Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Neurological Exam
Enviado por
joelh9Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Neurological Exam
Enviado por
joelh9Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Neurological examination
Motor function Observe look for signs of wasting or fasciculation (LMNL) Tonus see definition below Clonus see definition below
What is Tonus? basically the resting tone of muscles (or more specifically the muscles resistance to passive stretching during the resting state). Test: Roll LEx & UEx along their long axis. Pick up knee and drop Types of Tonus: Hypotonia (associated with LMNLs) Hypertonia (associated with UNMLs) Spasticity is velocity dependent and should be assessed by quick passive movement flex/ext pronation/sup (eg clasp knife) Rigidity is continuous non-velocity dependent eg lead-pipe Causes: UMNL (Spasticity), MS, Cerebral palsy What is Clonus? Simply the sustained repetitive maintenance of the reflex arc with stretch of the muscle (or series of involuntary, rhythmic, muscular contractions & relaxation ie. large movements normally initiated by a reflex). Clonus is a clinical sign of certain neurological conditions, particularly associated with UMNLs, and in many cases is, accompanied by spasticity. Unlike small, spontaneous twitches known as fasciculations (LMNL), clonus causes large motions that are usually initiated by a reflex Question when would you check for clonus? When you suspect an UMNL Types of Clonus: Physiological Pathological
Due to stress, exhaustion, fatigue, SNS. Repeat test. Tends to wear off. CNS lesion. Repeated response. Normal: no beats (sometimes few). Tests: Repetitive Dorsiflex ankle/wrist. Stretch Quads above patella.
Power Active resisted movements. Root C2, 3 C3,4 C5 C5 (6) C(5)6 C7 C8 T1 L1,2 L2,3 L3,4 L4 L5 S1 S2 Action Flex neck Shrug shoulders Abduct GH Flex elbow (palm up) Flex elbow (thumb up) Extend elbow Flex fingers Adduct fingers Flex hip Adduct thighs (need a wee) Extend knee (kick the door) Dorsiflex Talocrural Extend Hallux Flex knee Flex Hallux Muscle SCM Trapezius Deltoid Biceps Brachioradialis Triceps Flexor digitorum profundus Dorsi Interossei Iliopsoas Adductors Quadriceps Tib ant Extensor Hallucis Hamstrings Flexor Hallucis Brevis Peripheral Nerve CNXI CNXI Axillary Musculocutaneous Radial Radial Ulnar (2 med) Median (2 lat) Ulnar From spinal segment Obturator Femoral Deep fibular Deep fibular Sciatic Tibial
Combined motor/sensory function Types of Reflexes Internal (visceral), External (pupil, light), Deep Tendon / Superficial (Cutaneous Autonomic/visceral Internal (Pancreatic activity when eating) Stretch Reflex (Patella Hammer) A stretch reflex is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. The central nervous system can influence the stretch reflex via the gamma motoneurons (which control the sensitivity of the reflex). Inhibitory signals arrive at gamma neurons through the reticulospinal tract What are we testing when we test reflexes? Generally we are testing for a defect in nerve conduction but its important to remember that any link in the chain can cause a defect
Deep Tendon Reflexes Process/Structures of a Reflex Arc: a muscle lengthens > the muscle spindles are stretched causing an action potential travels up the sensory axon to the spinal cord where it synapses with a motorneuron > contraction of a muscle. Therefore Reflexes test the: response of muscles to stretch (reticulospinal tract): the sensory neuron, the synapse at that level of the spinal cord, motor neuron, and the motor end plates and the muscle). What is a mono-synaptic reflex? Its a reflex arc consisting of a single synapse between one sensory neuron and one motor neuron. Egs. Patella reflex What is a poly-synaptic reflex? By contrast one of more interneurons connect the afferent and efferent signals. Most reflexes are polysynaptic allowing for processing or inhibition of the reflexes
Reflex Jaw Biceps Supinator Triceps Fingers Knee jerk Adductor Ankle / Achilles / Soleus / Gastrocs
Muscle Mms of mastication Biceps Brachioradialis Triceps Flexor digitorum Quadriceps femoris Adductor Tibial
Nerve CNV Musculocutaneous C5 (6) Radial C(5) 6 Radial C7 Median / Ulnar C8 Femoral L3,4 Obturator L2, 3 S1, 2
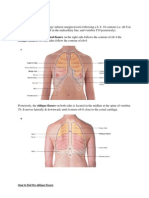
Skin/superficial Cutaneous stimulus causes skin distortion caused by pilorum muscles. Reflex Abdominal Plantar Test Navel toward stimulus. UMNLsuppress reflex Scrape up along lateral foot then inwards along MCPs. Normal response: flexion of big toe (adult) dorsiflex in babies Is an extension of int oblique. T12, L1,2 Nerve L5, S1
Cremaster
Genitofemoral nerve and illioinguinal nerve
Co-ordination Observe Static posture Balance/swaying. Terms: Ataxia lack of voluntary coordination of movement Hemiplegia total paralysis of the arm, leg, trunk on same side of the body. It is a form of spasticity Paraplegia - Quadriplegia Diplegia paralysis affecting symmetrical parts of the body (common in kids with Cerebral Palsy) Spasticity hypertonia (see tonus above) Gait Wide stance, trunk jerk sideways, difficult to balance. Test heel to toe. Cerebellar Circumduction, drag+ int rot of affected leg, ipsilateral arm bend + fist LEX>UEX. Flex hip/knees. Tight adductors, extend+ int rot ankles. LEX swinging bilateral gait. UEXlow guard (arms bent) Weak unstable pelvis with sideway sway/drop and hyperlordosis Pt cant dorsiflexfoot dropfoot drag or high step to lift foot of ground Hyperkinetic. Balanced + involuntary movements Loss of sensation/joint position. Dorsal column. Walk on the spot (eyes open/closed) CNVII (turning toward lesion)
Ataxic (lack of voluntary coordination movement) Hemiplegic Diplegic
Myopathic Neuropathic Choreiform Stamping
Tremor Intention Resting
Cerebellum (shake when moving closer to target) Cerebrum (Parkinsons) Cerebellum Cerebellum Cerebellum
Finger-nose test Heel-shin test Rapid alternating movements
Sensory function Observe, Light Touch, Pinprick, Deep touch/pain/squeeze, Joint position sense, Vibration, Temperature sense.
Spinal Roots C5 C5/6 C6 C7 C6 C7 C8
Movement Shoulder Abduction Elbow flexion Elbow flexion Elbox extension Radial wrist extension Finger extension Finger flexion
Upper Extremity Weakness implies UMNL Reflex + + + +
Named nerve Axillary nerve Musculotcutaneous nerve Radial nerve Radial nerve Radial nerve Posterior interosseus nerve Anterior interosseus nerve
T1
Finger abduction
Lower Extremity Weakness implies UMNL Reflex + + +
Ulnar nerve Ulnar nerve Median nerve Named nerve Obturator nerve Sciatic nerve Sciatic nerve Femoral nerve Deep peroneal nerve Superficial peroneal Tibial nerve Deep peroneal nerve
Muscle Deltoid Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Triceps Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor digitorum communis Flexor pollicis longus Flexor digitorum profundus (index) Flexor digitorum profundus (ring & little) First dorsal interosseous Abductor pollicis brevis Muscle Illiopsoas Adductors Gluteus maximus Hamstrings Quadriceps Tibialis anterior Peroneus longus & brevis Gastrocnemius & Soleus Extensor hallucis longus
Spinal Roots L1/2 L2/3 L5/S1 S1 L3/4 L4 L5/S1 S1/S2 L5
Movement Hip flexion Hip adduction Hip extension Knee flexion Knee extension Ankle dorsiflexion Ankle eversion Ankle plantarflexion Big toe extension
Named Nerve Musculocutaneous nerve
Motor supply Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii Brachialis Deltoid Teres minor Triceps - all 3 heads Brachioradialis Extensor carpi radialis longus Extensor carpi radialis brevis Supinator Extensor carpi ulnaris Extensor digitorum Extensor digiti minimi Abductor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis longus Extensor pollicis brevis Extensive indicis
Upper Extremity Sensory supply Lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
Sensory pattern Lateral half of forearm elbow to wrist anterior and posterior
Axillary nerve
Upper cutaneous nerve of the forearm
Sergents stripes on superiolateral arm
Radial nerve
Superficial radial nerve
Thin strip down the posteriolateral aspect of arm and forearm including back of up to base of thumb and 1st two fingers
Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Flexor digitorum superficialis Flexor digitorum profundus 1 & 2 Flexor pollicis longus Pronator quadratus Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis
Lesions in the forearm: From wrist to finger tips of thumb to half of 4th finger on palmar surface Tips of thumb and up to half of 4th finger from distal joint
Median nerve
Palmar branch of median nerve Lesions in carpal tunnel: Tip of thumb from distal joint and length of fingers up to half of 4th finger on palmar surface Tips of thumb and up to half of 4th finger from distal joint Medial cutaneous nerve of the arm Including: Dorsal cutaneous branch Palmar cutaneous branch Superficial terminal branches
Opponens pollicis 1st & 2nd lumbricals Flexor carpi ulnaris Flexor digitorum profundus 3 & 4 Adductor pollicis Flexor pollicis brevis Interssoei abductor digiti minimi Opponens digit minimi Flexo digiti minimi
Medial half of forearm elbow to wrist anterior and posterior
Ulnar nerve
Lesions from elbow to first cutaneous branch: From wrist to fingers tips of little and half ring finger on palmar and dorsal surfaces
Named Nerve
Motor supply
Lower Extremity Sensory supply Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Sensory pattern Small patch on lateral aspect of thigh just superior to knee Anterior aspect of thigh beginning at mid thigh on medial aspect, extending in the midline back up towards the groin, covering across the knee and medial aspect of the leg to ankle Posterior acpect of thigh beginning at mid thigh on medial aspect, covering medial 1/3 posterior knee and medial aspect of leg to ankle Medial anterior and posterior aspects of leg from knee to ankle and small piece on medial arch of foot Middle 1/3 lateral aspect of thigh
Femoral nerve
Quadriceps femoris: Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus intermedius
Medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Vastus medialis
Saphenous nerve Obturator nerve Adductor brevis Adductor longus Gracilis Adductor magnus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Tensor fascia latae Gluteus maximus Cutaneous branch of obturator nerve
Superior gluteal nerve Inferior gluteal nerve
Semitendinosus Semimebranosus Sciatic nerve
Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Triangular middle 1/3 of posterior aspect of thigh with base of triangle at crease of buttocks and point at back of knee Lesions from trunk of sciatic nerve: Lateral half of anterior and posterior leg from below the knee to the ankle, and the foot except the immediate area around medial malleolus to the first 1/2 of medial aspect of foot
Adductor magnus Biceps femoris
Peroneus longus
Common peroneal
Peroneus brevis Common peroneal nerve
Superficial peroneal nerve
Lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf
Lateral half of anterior and posterior leg from below the knee to the ankle, and the foot except the immediate area around calcaneous and lateral border of the foot, includes dorsum of foot except distal tips of toes Posterior acpect of thigh beginning at mid thigh on medial aspect, covering medial 1/3 posterior knee and medial aspect of leg to ankle Small oval patch on lateral aspect of leg just below knee, extending to 1/3 anterior and posterior leg
Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum longus Extensor hallucis longus Peroneus tertius Extensor digitorum brevis
Deep peroneal nerve
Small horseshoe patch over web space between great and 2nd toe including half of each toe
Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis posterior Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis longus Tibial nerve Calcaneous and sole of foot, including dorsum tips of toes
Calcaneal branch Abductor hallucis Tibial nerve Flexor digitorum brevis Flexor hallucis brevis Cutaneous branches Abductor digiti minimi Flexor digiti minnimi Adductor hallucis Interssoei Cutaneous branches Lateral plantar nerve Medial plantar nerve
Calcaneous and dorsal 1/2 of platar surface of foot
Medial 2/3 of plantar surface of foot, including toes to middle of 4th toe and excluding calcaneous
Lateral 1/3 of plantar surface of foot, including toes to middle of 4th toe and excluding calcaneous
Sural nerve Mix of Tibial and Common peroneal nerves
Small slice on lateral arch of foot but not including little toe and lateral aspect of ankle surrounding lateral malleolus
Você também pode gostar
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Case StudyDocumento4 páginasCase Studyjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5795)
- Respiratory ExamDocumento9 páginasRespiratory Examjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- Abdominal ExamDocumento4 páginasAbdominal Examjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Respiratory Surface AnatomyDocumento3 páginasRespiratory Surface Anatomyjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- CVS Exam Routine & Script: KoilonychiaDocumento4 páginasCVS Exam Routine & Script: Koilonychiajoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- Abdominal ExamDocumento4 páginasAbdominal Examjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Applied Functional Science CertificateDocumento1 páginaApplied Functional Science Certificatejoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology NotesDocumento20 páginasObstetrics and Gynaecology Notesjoelh9100% (2)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- Coracobrachialis: Tip of Coracoid Process of ScapulaDocumento8 páginasCoracobrachialis: Tip of Coracoid Process of Scapulajoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Muscle Flash CardsDocumento127 páginasMuscle Flash Cardsjoelh9100% (3)
- Joint ExaminationsDocumento6 páginasJoint Examinationsjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Random Patient GeneratorDocumento1 páginaRandom Patient Generatorjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- Pyramid & Extrapyramidal DisordersDocumento5 páginasPyramid & Extrapyramidal Disordersjoelh9Ainda não há avaliações
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- SATB All Glory Laud and HonorDocumento1 páginaSATB All Glory Laud and HonorGeorge Orillo BaclayAinda não há avaliações
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- Republic Act No. 1125Documento8 páginasRepublic Act No. 1125Jazlynn WongAinda não há avaliações
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- Constitution & By-LawsDocumento15 páginasConstitution & By-LawsMichael C. AndradeAinda não há avaliações
- SF3300Documento2 páginasSF3300benoitAinda não há avaliações
- Victorian AOD Intake Tool Turning Point AuditDocumento8 páginasVictorian AOD Intake Tool Turning Point AuditHarjotBrarAinda não há avaliações
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- Slides - Simple Linear RegressionDocumento35 páginasSlides - Simple Linear RegressionJarir AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- IDLC Finance Limited: Assignment (Research Report)Documento29 páginasIDLC Finance Limited: Assignment (Research Report)Nishat ShimaAinda não há avaliações
- Description: S&P 500 Dividend AristocratsDocumento7 páginasDescription: S&P 500 Dividend AristocratsCalvin YeohAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Paper For Business ResearchDocumento4 páginasConcept Paper For Business ResearchRobertchristian RagaAinda não há avaliações
- A Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalDocumento6 páginasA Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalJoko Cahyo BaskoroAinda não há avaliações
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- Docshare - Tips Upstream Advanced c1 Test BookletDocumento3 páginasDocshare - Tips Upstream Advanced c1 Test BookletCosmin OaieAinda não há avaliações
- EikonTouch 710 ReaderDocumento2 páginasEikonTouch 710 ReaderShayan ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Brief Orientation To Counseling 1st Edition Neukrug Test BankDocumento25 páginasBrief Orientation To Counseling 1st Edition Neukrug Test BankStevenAdkinsyjmd100% (55)
- Contoh Soal TOEFL PBTDocumento3 páginasContoh Soal TOEFL PBTiwanAinda não há avaliações
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Draft Cavite MutinyDocumento1 páginaDraft Cavite MutinyaminoacidAinda não há avaliações
- TENSES ExerciseDocumento28 páginasTENSES ExerciseKhanh PhamAinda não há avaliações
- Script - Macbeth A La MafiosiDocumento27 páginasScript - Macbeth A La MafiosiMohd Afiq Mat RazaiAinda não há avaliações
- Electoral Politics Module-2, Hand Out 2, Class 9, Civics, Lesson-3, Electoral PoliticsDocumento4 páginasElectoral Politics Module-2, Hand Out 2, Class 9, Civics, Lesson-3, Electoral PoliticsSaiAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Management Assignment (Project)Documento9 páginasBrand Management Assignment (Project)Haider AliAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentation. Between Science, State and IndustryDocumento271 páginasInstrumentation. Between Science, State and IndustryMichel GautamaAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Sunday After TrinityDocumento11 páginas3rd Sunday After TrinityHmkEnochAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 3 MathematicsDocumento3 páginasGrade 3 Mathematicsailaine grace alapAinda não há avaliações
- Why Do We Hate Hypocrites - Evidence For A Theory of False SignalingDocumento13 páginasWhy Do We Hate Hypocrites - Evidence For A Theory of False SignalingMusic For youAinda não há avaliações
- 9300 Servo Inverter TRDocumento10 páginas9300 Servo Inverter TRIhsan CanakogluAinda não há avaliações
- Per User Guide and Logbook2Documento76 páginasPer User Guide and Logbook2Anthony LawAinda não há avaliações
- How To Write A ThesisDocumento14 páginasHow To Write A ThesisPiyushAinda não há avaliações
- Letter From MomDocumento3 páginasLetter From MomSonia Beron-Mosot Guias75% (20)
- Javier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Documento4 páginasJavier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- New Memories by Ansdrela - EnglishDocumento47 páginasNew Memories by Ansdrela - EnglishB bAinda não há avaliações
- Architectural Design I: SyllabusDocumento3 páginasArchitectural Design I: SyllabusSrilakshmi PriyaAinda não há avaliações