial AccountingGhalib HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 2 PDFDocumento11 páginasModule - 2 PDFKeyur PopatAinda não há avaliações
- CH 18Documento20 páginasCH 18Ahmed Al Ekam100% (1)
- AFM Sample Model - 2 (Horizontal)Documento18 páginasAFM Sample Model - 2 (Horizontal)munaftAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting and Finance For ManagersDocumento322 páginasAccounting and Finance For ManagersNagesh Jorrigala83% (6)
- Financial Calculation of EBLDocumento38 páginasFinancial Calculation of EBLAbdullah Al-RafiAinda não há avaliações
- Full Sets For One Type of Harp / According To One String ChartDocumento1 páginaFull Sets For One Type of Harp / According To One String ChartklausAinda não há avaliações
- Case Digest CreditDocumento32 páginasCase Digest CreditEnzoAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 1Documento8 páginasWorksheet 1Kevin Espiritu100% (1)
- TP 2Documento36 páginasTP 2Dolly Singh OberoiAinda não há avaliações
- Cost of CapitalDocumento36 páginasCost of CapitalAayushAinda não há avaliações
- Goal Solution: in This DocumentDocumento3 páginasGoal Solution: in This DocumentvimaldoolhurAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 23 SMEs (Concept Map)Documento2 páginasCHAPTER 23 SMEs (Concept Map)kateyy99Ainda não há avaliações