Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Iron Sucrose
Enviado por
Atul KumarDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Iron Sucrose
Enviado por
Atul KumarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
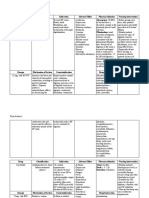
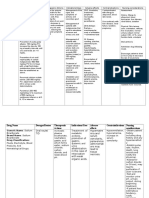
Iron sucrose inj
Trade name Drug class Presentation Cost Prescriber Indication Venofer Iron salt 5ml ampoule containing 100mg of iron RM 43.00 per ampoule Nephrologist Parenteral treatment of iron-deficiency anemia in chronic renal failure, including nondialysis-dependent patients (with or without erythropoietin therapy) and dialysisdependent patients receiving erythropoietin therapy, in cases where oral iron preparations cannot provide for supplementation such as: Patients who cannot tolerate oral iron therapy Patients who cannot sufficiently absorb orally administered iron Dose Dosage has to be individually adapted according to the total iron deficit calculated with the following formula: Total iron deficit [mg] = body weight [kg] x (target Hb actual Hb) [g/l] x 0.24* + depot iron [mg] 35 kg body weight: target Hb=130 g/l resp. depot iron=15 mg/kg body weight >35 kg body weight: target Hb=150 g/l resp. depot iron=500 mg *Factor 0.24=0.0034 x 0.007 x 1000 (Iron content of haemoglobin=0.34% / Blood volume=7% of body weight / Factor 1000= conversion from g to mg) Total amount of iron sucrose to be administered (in ml) = Total iron deficit [mg] 20 mg/ml If the total necessary dose exceeds the maximum allowed single dose, the administration has to be split. If no response of the haematological parameters is observed after 1-2 weeks the original diagnosis should be reconsidered. Normal posology: 5-10ml (100 to 200mg iron) twice or three times a week depending on the haemoglobin level. Maximum tolerated single dose: Adults and the elderly: As injection: 5-10 ml (100 to 200 mg of iron) injected in as least 10 min. As infusion: if the clinical situation demands the single dose may be increased to 0.25 ml iron sucrose kg / body weight (=7 mg iron/kg bw) not exceeding 25 ml iron sucrose (500 mg iron), diluted in 500 ml 0.9% w/v NaCl infused over at least 3.5 h, once a week. Test dose Adults: 1-2.5 ml (20 to 50 mg iron) Children > 14 kg: 1 ml (20 mg iron)
Children < 14 kg: 1.5 mg/kg Location Administration In-patient pharmacy: warded patients; Kedai PharmUMMC: outpatient. IM injection: NA SC injection: NA IV injection: Slow injection or directly into the venous limb of the dialyser. Administer at a rate of 1 mL undiluted solution over minute (i.e. 5 min per 5 mL ampoule) not exceeding 10mL iron sucrose per injection. After injection, extend the arm of the patient. IV infusion: Each mL (20 mg) of iron sucrose has to be diluted exclusively in maximum of 20 mL 0.9% w/v NaCl, immediately prior infusion and infused at a rate of : 100mL (100 mg) in at least 15 min ; 200 mL (200mg) in at least 30 min ; 300 mL in at least 1.5 h ; 400 mL in at least 2.5 h ; 500mL in at least 3.5h. For stability reasons, dilution of lower concentrations are not permissible. If clinical circumstances demand, iron sucrose may be diluted in less than specified amount of 0.9% w/v NaCl solution, producing a higher concentration. The rate of infusion must be adapted according to the amount of iron given per minute (200mg iron should be infused in at least 30 minutes ; 500 mg iron should be infused in at least 3.5h). Intrathecal: NA Intraperitoneal: NA Stability / expiry Reconstituted solution: Stable at controlled room temperature for 12 hours if stored between 4-25C in the day light. Undiluted solution: Store a controlled room temperature of 4 to 25C Compatibility Compatible fluids: NS Compatible drugs: NA Compatible via Y site: NA Compatible in syringe: NA Incompatibility Special precautions Incompatible fluids: NA Incompatible drugs: Oral iron preparation Should only be administered where the indication is confirmed by appropriate investigations (e.g. serum ferritin, haemoglobin, haematocrit, erythrocyte count or red cell indices MCV, MCH, MCHC). Parenterally administered iron preparations can cause allergic or anaphylactoid reactions, including serious or life-threatening reactions. Patients with bronchial asthma, with low iron binding capacity and/or folic acid deficiency are particularly at risk of an allergic or anaphylactic reaction. Before administration of the 1st therapeutic dose of iron sucrose in a new patient, a test dose should be given by the chosen method of administration with facilities for cardiopulmonary resuscitation being made available. If no adverse reactions occur
within 15 min after administration, the remaining portion of the initial dose can be given Hypotension has been reported frequently in hemodialysis dependent patients. Used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. Caution during lactation. Safety and efficacy in children have not been established. Should not be administered concomitantly with oral iron preparations since the absorption of iron is reduced. Oral iron therapy should at least be started 5 days after the last injection. Overdosage can cause acute iron overloading which may manifest as haemosiderosis. Symptoms: hypotension, headache, vomiting, nausea, dizziness, joint aches, parasthesia, abdominal and muscle pain, oedema and cardiovascular collapse. Treated with supportive measures (IV fluids, hydrocortisone, and/or antihistamines) and, if required, an oral chelating agent. Special notes Patient information Stock from Inpatient pharmacy is for inpatients only. Outpatients are required to purchase from Kedai PharmUMMC Side effects: hypotension (caution when driving or climbing stairs); black tarry stools (normal), nausea, vomiting (taking with meals with reduce this), constipation (adequate fluids and exercise may help, may need a stool softener); or diarrhea (buttermilk, boiled milk or yogurt may help). Report severe unresolved GI irritation (cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation); headache, lethargy, fatigue, dizziness or other CNS changes; rapid respiration; leg cramps chest pain or palpitations; swelling of extremities or unexplained weight gain; vision changes; choking sensation; loss of consciousness; or convulsion. Prepared/checked by Date compiled/edition Yeap Li Ling / PDS / HKD / PL 20 July 2009, 1st edition
Você também pode gostar
- Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasDrug StudyHerwincayeAinda não há avaliações
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocumento3 páginasDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyGian Era100% (1)
- Miglitol (Glyset)Documento1 páginaMiglitol (Glyset)EAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento13 páginasDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioAinda não há avaliações
- AtroventDocumento2 páginasAtroventKatie McPeekAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study KeterolacDocumento2 páginasDrug Study KeterolacKillerBall RegioAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaDocumento2 páginasDrug Analysis: Malaise, Fatigue, Dizziness, Tremors, AtaxiaFerdinand Sherwin MorataAinda não há avaliações
- Drug AnalysisDocumento3 páginasDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocumento4 páginasGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsAinda não há avaliações
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakDocumento2 páginasNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: Zithromax, Zmax, Z-PakJanet Sheldon50% (2)
- Sodium BicarbonateDocumento1 páginaSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoAinda não há avaliações
- AminophyllineDocumento9 páginasAminophyllineZaira BataloAinda não há avaliações
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Documento1 páginaErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento10 páginasDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocumento4 páginasMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenAinda não há avaliações
- DiphenhydramineDocumento5 páginasDiphenhydramineShyrra Edades PinderAinda não há avaliações
- Drug AnalysisDocumento3 páginasDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienAinda não há avaliações
- The Format of This Leaflet Was Determined by The Ministry of Health and Its Content Was Checked and Approved by It On February 2016Documento10 páginasThe Format of This Leaflet Was Determined by The Ministry of Health and Its Content Was Checked and Approved by It On February 2016ddandan_2Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study-Sodium BicarbonateDocumento7 páginasDrug Study-Sodium BicarbonateTrisha Faye OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study FinalDocumento6 páginasDrug Study FinalJade HemmingsAinda não há avaliações
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocumento1 páginaGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490Ainda não há avaliações
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Documento2 páginasDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaAinda não há avaliações
- Lasix - Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasLasix - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoAinda não há avaliações
- MethergineDocumento2 páginasMetherginebdumaranAinda não há avaliações
- Methylprednisolone AlphapharmDocumento5 páginasMethylprednisolone AlphapharmMarthin TheservantAinda não há avaliações
- NiacinDocumento2 páginasNiacinΚωνσταντίνος ΓκάργκαςAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study FDocumento3 páginasDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocumento5 páginasDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocumento2 páginasDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenAinda não há avaliações
- KaliumDocumento2 páginasKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaAinda não há avaliações
- MIFEPREX™ (Mifepristone) Tablets, 200 MG For Oral Administration OnlyDocumento16 páginasMIFEPREX™ (Mifepristone) Tablets, 200 MG For Oral Administration OnlyIniya RajendranAinda não há avaliações
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreAinda não há avaliações
- Drug NystatinDocumento1 páginaDrug NystatinSrkocherAinda não há avaliações
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Documento3 páginasFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarAinda não há avaliações
- Drug AnalysisDocumento8 páginasDrug AnalysisJonie Vince SañosaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Documento11 páginasDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�AAinda não há avaliações
- BretyliumDocumento4 páginasBretyliumButchay LumbabAinda não há avaliações
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocumento2 páginasDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTAinda não há avaliações
- Dimenhydrinate PDFDocumento2 páginasDimenhydrinate PDFWindy SengiAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoAinda não há avaliações
- HNBBDocumento3 páginasHNBBManelle SingzonAinda não há avaliações
- SimethiconeDocumento1 páginaSimethiconeDivine Dela PenaAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Study (Room 104)Documento4 páginasDrug Study (Room 104)Maeshe Pryll TanamorAinda não há avaliações
- Levothyroxine (Synthroid)Documento1 páginaLevothyroxine (Synthroid)E50% (2)
- Emergency Room Drug ListDocumento28 páginasEmergency Room Drug Listiscariot02Ainda não há avaliações
- Chart View Admission Lab WorkDocumento4 páginasChart View Admission Lab Workania ojedaAinda não há avaliações
- FlecainideDocumento3 páginasFlecainideAlexandra AntondyAinda não há avaliações
- Betahistine (DRUG LIST)Documento2 páginasBetahistine (DRUG LIST)Bon- BonAinda não há avaliações
- Drug StudyDocumento33 páginasDrug Studyjefwy8Ainda não há avaliações
- Drug Study MetforminDocumento5 páginasDrug Study MetforminSabita PaudelAinda não há avaliações
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocumento9 páginasAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyAinda não há avaliações
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Documento6 páginasDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezAinda não há avaliações
- VenoferinfDocumento10 páginasVenoferinfzerin_atinAinda não há avaliações
- Preparations of Intravenous IronDocumento5 páginasPreparations of Intravenous IronSri Siti KhadijahElfAinda não há avaliações
- Oral and Parenteral Iron Preparations in PregnancyDocumento45 páginasOral and Parenteral Iron Preparations in PregnancyArun George100% (3)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia in Pregnant Woman (RAD)Documento24 páginasIron Deficiency Anemia in Pregnant Woman (RAD)Radziah Abd malekAinda não há avaliações
- Ferosac InjDocumento2 páginasFerosac InjMohamed Taleb75% (4)
- Anemia - PPTX PHDDocumento67 páginasAnemia - PPTX PHDReyadh JassemAinda não há avaliações
- DNB Questions Year WiseDocumento104 páginasDNB Questions Year Wiseakish4uAinda não há avaliações
- Kebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Documento32 páginasKebutuhsn Implan Urologi Desember 2021 - November 2022 - 3Ilham ApriansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Biolase TimelineDocumento19 páginasBiolase Timelinemohamed radwanAinda não há avaliações
- Cardiogeneicpulmonaryedema December2019Documento9 páginasCardiogeneicpulmonaryedema December2019Amaranto Santoso ongkoAinda não há avaliações
- PolytraumaDocumento41 páginasPolytraumaFrederick Mars UntalanAinda não há avaliações
- Ultrasonography of The EyeDocumento8 páginasUltrasonography of The Eyetaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- Surgery History and PhysicalDocumento23 páginasSurgery History and PhysicalBilal RowaihiAinda não há avaliações
- RumenotomyDocumento1 páginaRumenotomymake it make senseAinda não há avaliações
- "God's Hotel: A Doctor A Hospital, and A Pilgrimage Into The Heart of Medicine" by Victoria SweetDocumento43 páginas"God's Hotel: A Doctor A Hospital, and A Pilgrimage Into The Heart of Medicine" by Victoria Sweetwamu885Ainda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento8 páginasUntitledapi-271638639Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Language and Linguistics BIT10703 Ahmad Taufik Hidayah Bin AbdullahDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Language and Linguistics BIT10703 Ahmad Taufik Hidayah Bin AbdullahMuhammad Ikhwan RosmanAinda não há avaliações
- DocxDocumento20 páginasDocxHarrington_773951393100% (1)
- Sample Questions For HAAD Prometric and DHA For NursesDocumento46 páginasSample Questions For HAAD Prometric and DHA For NursesJaezelle Ella Sabale100% (4)
- Pharmacy Bulletin Aug11Documento6 páginasPharmacy Bulletin Aug11Rema Panickar SugunanAinda não há avaliações
- Essentials of Palliative CareDocumento525 páginasEssentials of Palliative Caretaha100% (2)
- BupropionDocumento3 páginasBupropionRJ HAinda não há avaliações
- Rectovaginal FistulaDocumento8 páginasRectovaginal FistulaRomi Mauliza FauziAinda não há avaliações
- Mamography PPT Nov 15 - 2022Documento23 páginasMamography PPT Nov 15 - 2022Fouzia NoorAinda não há avaliações
- COPD ExacerbationDocumento2 páginasCOPD ExacerbationjusthoangAinda não há avaliações
- Pinhole NDocumento4 páginasPinhole NNizam MohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study EssayDocumento19 páginasCase Study EssaylecharmedenuitAinda não há avaliações
- Manejo de Conducta en Niños Ansiosos. (ING)Documento6 páginasManejo de Conducta en Niños Ansiosos. (ING)Ale RamírezAinda não há avaliações
- Medicine 018 Final PDFDocumento22 páginasMedicine 018 Final PDFdrkefyalewtayeAinda não há avaliações
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Documento8 páginasCOPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)Emily Anne86% (7)
- Thesis Related To Breast Self ExaminationDocumento6 páginasThesis Related To Breast Self Examinationfjfyj90y100% (3)
- Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia: A Clinical and Histological InsightDocumento3 páginasFocal Fibrous Hyperplasia: A Clinical and Histological InsightIJAR JOURNALAinda não há avaliações
- 1339-Article Text-24955-2-10-20220330Documento6 páginas1339-Article Text-24955-2-10-20220330Kevean Kimi LimAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Statement 5Documento17 páginasProblem Statement 5priyankaAinda não há avaliações
- Healthy Pond Fish: GuideDocumento62 páginasHealthy Pond Fish: GuideGoran MatovicAinda não há avaliações
- 4th Year Write Up 2 - Int. MedDocumento11 páginas4th Year Write Up 2 - Int. MedLoges TobyAinda não há avaliações