Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Exam 1 Study Guide
Enviado por
Iesha ClarkTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Exam 1 Study Guide
Enviado por
Iesha ClarkDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Chapter 1
Levels of organization o chemicals cells tissues organs organ systems organism Organ systems & their purposes o Integumentary skin protection, support, movement o Skeletal bones - protection, support, movement o muscular skeletal muscles - protection, support, movement o nervous brain, spinal cord, nerves coordination and control o endocrine glands, produce hormones coordination and control o cardiovascular heart, blood vessels - circulation o lymphatic lymph nodes, vessels circulation, immunity o respiratory lungs, airways nutrition and fluid balance o digestive mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines nutrition and fluid balance o urinary kidneys, bladder, urethra nutrition and fluid balance o reproductive testes, ovaries, external sex organs produce offspring Metabolism o catabolism break down, produces ATP (cells energy) o anabolism build up Homeostasis o extracellular, intracellular fluid o Feedback positive oxytocin during birth negative insulin in glucose absorption Directional Terms o superior o cranial o inferior o caudal o ventral o anterior o dorsal o posterior o medial o lateral o proximal o distal o deep o superficial Planes of division o frontal/coronal o sagittal o transverse Body cavities
o dorsal cranial spinal o ventral Thoracic (separated by diaphragm from a.p. cavity) pleural pericardial mediastinum Abdominopelvic Abdominal Pelvic Regions of abdomen Right hypochondriac Epigastric Left hypochondriac Right lumbar Right inguinal o Quadrants Right upper quadrant umbilical hypogastric Left lumbar Left inguinal
Left upper quadrant
Right lower quadrant
Left lower quadrant
Metric system o length meter (m) o weight gram (g) o volume liter (l) o temperature degrees Celsius/centigrade (oC) o Prefixes (k) kilo 1,000 (c) centi 1/100 (m) milli 1/1,000 (u) micro 1/1,000,000
Chapter 2
Elements o atoms nucleus protons (+) neutrons
electrons (-) atomic number (protons + neutrons) Molecules & Compounds Water o universal solvent (polar) o hydrophobic (fats, lipids) o hydrophilic (salts, glucose) Mixtures o solution (homogenous mixture) solvent (when water, aqueous solution) solute o suspension (heterogenous mixture) Chemical bonds o Ionic electrons given by one atom, taken by another anion cation electrolytes o Covalent electrons shared by atoms Acids, Bases o Acids donate hydrogen ion, H+ (proton) decrease pH (0-7) o Bases accept H+ usually contains hydroxide ion, OH increase pH (7-14) o Blood pH = 7.35-7.45, slightly alkaline/basic o Buffers weak acid + its conjugate base accepts H+ (acts as base) when pH drops too low donates H+ (acts as acid) when pH gets too high evens out pH Radioactivity o Isotopes elements have extra neutrons o Used as tracers in diagnostic procedures PET CT NMI Organic compounds o carbohydrates (CnH2nOn) monosaccharides (simple sugars) single glucose molecule disaccharides sucrose (table sugar, glucose + fructose)
polysaccharides long chains of monosaccharides glycogen, starch
o lipids fats glycerol + three fatty acid chains Phospholipids contain phosphorous cell membrane cholesterol cell membrane steroids (hormones testosterone, estrogen) o proteins shaped polypeptide chain pleated sheats, coils amino acids amino group (NH2) acid group (COOH) enzymes catalyze (speed up) reactions substrate o nucleic acids
Chapter 3
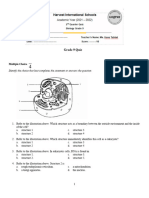
Cells o simplest form of life o Cytology Microscopes o compound light 1,000 x stains o scanning electron (SEM) 100,000 x o transmission electron (TEM) a million x Cell structure o Plasma Membrane phospholipid bilayer cholesterol proteins channels transporters receptors enzymes linkers cell identity markers carbohydrates (as glycoprotein, glycolipid)a
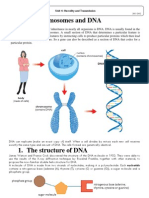
microvilli o Nucleus contains DNA in chromosomes loosely packed around protein = chromatin nucleolus assembles ribosomes o Cytoplasm everything else cytosol liquid between organelles Endoplasmic reticulum Rough ER o ribosomes (assemble proteins) Smooth ER o synthesize lipids mitochondria produce ATP Golgi apparatus sort, modify, export proteins lysosomes digestive enzymes for worn out organelles, autolysis peroxisomes enzymes for removal of free radicals centrioles function in cell division vesicles Surface organelles o cilia o flagella Protein Synthesis o DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) double stranded nucleotides phosphate sugar (deoxyribose) nitrogenous base, A, T, G, C (Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine) double helix genes o RNA (ribonucleic acid) usually single stranded nucleotides phosphate sugar (ribose) nitrogenous base, A, U (Uracil), G, C mRNAsingle stranded sequence of RNA coded straight from DNA-transcription
rRNAcombined with proteins, makes up ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis tRNAbrings specific amino acids to the ribosome to form proteins as it reads the sequence contained in mRNA-translation
Cell division o Interphaseordinary cellular activity, DNA replication duplicated chromosomes held together at centromere o Meiosis results in sperm and egg cells with half the chromosomes of somatic cells o Mitosis (division of somatic cells) results in two identical daughter cells Prophase DNA condenses Metaphase Chromosomes align at cells center (meta means middle) Anaphase Spindle fibers from centrioles begin to separate duplicated chromosomes Telophase nuclear envelope appears around two sets of DNA at each end of cell, plasma membrane begins to pinch off to create 2 cells Movement of substances o Passive transport (no energy required) Diffusion moves from area of high concentration to low (with the concentration gradient) Osmosis water moves from area of low solute to high solute Filtration external force pushes fluids through Facilitated diffusion diffusion, using transporters in the cell membrane o Active transport transport proteins Endocytosis Phagocytosis o Cells eat things Pinocytosis o Cells sip surrounding fluid Exocytosis Cells throw up things Osmosis affecting cells o Hypotonic, Hypertonic, Isotonic solutions o Crenation, hemolysis Cell aging o Radiation exposure, lysosomes, inaccurate DNA replication introduce mutations, alteration of genes o ineffectiveness or reduced effectiveness of proteins (stuff doesnt work as well as it used to)
o mutations in cell cycle regulation (that tell a cell when to dieapoptosis) may result in uncontrolled proliferation and cell division, resulting in a tumor and possibly cancer
Você também pode gostar
- Academic Catalog 2011-2012 For William Peace University PDFDocumento196 páginasAcademic Catalog 2011-2012 For William Peace University PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Double Cheese Pasta PrimaveraDocumento1 páginaDouble Cheese Pasta PrimaveraIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Associate in Science Degree A10400 PDFDocumento4 páginasAssociate in Science Degree A10400 PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Academic - Catalog - 2012-2013 For William Peace University PDFDocumento172 páginasAcademic - Catalog - 2012-2013 For William Peace University PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Creamy Bow - Tie Pasta With Chicken BroccoliDocumento1 páginaCreamy Bow - Tie Pasta With Chicken BroccoliIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Requirements For Transfer StudentsDocumento2 páginasRequirements For Transfer StudentsIesha Clark100% (1)
- Unit 1.3Documento1 páginaUnit 1.3Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Humanities 110 Power Point 1Documento17 páginasHumanities 110 Power Point 1Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1.4 Part 1Documento1 páginaUnit 1.4 Part 1Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Off Campus Housing Options PDFDocumento3 páginasOff Campus Housing Options PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- The Industrial Revolution: A Closer LookDocumento8 páginasThe Industrial Revolution: A Closer LookIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Rustic Chicken Salad With Spring VegetablesDocumento1 páginaRustic Chicken Salad With Spring VegetablesIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Highlights From Chapter 7 of Science Indicators 2012Documento4 páginasHighlights From Chapter 7 of Science Indicators 2012Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Brief History of Technology HUM PP 2Documento19 páginasBrief History of Technology HUM PP 2Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Checklist Foraccepted Transfer Students PDFDocumento1 páginaChecklist Foraccepted Transfer Students PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Campbell University Visitation DaysDocumento1 páginaCampbell University Visitation DaysIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Metapopulation Dynamics of Bubonic Plague PDFDocumento6 páginasMetapopulation Dynamics of Bubonic Plague PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- JokeDocumento1 páginaJokeIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Nefertiti 2 PDFDocumento2 páginasNefertiti 2 PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Nefertiti vs. CleopatraDocumento1 páginaNefertiti vs. CleopatraIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Argumentaion Presentation - OdpDocumento7 páginasArgumentaion Presentation - OdpIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Shrimp and GritsDocumento2 páginasShrimp and GritsIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- William Shakespeare and the Black DeathDocumento2 páginasWilliam Shakespeare and the Black DeathIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Nefertiti PDFDocumento2 páginasNefertiti PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- English 111 Comparison Essay Suggested Topics (You May Develop Your Own Topic With Approval by Instructor)Documento3 páginasEnglish 111 Comparison Essay Suggested Topics (You May Develop Your Own Topic With Approval by Instructor)Iesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Cleopatra - From History To Myth PDFDocumento2 páginasCleopatra - From History To Myth PDFIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Medieval and Renaissance MusicDocumento2 páginasMedieval and Renaissance MusicIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- The 20th CenturyDocumento4 páginasThe 20th CenturyIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- ClassicalDocumento3 páginasClassicalIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- MUS 110 Project. Wolfgang Amadeus MozartDocumento3 páginasMUS 110 Project. Wolfgang Amadeus MozartIesha ClarkAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Genetics - For NEET, Medical & B - Sanjay KhareDocumento139 páginasGenetics - For NEET, Medical & B - Sanjay Khareteamindian gamersAinda não há avaliações
- Bs Merged SearchableDocumento90 páginasBs Merged SearchableShomak BakshiAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento45 páginasUntitledjemAinda não há avaliações
- IB Biology Core Syllabus NotesDocumento31 páginasIB Biology Core Syllabus NotesKashish Doshi100% (1)
- Cell Organelles ReviewDocumento19 páginasCell Organelles ReviewJelin VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Structure and Identification of Bacteria 2014 2 1 PDFDocumento74 páginas1 Structure and Identification of Bacteria 2014 2 1 PDFKaleem AfridiAinda não há avaliações
- Protein Synthesis: From DNA to Polypeptide ChainsDocumento23 páginasProtein Synthesis: From DNA to Polypeptide ChainsBelajar dan berdoaAinda não há avaliações
- 358 - Cell-Biology Physiology) Translation - Protein Synthesis001Documento5 páginas358 - Cell-Biology Physiology) Translation - Protein Synthesis001Leen AlhussainAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/13Documento20 páginasCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/13maya 1DAinda não há avaliações
- Determination of the Optimal Aligned Spacing Between the Shine-Dalgarno Sequence and Translation Initiation CodonDocumento5 páginasDetermination of the Optimal Aligned Spacing Between the Shine-Dalgarno Sequence and Translation Initiation CodonMarco Aurelio OliveiraAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Transcription and TranslationDocumento27 páginasUnderstanding Transcription and Translationᴅᴇᴀᴅ ᴋɪʟʟᴇʀAinda não há avaliações
- Central DogmaDocumento4 páginasCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 4Documento7 páginasTopic 4Antonio López JiménezAinda não há avaliações
- A Tour of The Cell: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento16 páginasA Tour of The Cell: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianAinda não há avaliações
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocumento10 páginasDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAKienlevyAinda não há avaliações
- Imat Specimen PaperDocumento40 páginasImat Specimen PaperEirini StypsianouAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance MCQsDocumento23 páginasMolecular Basis of Inheritance MCQsUrja MoonAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento18 páginasMolecular Basis of InheritanceAfzal MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- The Mechanism of TranslationDocumento68 páginasThe Mechanism of TranslationRama KishoreAinda não há avaliações
- Concept of Gene and Protein SynthesisDocumento39 páginasConcept of Gene and Protein SynthesisTabada NickyAinda não há avaliações
- TranscriptionDocumento31 páginasTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashAinda não há avaliações
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocumento11 páginasEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Cells and TissuesDocumento53 páginas3-Cells and TissuesTwelve Forty-fourAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics: The Genetic MaterialDocumento25 páginasGenetics: The Genetic Materialعمار مصعب عادلAinda não há avaliações
- Special Articles Serum Albumin: Marcus Murray Oratz Sidney S. SchreiberDocumento17 páginasSpecial Articles Serum Albumin: Marcus Murray Oratz Sidney S. SchreiberTuấn AnhAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 9 QDocumento4 páginasGrade 9 Qhanatabbal19Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1Documento50 páginasLecture 1AMRAPALI SANTOSH PAWARAinda não há avaliações
- GeneticDocumento117 páginasGeneticFiza RizviAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Final Review Exam SCI 100Documento14 páginasBio Final Review Exam SCI 100revel75Ainda não há avaliações
- Introductory Botany - Plants, People, and The Environment PDFDocumento649 páginasIntroductory Botany - Plants, People, and The Environment PDFGiovanni Ataíde100% (10)