Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
7 GSM Network Connectivity R
Enviado por
Jayan KulathoorDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
7 GSM Network Connectivity R
Enviado por
Jayan KulathoorDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Mobile Communications
GSM Network Connectivity
7 GSM NETWORK CONNECTIVITY
STRUCTURE 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE:OVERVIEW BTS-BSC CONNECTIVITY BSC-MSC CONNECTIVITY CONNECTIVITY OF OTHER NODES:GSM INTERFACES SUMMERY REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED FURTHER READINGS
7.1
INTRODUCTION
This chapter deals with connectivity of various GSM nodes.
7.2
OBJECTIVE:After reading this unit, you should be able to understand: Connectivity of BTS-BSC Connectivity of BSC-MSC and other nodes GSM Interfaces
7.3
OVERVIEW
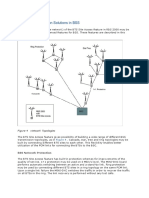
Connectivity among various nodes is shown in figure-1. MS (mobile station) communicate to BTS over Um(air interface). It communicates to BTS via antenna placed over tower. Generally three antennas are place over tower to cover one cell in city. Each antenna provides its services in one particular sector. To provide coverage over roads/highway generally two back to back antennas radiate in two sectors.
BSNL Online Awareness Programme For Restricted Circulation
Page 1 of 5
Mobile Communications
GSM Network Connectivity
NMS
HLR
AuC
PSTN ISDN
B T S
S CP
MSC/ VLR
EIR
S MP
Data Network s
Un
Transcoder
B T S
BSC
Application Server (Content Provider)
Billing Server
Fig : 1 7.4
Architecture of the GSM network
BTS-BSC CONNECTIVITY
Antennas are connected to duplexer unit of BTS via feeder cables. Two feeder cables (main & diversity) are feed to duplexer.
BTSs are connected with BSC via PCM cable, OFC, IP, satellite or microwave. 7.4.1 DECISION ON MEDIA B/W BTS-BSC
Microwave Link is used where line of sight radio path is available. Leased Line (Copper Cable or Fiber Optic) used where the distance between the BSC and BTS is too great for microwave. Satellite Link is used where Previous two methods are not possible BTS & BSC may be interconnected with simple PCM cable if they are situated collocated. If the distance between two is less then 100m, then also PCM cable can be used to connect the both. Microwave is suitable for hilly, inaccessible and difficult terrain areas & its deployment is also quick. It can provide both TDM & IP Connectivity. But it support maximum STM-1 system & it is less reliable as compare to physical connectivity. Also fading & interference are few drawbacks of microwave connectivity.
BSNL Online Awareness Programme For Restricted Circulation
Page 2 of 5
Mobile Communications
GSM Network Connectivity
With the help of Minilink up to 16 PCMs can be utilized with 15 & 18 Ghz. Satellite connectivity can be better option to service remote areas. It also takes less time to deploy. Terrestrial build-outs can take years to plan and implement. BTS-BSC connectivity in areas of minor interest can be provided by it. These can include small isolated centers such as tourist resorts, islands, mines, oil exploration sites, hydro-electric facilities, etc. 7.4.2 CHAINING OF BTSS
Generally one PCM is sufficient to connect a BTS with BSC (up to 4+4+4 configuration). BTS can also be chained. One BTS me be connected with BSC and rest BTSs may be connected to BSC via master BTS. This may save the media but reduce reliability.
BSC BSC
Figure-2 Chaining of BTSs
7.5
BSC-MSC CONNECTIVITY
BSCs are connected with MSC via E1. BSC works on 16kbps while MSC perform
64Kbps switching , thats why a transcoder is placed between BSC & MSC that convert 16kbps to 64 Kbps and vice versa.
BSC
Transcoder
MSC
Figure-3 BSC-MSC connectivity through transcoder It can be viewed in figure-3 that one PCM is feed to transcoder from BSC side and transcoder output four PCMs that are feed to MSC. CCS-7 signaling is used between BSC & MSC while LAP-D (link access protocol on channel D ) is used between BSC & transcoder. Transcoder is transparent to CCS-7 BSNL Online Awareness Programme For Restricted Circulation Page 3 of 5
Mobile Communications
GSM Network Connectivity
signaling between BSC & MSC. Now a days TFO (transcoder free operation) BSCs are also used.
7.6
CONNECTIVITY OF OTHER NODES:-
MSCs are connected with gateway MSC/ other MSCs via E1 for inter MSC communication. It may also connect to other PSTN switches for communication with land line subscribers. Generally in one PLMN(public land mobile network) all MSCs are connected with GMS and inter PLMN traffic is handle via GMSC.
MSC A
MSC 1
MSC B
GMSC
GMSC
MSC 2
MSC Z
MSC n
PLMN-A
PLMN-B
Figure-4 Connectivity among PLMNs VLR is generally integrated in MSC and it communicates with HLR via E1. Signaling between MSC & HLR is CCS-7. SCP (service control point) is node to control IN services (mostly pre paid calls). It is with MSC/VLR and provides call control functionality. Camel protocol (CAP) is used between MSC/VLR and SCP. Billing server is connected with MSCs/GMSC and process CDRs transferred by these nodes. Integrated customer care, billing and accounting platform (B&CCS) is used to support a wide range of GSM Services like GPRs, WAP, IN Services. NMS (Network management sub system) is a centralized node and connected with BSCs, MSCs and HLRs etc. It provides centralized management of these nodes and can generate network quality report.
7.7
GSM INTERFACES
Following are the specified interfaces: BSNL Online Awareness Programme For Restricted Circulation Page 4 of 5
Mobile Communications Um A Abis Ater/(Asub) B C D E F G : : : : : : : : : : MS - BTS (air or radio interface) MSC BSC BSC BTS (proprietary interface) BSC TRAU (proprietary interface) MSC VLR MSC HLR HLR VLR MSC MSC MSC EIR VLR - VLR.
GSM Network Connectivity
7.8
SUMMERY
Antennas are connected to duplexer unit of BTS via feeder cables. Two feeder cables (main & diversity) are feed to duplexer. Microwave, lease line or satellite connectivity can be provided between BTS and BSC. BTSs can be connected in chain also, but it reduces the reliability. BSCs are connected with MSC via E1. BSC works on 16kbps while MSC perform 64Kbps switching , thats why a transcoder is placed between BSC & MSC that convert 16kbps to 64 Kbps and vice versa. MSCs are connected with gateway MSC/ other MSCs via E1 for inter MSC communication.
7.9
REFERENCES AND SUGGESTED FURTHER READINGS
www.etsi.org www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GSM GSM Architecture, Protocols and Services by Gorg Eberspachers.
BSNL Online Awareness Programme For Restricted Circulation
Page 5 of 5
Você também pode gostar
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksNo EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Abis Link SignallingDocumento7 páginasAbis Link Signallingsrikanth.2335528Ainda não há avaliações
- Functionality MCBSC NokiaDocumento6 páginasFunctionality MCBSC NokiaAlieAinda não há avaliações
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GNo EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandAinda não há avaliações
- SDH Interface With STM-1 ShelfDocumento2 páginasSDH Interface With STM-1 ShelfKazeem K. AdedayoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment (3) (1602062) PDFDocumento7 páginasAssignment (3) (1602062) PDFnusratAinda não há avaliações
- 08 Cisco Catalyst 2960 QoS Design AAGDocumento2 páginas08 Cisco Catalyst 2960 QoS Design AAGpaulo_an73810% (1)
- What Is GSMDocumento17 páginasWhat Is GSMBhawesh kafleAinda não há avaliações
- CELL BROADCAST SERVICE (Comprehensive Document)Documento49 páginasCELL BROADCAST SERVICE (Comprehensive Document)Rahul SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- GSM Over SatelliteDocumento22 páginasGSM Over Satellitenguyenduke83Ainda não há avaliações
- Principles of Communication SystemsDocumento21 páginasPrinciples of Communication SystemsOdoch HerbertAinda não há avaliações
- Home Work Mark 1Documento10 páginasHome Work Mark 1RaphaelAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11 Development of Network Planning Technology .................................................... 11-1Documento47 páginasChapter 11 Development of Network Planning Technology .................................................... 11-1Anjit RajkarnikarAinda não há avaliações
- WMN Chapter 1 Notes by Ur Engineering FriendDocumento12 páginasWMN Chapter 1 Notes by Ur Engineering FriendKaran ChaudhariAinda não há avaliações
- GSMDocumento11 páginasGSMLinduxAinda não há avaliações
- Roupe Pecial Obile: Page 1 of 17Documento17 páginasRoupe Pecial Obile: Page 1 of 17shwetaecAinda não há avaliações
- Base Station SubsystemDocumento72 páginasBase Station SubsystemDivya GoelAinda não há avaliações
- Report On Visit To Regional Telecom Training Centre Mysuru: GSM IntroductionDocumento6 páginasReport On Visit To Regional Telecom Training Centre Mysuru: GSM IntroductionMallikarjunAinda não há avaliações
- MTRCDocumento16 páginasMTRCPrapti AlokAinda não há avaliações
- Base Station SubsystemDocumento65 páginasBase Station SubsystemRicardo Ngeng PitpituAinda não há avaliações
- My Seminar 222Documento18 páginasMy Seminar 222Rajat NegiAinda não há avaliações
- WCC Module 2 NotesDocumento43 páginasWCC Module 2 NotesMadhan Gowda KAinda não há avaliações
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Documento17 páginasMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #13Student Lecture Notes75% (4)
- Research Paper On GSM ArchitectureDocumento7 páginasResearch Paper On GSM Architecturenodahydomut2100% (1)
- 2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyDocumento20 páginas2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyultimoridigAinda não há avaliações
- GSM AterDocumento21 páginasGSM Atereabhishek222100% (6)
- Application NoteDocumento12 páginasApplication NoteHussein ManafAinda não há avaliações
- Generations of MobileDocumento28 páginasGenerations of MobileIqra YasmeenAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Digital Cellular: Chapter NoDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Digital Cellular: Chapter NoFakhar Muhammad Hussain NaqviAinda não há avaliações
- Planning UMTS Radio NetworksDocumento7 páginasPlanning UMTS Radio NetworksAhmed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Base Station SubsystemDocumento4 páginasBase Station SubsystemDaniyal AliAinda não há avaliações
- BSS InterfacesDocumento2 páginasBSS InterfacesSherif KamalAinda não há avaliações
- GPRS PDFDocumento7 páginasGPRS PDFHandy MoseyAinda não há avaliações
- BssDocumento23 páginasBssXaferAinda não há avaliações
- WMN Practical Exam QuestionsDocumento3 páginasWMN Practical Exam Questionslaxmimane245Ainda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Leased LineDocumento38 páginasIntroduction To Leased LineAnkit Ashok Aggarwal50% (2)
- BSC Configuration Bss OverviewDocumento17 páginasBSC Configuration Bss OverviewJesus Percival BarattaAinda não há avaliações
- GPRS PDFDocumento6 páginasGPRS PDFHandy MoseyAinda não há avaliações
- WCC VTU Module 2 NotesDocumento10 páginasWCC VTU Module 2 NotesSushíl kanikeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Introducing GSMDocumento12 páginasChapter 1: Introduction: 1.1 Introducing GSMTafadzwa MashyAinda não há avaliações
- Communication System Lecture 6-2 PDFDocumento9 páginasCommunication System Lecture 6-2 PDFmiro jasimAinda não há avaliações
- GSM ProtocolsDocumento12 páginasGSM ProtocolsraymondushrayAinda não há avaliações
- Apis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemDocumento6 páginasApis Training GSM System Overview - Base Station SystemKhaja MohiuddinAinda não há avaliações
- GSM TechnologyDocumento29 páginasGSM TechnologyrgkripaAinda não há avaliações
- Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service, MBMSDocumento24 páginasMultimedia Broadcast Multicast Service, MBMSAsadKhanAinda não há avaliações
- Gprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelDocumento316 páginasGprs Qos and Parameters - AlcatelOcira OyaroAinda não há avaliações
- GSM OverviewDocumento8 páginasGSM OverviewAnuj ThakurAinda não há avaliações
- Wireless CommunicationDocumento16 páginasWireless CommunicationhaiderifulAinda não há avaliações
- Network Transmission Solutions in BSSDocumento2 páginasNetwork Transmission Solutions in BSSpoteAinda não há avaliações
- PLMNDocumento4 páginasPLMNRicky OcateAinda não há avaliações
- WCN Unit III - Wireless Data Services Dec-11Documento56 páginasWCN Unit III - Wireless Data Services Dec-11Atluri Sri Harsha100% (1)
- LTE E-MBMS Capacity and Intersite Gains: Américo Correia, Rui Dinis, Nuno Souto, and João SilvaDocumento23 páginasLTE E-MBMS Capacity and Intersite Gains: Américo Correia, Rui Dinis, Nuno Souto, and João SilvaIgor MalianovAinda não há avaliações
- BSNL MT Exam 2019 Test Series: Chapter 10 - Telecom KnowledgeDocumento57 páginasBSNL MT Exam 2019 Test Series: Chapter 10 - Telecom KnowledgeSandeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Ece Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarDocumento40 páginasEce Department: Associated Minds With This SeminarSankha MullickAinda não há avaliações
- The Market Forecast of HLR (English Version)Documento26 páginasThe Market Forecast of HLR (English Version)Ian YeonAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocumento25 páginasLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- Report MBMSDocumento19 páginasReport MBMSAshish AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Documento4 páginasBase Station Subsystem (BSS) : CH 1: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Qahwagi MochaAinda não há avaliações
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesNo EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsNo EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- 2G Call FlowDocumento5 páginas2G Call FlowGaurav MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Newest PP IconsDocumento81 páginasNewest PP IconsDaniela Lara CisternasAinda não há avaliações
- File Chuan Pon ZTEDocumento2 páginasFile Chuan Pon ZTEQuỳnh Nguyễn ĐứcAinda não há avaliações
- 40G QSFP+ Modules Installation GuideDocumento8 páginas40G QSFP+ Modules Installation GuidedbscriAinda não há avaliações
- Extreme Updated Product Eos End of Sale Report 30sept22 Dot PDFDocumento79 páginasExtreme Updated Product Eos End of Sale Report 30sept22 Dot PDFedison marquesAinda não há avaliações
- Ethernet 101Documento62 páginasEthernet 101mjrbacon100% (1)
- Cisco Viptela SDWAN SeriesDocumento3 páginasCisco Viptela SDWAN SeriesWilson Gabriel Veliz PluaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring TrunksDocumento6 páginas3.2.2.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring Trunksfranky rugeAinda não há avaliações
- Cisco Networking Academy ProgramDocumento1 páginaCisco Networking Academy Programarian khanAinda não há avaliações
- Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot VTP and DTPDocumento3 páginasPacket Tracer - Troubleshoot VTP and DTPetitahAinda não há avaliações
- Ericsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SR01241237Documento18 páginasEricsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SR01241237sam100% (1)
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Circuitos RCDocumento9 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Circuitos RCimeldoAinda não há avaliações
- About DSL Modem Lights - SpeedTouch Modems - SupportDocumento5 páginasAbout DSL Modem Lights - SpeedTouch Modems - SupporttsibiAinda não há avaliações
- Tac03001-Ho04-i1.6-7302 7330 Isam Product Overview FDDocumento79 páginasTac03001-Ho04-i1.6-7302 7330 Isam Product Overview FDNathaly100% (1)
- ADTRAN - CenturyLink 2014 Roadshow Mark RichmondDocumento80 páginasADTRAN - CenturyLink 2014 Roadshow Mark Richmondaarnulfo100% (1)
- IPRAN TroubleshootingDocumento16 páginasIPRAN TroubleshootingGiordano Smith Alvarado RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Comenzi CiscoDocumento3 páginasComenzi CiscofpertreusAinda não há avaliações
- XDM Bg20 Sdh-System enDocumento5 páginasXDM Bg20 Sdh-System enMr_THINHAinda não há avaliações
- ISDNDocumento17 páginasISDNRaymond GaboutloeloeAinda não há avaliações
- CSFB ConceptsDocumento12 páginasCSFB Conceptsjitu_rfAinda não há avaliações
- Cabling Lans and Wans: Ccna 1 Chapter 4, Part 2Documento35 páginasCabling Lans and Wans: Ccna 1 Chapter 4, Part 2api-3771536Ainda não há avaliações
- Day One Poster Junos Fusion EnterpriseDocumento1 páginaDay One Poster Junos Fusion EnterpriseYibrail Veliz PluaAinda não há avaliações
- Allen TelDocumento1 páginaAllen TelswfbopertbAinda não há avaliações
- EP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsDocumento18 páginasEP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsShazul Afizi Zulkiflee100% (1)
- Cisco Monitor Performance NCS 2000 DWDMDocumento100 páginasCisco Monitor Performance NCS 2000 DWDMp4i9e8r5Ainda não há avaliações
- RTTC Presentation 2019 SkillDocumento36 páginasRTTC Presentation 2019 SkillNILESH WANKHEDE100% (1)
- Huawei MA5600T Series OLT Configuration For HSI, VOIP, and IPTV Services in FTTH Gateway Mode ONT - NGCOMDocumento18 páginasHuawei MA5600T Series OLT Configuration For HSI, VOIP, and IPTV Services in FTTH Gateway Mode ONT - NGCOMAngad Kumar100% (1)