Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Double-Stranded DNA Viruses: 1. Herpesviridae
Enviado por
Gerald John PazDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Double-Stranded DNA Viruses: 1. Herpesviridae
Enviado por
Gerald John PazDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
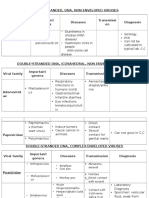
Double-stranded DNA viruses
dsDNA
Enveloped Icosahedral Naked Icosahedral
Complex
2. Poxviridae
Orthopoxvirus (Variola, Vaccinia)
1. Herpesviridae
Simplexvirus Varicellovirus
3. Papillomaviridae
Papillomavirus
4. Adenoviridae
Mastadenovirus
1. Herpesviridae dsDNA Enveloped Icosahedral Latency and lifelong persistence A. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV / HHV) i. MOT Contact with secretions Sexual contact Birth canal in neonates ii. Diseases 1. HSV 1 Oral Herpes 2. HSV 2 Genital Herpes Herpes whitlow Very painful lesions that may inflame the hand Eczema herpeticum Seen in patients with underlying skin disorder Icthyosis vulgaris severe drying Herpes gladiatorum on the face Acquired through wrestling (body contact) Neonatal herpes Vertical transmission (in utero) In partum ( durin birth) Vaginal delivery iii. Specimen Aspirates from vesicles & lesions CSF and Brain Biopsy iv. Isolation & Serology WI-38, MRC-5, HDF, RK, HEp2, A549
EIA, Strip immunoblot, etc. B. Cytomegalovirus i. MOT Close contact with secretions and excretions Transplacental ii. Disease Latency in mononuclear cells Congenital infections Symptomatic congenital infection Petechiae, hepatosplenomegaly, microcephaly and choriorenitis iii. Specimens Sterile body fluids and tissues Urine and respiratory secretions iv. Serology, Culture, Molecular tests P65 Ag detection (WBC) Diploid fibroblasts cell lines, SVCE PCR, branched DNA, hybridization C. Epstein-barr Virus i. MOT Close contact with saliva ii. Disease Hodgkin disease. Infectious Mononucleosis (Kissing Disease) Common to adolescence period Photophobia, loss of appetite, tonsillar swelling, white patches on the tonsils, sore throat, spleenomegaly, abdominal pain, nausea Glandular fever Commonly mistaken as S.pyogenes Dont respond to antibiotic Burkitt lymphoma Starry sky pattern in tissue preparation Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Nosebleed, lose sense of smell Change in voice production, bad breath iii. Specimen B-lymphocytes and serum iv. Serology Paul-Bunnel Heterophile Ab test Anti-VCA: Ab to viral capsid Ag Anti-EA IgG: IgG Ab to early Ag Anti-EA/D: Ab to early Ag, diffuse Anti-EA/R: Ab to early Ag, restricted Anti-EBNA: Ab to EBV nuclear Ag D. Varicella Zoster i. MOT Droplet inhalation Direct contact with lesions ii. Disease Varicella (Chickenpox)
- dsDNA
- Enveloped - Capsid: complex a. Orthopoxvirus Vaccinia (cowpox) Variola (smallpox) b. Monkeypox virus 3. Papillomaviridae (Papovaviridae) dsDNA Naked Capsid: Icosahedral i. MOT Direct contact ii. Disease Papilloma, warts Cutaneous Papilloma HPV 1 4: no significant consequences Mucosal Papilloma HPV 42 44 HPV 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, HPV 16, 18, 45, 56, 58, 59, 68 Condylomata acuminate - genital wart formation iii. Specimen Tissue iv. Diagnosis Cannot be grown in cell culture Cytopathic effect - Koilocytosis 4. Adenoviridae - dsDNA -Naked - Capsid: Icosahedral i. MOT Aerosols, fomites Oral-fecal route Direct contact The virus infects the epithelium of the respiratory tract, eyes and the intestines ii. Disease / Patholgy Pneumonia Gastroenteritis - Adenovirus 40 & 41 enteric adenovirus Keratoconjunctivitis Inflammation of cornea and conjunctiva Acute hemorrhagic cystitis Inflammation of the urinary bladder Patient may experience hematuria Pharyngoconjunctival fever Sore eyes & sore throat with fever MOT: Respiratory droplets Waldeyer's Ring
- Febrile illness, rash and vesicular lesions - Dry, crusty lesions, heals in 1 2 weeks - Painful oral mucosal lesions may develop in adults
Zoster (Shingles) - Reactivation of VZV - Located only to one area (lesions for a week) - Postherpetic neuralgia nerve pain due to damage caused by the VZV, may last for months iii. Specimens Lesions (vesicles) iv. Culture Human embryonic lung Vero cells E, F. Human Herpesvirus 6 /7 i. MOT Droplet Inhalation & close contact ii. Disease Roseola (roseola infantum, exanthem subitum, sixth disease) iii. Laboratory Diagnoses Lymphocyte culture and serology G. Human Herpesvirus 8 i. MOT - Sexual contact ii. Disease - Kaposi Sarcoma iii. Laboratory Diagnoses - PCR and Serology
2. Poxviridae (Refer to the book)
Found in pharyng with 5 lymphoid tissue 1st pair: pharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) 2nd pair: pallatine tonsil One lingual tonsil Adenoids close to the eustachian tube May lead to otitis media iii. Diagnosis Human Embryonic Kidney Continuous epithelial cell lines CPE: swollen cells in grapelike clusters Serology: Serum neutralization E. Parvoviridae -ssDNA - nake - icosahedral a. Parvovirus B19 i. MOT Contact with secretions ii. Disease Erythema infectiosum Fifth disease Transient aplastic crises Hydrops fetalis iii. Specimen Aspirates from vesicles & lesions CSF and Brain Biopsy iv. Isolation and Serology WI-38, MRC-5, HDF, RK, HEp2, A549 EIA, Strip immunoblot, etc. b. Human bocavirus i. MOT Contact with secretions ii. Disease Respiratory tract illness Co-infection with RSV and hMPV iii. Specimen Aspirates from vesicles & lesions CSF and Brain Biopsy iv. Isolation and Serology WI-38, MRC-5, HDF, RK, HEp2, A549 EIA, Strip immunoblot, etc.
Você também pode gostar
- Mental Status ExamDocumento10 páginasMental Status ExamSrini VoruAinda não há avaliações
- Get in Shape Month2Documento5 páginasGet in Shape Month2Caroline Sandry100% (1)
- Australian Drinking Water Guidelines 2004Documento615 páginasAustralian Drinking Water Guidelines 2004Chicken little83% (6)
- Homeopathy: 1 HistoryDocumento32 páginasHomeopathy: 1 HistoryslowdogAinda não há avaliações
- Virology TableDocumento10 páginasVirology TablekevinAinda não há avaliações
- 11 NCP Pressure UlcerDocumento6 páginas11 NCP Pressure UlcerICa MarlinaAinda não há avaliações
- VirologyDocumento24 páginasVirologyRohama Qubra 279Ainda não há avaliações
- Otologic Manifestation of Systemic DiseaseDocumento57 páginasOtologic Manifestation of Systemic DiseaseHERIZALAinda não há avaliações
- Interpretation of MriDocumento12 páginasInterpretation of Mrijimitkapadia100% (1)
- Chapter 024Documento49 páginasChapter 024Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- All Pediatric Seminars - AsemDocumento356 páginasAll Pediatric Seminars - AsemAsem Shadid100% (1)
- Virus PDFDocumento60 páginasVirus PDFrenz bartolomeAinda não há avaliações
- Infectious Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocumento51 páginasInfectious Diseases of The Respiratory SystemFachriza EffendiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 022Documento100 páginasChapter 022Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Homeopathy and PaediatricsDocumento15 páginasHomeopathy and PaediatricsCristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial and Viral Infection in ChildrenDocumento62 páginasBacterial and Viral Infection in ChildrenislawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Intravenous TherapyDocumento30 páginasIntravenous TherapyKoass14 2012Ainda não há avaliações
- VirologyDocumento55 páginasVirologySelvenThirumalai100% (4)
- Chapter 025Documento31 páginasChapter 025Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Case Studies On CoagulationDocumento3 páginasCase Studies On CoagulationGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Bacteriological Quality of Street Vended Food PanipuriDocumento5 páginasBacteriological Quality of Street Vended Food PanipuriYus EfendiAinda não há avaliações
- DNA VirusesDocumento154 páginasDNA VirusesRod Pasion0% (1)
- Small Pox Is DeadDocumento46 páginasSmall Pox Is Deadtummalapalli venkateswara raoAinda não há avaliações
- How To Measure Dialysis Adequacy - Edit 3Documento42 páginasHow To Measure Dialysis Adequacy - Edit 3Dicky SaputraAinda não há avaliações
- Tai Chi LiteratureDocumento2 páginasTai Chi LiteratureMichael Fong100% (1)
- Infeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutDocumento41 páginasInfeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutFaris MahdaniAinda não há avaliações
- Adenoviruses AdenovirusesDocumento25 páginasAdenoviruses AdenovirusesstudymedicAinda não há avaliações
- Enterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Documento12 páginasEnterovirus: Virologi Klinik KDM 726 Pembimbing: Dr. Abu Rohiman, MS, SPMK (K)Daniel EdbertAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Notes VirusPartTwo 13 STUDENTDocumento28 páginasMicro Notes VirusPartTwo 13 STUDENTSutapa Pawar0% (1)
- 1.non Keratotic Lesion PDFDocumento57 páginas1.non Keratotic Lesion PDFElamaaraeen MadhvanAinda não há avaliações
- Adeno Viruses: MRS. D. BINDU MSC., PHD., Assistant Professor Dept of MicrobiologyDocumento10 páginasAdeno Viruses: MRS. D. BINDU MSC., PHD., Assistant Professor Dept of Microbiologybindu dhanapalAinda não há avaliações
- DNA VirusesDocumento62 páginasDNA VirusesGabriella CrooksAinda não há avaliações
- DNA Viruses 2Documento28 páginasDNA Viruses 2sairahhannahAinda não há avaliações
- Pox, Parvo, Adeno and Papova VirusesDocumento33 páginasPox, Parvo, Adeno and Papova VirusesmicroperadeniyaAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Gingival InfectionsDocumento101 páginasAcute Gingival InfectionsNeelam KhaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Virology Lecture 7 Viral DiseseDocumento21 páginasVirology Lecture 7 Viral Diseseao868598Ainda não há avaliações
- Lec8 Infectious DiseasesDocumento32 páginasLec8 Infectious DiseasesmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- 13ffd1fa Eda0 4eb8 Bb3a 7802feec40daDocumento40 páginas13ffd1fa Eda0 4eb8 Bb3a 7802feec40daapi-26938624Ainda não há avaliações
- Kuliah PoliovirusDocumento41 páginasKuliah PoliovirusNr FdllhAzZhraAinda não há avaliações
- MeaslesDocumento58 páginasMeaslesDr.P.NatarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Pharyngitis 0104 SlidesDocumento144 páginasPharyngitis 0104 SlidesZammira MutiaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbiology Case 1: Ustnotesgroup2009Documento19 páginasMicrobiology Case 1: Ustnotesgroup2009nkivcAinda não há avaliações
- 5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFDocumento8 páginas5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFVince Alvin DaquizAinda não há avaliações
- Viral Diseases 45Documento27 páginasViral Diseases 45Mujtaba AlsalehAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Virology (RNA Viruses)Documento56 páginasMedical Virology (RNA Viruses)Bayu HamengkuAinda não há avaliações
- Smallpox A Dead Disease: Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocumento46 páginasSmallpox A Dead Disease: Dr.T.V.Rao MDshravaniAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnosis of Viral DiseaseDocumento20 páginasDiagnosis of Viral Diseaseapi-19969058Ainda não há avaliações
- Macules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesDocumento6 páginasMacules Macules and Papules Papules VesiclesLanaAmerieAinda não há avaliações
- Scabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportDocumento4 páginasScabies Norwegian Presenting As Erythroderma in HIV A Case ReportfakhrunnisaAinda não há avaliações
- 21 - Virology I (DNA) LectureDocumento47 páginas21 - Virology I (DNA) LectureSamqureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Bacterial InfectionsDocumento91 páginasBacterial InfectionsIoana DănilăAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation-ChickenpoxDocumento41 páginasCase Presentation-ChickenpoxShaliniAinda não há avaliações
- VirologyDocumento5 páginasVirologyAmnah ✨Ainda não há avaliações
- Poultry Farmer Workshop: Husbandry / / Pasture Management: DiseaseDocumento96 páginasPoultry Farmer Workshop: Husbandry / / Pasture Management: DiseaseequalizertechmasterAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Virology: Scott M. Hammer, M.DDocumento46 páginasIntroduction To Virology: Scott M. Hammer, M.DAkmal Faiz100% (1)
- Opportunistic Fungal Infection PDFDocumento48 páginasOpportunistic Fungal Infection PDFMalvika BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah Respi Bakteri TDK Lazim Revisi TambahanDocumento23 páginasKuliah Respi Bakteri TDK Lazim Revisi TambahanIzza Ayudia HakimAinda não há avaliações
- Virology Lec 04Documento47 páginasVirology Lec 04Powell KitagwaAinda não há avaliações
- DNA VirusesDocumento99 páginasDNA VirusesCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaAinda não há avaliações
- Microbial Diseases of The Different Organ System and Epidem.Documento36 páginasMicrobial Diseases of The Different Organ System and Epidem.Ysabelle GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Enterovirus: Regati Meenakshi ROLL: B30Documento27 páginasEnterovirus: Regati Meenakshi ROLL: B30Meena RajAinda não há avaliações
- Cutaneous Manifestation of HivDocumento36 páginasCutaneous Manifestation of Hivyunita hapsariAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnosis of Oral InfectionDocumento72 páginasDiagnosis of Oral InfectionMohit_Gupta_9876Ainda não há avaliações
- Viral InfectionDocumento36 páginasViral InfectionHani El-asferAinda não há avaliações
- Dengue Malaria Group2Documento100 páginasDengue Malaria Group2Arvinth Guna SegaranAinda não há avaliações
- 2° Parte Brunetti BertinoroDocumento41 páginas2° Parte Brunetti BertinoroGergis OnsyAinda não há avaliações
- Presented By:-Pallavi Chawla Pallavi Dhiman (BDS - 3 Year)Documento28 páginasPresented By:-Pallavi Chawla Pallavi Dhiman (BDS - 3 Year)tinu989Ainda não há avaliações
- Cocci X11 PDFDocumento24 páginasCocci X11 PDFMustafa GenoveAinda não há avaliações
- ParamyxovirusesDocumento36 páginasParamyxovirusesRandy BerryAinda não há avaliações
- Corona VirusesDocumento61 páginasCorona VirusesNaing Lin SoeAinda não há avaliações
- Final Review - Microbio - paraDocumento5 páginasFinal Review - Microbio - parajcarysuitos67% (3)
- AIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFDocumento35 páginasAIR DROP EXAMنسختي PDFYara AlmouallemAinda não há avaliações
- Handbook for Microbiology Practice in Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnosis: A Study Guide to Laboratory Techniques in Oral MicrobiologyNo EverandHandbook for Microbiology Practice in Oral and Maxillofacial Diagnosis: A Study Guide to Laboratory Techniques in Oral MicrobiologyAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Based Learning PDFDocumento1 páginaProblem Based Learning PDFGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Phlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Documento5 páginasPhlebotomy: Phlebos - Greek Word Meaning "Vein" & Tome - "To Cut"Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Gene Therapy May Prevent Retinoschisis in Boys: ReviewDocumento2 páginasGene Therapy May Prevent Retinoschisis in Boys: ReviewGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- GROUP11 Section1 PBL2 Gerald John PazDocumento1 páginaGROUP11 Section1 PBL2 Gerald John PazGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- The Impact of Teacher Presentation Style: (Please Email Me at For A References List.)Documento5 páginasThe Impact of Teacher Presentation Style: (Please Email Me at For A References List.)kashanpirzadaAinda não há avaliações
- Problem BasedDocumento3 páginasProblem BasedLady KweeAinda não há avaliações
- Videos On Drug Abuse. Guidelines For Finals Quiz 3 - 5Documento1 páginaVideos On Drug Abuse. Guidelines For Finals Quiz 3 - 5Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Concepts of Culture MediaDocumento1 páginaConcepts of Culture MediaGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Biobanking For Human Microbiome Research Promise, Risks, and EthicsDocumento15 páginasBiobanking For Human Microbiome Research Promise, Risks, and EthicsGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Microbiota in Immunity and InflammationDocumento12 páginasRole of Microbiota in Immunity and InflammationGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Geopolitical Challenges For Infectious Disease Prevention and ControlDocumento17 páginasGeopolitical Challenges For Infectious Disease Prevention and ControlGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0167701216302627 MainDocumento8 páginas1 s2.0 S0167701216302627 MainGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Different Laboratory Service ModelsDocumento1 páginaDifferent Laboratory Service ModelsGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Host Microbiomes and Their Interactions With Immune SystemDocumento9 páginasHost Microbiomes and Their Interactions With Immune SystemGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 021Documento49 páginasChapter 021Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 002Documento68 páginasChapter 002Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Managment and Planning PDFDocumento53 páginasManagment and Planning PDFGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 023Documento34 páginasChapter 023Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 023Documento34 páginasChapter 023Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4Documento39 páginasChapter 4Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- The First Blind Man On Top of The WorldDocumento1 páginaThe First Blind Man On Top of The WorldGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Managment and PlanningDocumento53 páginasManagment and PlanningGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Papa Bear of The Berenstain BearsDocumento1 páginaPapa Bear of The Berenstain BearsGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 001Documento83 páginasChapter 001Gerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- Short Report: Genetics Islet Autoantibodies Can Discriminate Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) From Type 1 DiabetesDocumento7 páginasShort Report: Genetics Islet Autoantibodies Can Discriminate Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) From Type 1 DiabetesGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- GROUP 6-Micro Biochem ResultsDocumento2 páginasGROUP 6-Micro Biochem ResultsGerald John PazAinda não há avaliações
- 220200320sathiya PrakashDocumento95 páginas220200320sathiya Prakashpriya selvaraj100% (1)
- Fucidin® OintDocumento1 páginaFucidin® OintIanthe SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocumento16 páginasPregnancy Induced Hypertensiondgraham36Ainda não há avaliações
- Hazardous Chemical Products in Home.Documento17 páginasHazardous Chemical Products in Home.taratarabuzuAinda não há avaliações
- Occupational Therapy - Kids Health Information: Scar ManagementDocumento4 páginasOccupational Therapy - Kids Health Information: Scar Managementmuambany1Ainda não há avaliações
- Music TherapyDocumento7 páginasMusic Therapyzakir2012Ainda não há avaliações
- DRUGSDocumento4 páginasDRUGSHoney Grace L LemorenasAinda não há avaliações
- KS4 Physical Education: The Circulatory SystemDocumento36 páginasKS4 Physical Education: The Circulatory SystemAjay Pal NattAinda não há avaliações
- 16-4 I The Truth About Physician Health ProgramsDocumento5 páginas16-4 I The Truth About Physician Health ProgramslbandrewAinda não há avaliações
- Cordymax Trifold BrochureDocumento2 páginasCordymax Trifold BrochureCherry San DiegoAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Vessels and Circulation 1Documento36 páginasBlood Vessels and Circulation 1Kuya RnJAinda não há avaliações
- UVA QuestionsDocumento61 páginasUVA QuestionsjhhjjhAinda não há avaliações
- Systematic Review - The Effectiveness ofDocumento15 páginasSystematic Review - The Effectiveness ofSabrinaAinda não há avaliações
- Oral 5Documento236 páginasOral 5Iodeh1985 OdehAinda não há avaliações
- PD 03-2020 PDFDocumento2 páginasPD 03-2020 PDFtimvrghs123Ainda não há avaliações
- Pharmacology of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid: Review ArticleDocumento12 páginasPharmacology of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid: Review ArticlepunitAinda não há avaliações
- Screening Questionnaire: Dha Eligibility LetterDocumento2 páginasScreening Questionnaire: Dha Eligibility LetterDr. Emad Elbadawy د عماد البدويAinda não há avaliações
- Miscellaneous For FinalsDocumento30 páginasMiscellaneous For Finalsjames.a.blairAinda não há avaliações
- Tea CaffeineDocumento3 páginasTea CaffeinedigitaltextAinda não há avaliações