Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Panel 13 02CitricAcid 2
Enviado por
Dian Agus SetyawatiDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Panel 13 02CitricAcid 2
Enviado por
Dian Agus SetyawatiDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
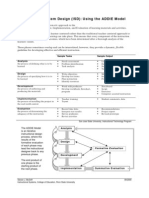
Panel 13-2 The complete citric acid cycle
AD+
CH3 C COOpyruvate
NADH
HS CoA
CO2 O CH3 C
next cycle acetyl CoA (2C)
S CoA HS CoA H2O COOCH2
Step 1
The complete citric acid cycle. The two carbons from acetyl CoA that enter this turn of the cycle (shadowed in red ) will be converted to CO2 in subsequent turns of the cycle: it is the two carbons shadowed in blue that are converted to CO2 in this cycle.
COONADH + H+
C O CH2 COOCOOoxaloacetate (4C)
NAD+
HO C COOCH2 COOcitrate (6C)
Step 2
Step 8
COOH C OH CH2 malate (4C) COOH 2O
C O CH2
oxaloacetate (4C)
COO-
COOCH2 isocitrate (6C) HC COOHO CH COO-
CITRIC ACID CYCLE Step 3
NAD+
fumarate (4C) Step 7
COOCH CH COOFADH2 Step 6 succinate (4C)
-ketoglutarate (5C) succinyl CoA (4C) Step 4
COOCH2 CH2 C O COO-
COOCH2 CH2 COOGTP Step 5
H 2O
COOCH2 CH2 S CoA
NAD+
C O
GDP + Pi NADH + H+
FAD
HS CoA
HS CoA
CO2
Details of the eight steps are shown below. For each step, the part of the molecule that undergoes a change is shadowed in blue, and the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction is in a yellow box.
Step 1
After the enzyme removes a proton from the CH3 group on acetyl CoA, the negatively charged CH2- forms a bond to a carbonyl carbon of oxaloacetate. The subsequent loss by hydrolysis of the coenzyme A (CoA) drives the reaction strongly forward.
COOO C CH3 S CoA + C CH2 COOacetyl CoA oxaloacetate
citrate synthase
S CoA
H2O
COOCH2 + HS CoA + H+
CH2 HO C CH2 COOS-citryl-CoA intermediate
COO-
HO
C CH2
COO-
COOcitrate
Step 2
An isomerization
reaction, in which water is first removed and then added back, moves the hydroxyl group from one carbon atom to its neighbor.
COOH HO H C C C H COOH
aconitase
H 2O H
COOC C H COOH
H2O
COOH H C C C H COOH
COOcitrate
H 2O
H2O
HO
COOcis-aconitate intermediate
COOisocitrate
Step 3
In the first of
COOisocitrate dehydrogenase
COO-
COO-
four oxidation steps in the cycle, the carbon carrying the hydroxyl group is converted a carbonyl group. Theto immediate product is unstable, losing CO2 while still bound to the enzyme.
H H HO
C C C
H COOH
H H
C C C
H COOO
H+ CO2
H H
C C C
H H O
NAD+ NADH + H+
COOisocitrate
COOoxalosuccinate intermediate
COOa-ketoglutarate
COOStep 4 The a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex closely resembles the large enzyme complex that converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA (pyruvate dehydrogenase). It likewise catalyzes an oxidation that produces NADH, CO2, and a high-energy thioester bond to coenzyme A (CoA).
COOa-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex + HS CoA
H H
C C C
H H O
H H
C C C
H H O
COOa-ketoglutarate
NAD+
NADH + H+ CO2
S CoA
succinyl-CoA
Step 5
A phosphate
COOH H C C C H H O H 2O
Pi GDP GTP
COOH H C C H H
+ HS CoA
molecule from solution displaces the CoA, forming a high-energy phosphate linkage to succinate. This phosphate is then passed to GDP to form GTP. (In bacteria and plants, ATP is formed instead.)
succinyl-CoA synthetase
COO-
S CoA
succinyl-CoA
succinate
Step 6
In the third
COOH H C C H H
oxidation step in the cycle, FAD removes two hydrogen atoms from succinate.
succinate dehydrogenase
COOC H C COOfumarate
COOsuccinate
FAD
FADH2
Step 7
The addition of
COOC H C COOfumarate
fumarase
COOHO H C C H H
water to fumarate places a hydroxyl next to a carbonyl group carbon.
H2O
COOmalate
Step 8
In the last of four
COO-
malate dehydrogenase
COO-
oxidation steps in the cycle, the carbon carrying the hydroxyl group is converted to a carbonyl group, regenerating the oxaloacetate needed for step 1.
HO H
C C
H H
NAD
+
C CH2
NADH + H
+
COOmalate
COOoxaloacetate
Siklus asam sitrat lengkap. kedua karbon dari asetil KoA yang masuk ini pergantian siklus (dibayangi merah) akan dikonversi menjadi CO2 secara bergiliran berikutnya dari siklus: itu adalah dua karbon dibayangi dengan warna biru yang dikonversi menjadi CO2 dalam siklus ini. Rincian dari delapan langkah yang ditunjukkan di bawah ini. Untuk setiap langkah, bagian dari molekul yang mengalami perubahan yang dibayangi dengan warna biru, dan nama enzim yang mengkatalisis reaksi dalam kotak kuning. Langkah 1 setelah Enzim menghilangkan proton dari kelompok CH3 pada asetil KoA, yang negatif dikenakan CH2-bentuk a ikatan karbon karbonil dari oksaloasetat. itu selanjutnya kerugian oleh hidrolisis koenzim A (CoA) drive reaksi kuat maju. Langkah 2 Reaksi isomerisasi, dimana air pertama dihapus dan kemudian ditambahkan kembali, bergerak hidroksil kelompok dari satu atom karbon ke tetangganya Langkah 3 Pada bagian pertama dari empat langkah oksidasi dalam siklus, karbon membawa gugus hidroksil dikonversi menjadi gugus karbonil. Produk langsung tidak stabil, kehilangan CO2 sementara masih terikat enzim. Langkah 4 A-ketoglutarat dehidrogenase kompleks erat menyerupai enzim besar kompleks yang mengkonversi piruvat untuk asetil (piruvat KoA dehidrogenase). Hal ini juga mengkatalisis oksidasi yang
menghasilkan NADH, CO2, dan energi tinggi thioester obligasi untuk koenzim A (CoA).
Langkah 5
Sebuah molekul fosfat dari solusi menggusur CoA, membentuk energi tinggi fosfat linkage untuk suksinat. ini fosfat ini kemudian diteruskan ke GDP untuk membentuk GTP. (Dalam bakteri
dan tanaman, ATP terbentuk sebagai gantinya.) langkah 6 Pada langkah oksidasi ketiga dalam siklus, FAD dehidrogenase suksinat menghilangkan atom hidrogen dari dua suksinat. Langkah 7 Penambahan air untuk fumarat menempatkan gugus hidroksil sebelah karbon karbonil. Langkal 8 Dalam terakhir dari empat langkah oksidasi dalam siklus, karbon yang membawa gugus hidroksil dikonversi menjadi gugus karbonil, regenerasi oksaloasetat yang diperlukan untuk langkah 1.
Você também pode gostar
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- MCQs Dr. Laila - Lipogenesis - Lipolysis - FA OxidationDocumento26 páginasMCQs Dr. Laila - Lipogenesis - Lipolysis - FA OxidationYoussef Mohamed100% (2)
- 5 +addie-1Documento2 páginas5 +addie-1Diwa SaadAinda não há avaliações
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteDocumento2 páginasCELLULAR RESPIRATION Review Worksheet KEY VufgteRosalyn Marie SugayAinda não há avaliações
- General Translation MechanismDocumento15 páginasGeneral Translation MechanismAishwarya KashyapAinda não há avaliações
- Silica SandDocumento7 páginasSilica SandHuru HaraAinda não há avaliações
- Hole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Twelfth Edition - Chapter 4 Lecture OutlineDocumento47 páginasHole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Twelfth Edition - Chapter 4 Lecture OutlineCharles AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- 6 - Biochemistry MCQs Carbohydrates MetabolismDocumento17 páginas6 - Biochemistry MCQs Carbohydrates Metabolismwanna learn100% (2)
- GenBio 1 Lesson 1 ATP and ADP CycleDocumento2 páginasGenBio 1 Lesson 1 ATP and ADP CycleLlaban MunicaAinda não há avaliações
- OrabyBiochemistry P.2 PDFDocumento232 páginasOrabyBiochemistry P.2 PDFJayadev Ch100% (1)
- LMR Biochemistry (2022) - DrAzam-1 - 230120 - 223221 PDFDocumento7 páginasLMR Biochemistry (2022) - DrAzam-1 - 230120 - 223221 PDFKuldip Patel100% (1)
- Biology M4 PhotosynthesisDocumento31 páginasBiology M4 PhotosynthesisDiana Dealino-SabandalAinda não há avaliações
- Absensi Siswa Kelas X Is 2Documento1 páginaAbsensi Siswa Kelas X Is 2Dian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Middle Tennessee State University, A Institution, 1301 East Main Street, Murfreesboro, TN 37132-0001 USADocumento1 páginaMiddle Tennessee State University, A Institution, 1301 East Main Street, Murfreesboro, TN 37132-0001 USADian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Nama Singkatan Rumus Jenis:: Oocch: Oocch NCH CH N CH COO: CH COODocumento5 páginasNama Singkatan Rumus Jenis:: Oocch: Oocch NCH CH N CH COO: CH COODian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- J. Biol. Chem.-1979-Foltmann-8447-56Documento11 páginasJ. Biol. Chem.-1979-Foltmann-8447-56Dian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- 530 nm 540 nm 578 nm 622 nm 640 nm 650 nm Panjang Gelombang (λ) Larutan (sampel)Documento6 páginas530 nm 540 nm 578 nm 622 nm 640 nm 650 nm Panjang Gelombang (λ) Larutan (sampel)Dian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Preprochymosin cDNA of Xinong Saanen Milk GoatDocumento1 páginaCloning and Sequence Analysis of Preprochymosin cDNA of Xinong Saanen Milk GoatDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- I GoDocumento1 páginaI GoDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Lee Hyun - Let's Go BackDocumento1 páginaLee Hyun - Let's Go BackDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Se7en - One More TimeDocumento2 páginasSe7en - One More TimeDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Alisha Chinai - Dheere DheereDocumento1 páginaAlisha Chinai - Dheere DheereDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- IDMDocumento1 páginaIDMDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Jo Kwan Woo - Day by DayDocumento1 páginaJo Kwan Woo - Day by DayDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Jang Nara - SnowmanDocumento1 páginaJang Nara - SnowmanjoonaslenkAinda não há avaliações
- HowL - Aeng Moo SaeDocumento1 páginaHowL - Aeng Moo SaeDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- TcaDocumento35 páginasTcaDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- B Vol 9. No 2 41Documento14 páginasB Vol 9. No 2 41Dian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- TCA CycleDocumento10 páginasTCA CycleDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- TCA CycleDocumento10 páginasTCA CycleDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- TcaDocumento35 páginasTcaDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Carboxylic AcidsDocumento3 páginasCarboxylic AcidsDian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Journal TCADocumento8 páginasJournal TCADian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Suffix: - Oic Acid: Chapter 18: Carboxylic Acids 18.1: Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature (Please Read)Documento18 páginasSuffix: - Oic Acid: Chapter 18: Carboxylic Acids 18.1: Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature (Please Read)Dian Agus SetyawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Respiration FoldableDocumento11 páginasCellular Respiration FoldableVivy LiuAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-04) - RM - Botany - 220725 - 192401Documento4 páginasConcept Strengthening Sheet (CSS-04) - RM - Botany - 220725 - 192401Jenish VavaiyaAinda não há avaliações
- III UG Physiology Respiration AVJDocumento27 páginasIII UG Physiology Respiration AVJHead 4KAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry Exam 2 (Outline)Documento9 páginasBiochemistry Exam 2 (Outline)stanly sotoAinda não há avaliações
- 8.1 (2.5 HL)Documento21 páginas8.1 (2.5 HL)SudeAinda não há avaliações
- Gaseous Exchange PPT 1Documento14 páginasGaseous Exchange PPT 1urooj fatimaAinda não há avaliações
- Urea CycleDocumento3 páginasUrea CycleHshshdhdAinda não há avaliações
- AP+Bio 013+Photosynthesis++Respiration+Worksheet WLDocumento2 páginasAP+Bio 013+Photosynthesis++Respiration+Worksheet WLVincent SuarezAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem PDFDocumento1 páginaBiochem PDFJohn JimsAinda não há avaliações
- Final Exam Study ProblemsDocumento6 páginasFinal Exam Study Problemsaboodh123Ainda não há avaliações
- Loss of Energy Released As Heat Favorable For Formation of Products, Occur On Its OwnDocumento3 páginasLoss of Energy Released As Heat Favorable For Formation of Products, Occur On Its OwnAshley Beatriz PascualAinda não há avaliações
- Biochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismDocumento6 páginasBiochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismSchat ZiAinda não há avaliações
- Icse/Cbse Class 10 PhotosynthesisDocumento18 páginasIcse/Cbse Class 10 PhotosynthesisLeelawati SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Photo RespirationDocumento4 páginasPhoto RespirationKasun WekasingheAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 1: A. B. C. DDocumento5 páginasTutorial 1: A. B. C. DSwarna15Ainda não há avaliações
- The Are in The For: BIOL 220 - Final (Page 1)Documento14 páginasThe Are in The For: BIOL 220 - Final (Page 1)Jad AwadAinda não há avaliações
- ch4 Section2Documento8 páginasch4 Section2api-318387471Ainda não há avaliações
- ChloroplastDocumento3 páginasChloroplastdrug123addict25Ainda não há avaliações
- Regulation of MetabolismDocumento42 páginasRegulation of Metabolismامجد حسين جواد كاظمAinda não há avaliações
- DCA and Avemar A Theoretical Protocol FoDocumento33 páginasDCA and Avemar A Theoretical Protocol FosiesmannAinda não há avaliações
- Superoksida Dismutase (Sod) Dan Radikal BebasDocumento6 páginasSuperoksida Dismutase (Sod) Dan Radikal BebasIvon PalenteAinda não há avaliações